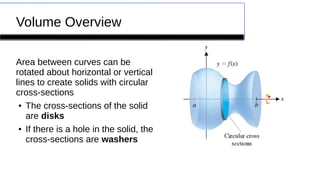
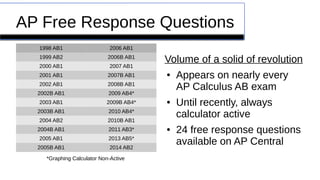
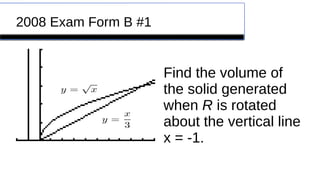
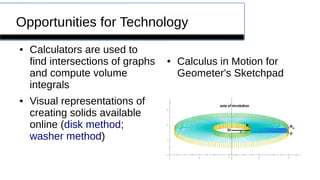
This document provides an overview of calculating volumes of solids using the disk and washer methods. It defines key concepts like using the disk method when the cross-sections are disks and the washer method when there is a hole. Examples are given of how to present these methods using a cucumber and cantaloupe. Remediation resources like videos are suggested to help with common issues like determining radii and limits of integration. Finally, several past AP exam questions involving volumes of revolution are referenced.