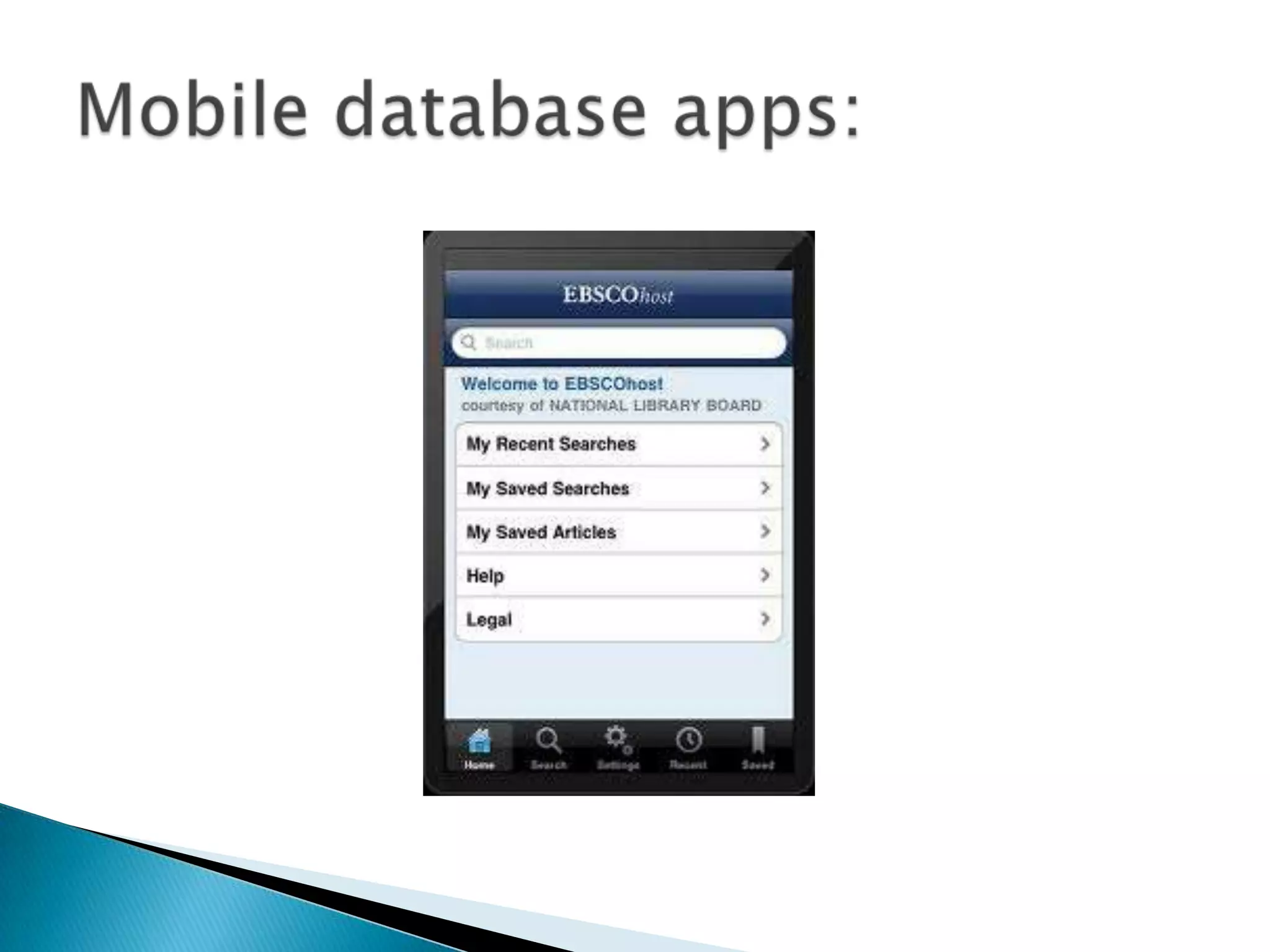
This document discusses trends in reference services in academic libraries. It notes that reference is moving from traditional service desks to a more distributed model with embedded librarians, virtual services, and tiered staffing. Key aspects of this model include merging service points, placing librarians in areas where users work as liaisons, and offering various virtual methods like chat and text in addition to in-person help. The goal is to meet users' needs through flexible and accessible reference services.