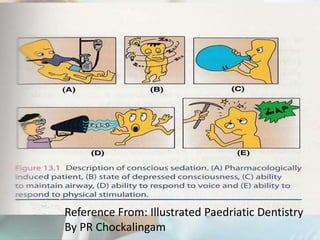
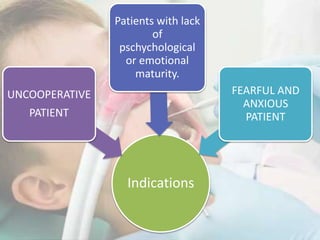
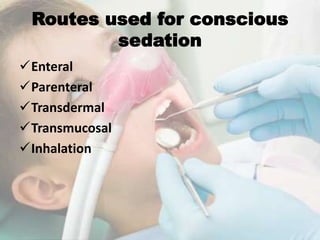
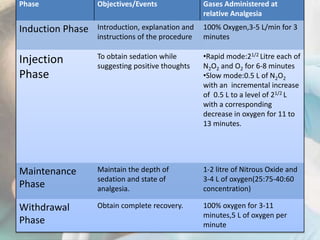
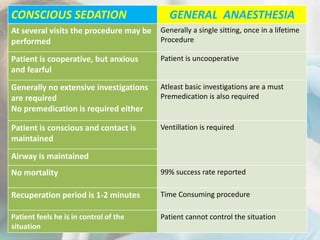
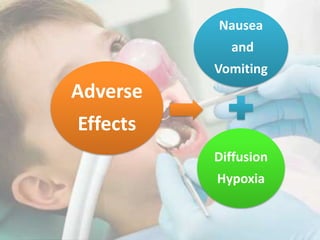
Conscious sedation is a minimally depressed level of consciousness using drugs like nitrous oxide and oxygen mixtures, fentanyl, diazepam or midazolam to relieve anxiety while maintaining the patient's ability to independently maintain their airway and respond to verbal commands. It has objectives of keeping vital signs stable, making the patient cooperative while conscious, increasing their pain threshold, and providing amnesia. It is commonly used for uncooperative or anxious patients and can be delivered enterally, parenterally, transdermally or via inhalation with monitoring of oxygen levels, ventilation and vital signs. Nitrous oxide is often used due to its rapid onset and recovery through 4 phases.