Embed presentation
Downloaded 71 times

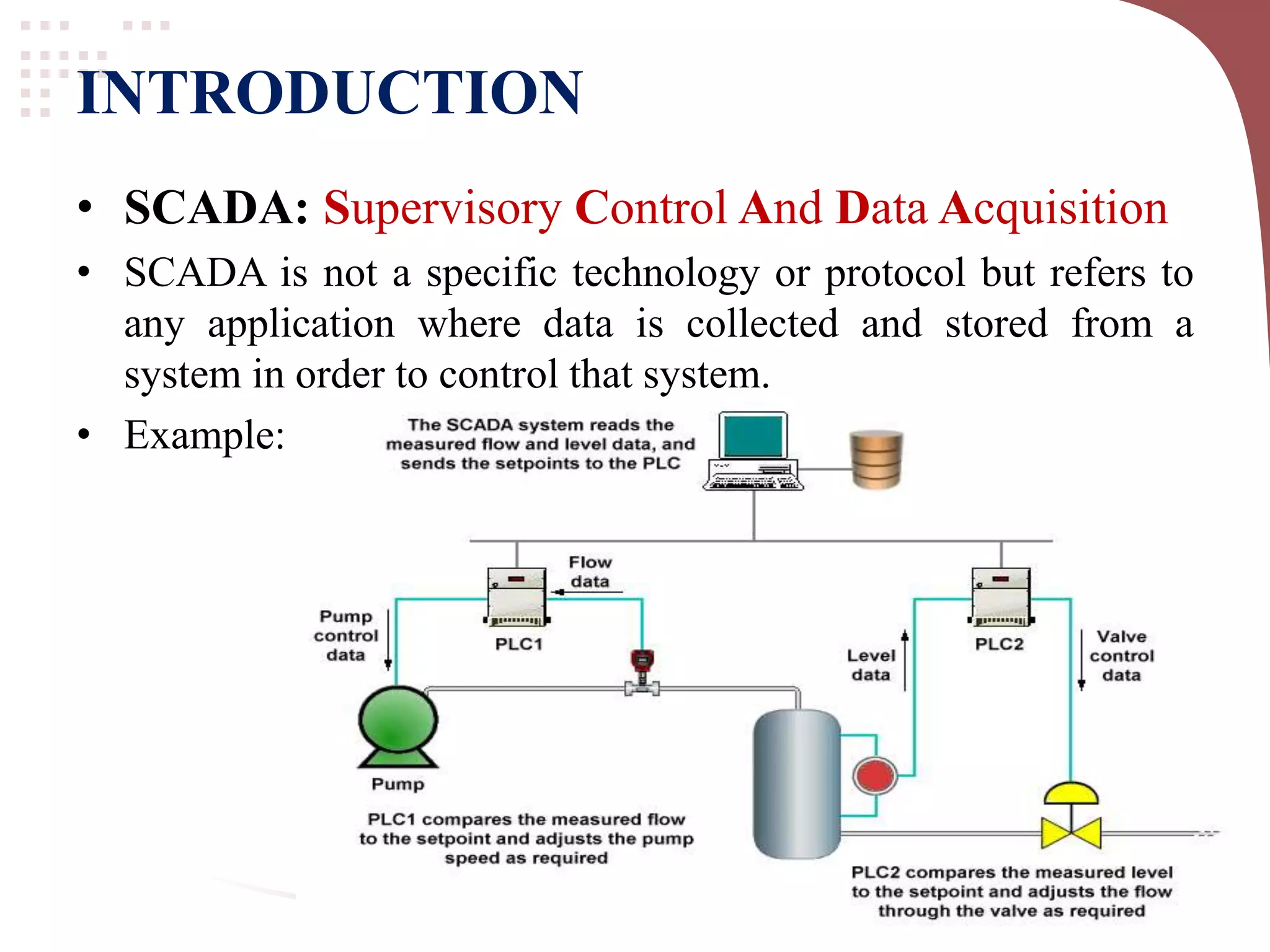
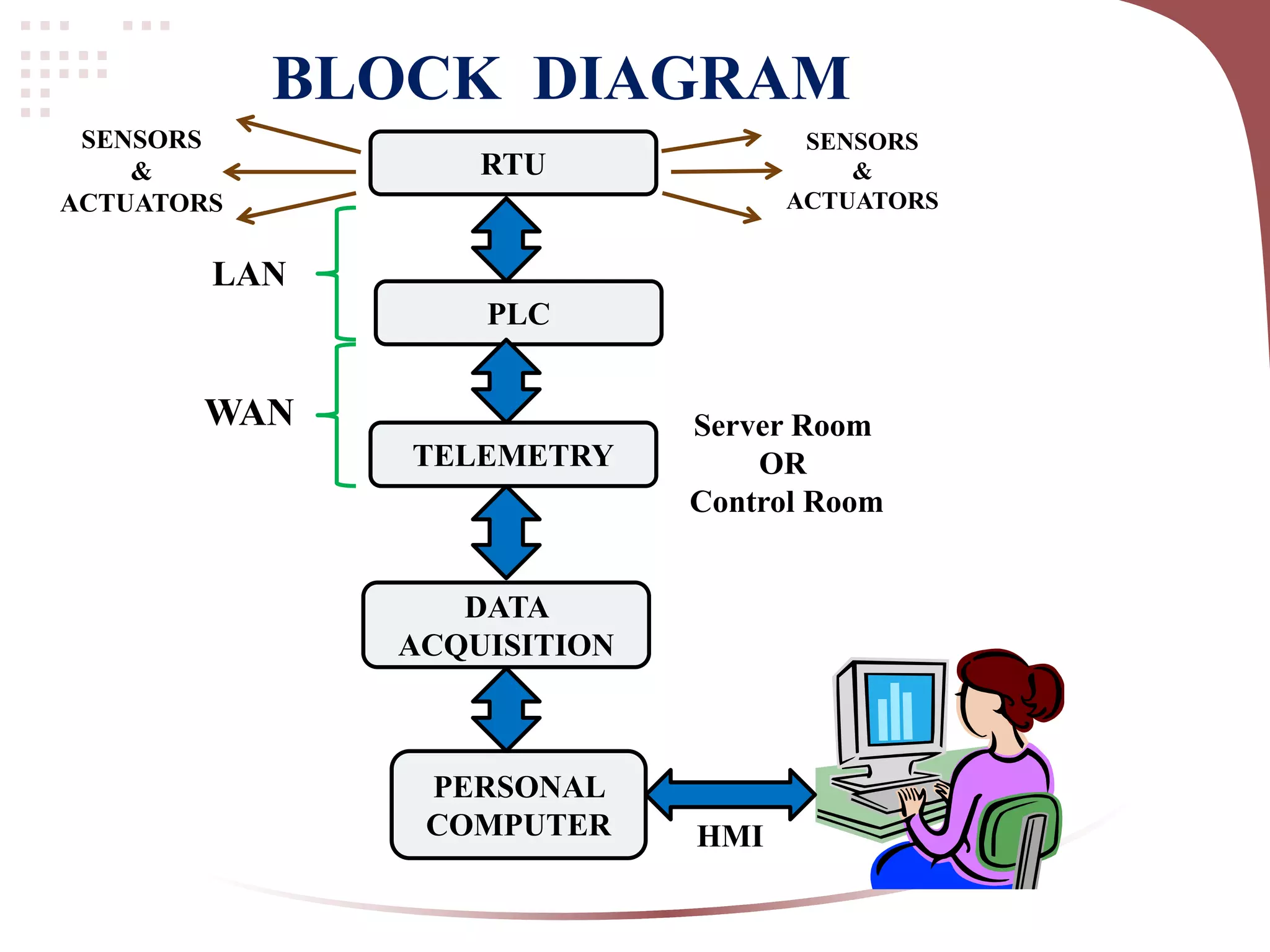
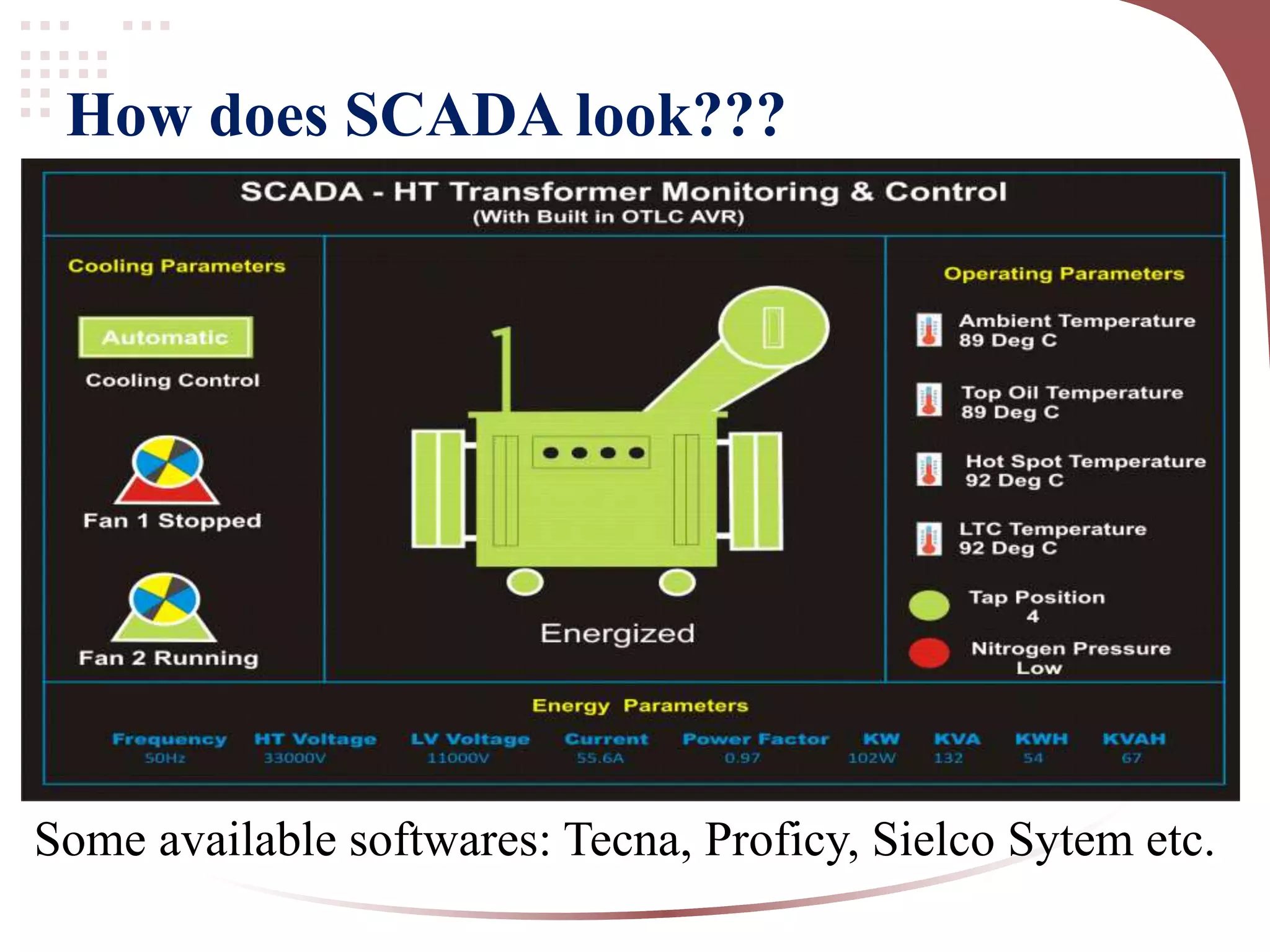





This document provides an introduction to fundamentals of SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition). It describes SCADA as software that collects and stores data from a system to control that system. The block diagram shows how sensors and actuators connect to RTUs, PLCs, and a server room/control room with HMIs over LAN/WAN. Key differences between PLC and SCADA are outlined, with PLC being hardware directly connected to field instruments to control outputs, while SCADA is software for monitoring and supervising over a visual interface. Main advantages of SCADA include data acquisition, remote access, efficiency gains, and reduced staffing needs. SCADA has applications in










Introduction to SCADA fundamentals covering various aspects including software and advantages.
Defines SCADA, its purpose in data collection and control, along with a block diagram representation.
Describes differences between PLC and SCADA showing their respective roles inside the system.
Lists key advantages of SCADA and its applications across various sectors like power and automation.
Summarizes the learning objectives related to SCADA, including its importance and workings.
Invites queries to clarify any doubts regarding the SCADA system and its functionalities.