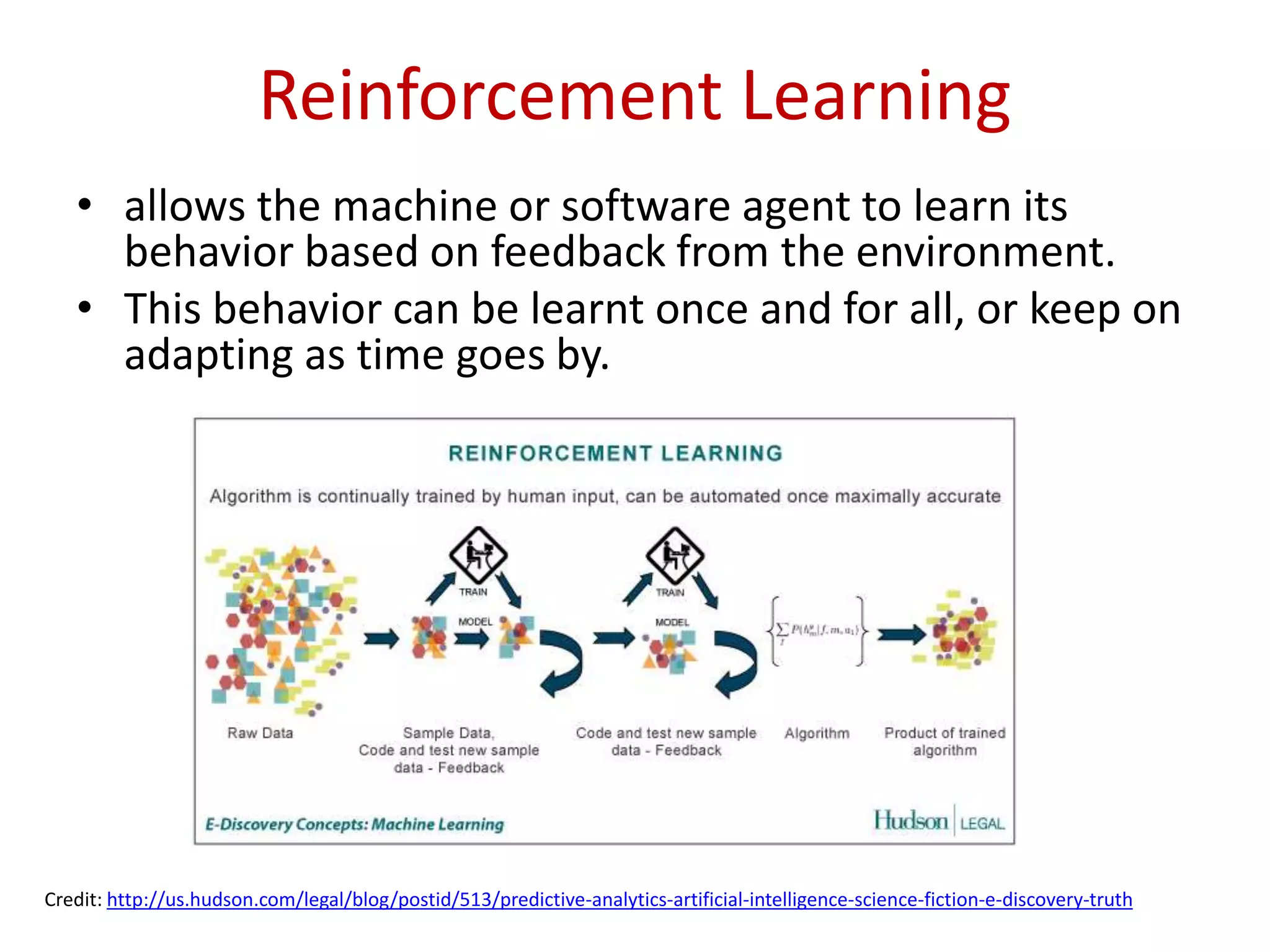
The document outlines an introduction to machine learning, covering key topics such as classification, clustering, and regression techniques, along with their use-cases like spam detection and sentiment analysis. It details different learning workflows including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning while also listing popular tools and frameworks for practical implementation. The meetup event aims to explore various cutting-edge technologies related to machine learning and information retrieval.