Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times
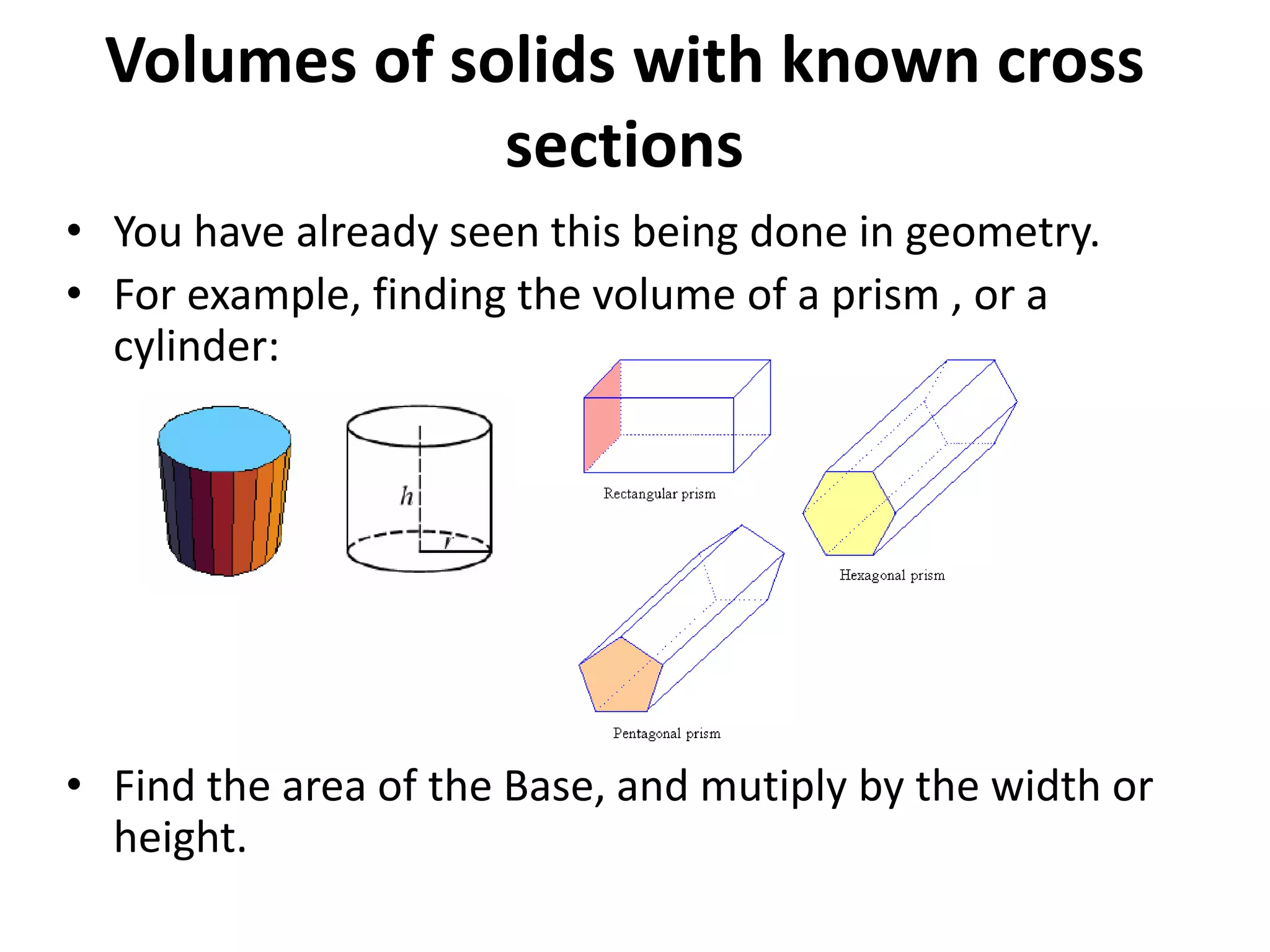


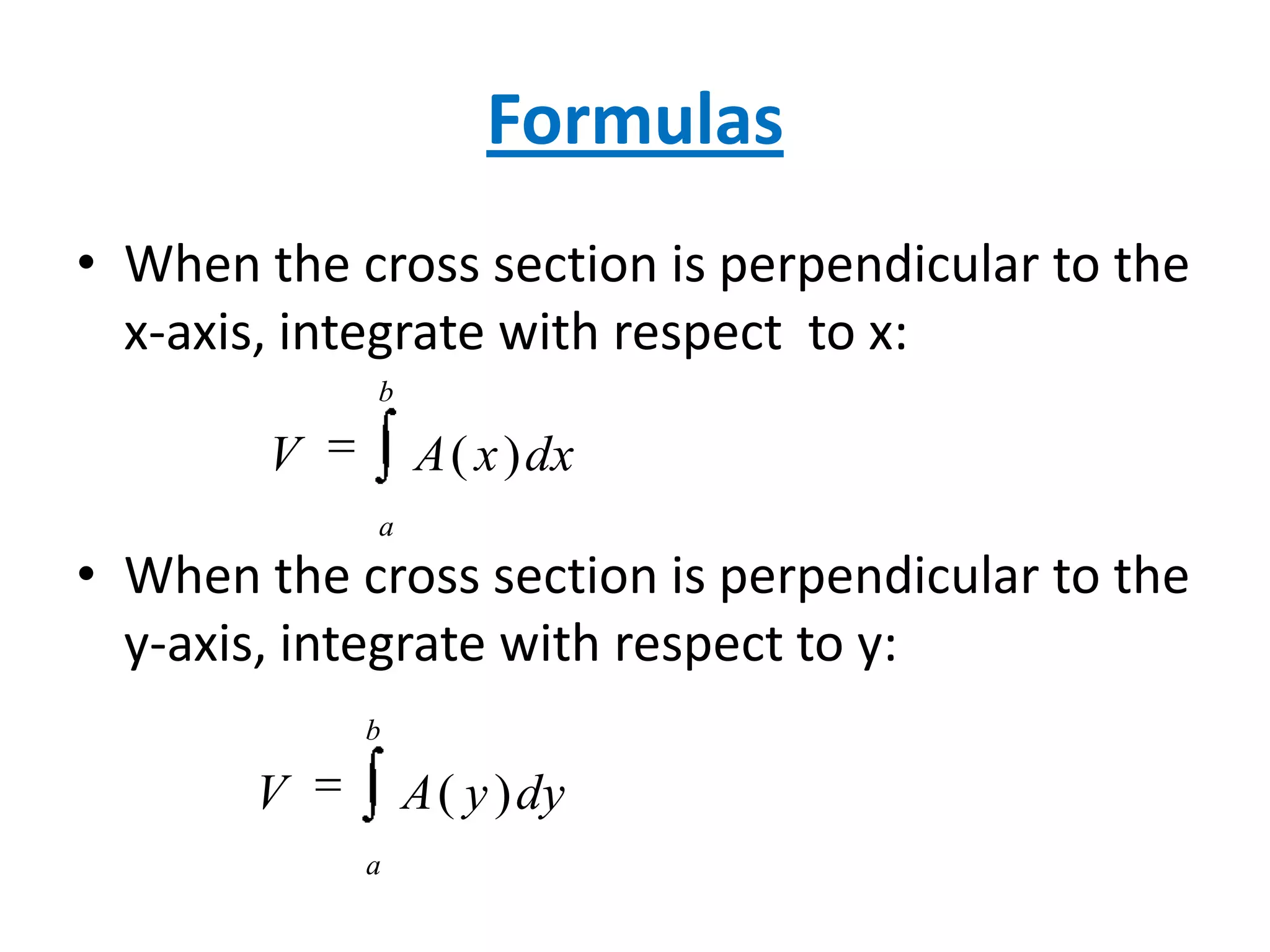
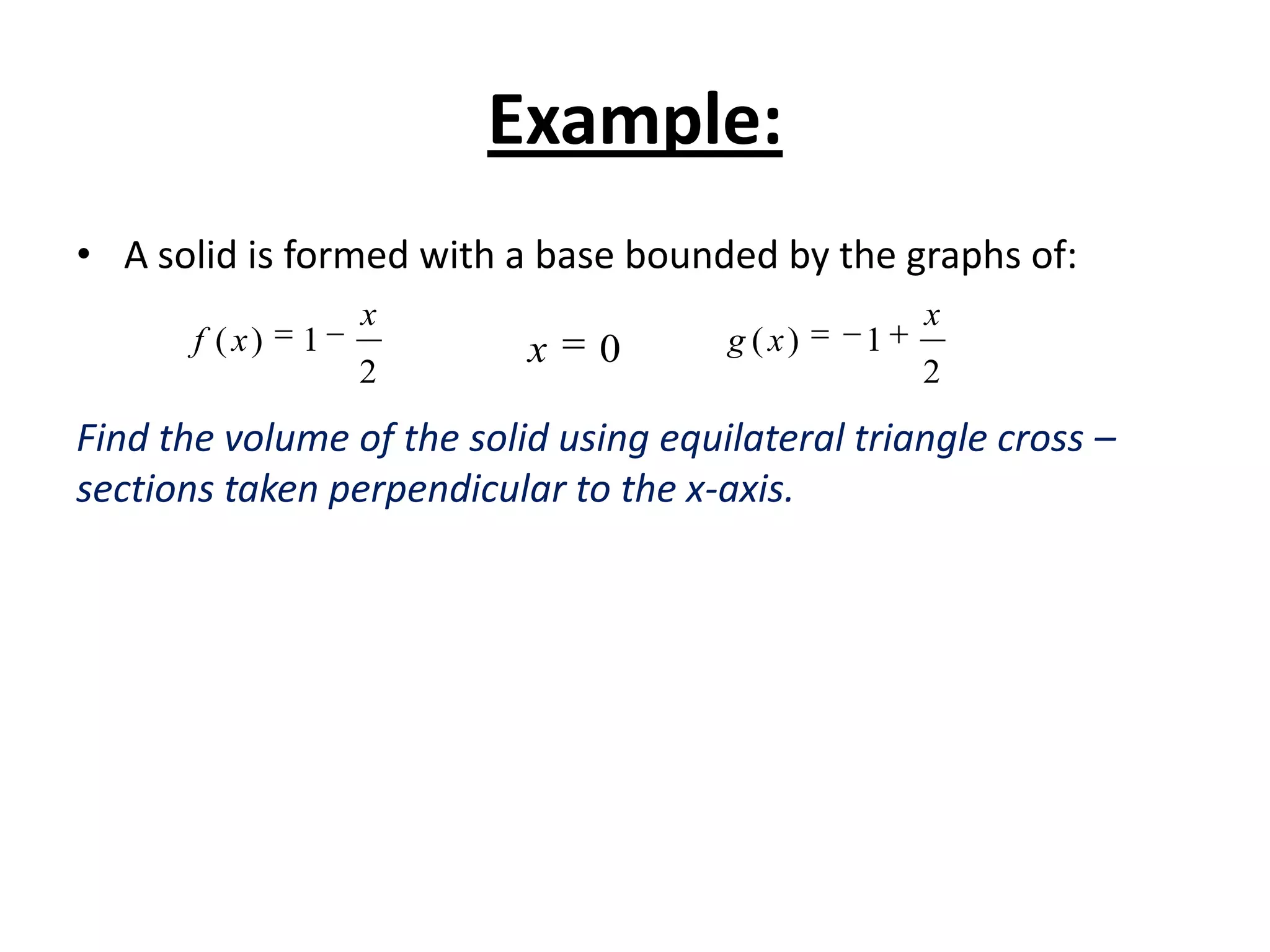
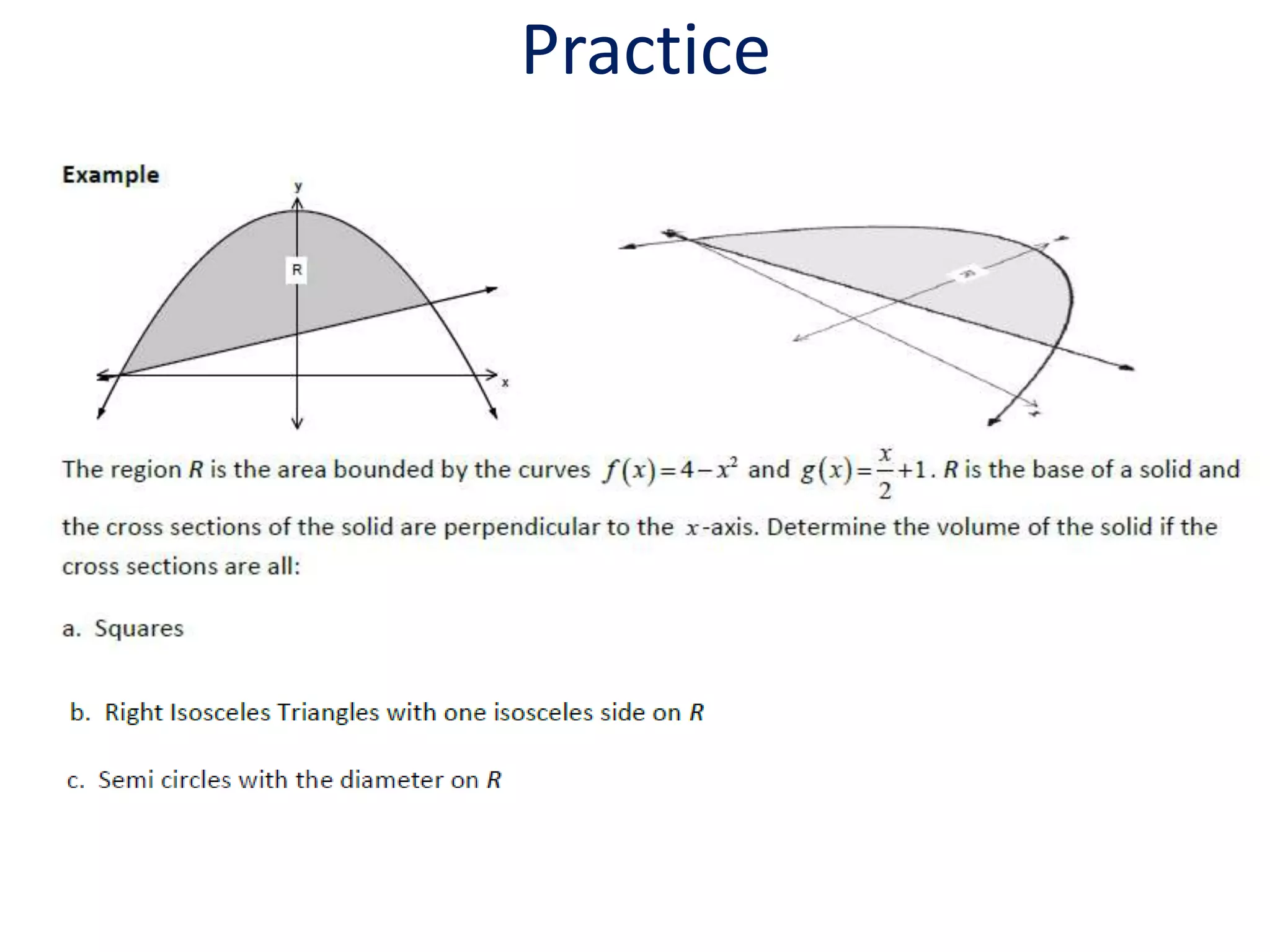

This document discusses several methods for calculating the volume of solids with known cross-sectional areas: calculating the volume of prisms and cylinders by multiplying the area of their circular or rectangular base by the height; using the disk method for solids of revolution by multiplying the circular cross-sectional areas by the width; and applying this method to solids with any shaped cross-section, such as squares, triangles, or ellipses, by multiplying the varying cross-sectional area by the width. Formulas for calculating volume by integrating the cross-sectional area with respect to x or y are also provided, along with an example problem.





