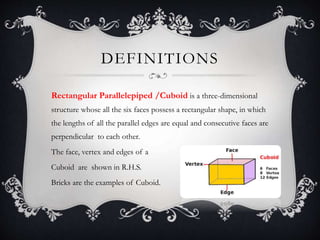
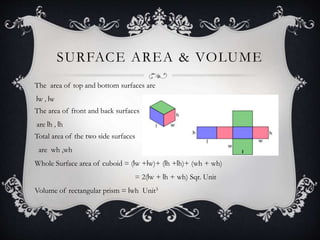
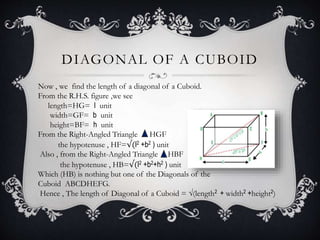
The document discusses cuboids and cubes. It defines a cuboid as a three-dimensional structure with six rectangular faces where parallel edges are equal length and faces meet perpendicularly. Bricks are given as examples of cuboids. A cube is defined as a special cuboid where all sides have equal length. The document provides formulas for calculating the surface area and volume of cuboids and cubes. It derives formulas showing that the diagonal of a cuboid is the square root of the sum of the squares of its dimensions, and the diagonal of a cube is three times the length of one side.