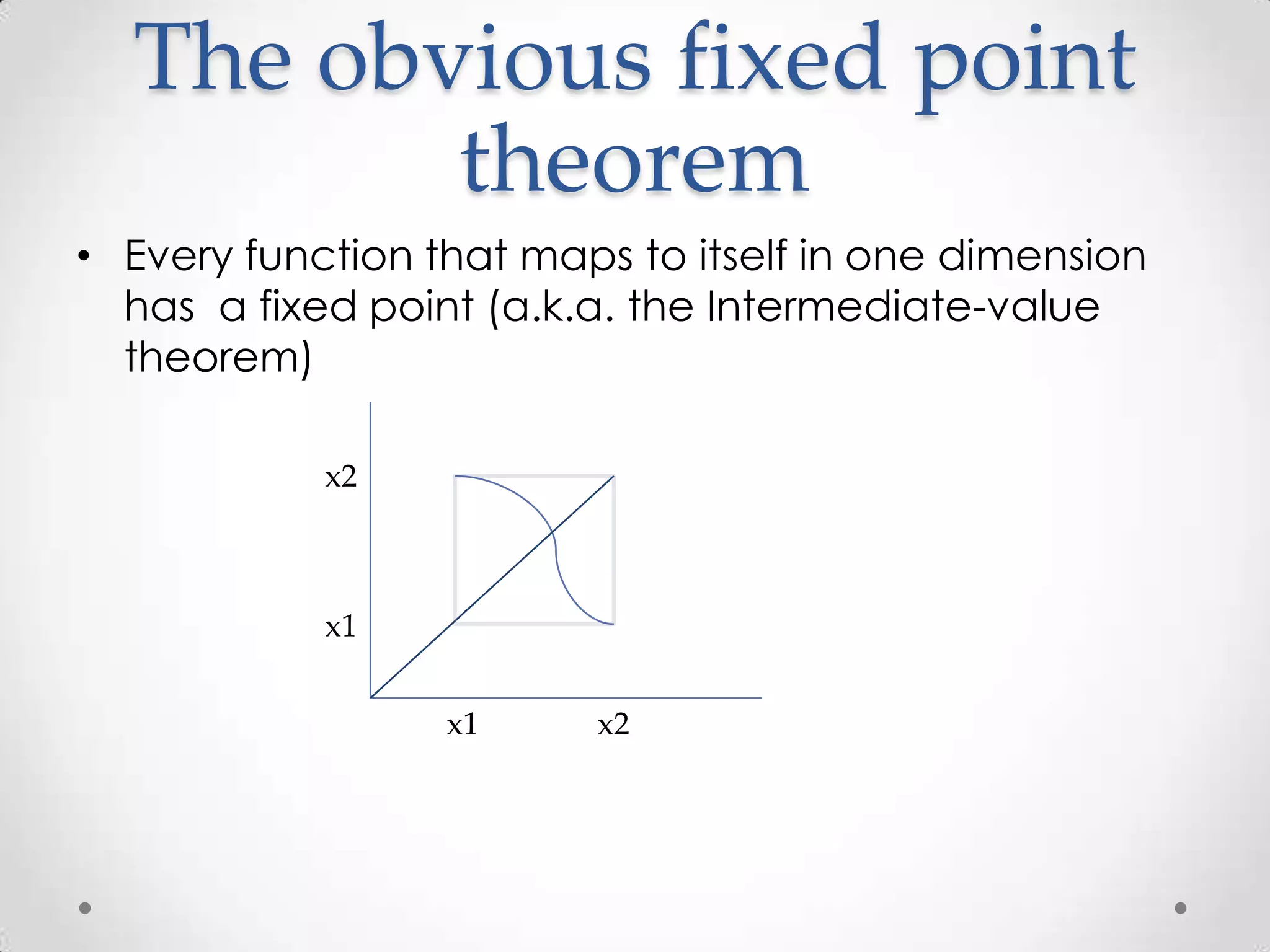
This document provides an overview of fixed point theorems. It defines fixed points as points where a function maps to itself (f(x)=x). Brouwer's fixed point theorem states that any continuous function mapping a closed ball in Euclidean space to itself must have a fixed point. Implications include that there is always a hurricane somewhere on Earth and a method for constructing fixed points by overlaying maps. The hairy ball theorem and Kakutani's fixed point theorem are also discussed.