1. The document summarizes a seminar on machine learning presented by Amit Kumar to the Rajkiya Engineering College.
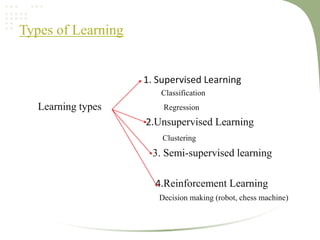
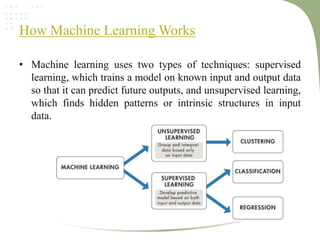
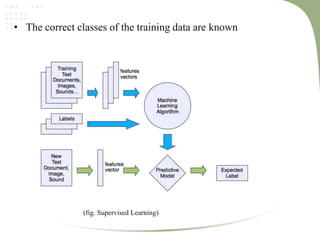
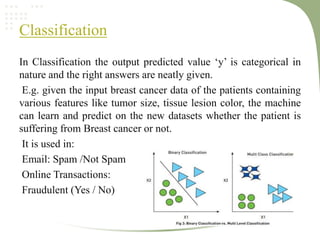
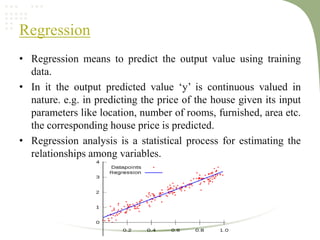
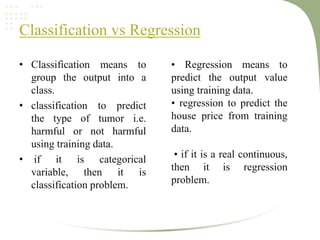
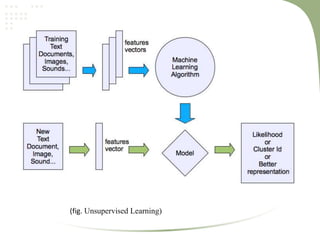
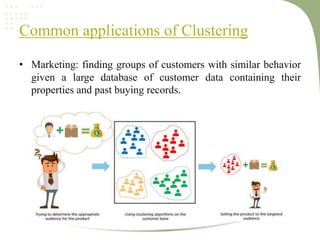
2. It discusses key machine learning concepts like supervised learning techniques of classification and regression, as well as unsupervised learning techniques like clustering.
3. Applications of machine learning discussed include virtual assistants, social media services, image recognition, and medical diagnosis.