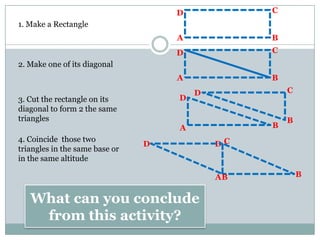
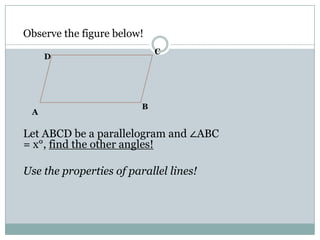
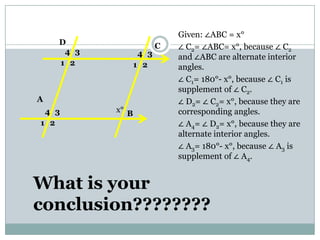
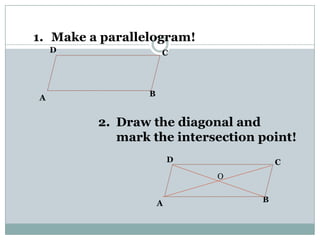
This document defines and describes properties of various quadrilaterals:
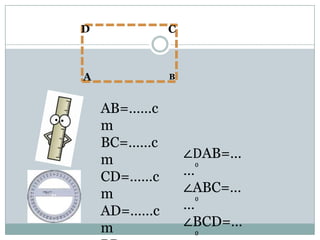
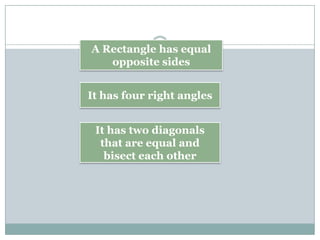
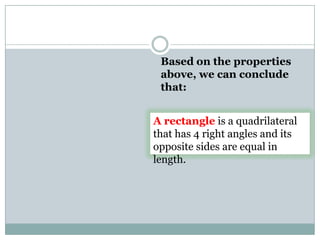
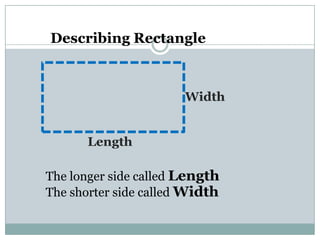
- Rectangles have four right angles and opposite sides of equal length. The area formula is length x width.
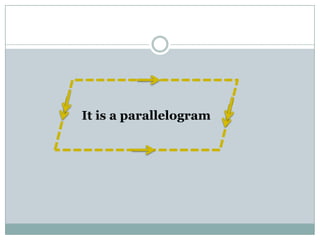
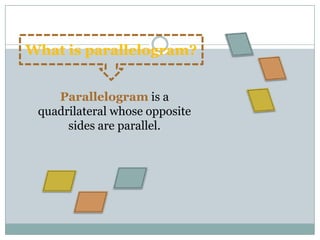
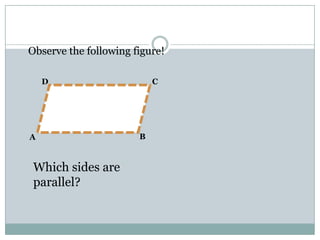
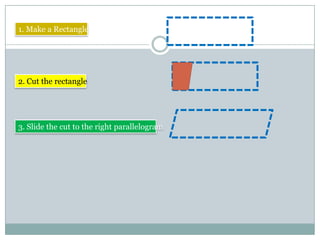
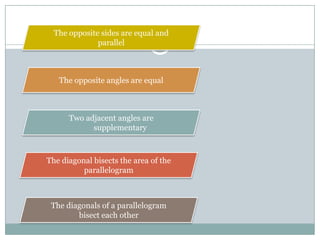
- Parallelograms have two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite angles are equal and adjacent angles sum to 180 degrees. Diagonals bisect each other.
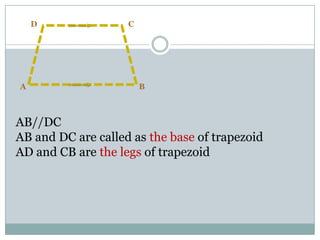
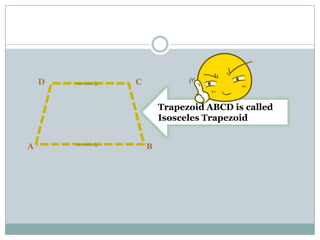
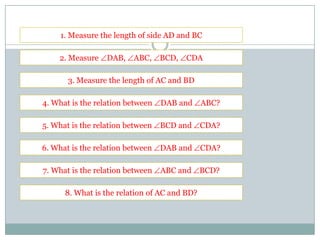
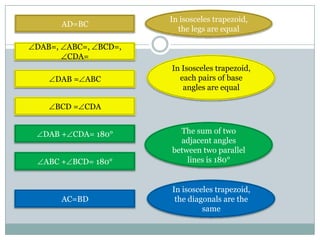
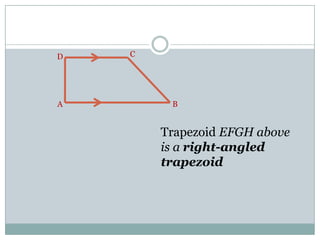
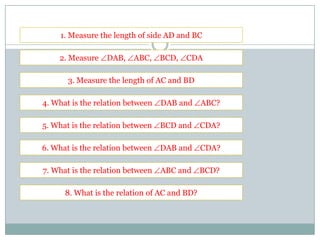
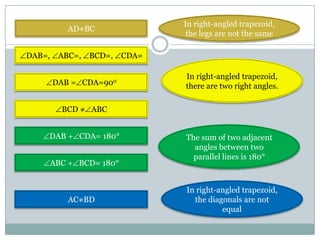
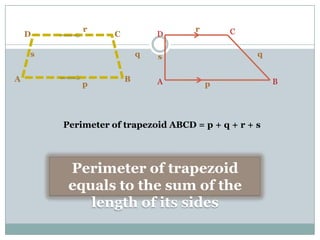
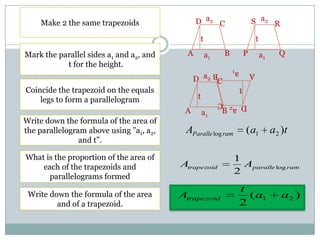
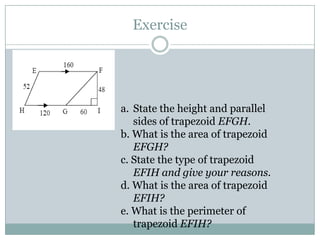
- Trapezoids have one pair of parallel sides. Isosceles trapezoids have two pairs of equal angles and equal or equal length diagonals. Right trapezoids contain one right angle. The area of any trapezoid is half the product of the height and sum of the parallel sides.