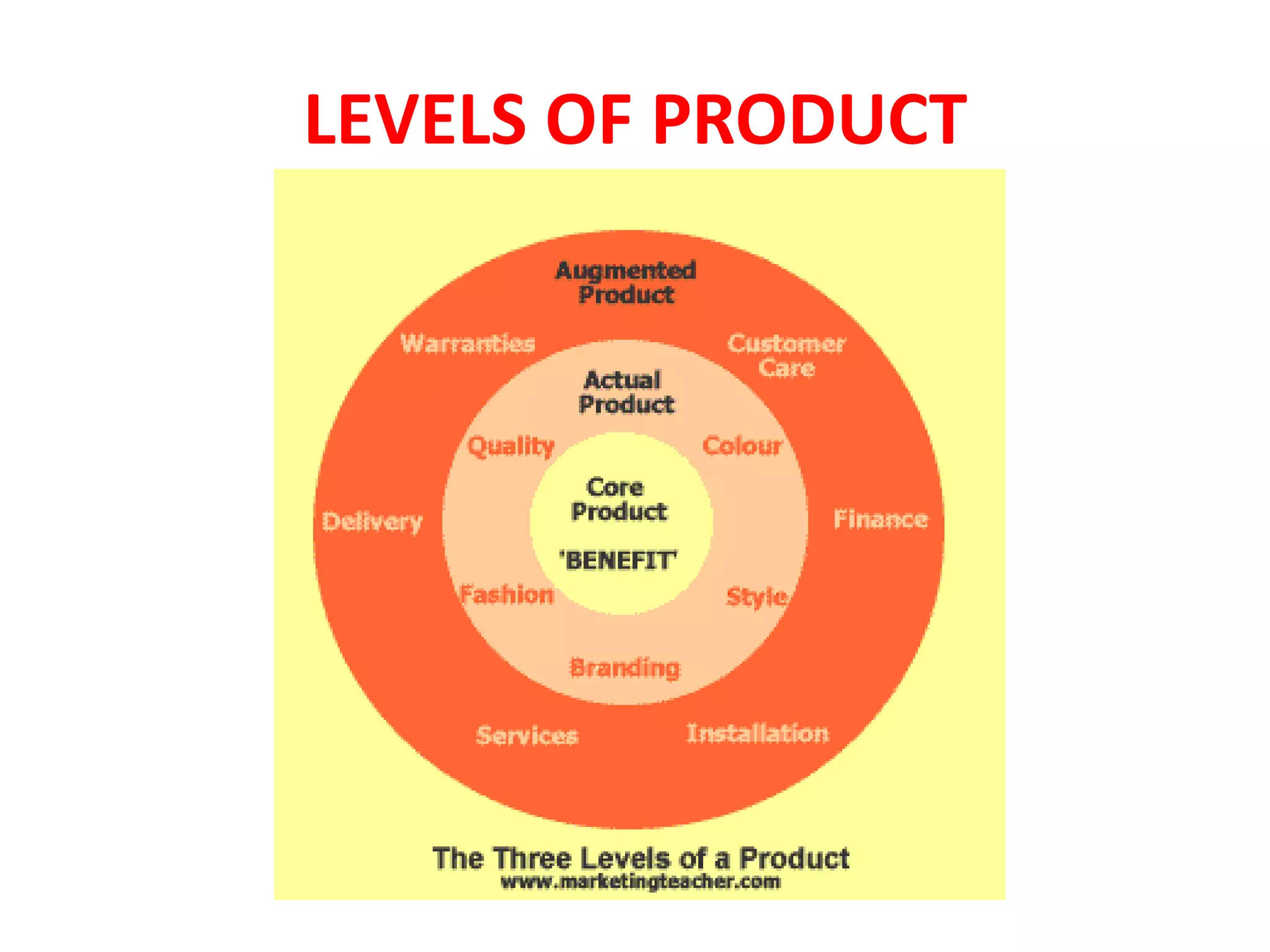
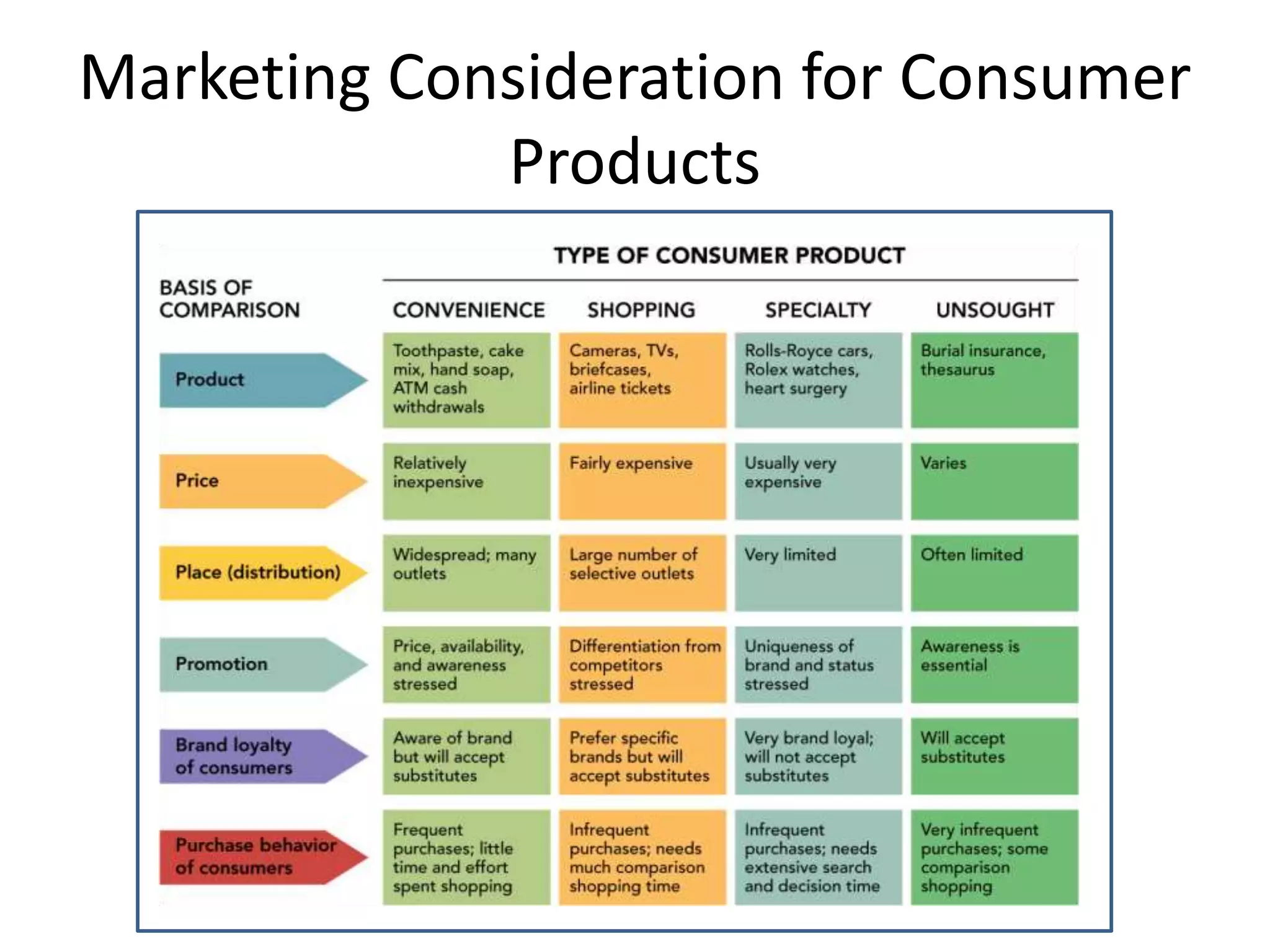
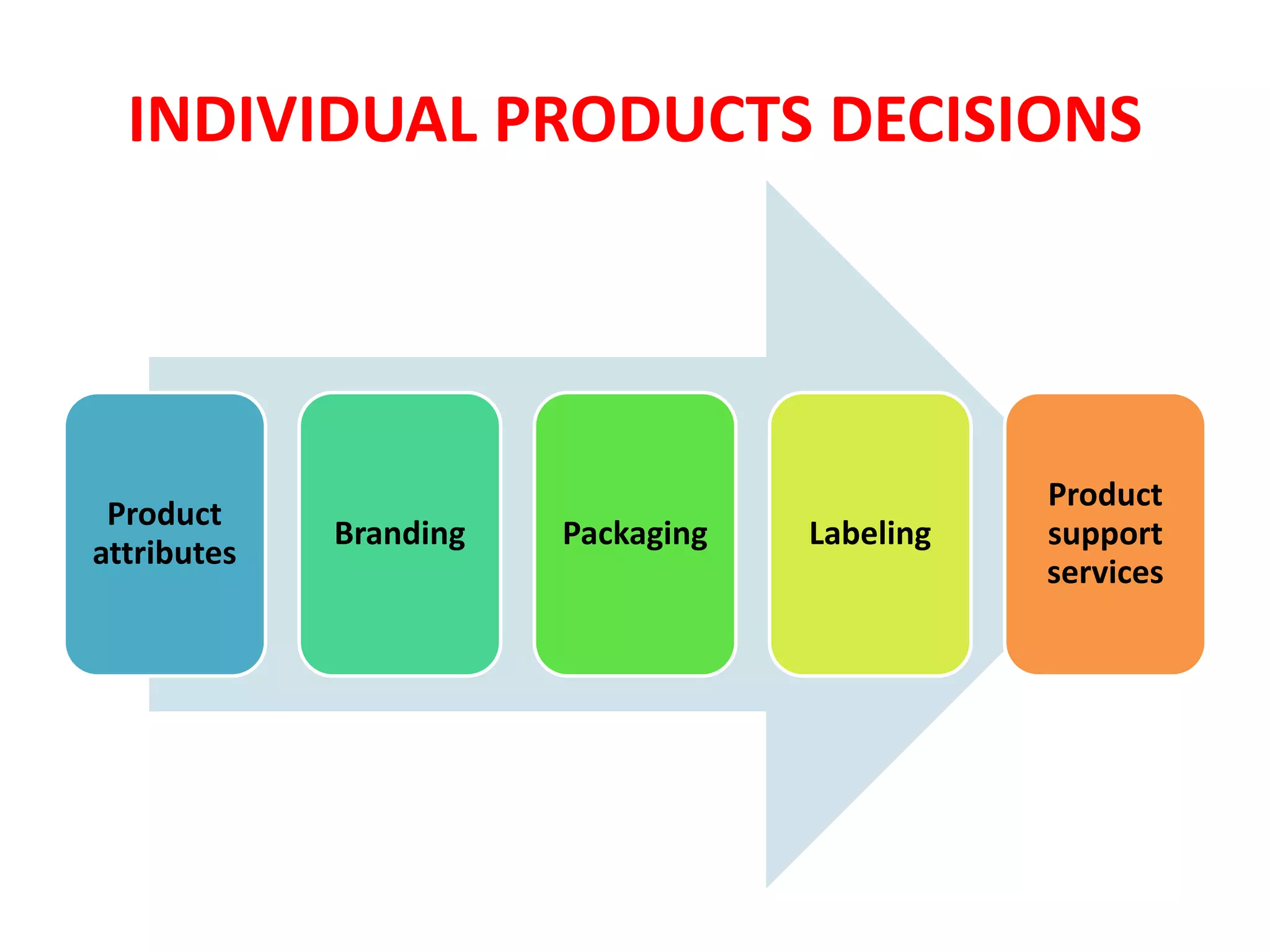
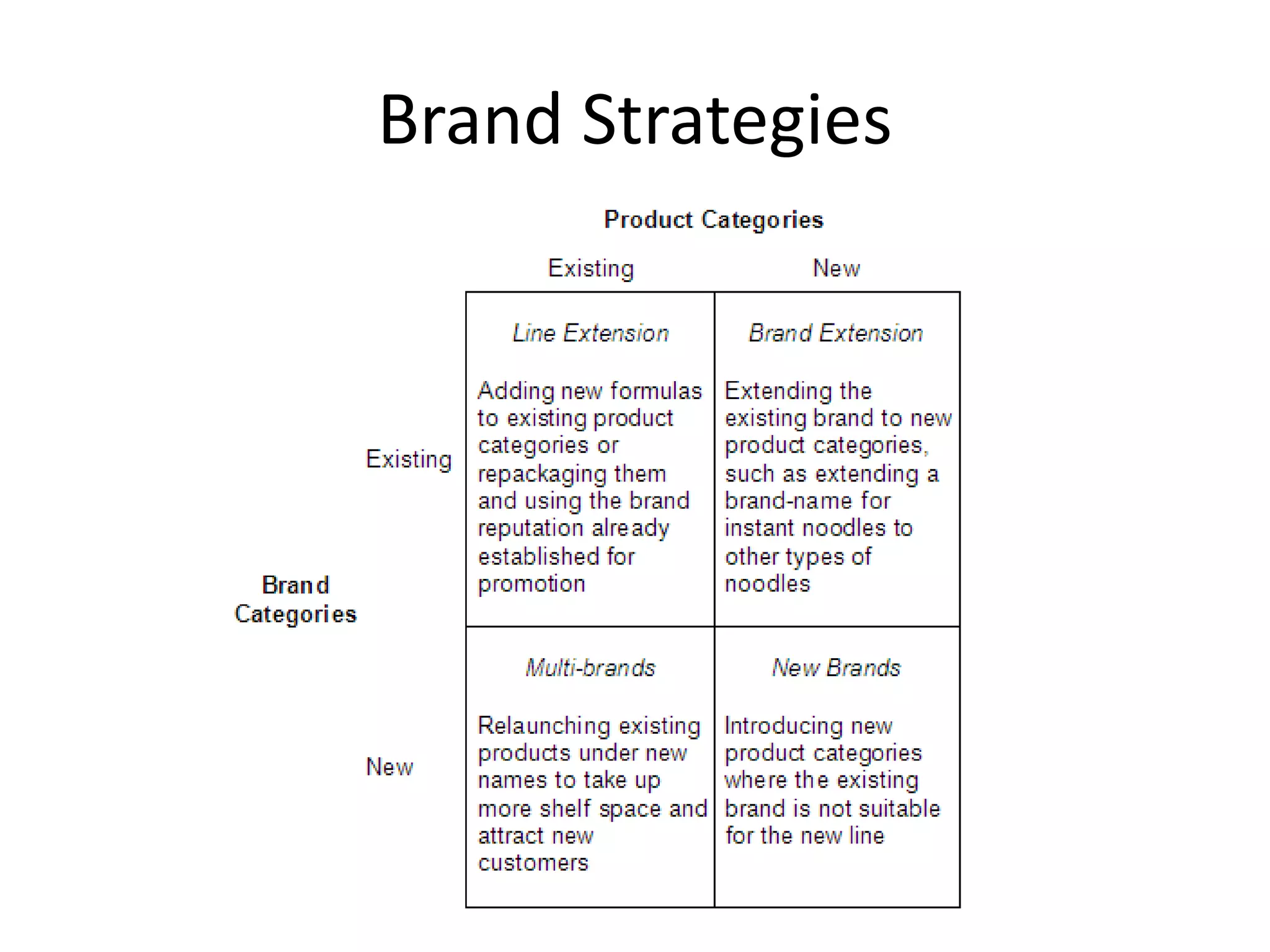
Chapter 5 discusses product strategy, defining a product as anything offered to satisfy consumer needs, which includes core, actual, and augmented products. It outlines various product classifications (consumer and industrial products), marketing considerations, and attributes such as branding and packaging. The chapter also explores brand strategies like line extensions, brand extensions, and the importance of packaging and labeling in product marketing.



















![Brand Strategies
• Brand Extensions
– Involves the use of a successful brand name to
launch a NEW or MODIFIED PRODUCTS in a NEW
CATEGORY]
– Example: Honda (Motorcycles, Cars, etc.)
– Pro: Instant recognition & faster acceptance
– Cons: if the brand extension fails, it may harm the
consumer attitude towards the brand name.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-productstrategy-150412201839-conversion-gate01/75/Chapter-5-Product-Strategy-26-2048.jpg)





