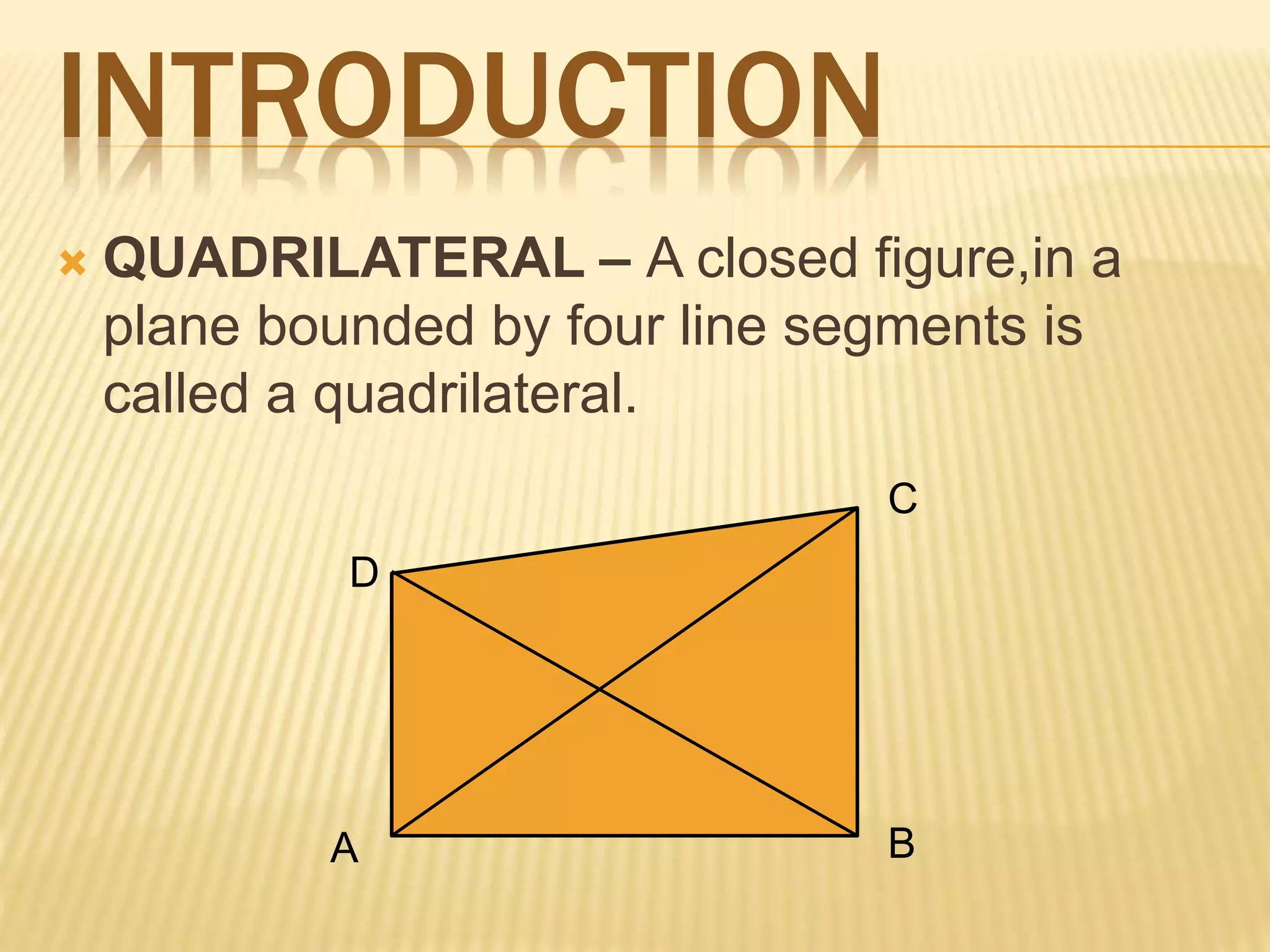
The document defines and describes different types of quadrilaterals. It states that a quadrilateral is a closed figure bounded by four line segments. The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral is always 360 degrees. The main types of quadrilaterals discussed are trapezium, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square, and kite. Each shape is defined by the properties of the lengths and orientations of its sides.