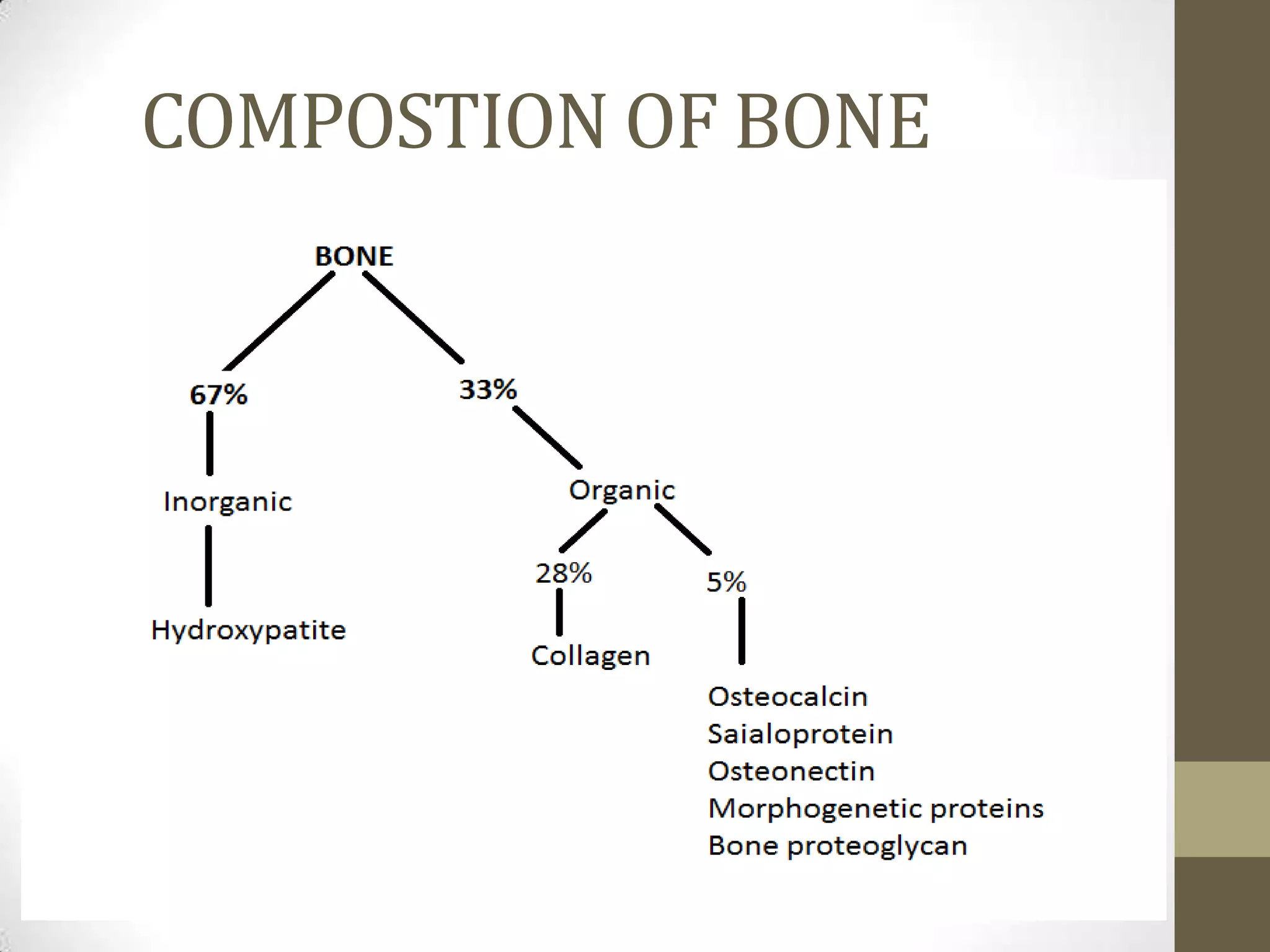
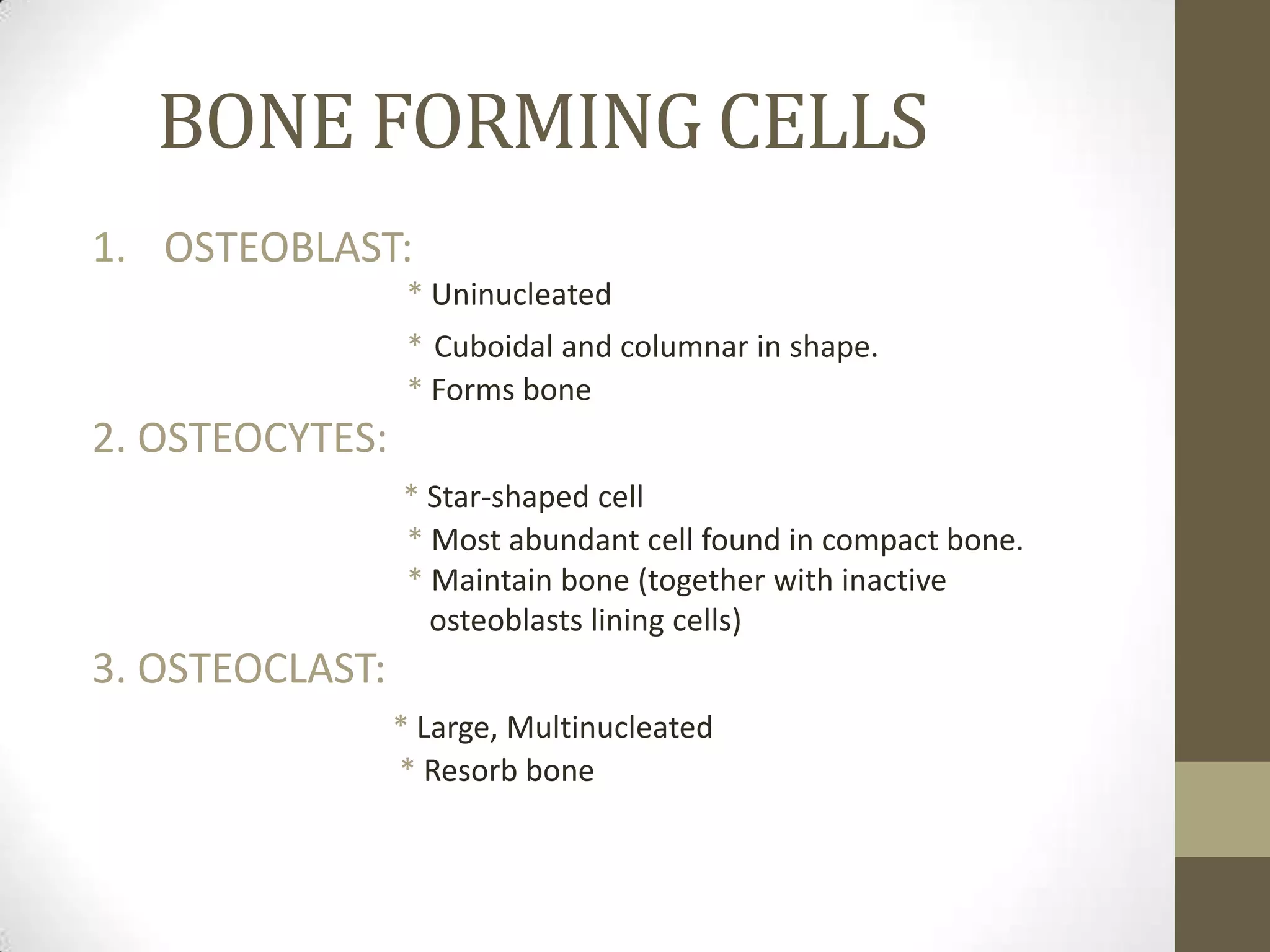
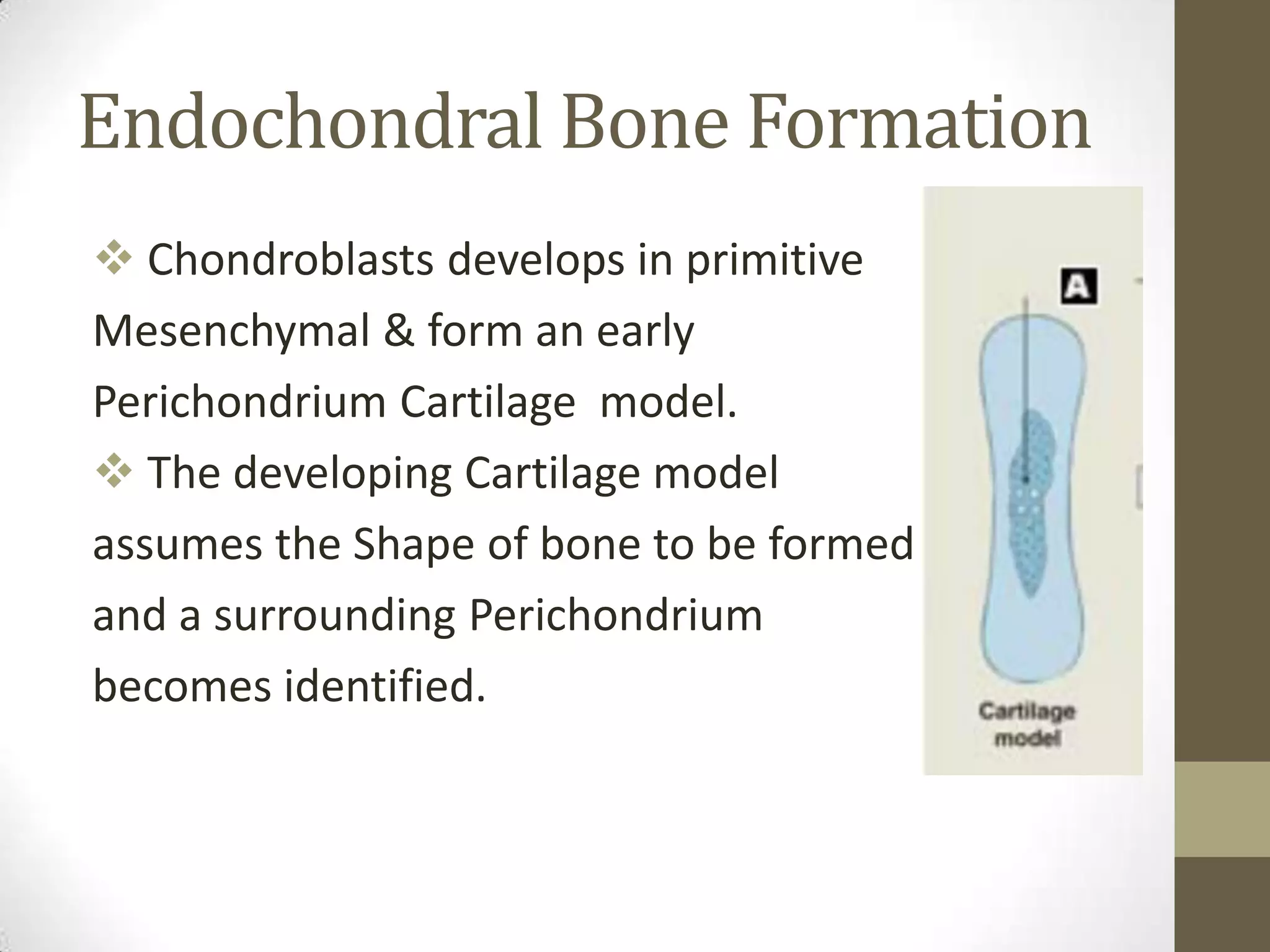
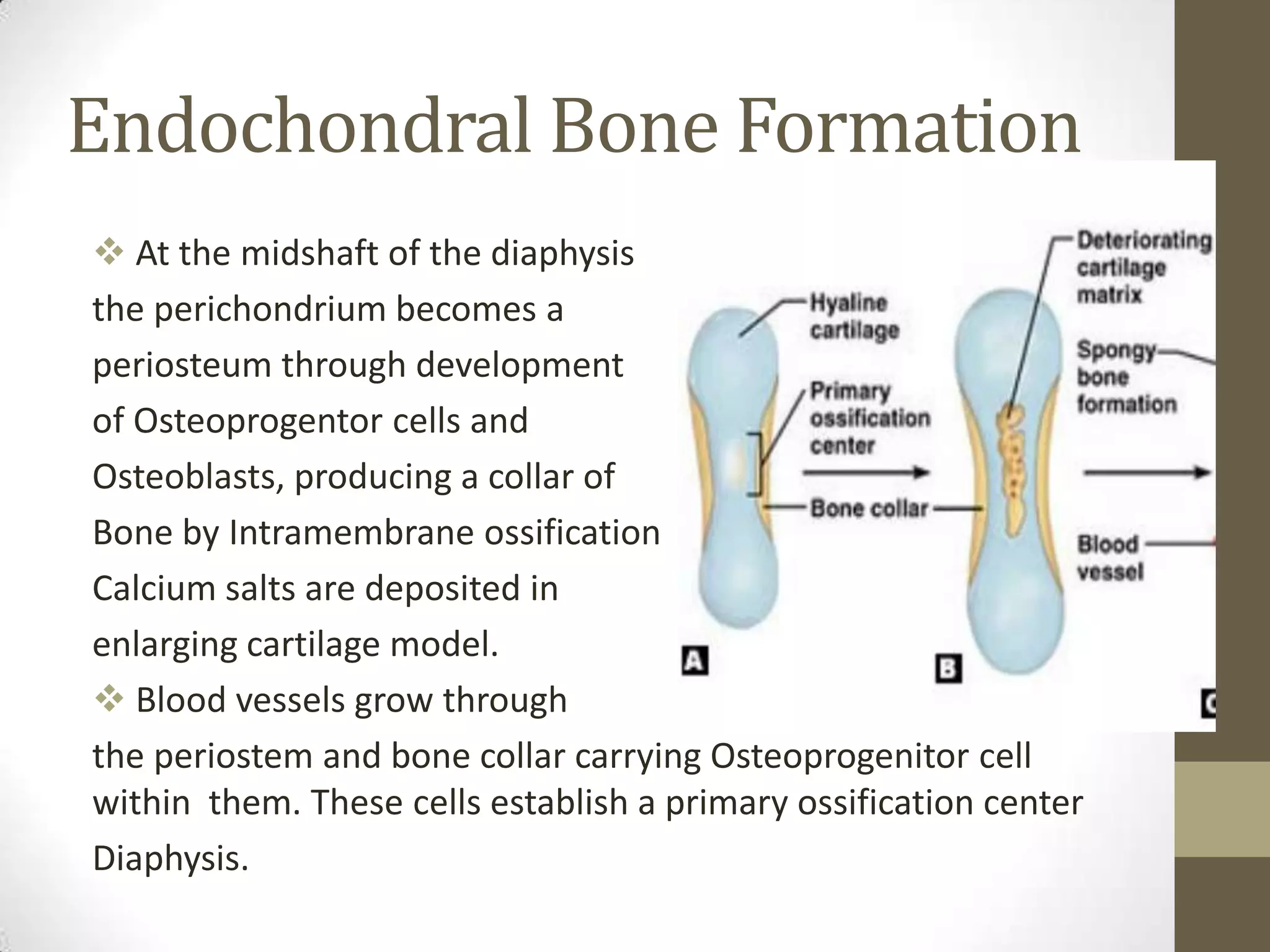
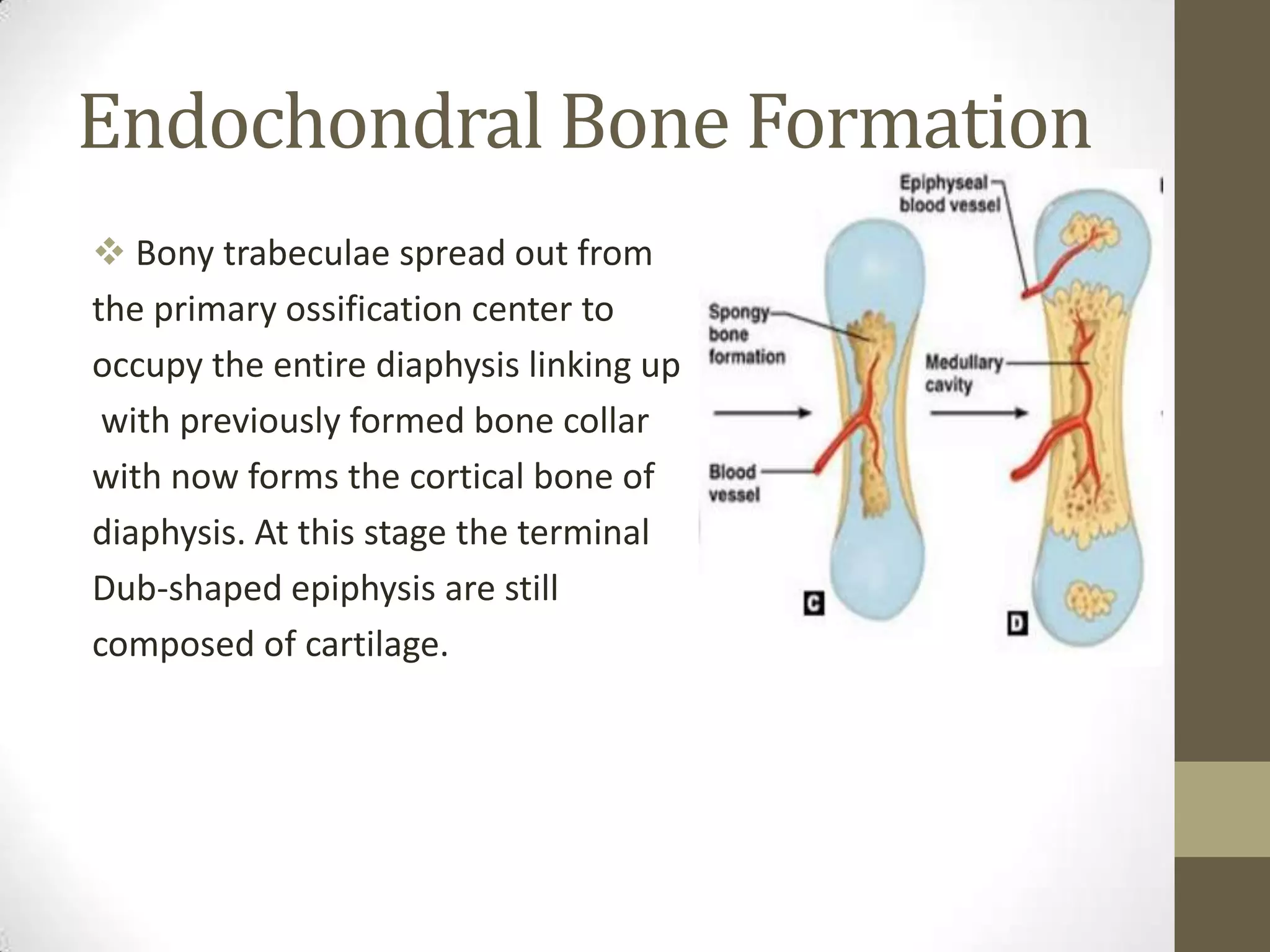
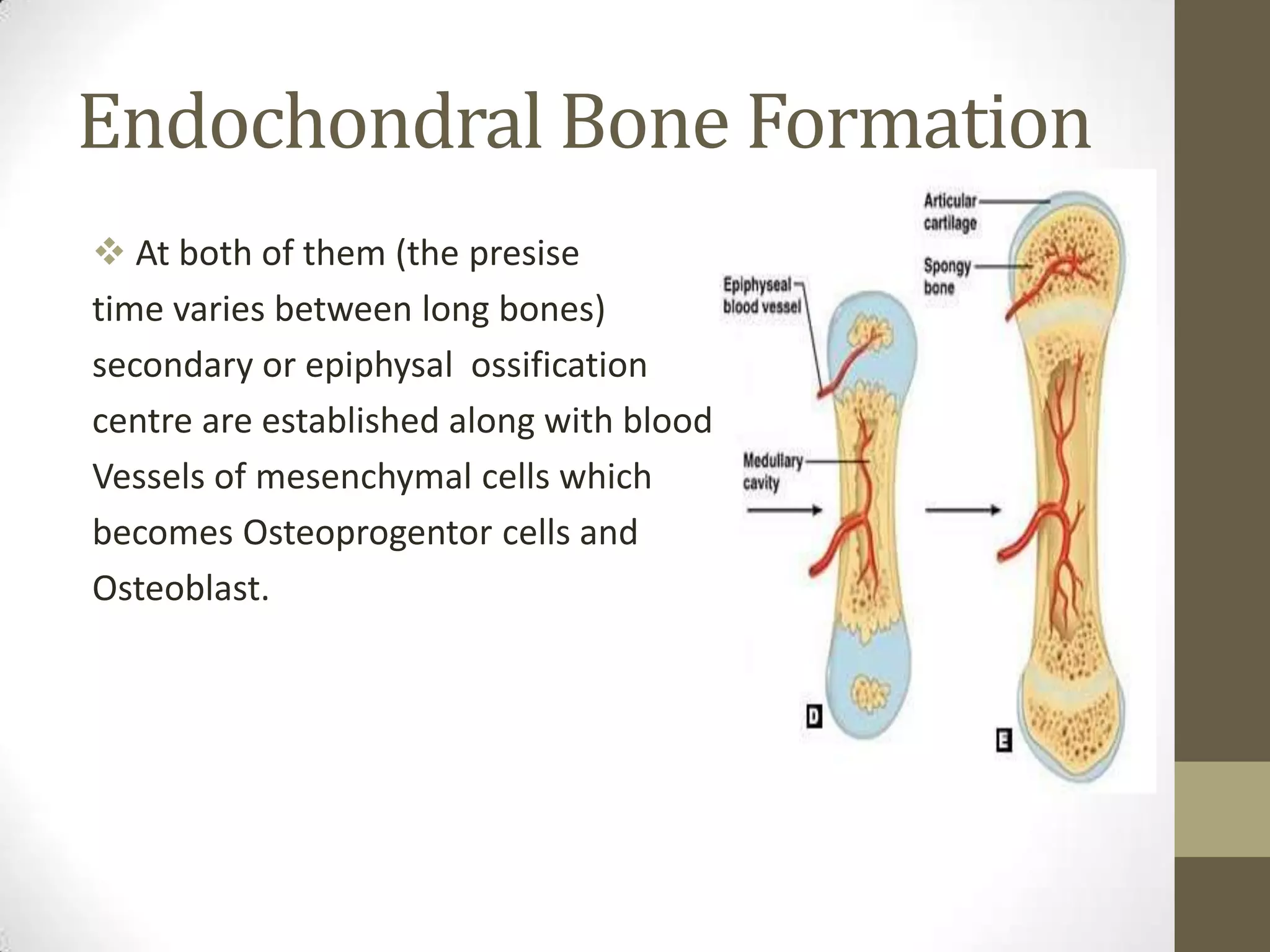
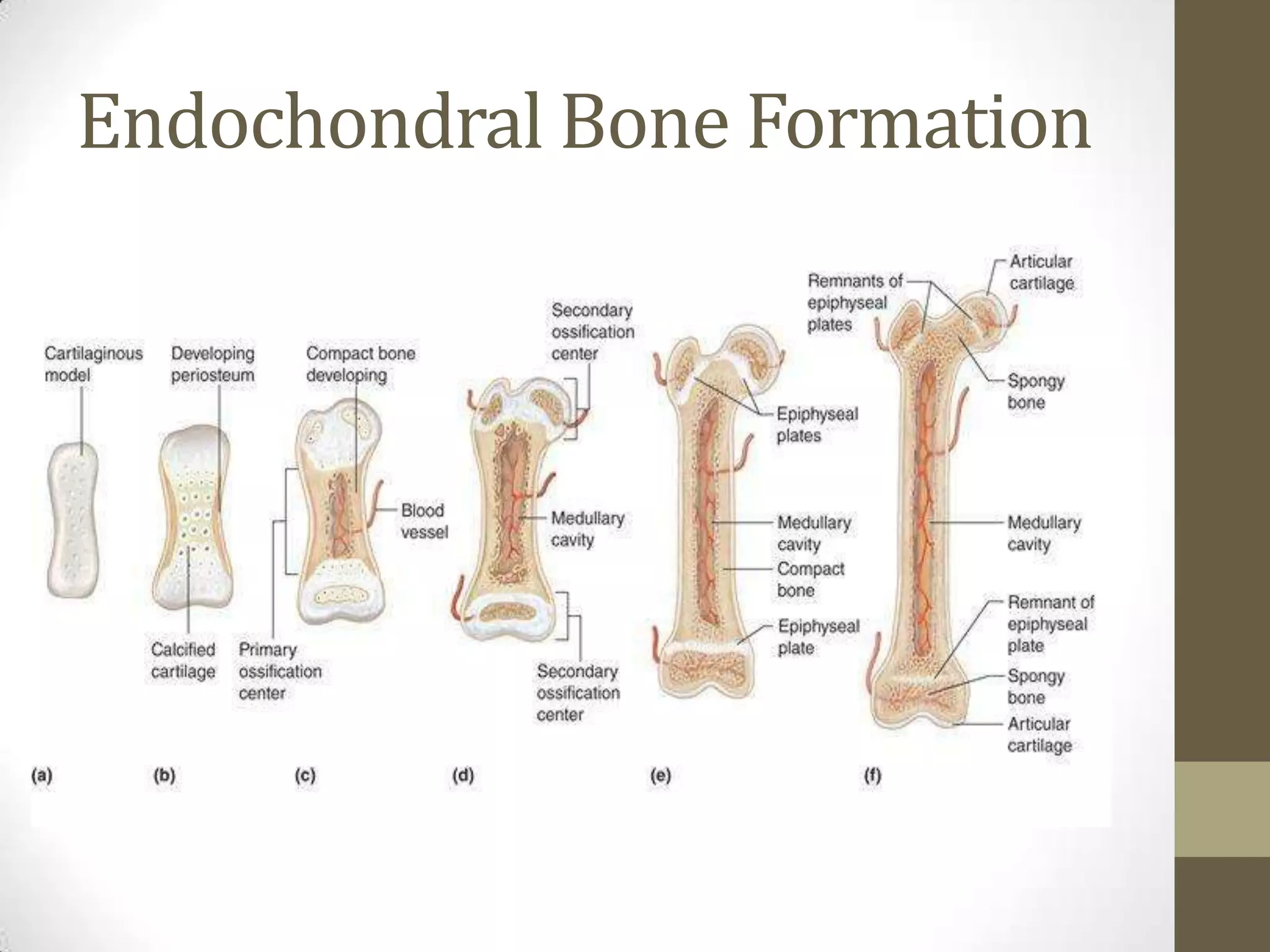
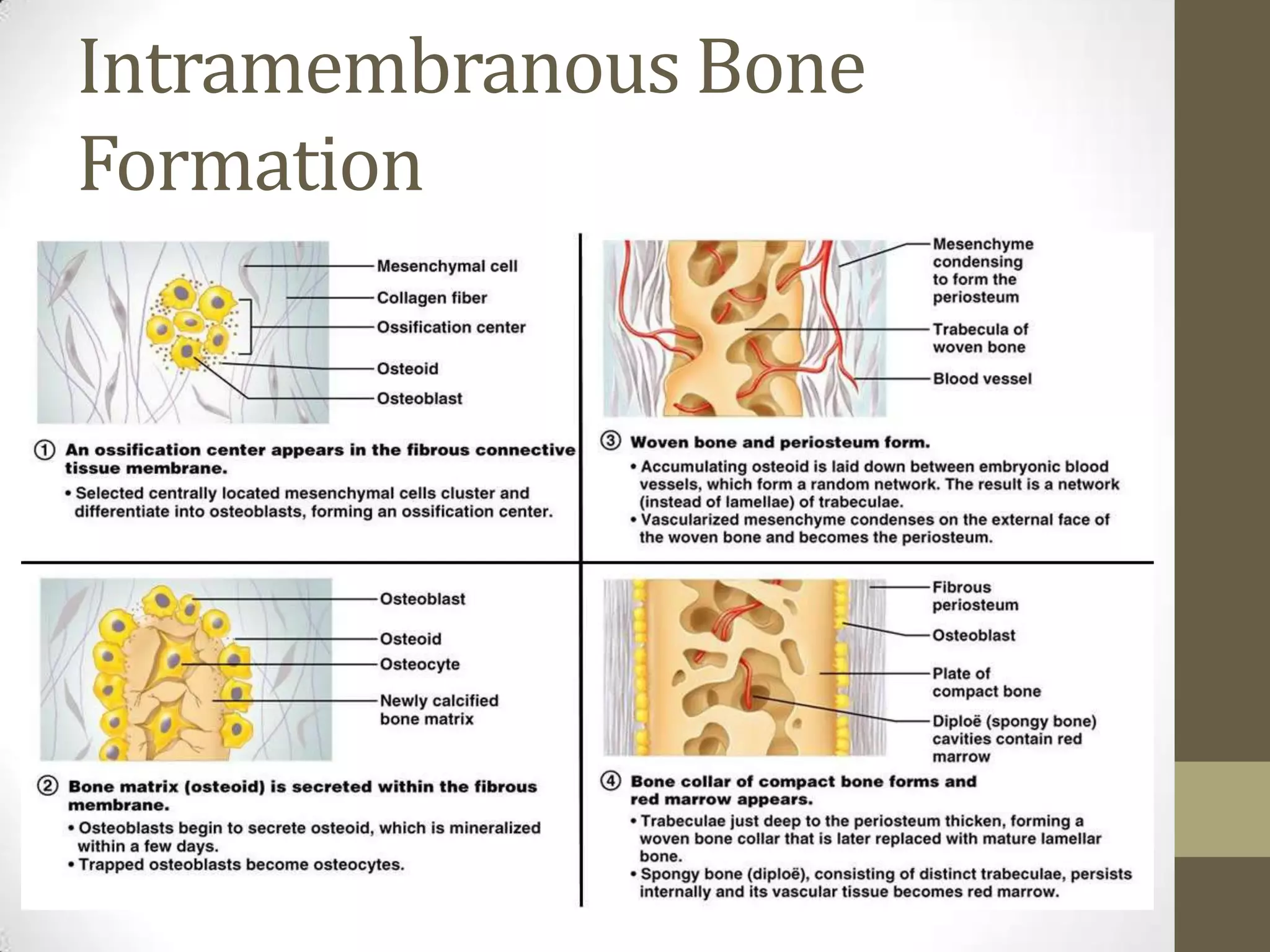
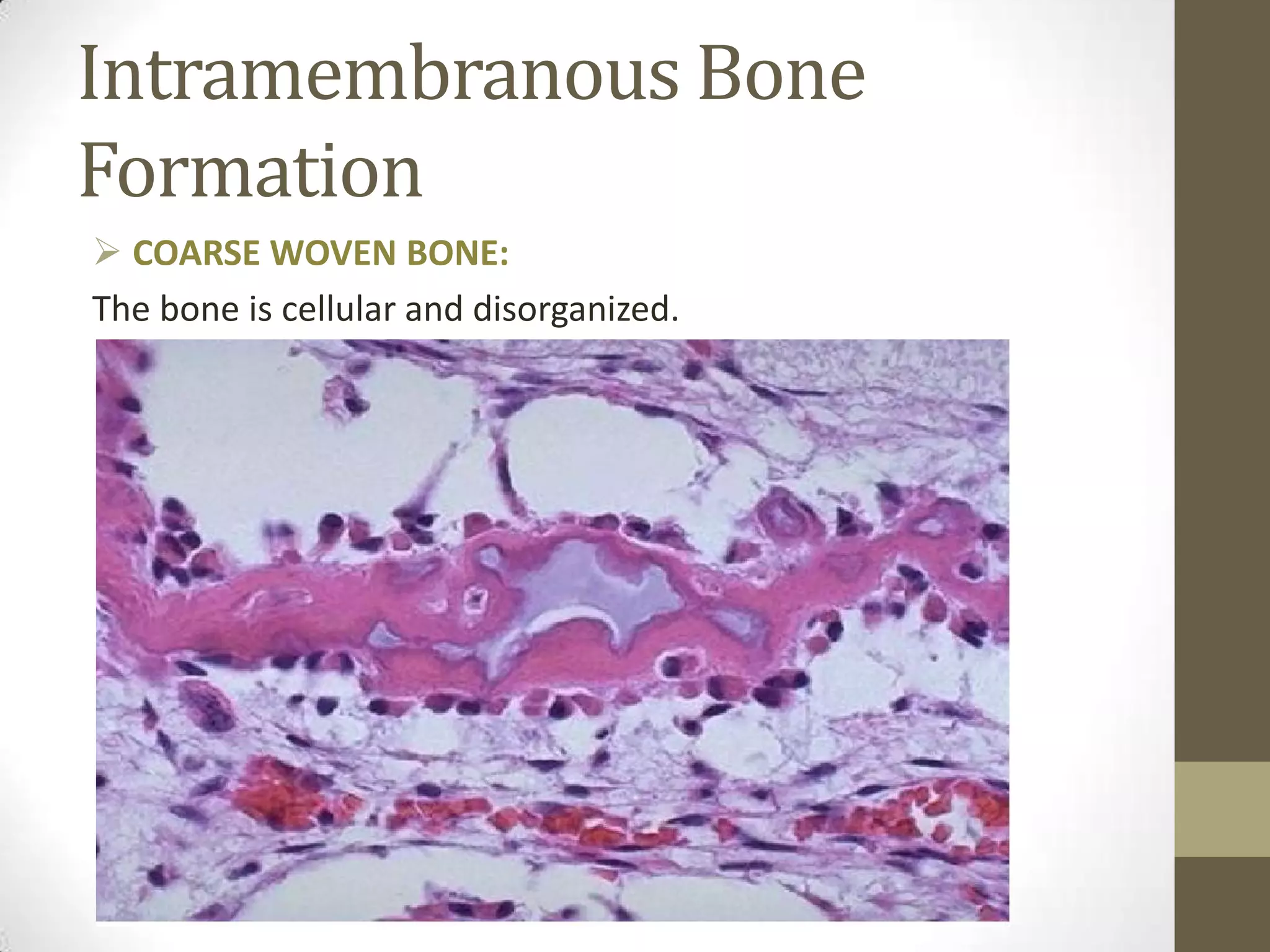
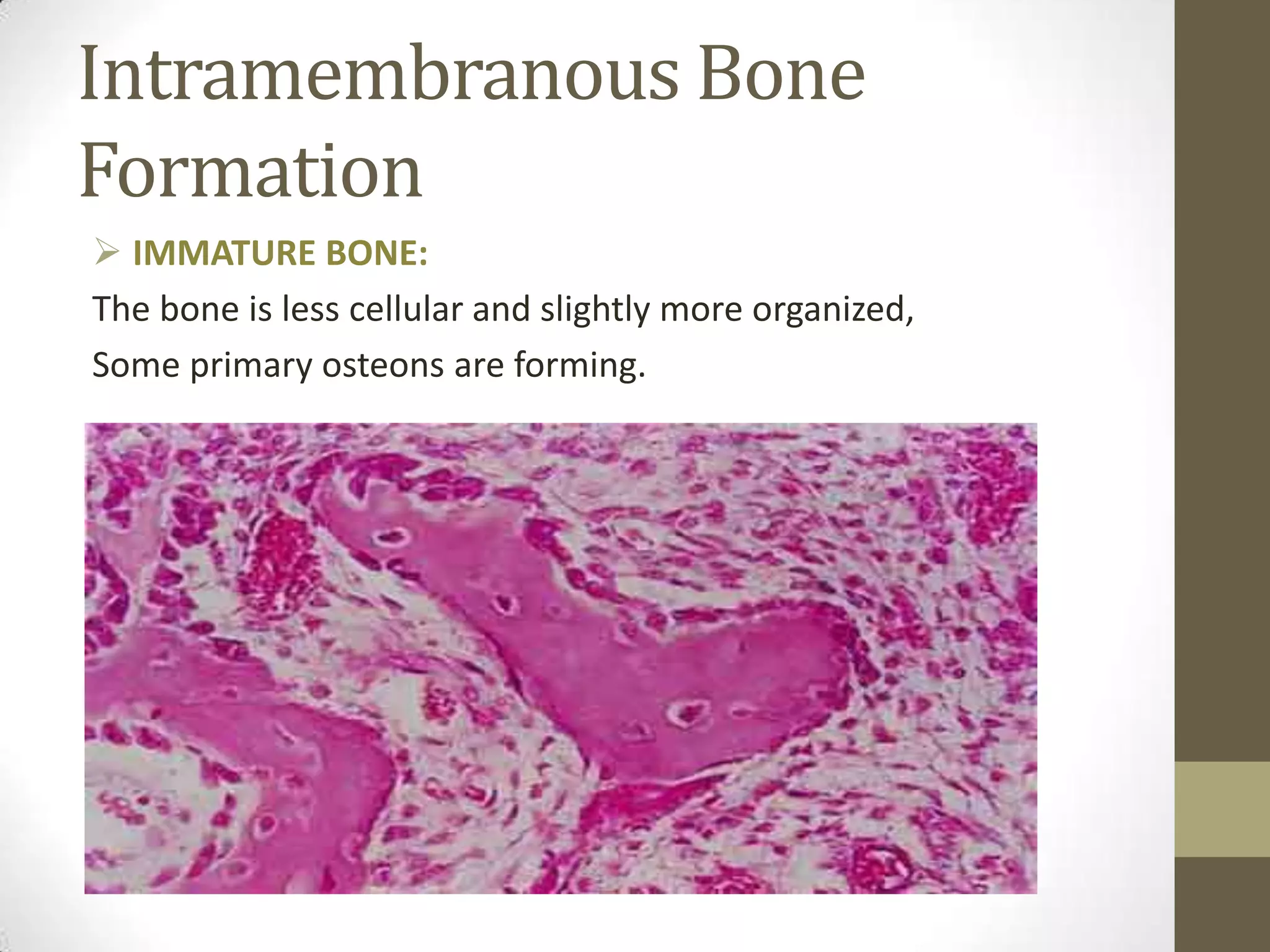
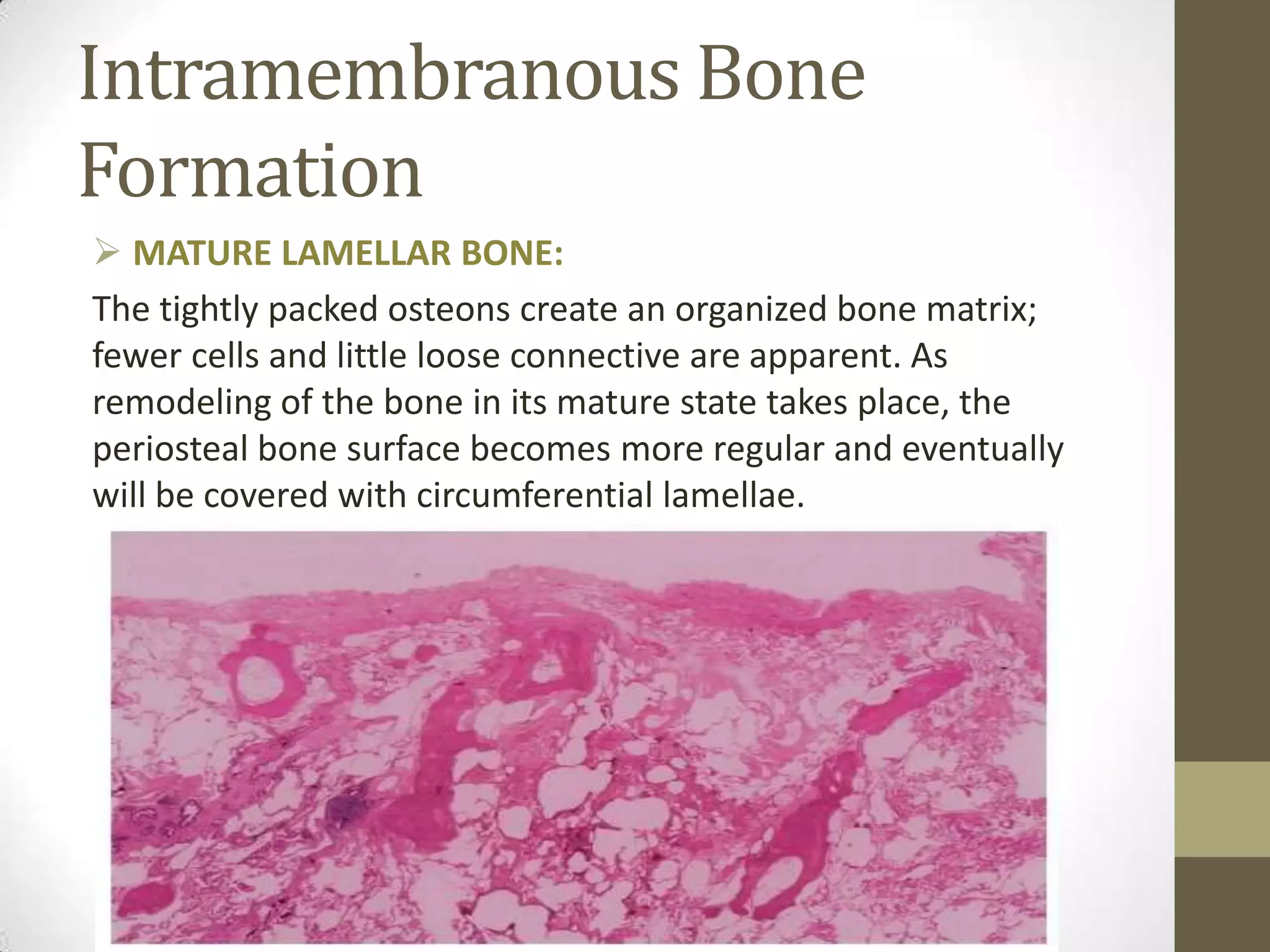
Bone develops through two main processes: endochondral and intramembranous ossification. Endochondral ossification involves the development of a cartilage model that is later replaced by bone tissue. It occurs in long bones and involves chondroblasts forming cartilage, blood vessels infiltrating and bringing osteoprogenitor cells, and the formation of primary and secondary ossification centers. Intramembranous ossification occurs in flat bones where mesenchymal cells directly develop into bone, forming woven bone that matures into lamellar bone. Bone is made up of an organic collagen matrix and inorganic hydroxyapatite, with three main cell types involved in formation and maintenance.