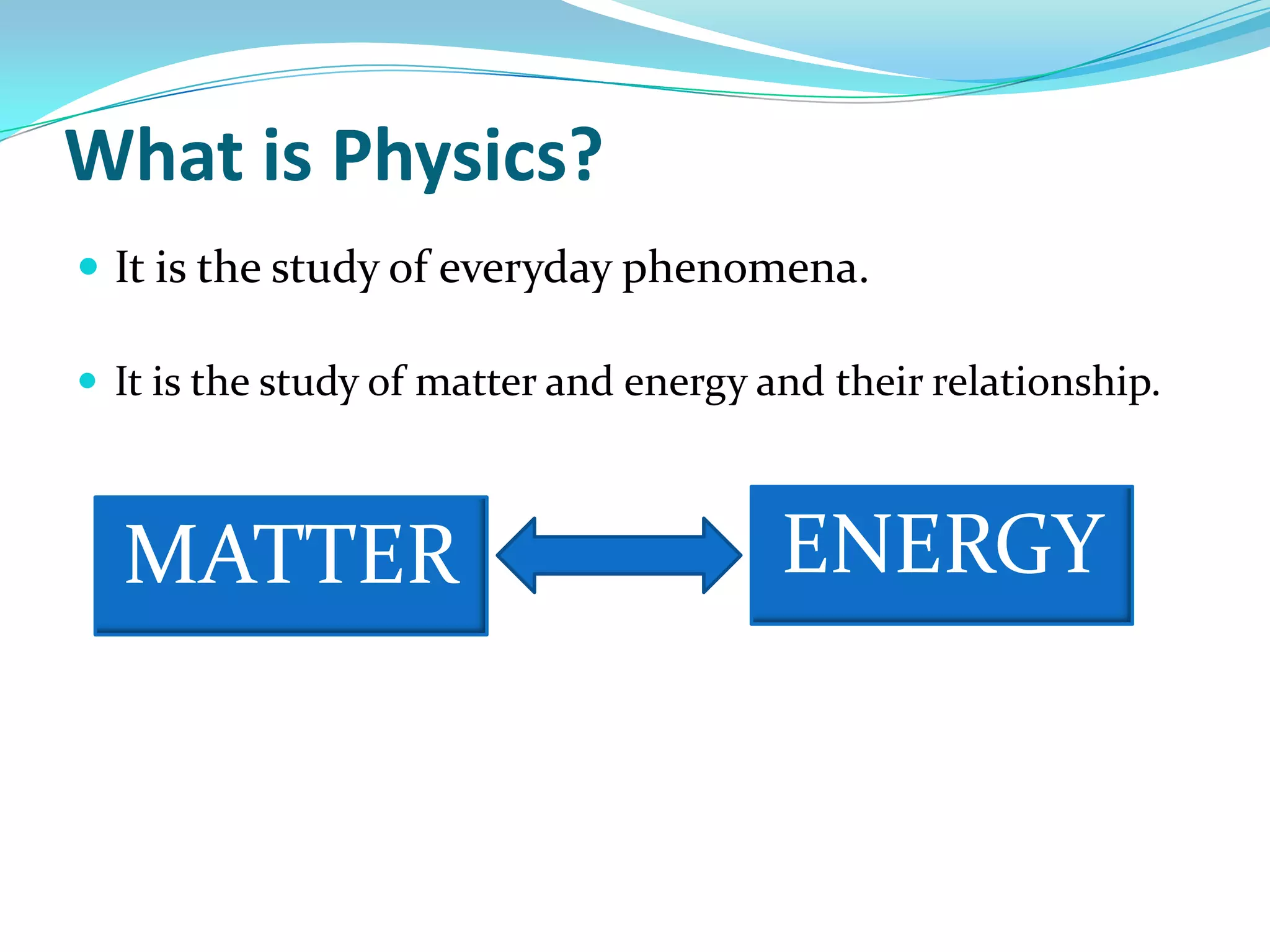
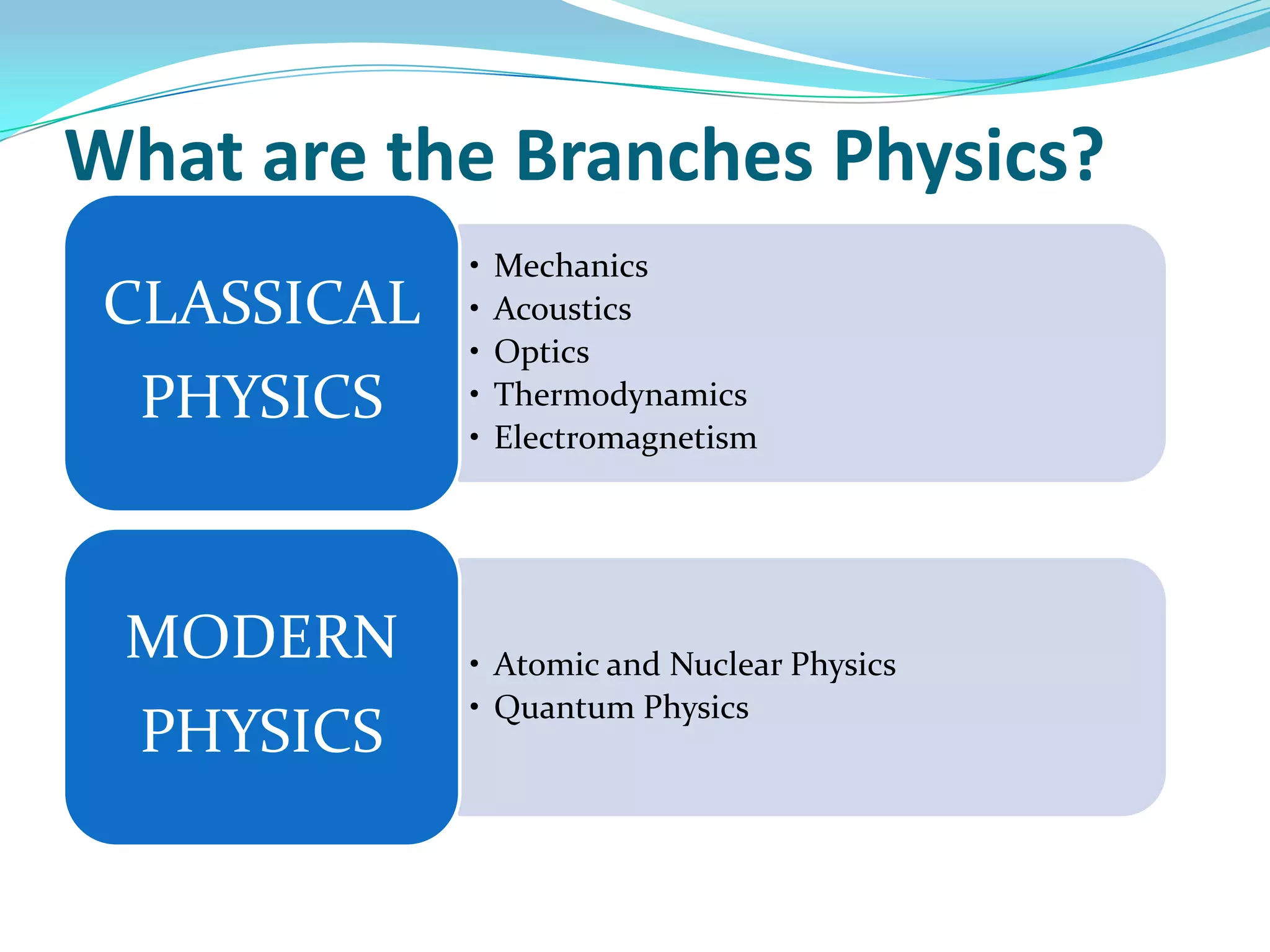
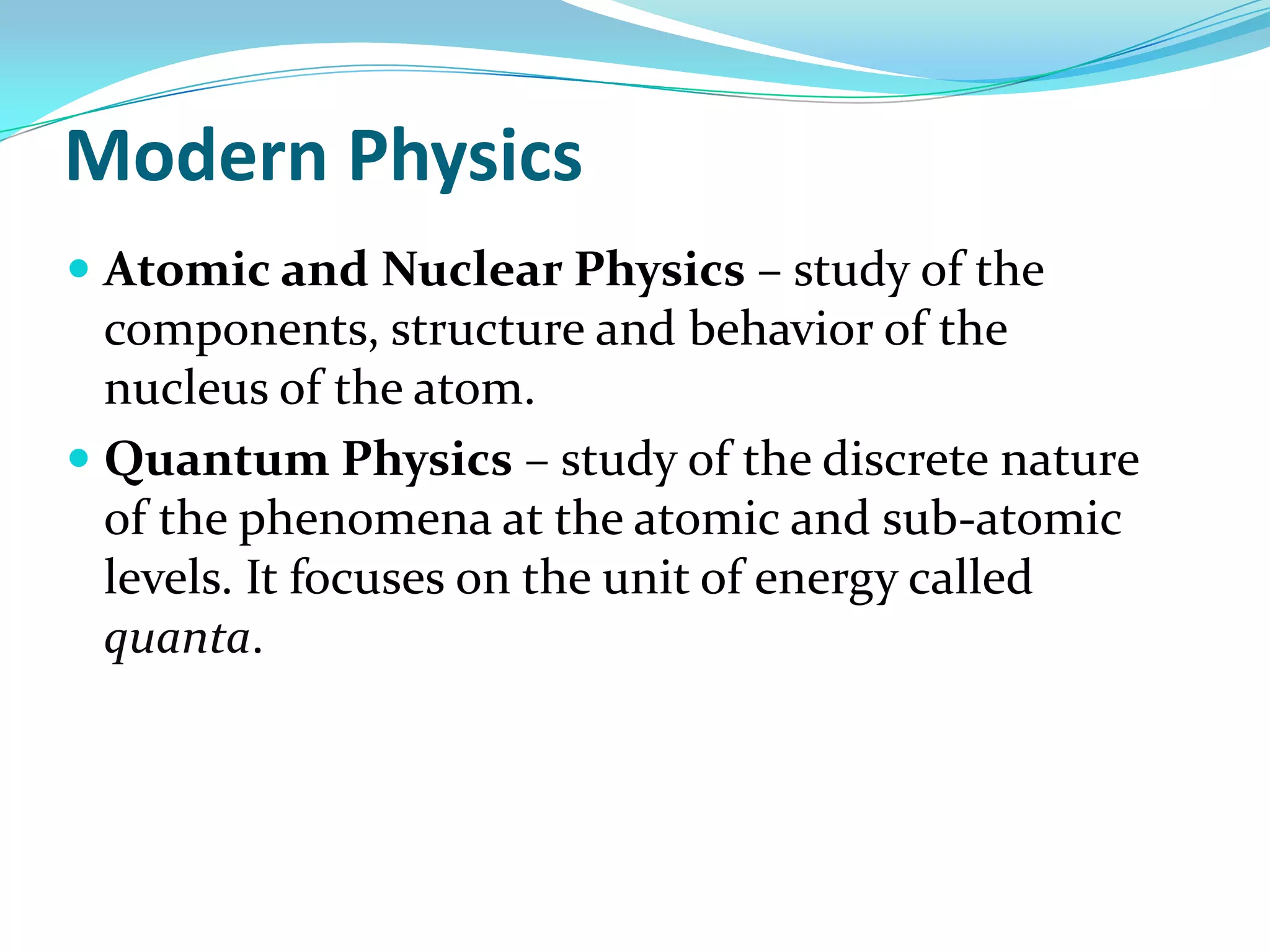
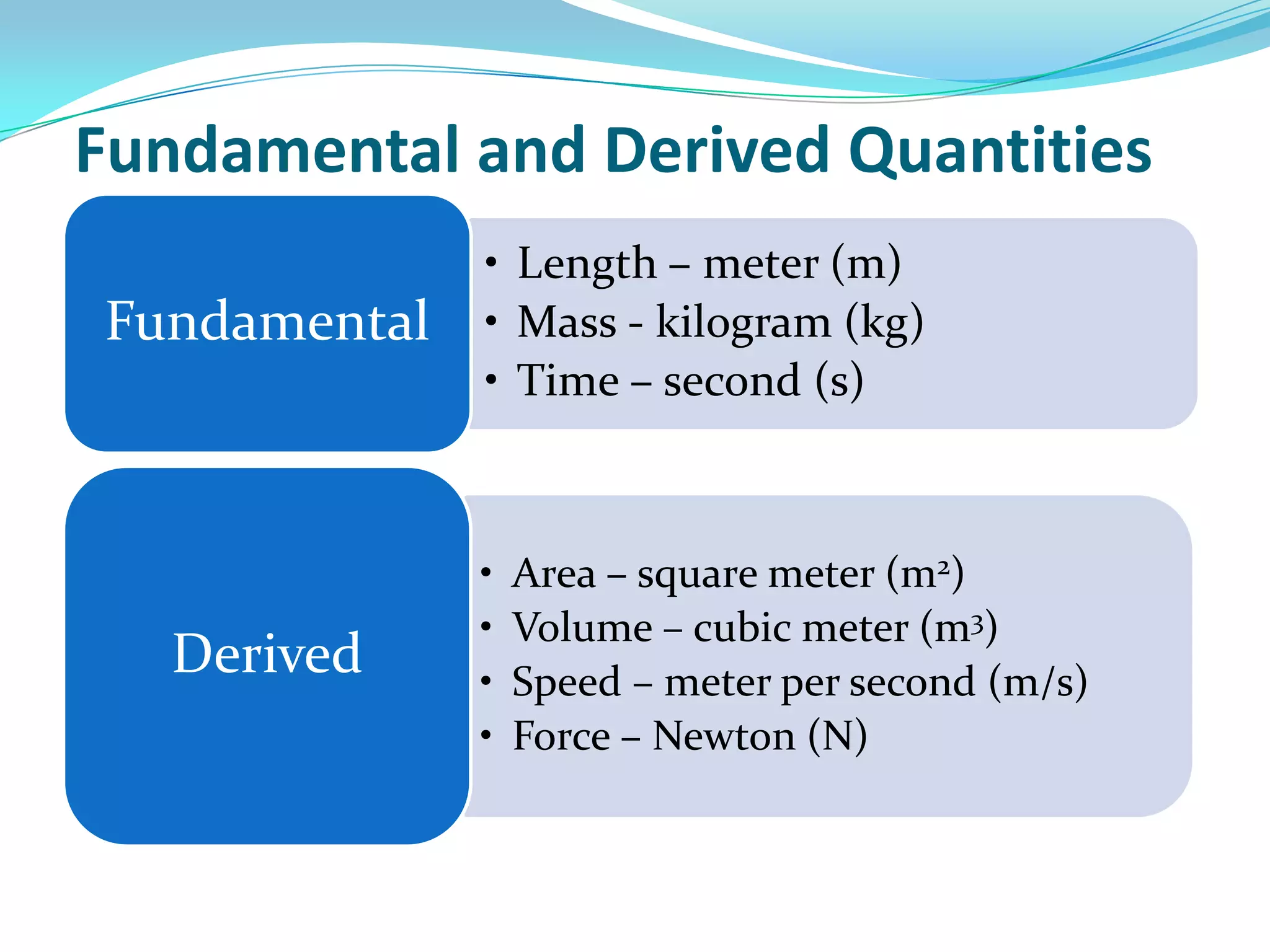
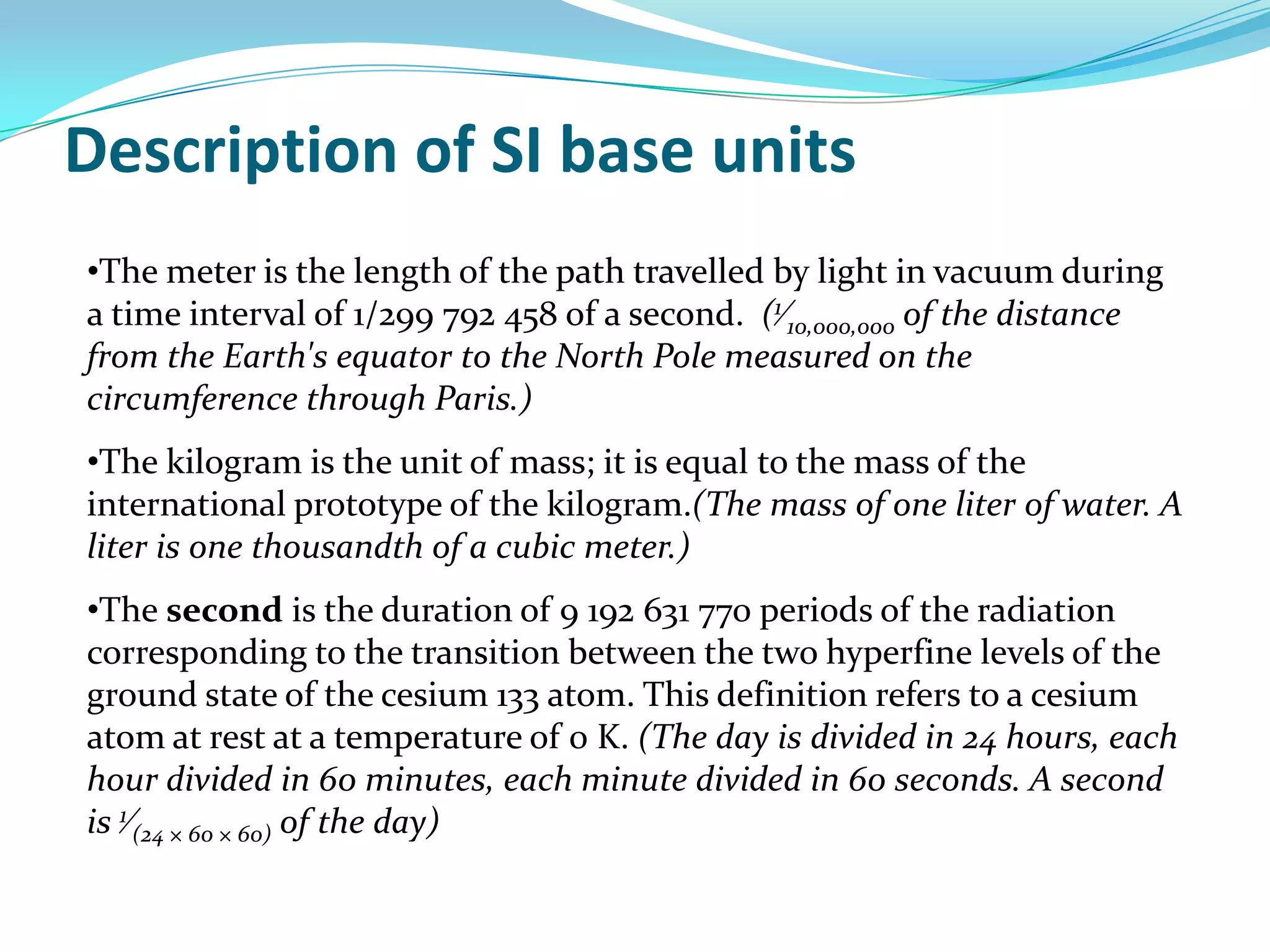
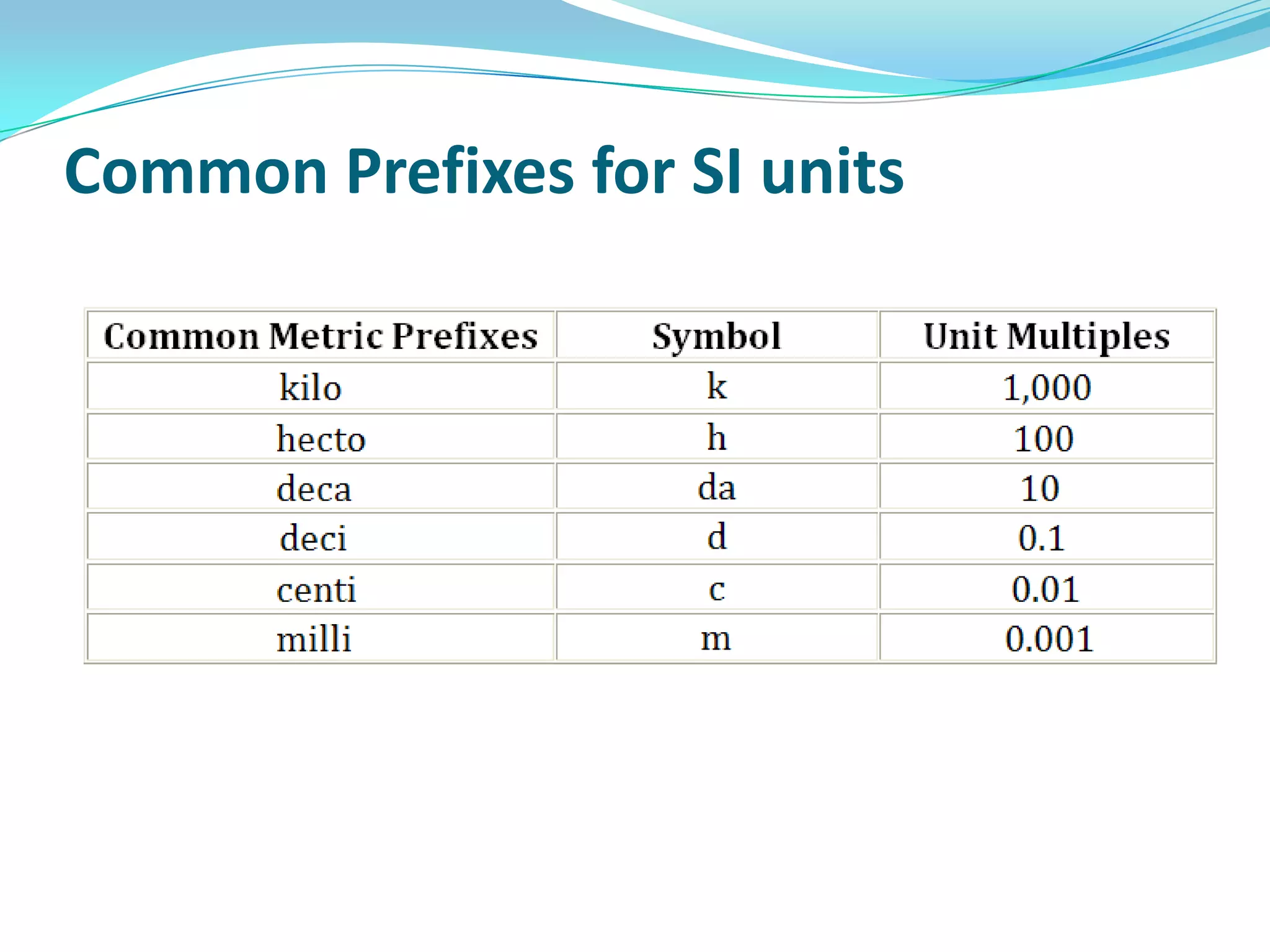
Physics is the study of matter, energy, and their interaction. It has two main branches: classical physics which studies mechanics, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism, and modern physics which studies atomic and nuclear physics and quantum physics. Measurement is the process of comparing quantities using standard units like the metric system which defines fundamental units like meters, kilograms, and seconds. Conversion between units can be done using conversion factors in a chain-link method.