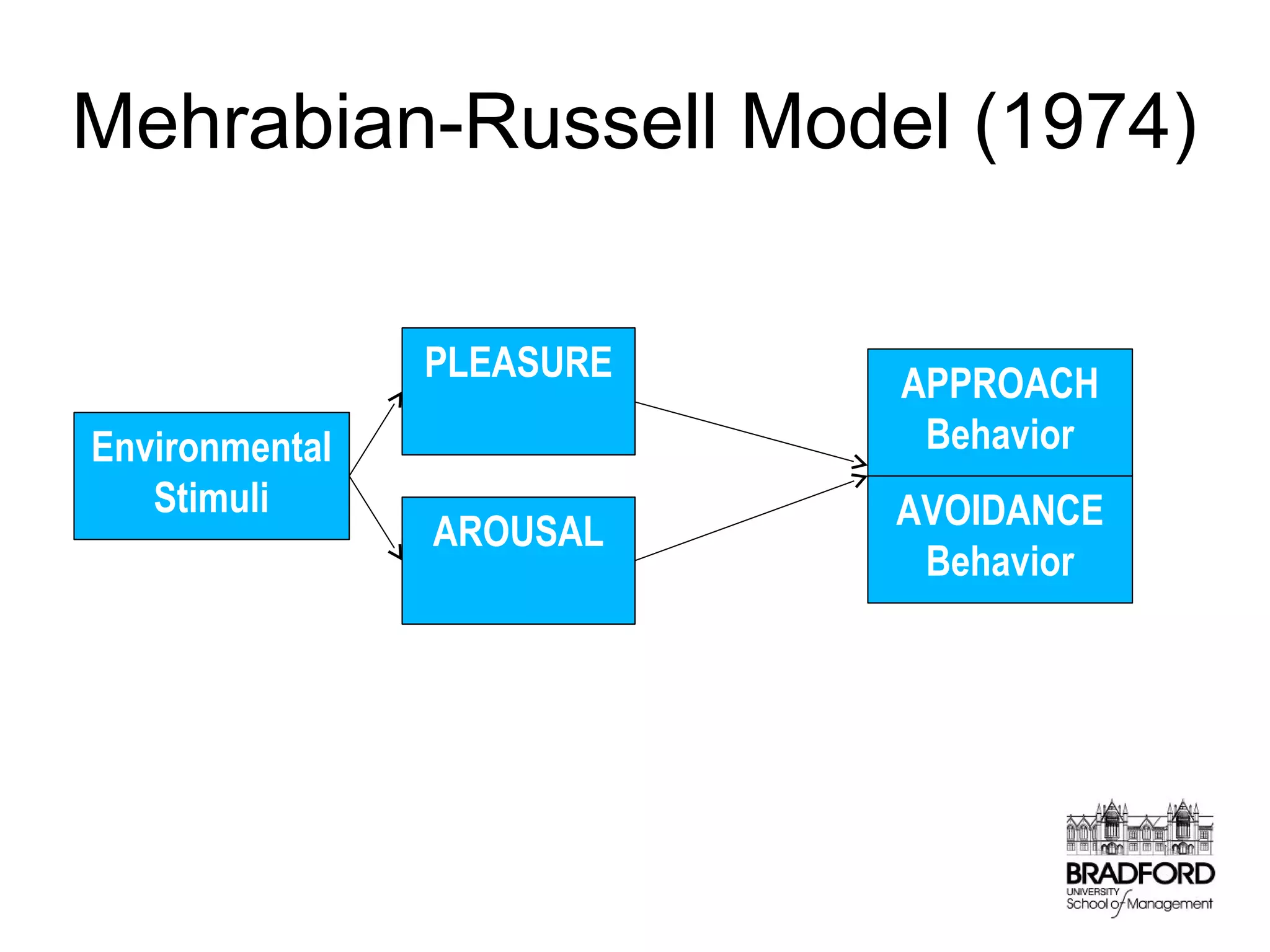
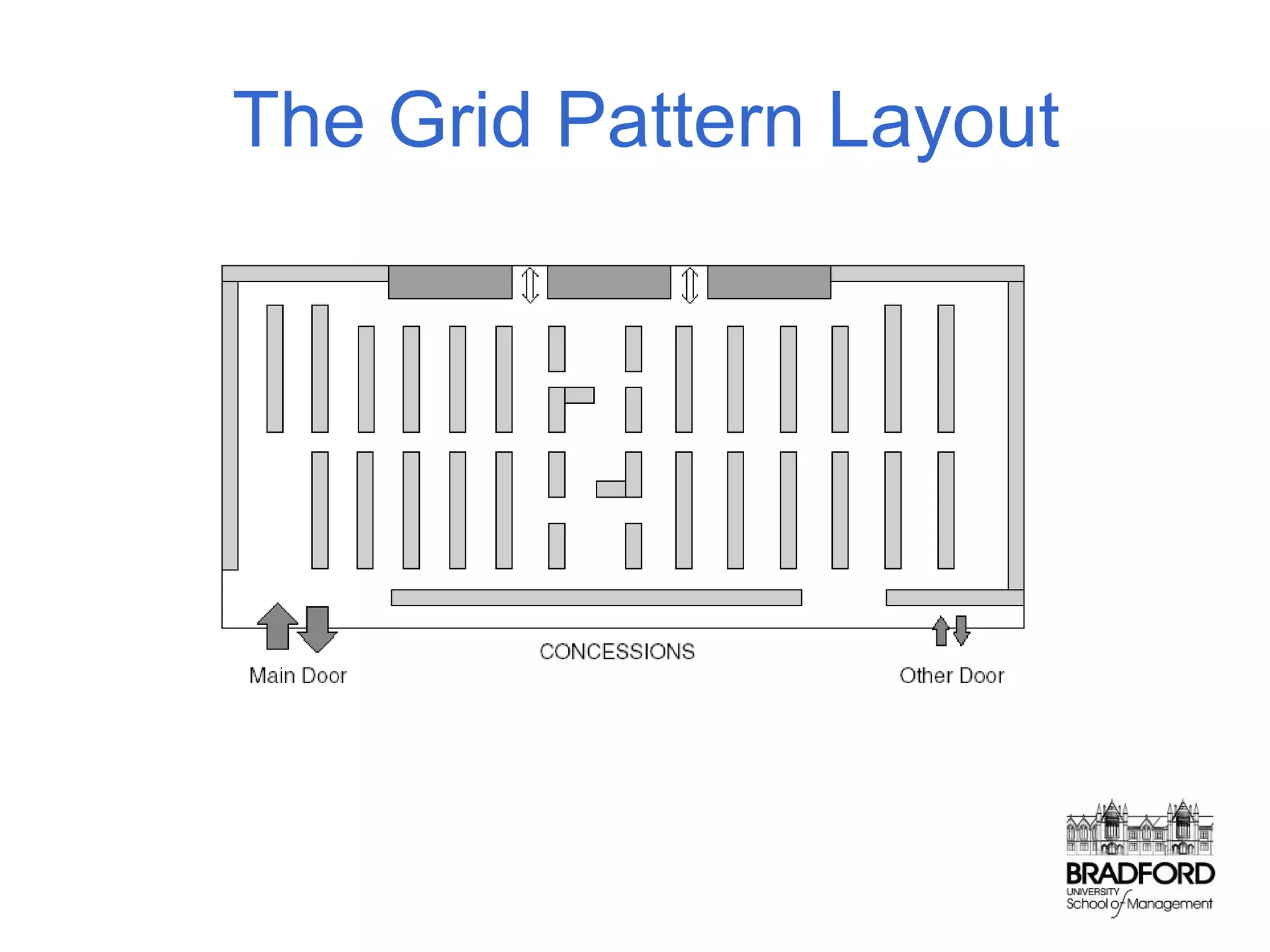
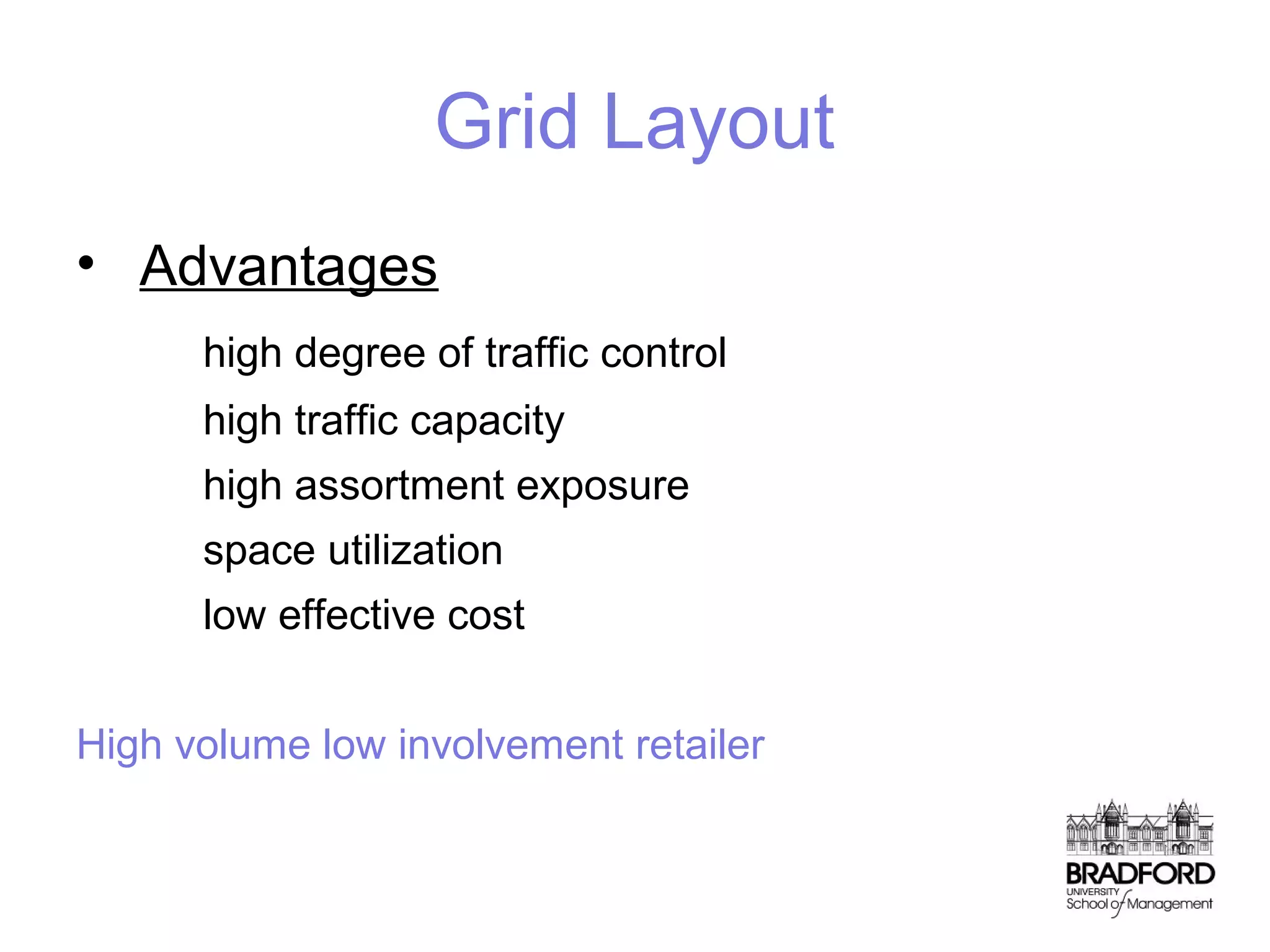
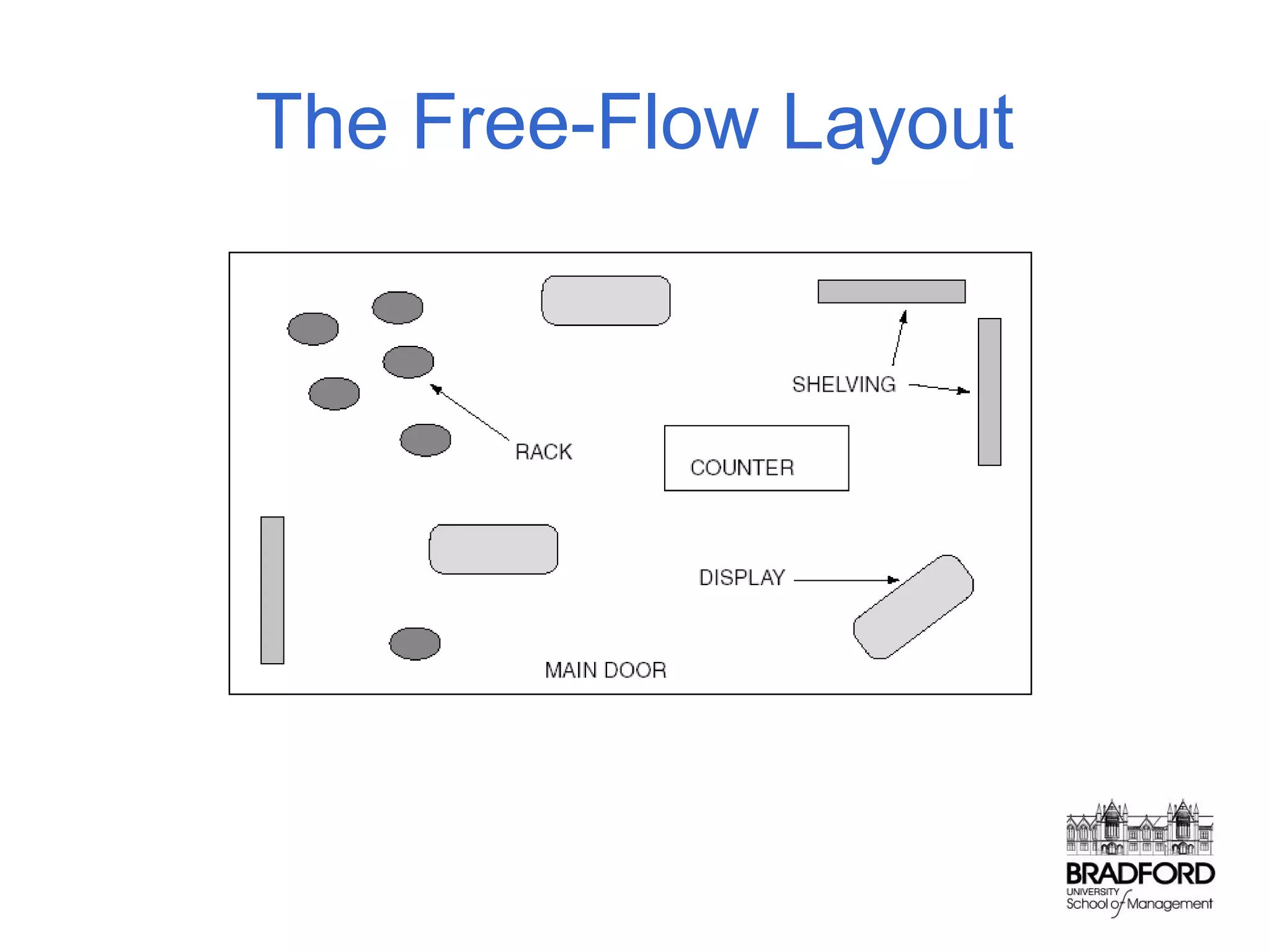
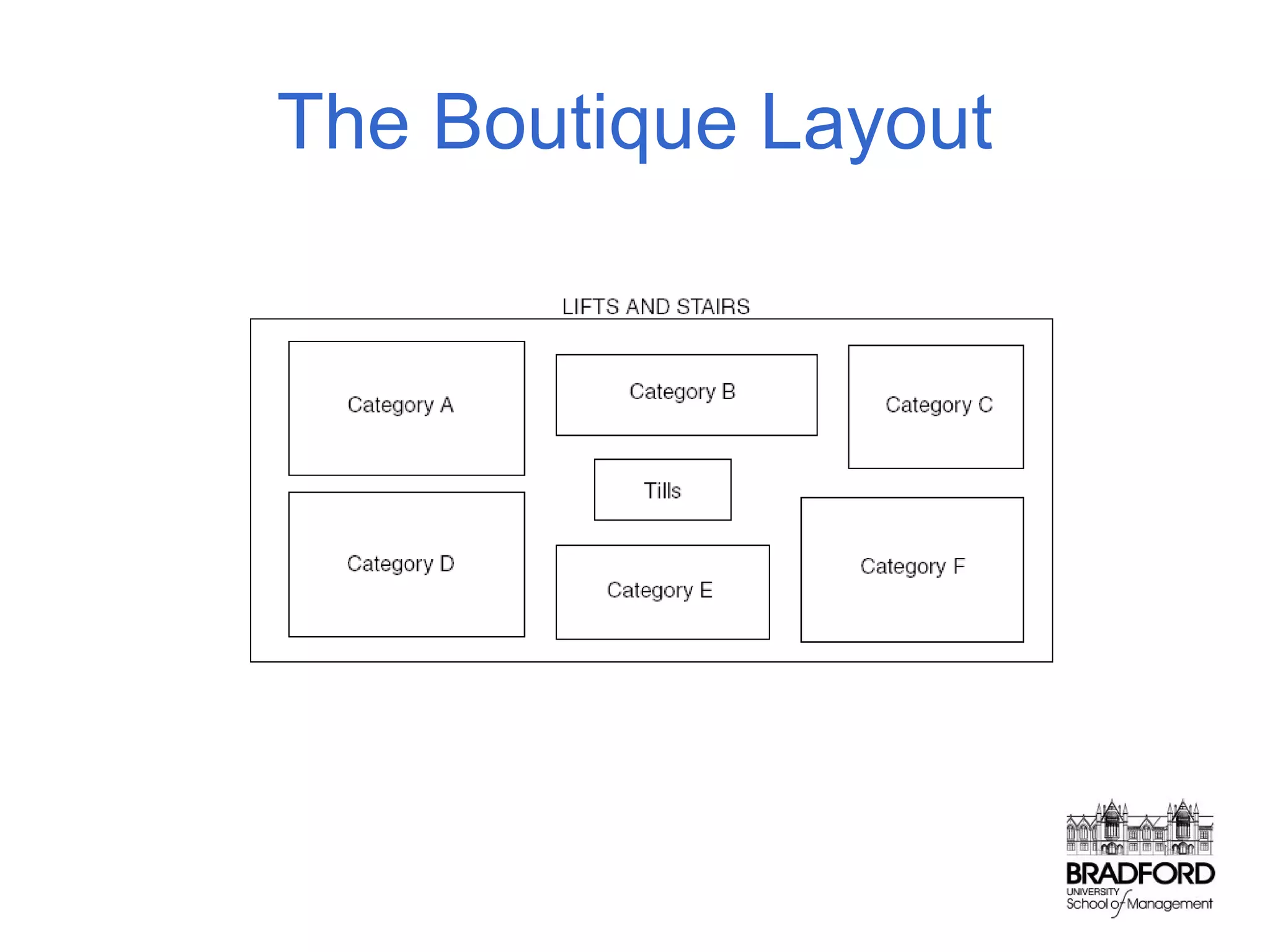
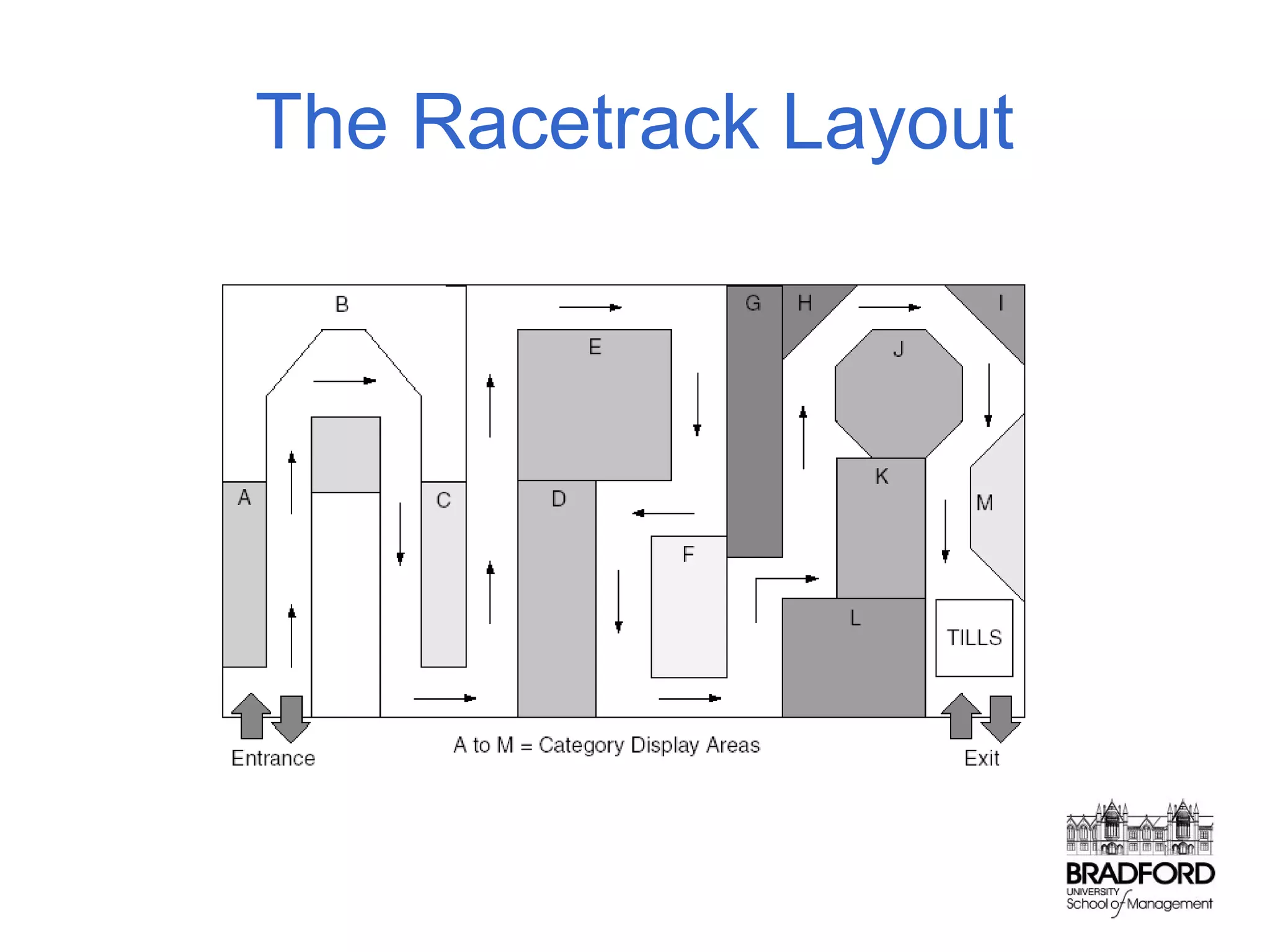
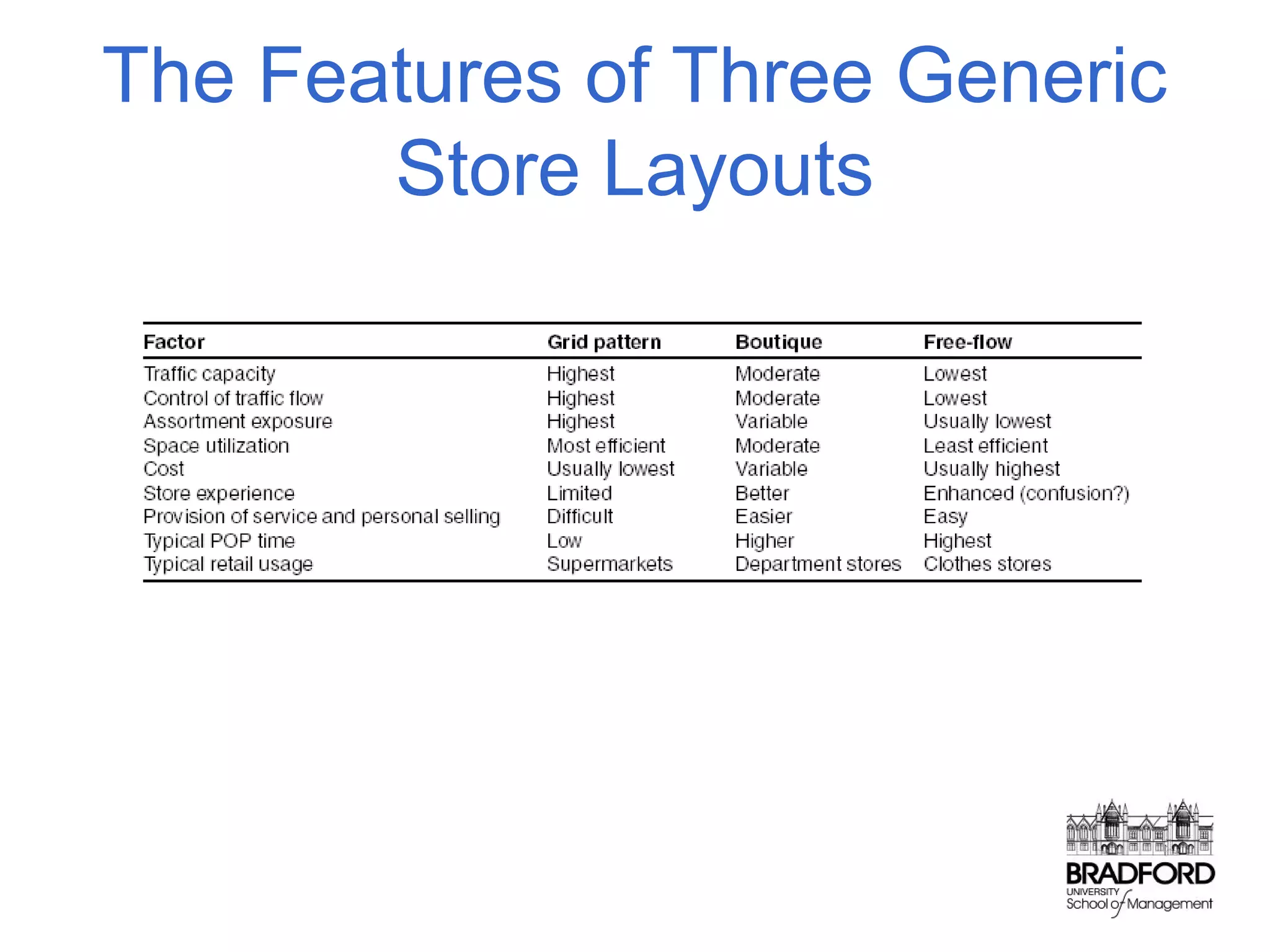
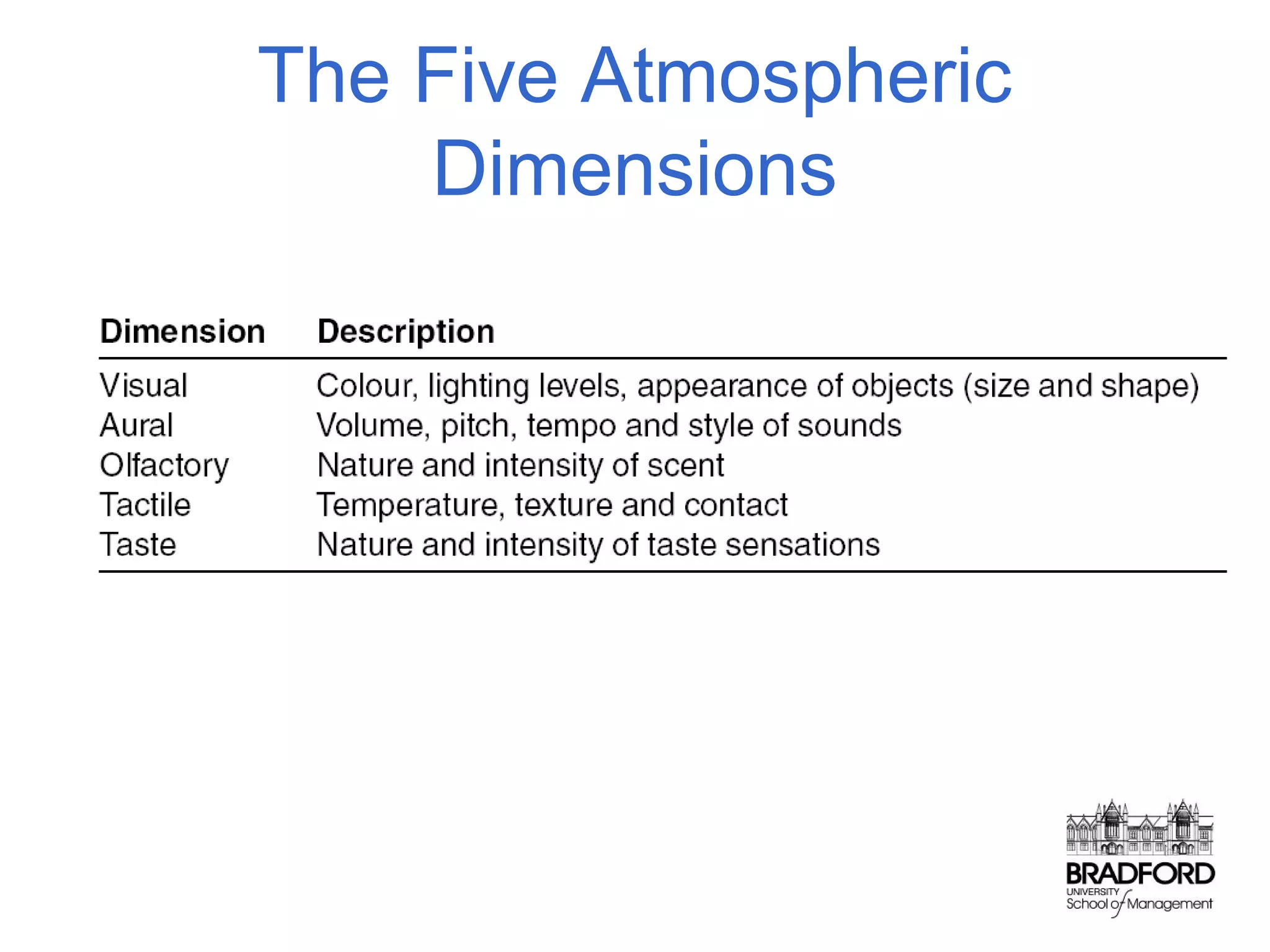
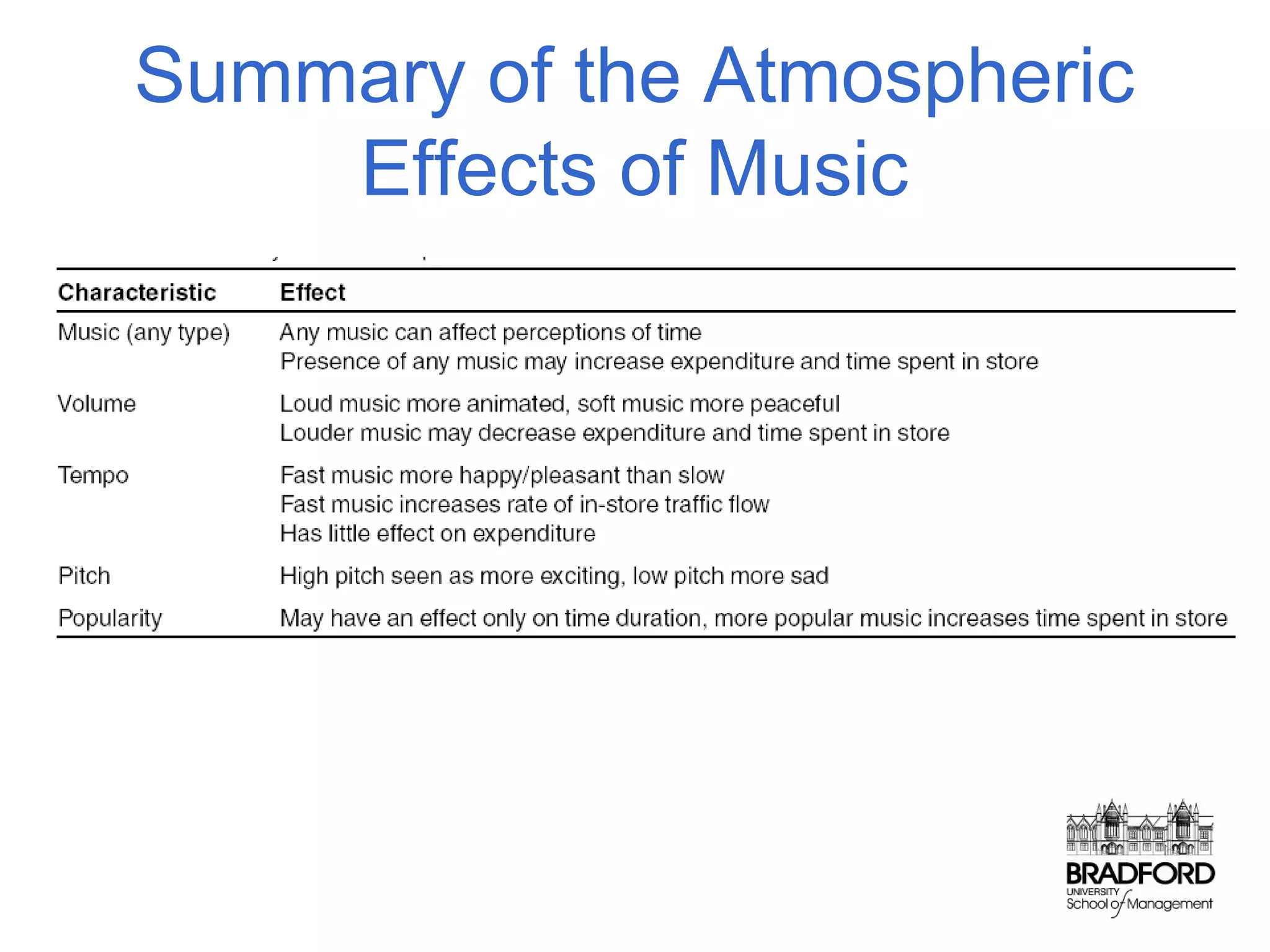
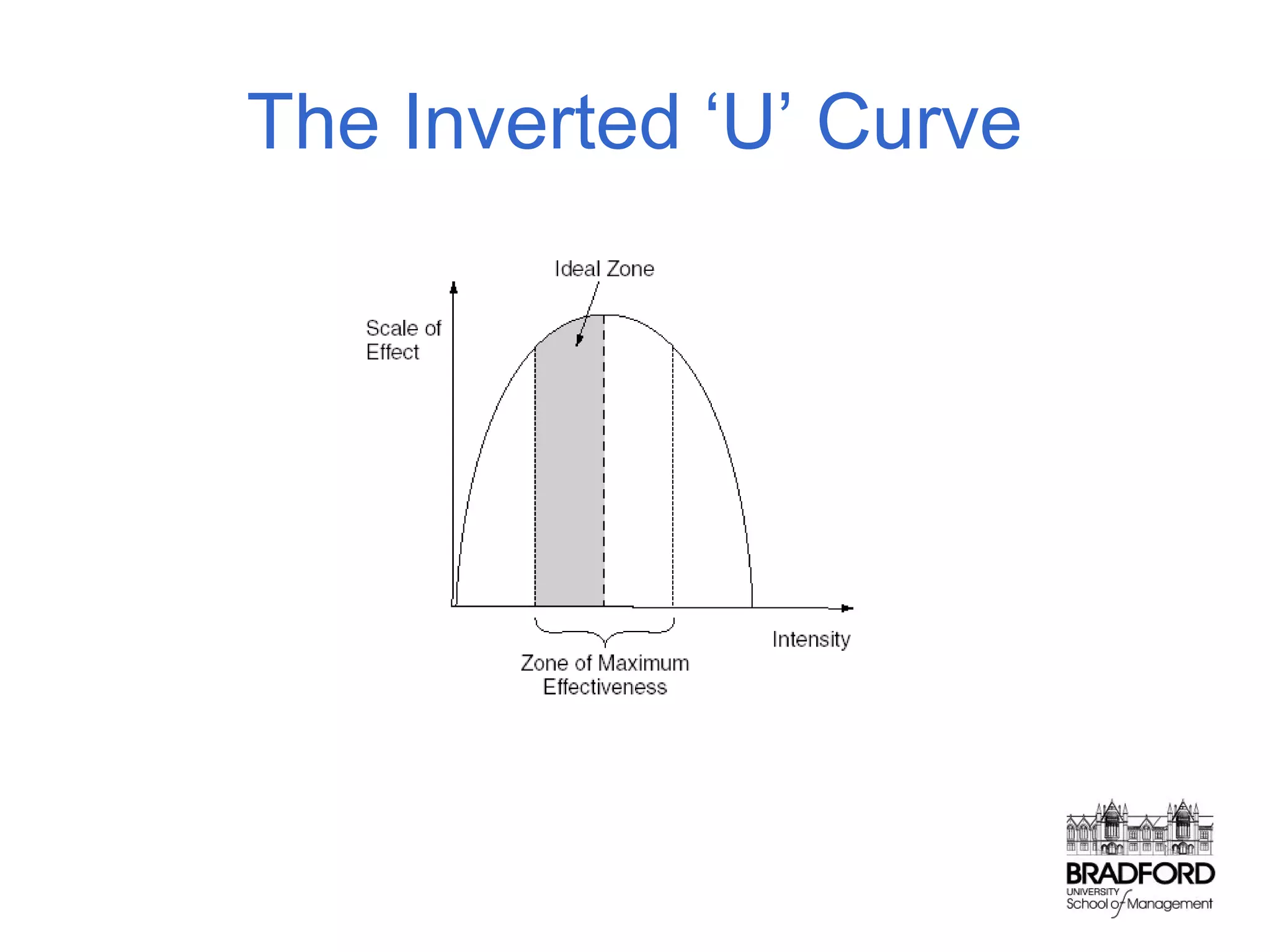
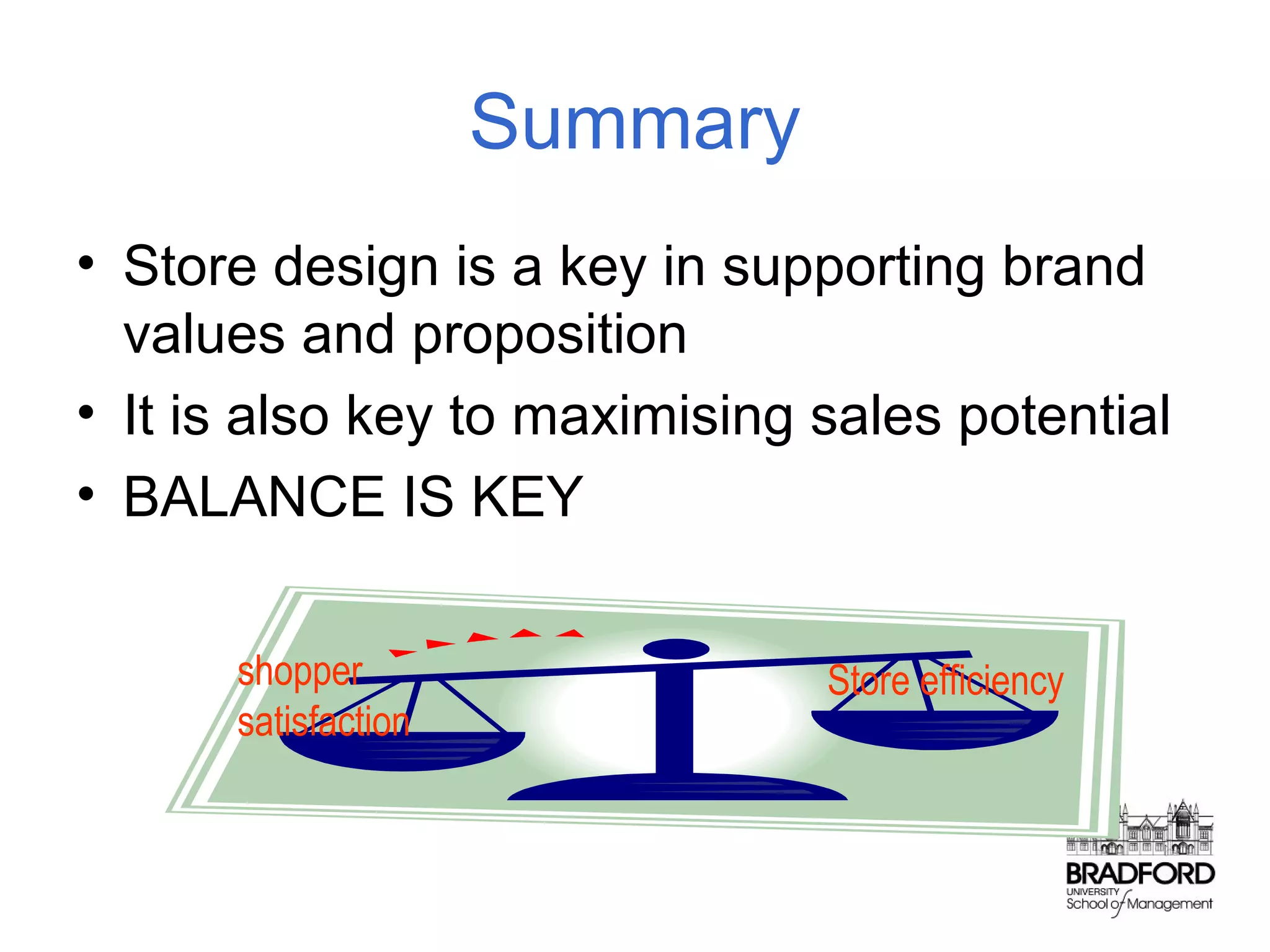
This document discusses store design and its influence on shopper behavior. It outlines Baker's framework, which identifies three dimensions of store environment: design (layout, architecture, displays), social (level of contact), and ambient (atmospheric factors). Mehrabian-Russell and Elaboration Likelihood models are also referenced to explain how environmental stimuli impact shopper pleasure, arousal, and approach/avoidance behaviors. The lecture emphasizes that store design should create a controlled environment that conveys brand messages through layout, displays, and atmospheric elements to enhance the shopping experience.