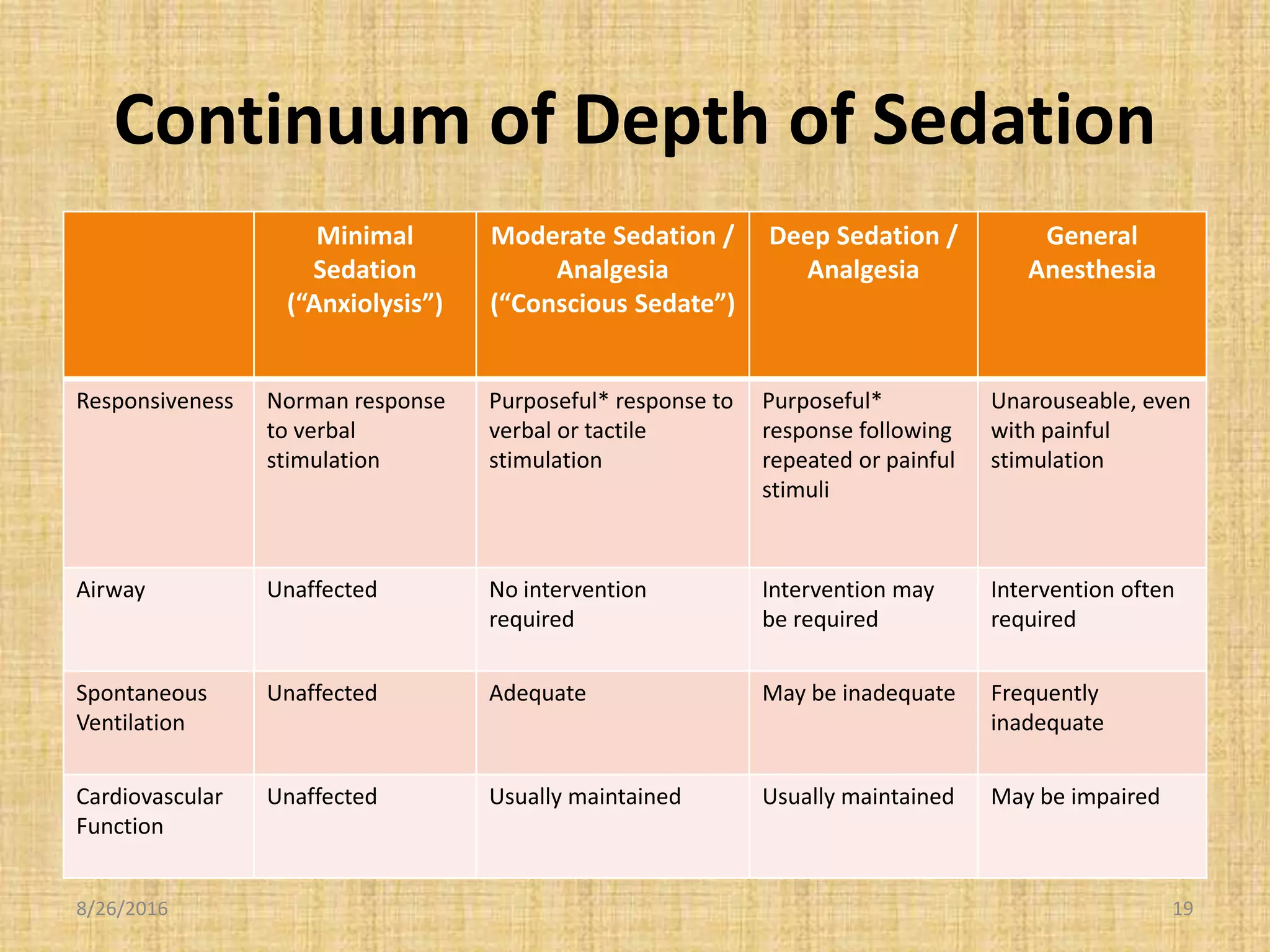
This document provides an introduction to conscious sedation, including the objectives, responsibilities, equipment, medications, and patient risk factors involved. The key points are:
1) Conscious sedation requires careful monitoring as patients can easily slip into deeper sedation, so providers must be prepared to rescue patients and understand sedation levels.
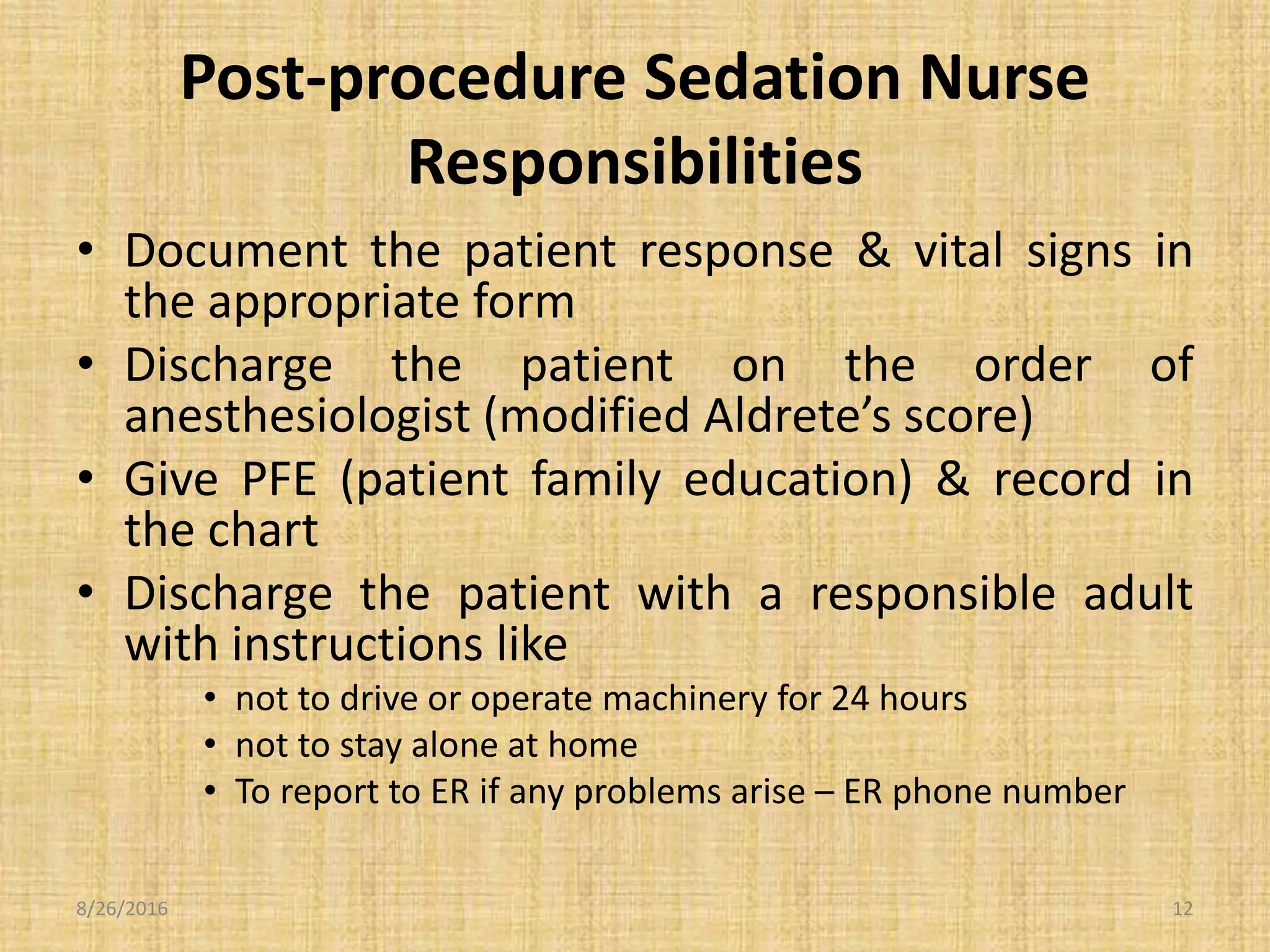
2) Responsibilities include proper patient assessment, monitoring, documentation, discharge criteria and patient education.
3) A hospital policy is needed to outline privileged providers, areas, equipment, monitoring requirements and discharge standards.
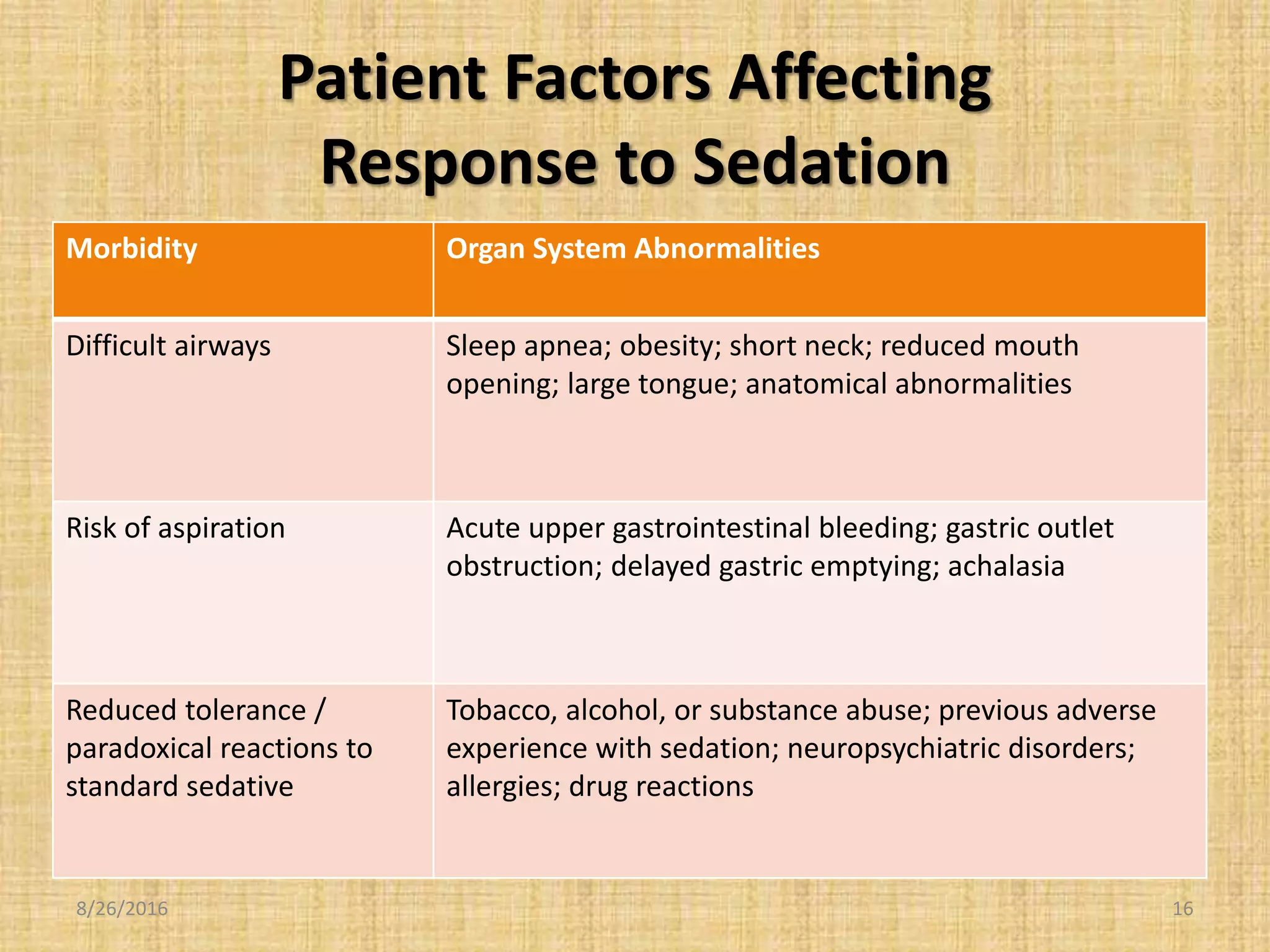
4) Patient safety is the top priority, requiring policy, screening, monitoring during and after procedures, and prudent sedation administration combined with vigilant monitoring.