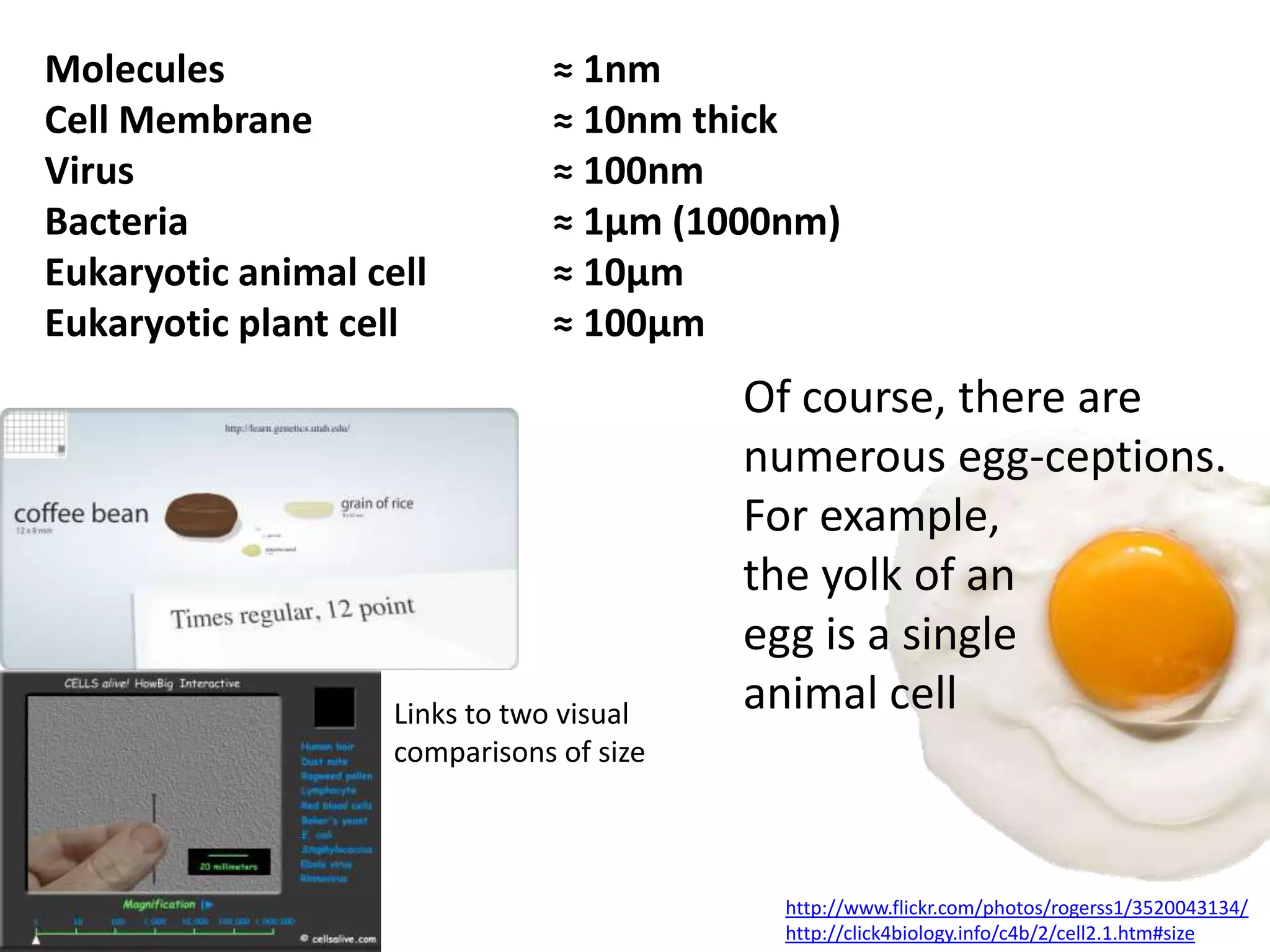
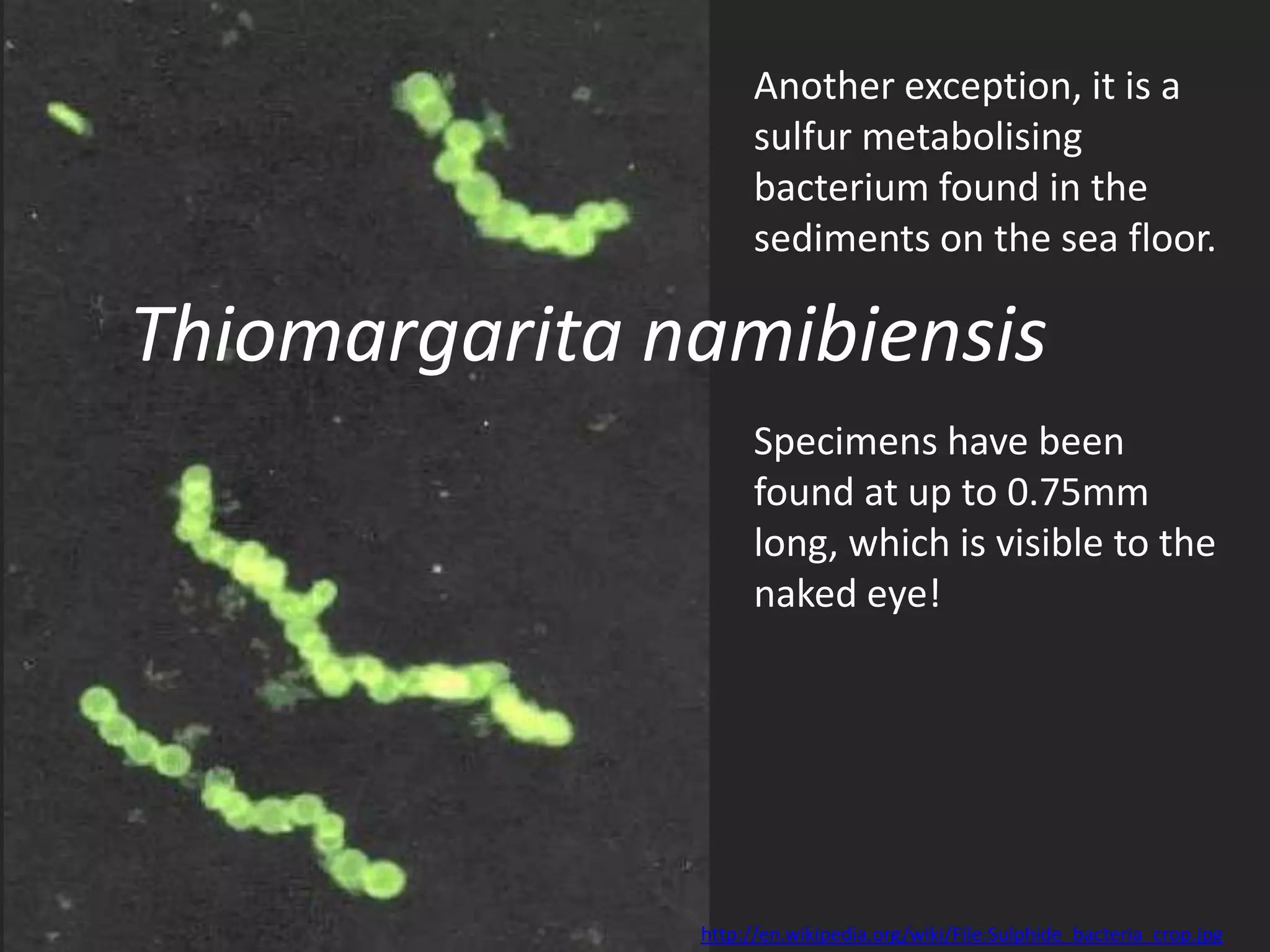
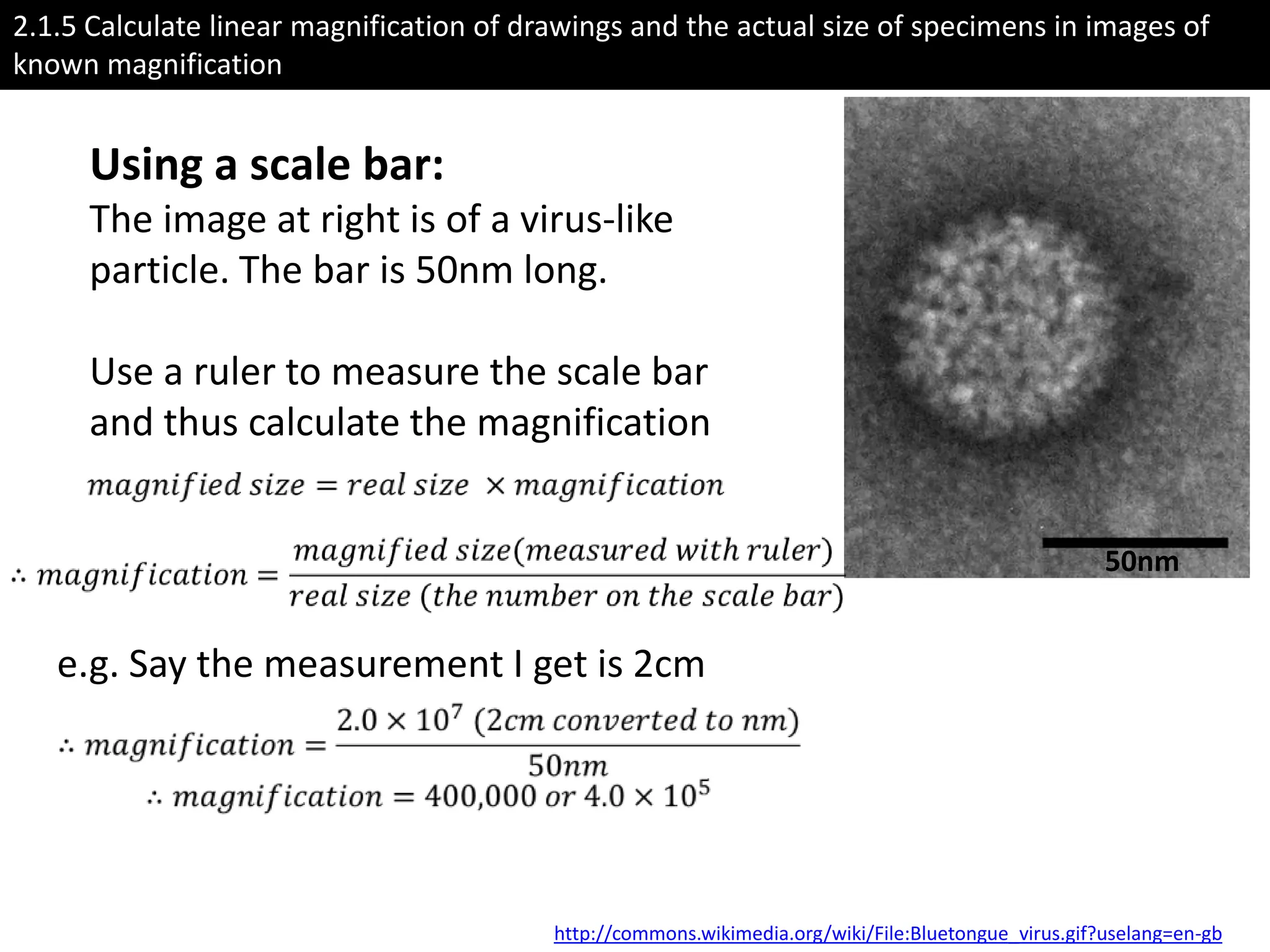
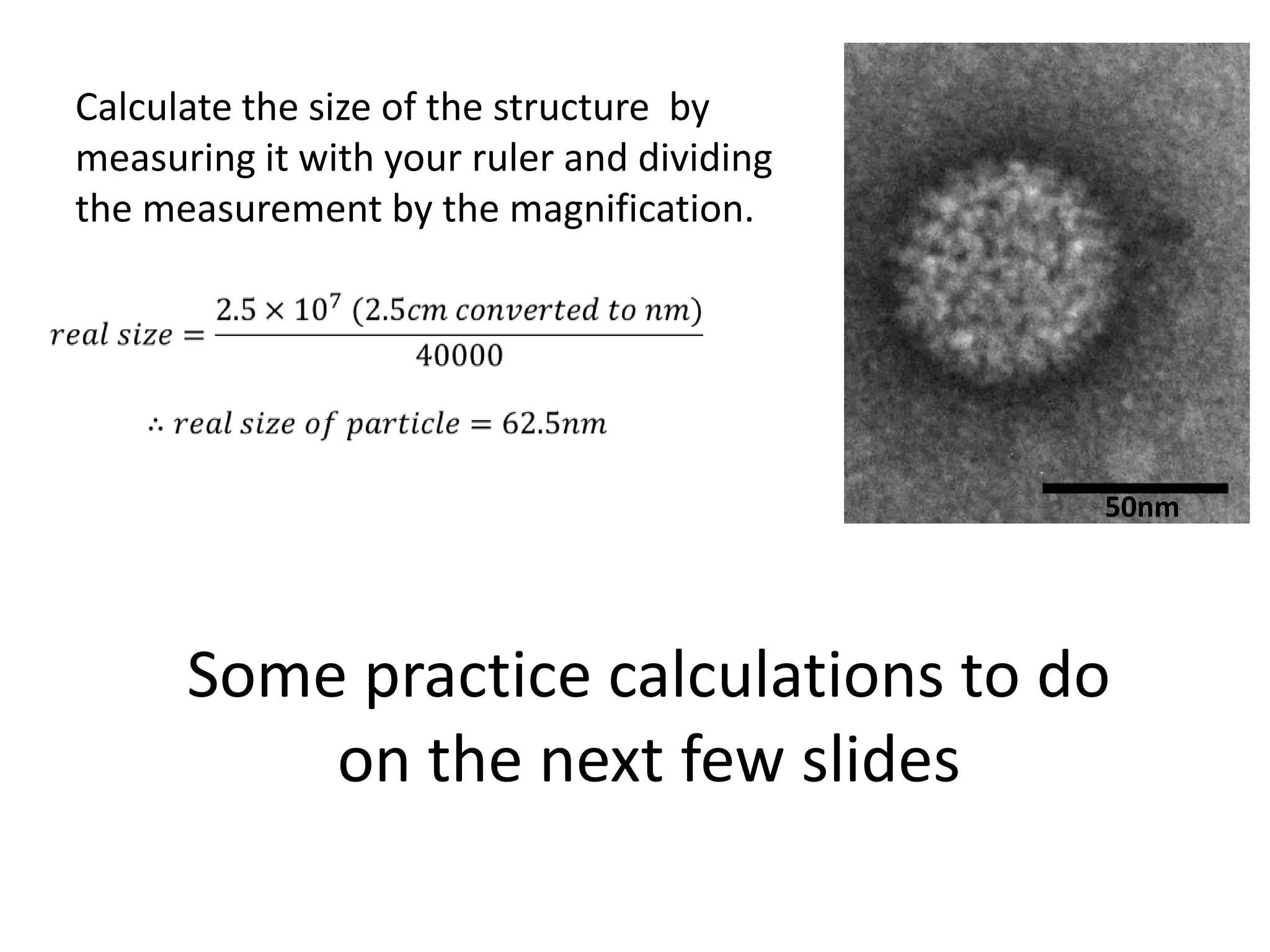
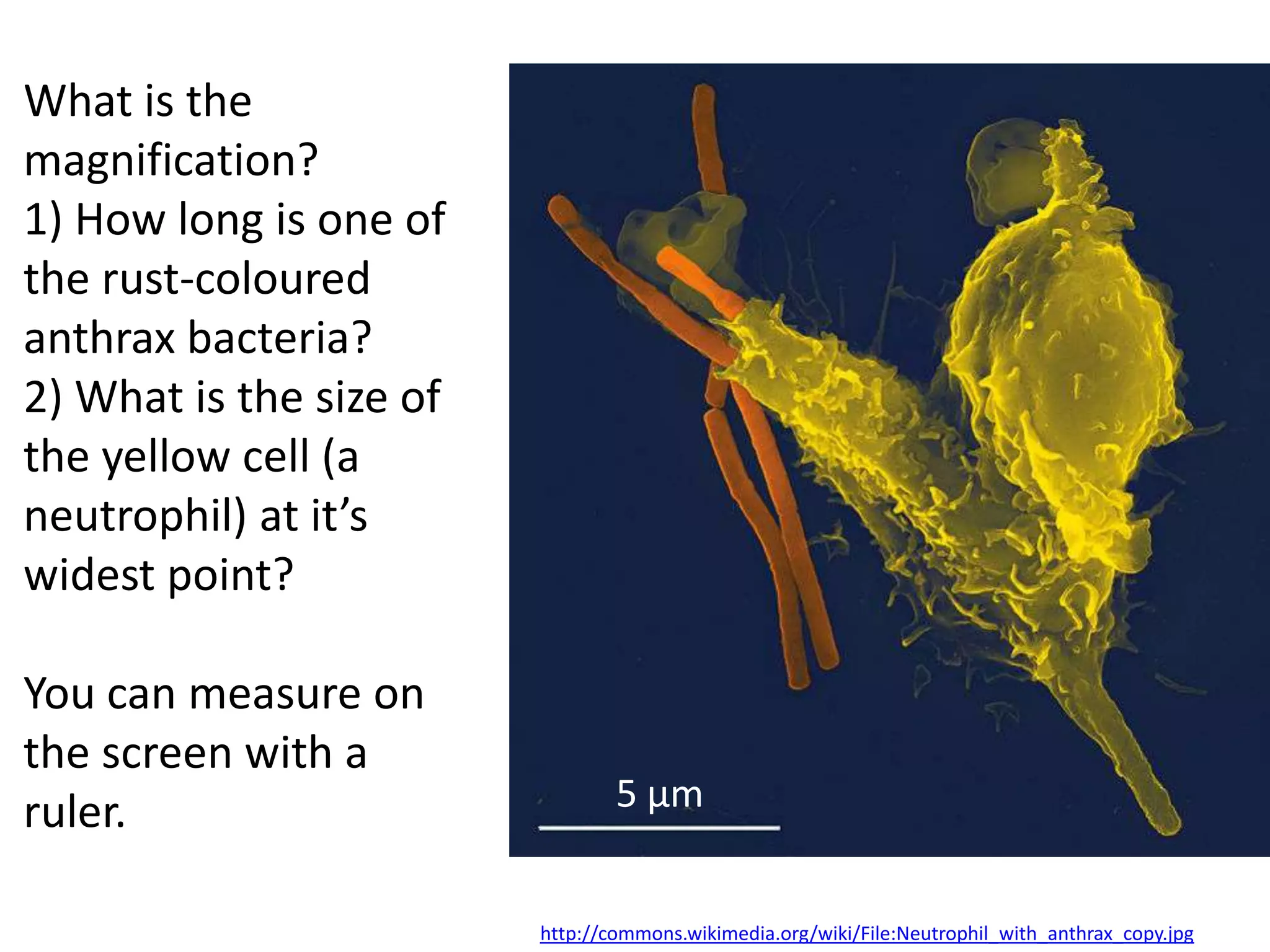
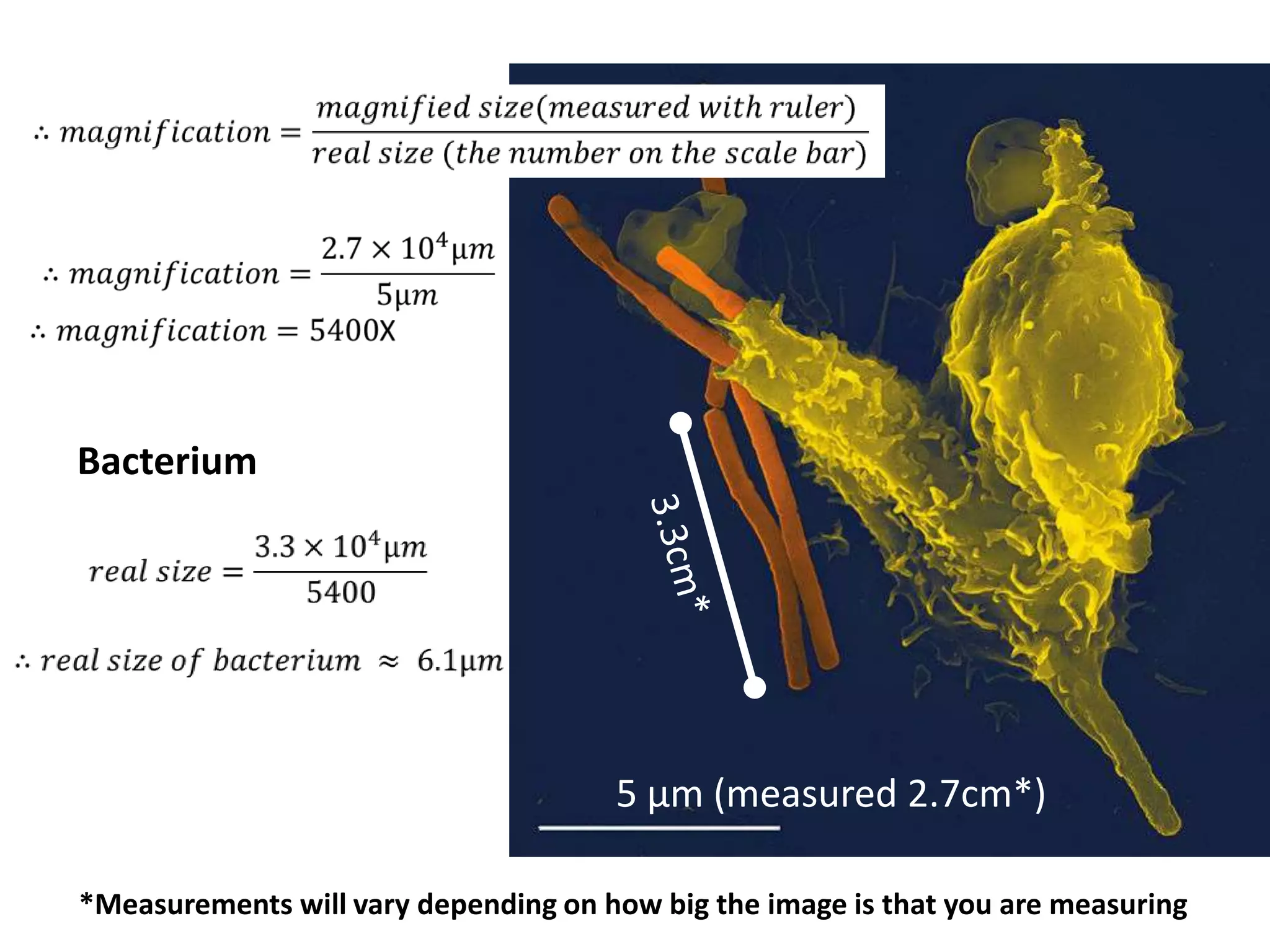
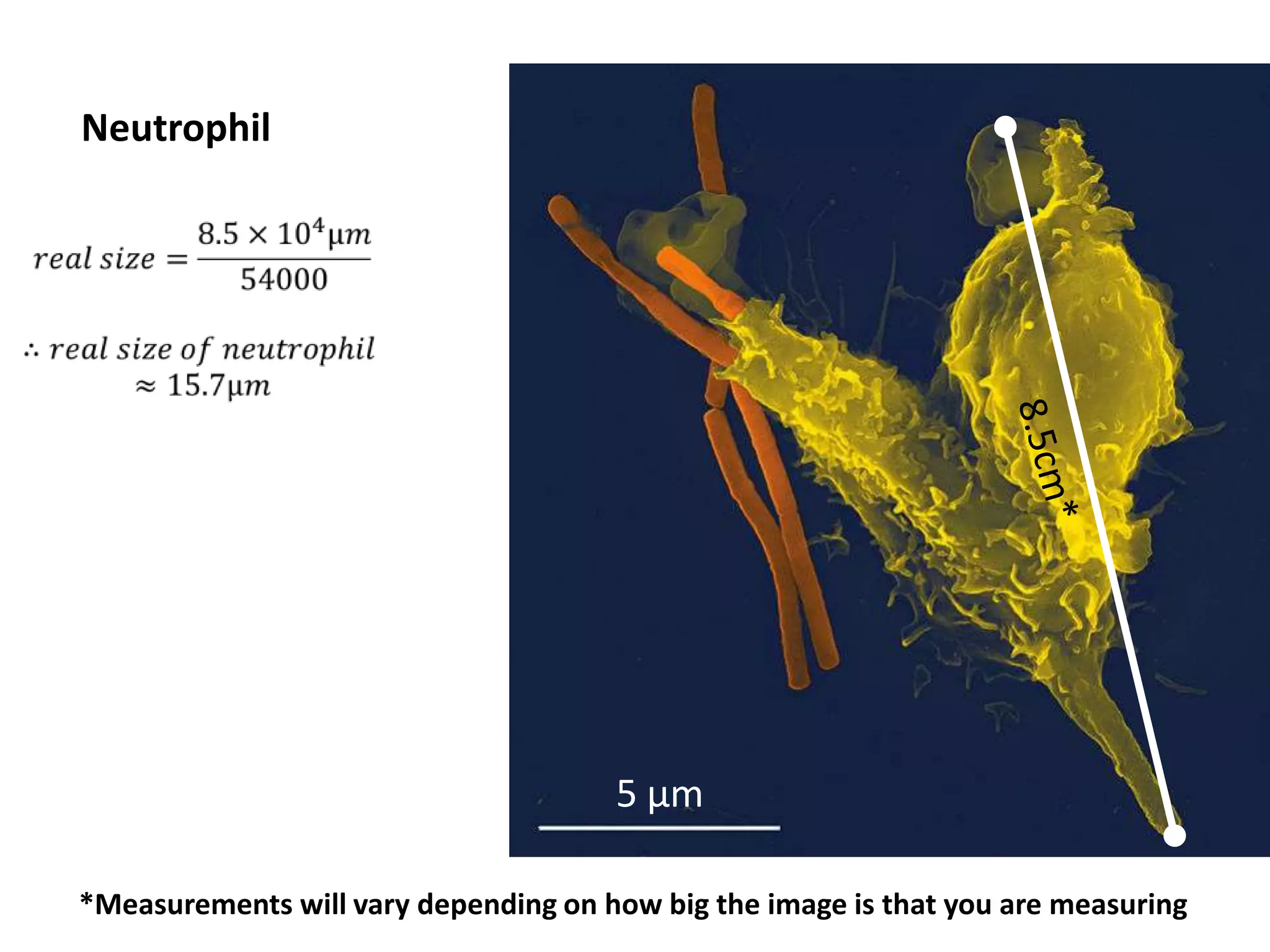
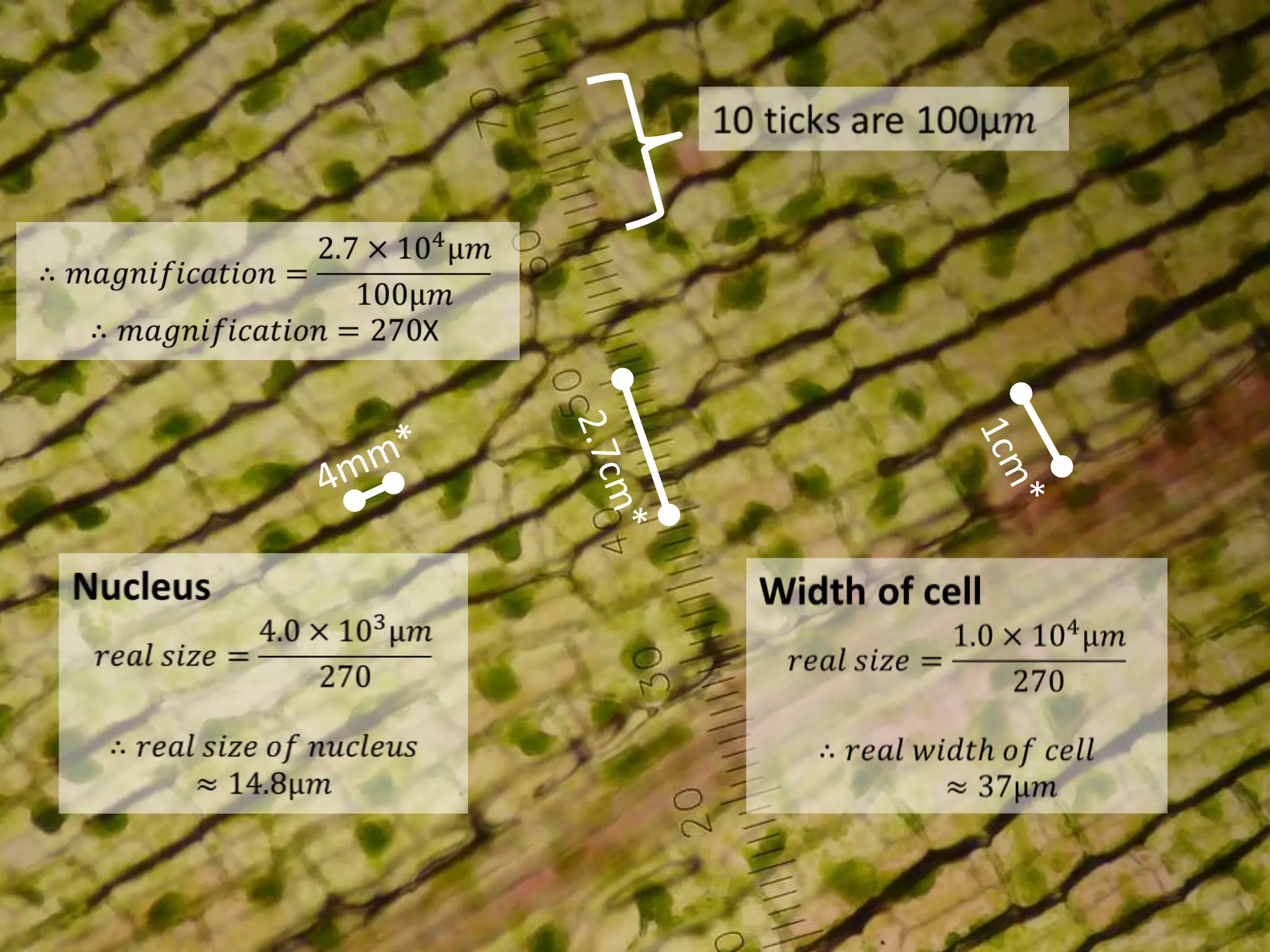
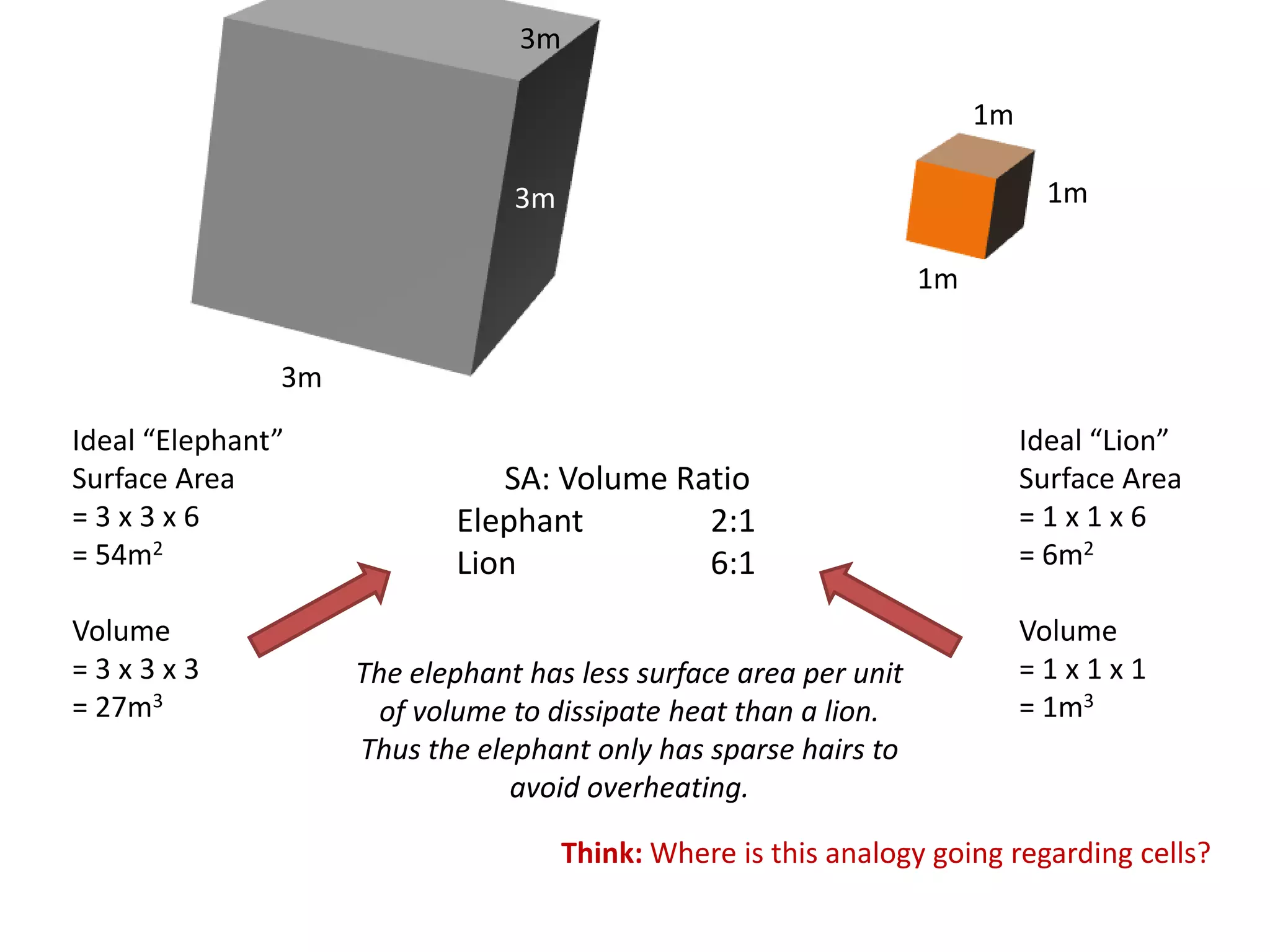
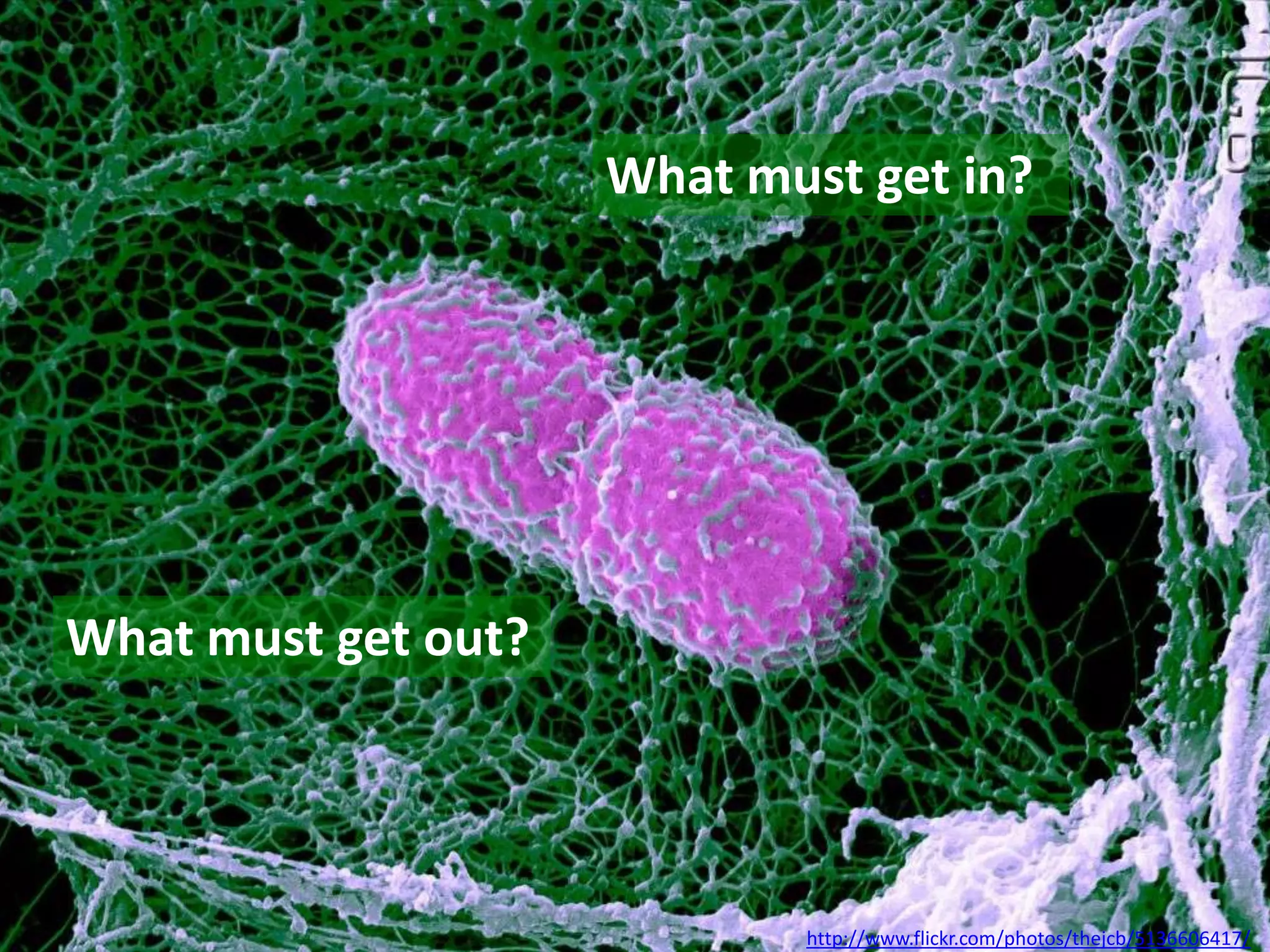
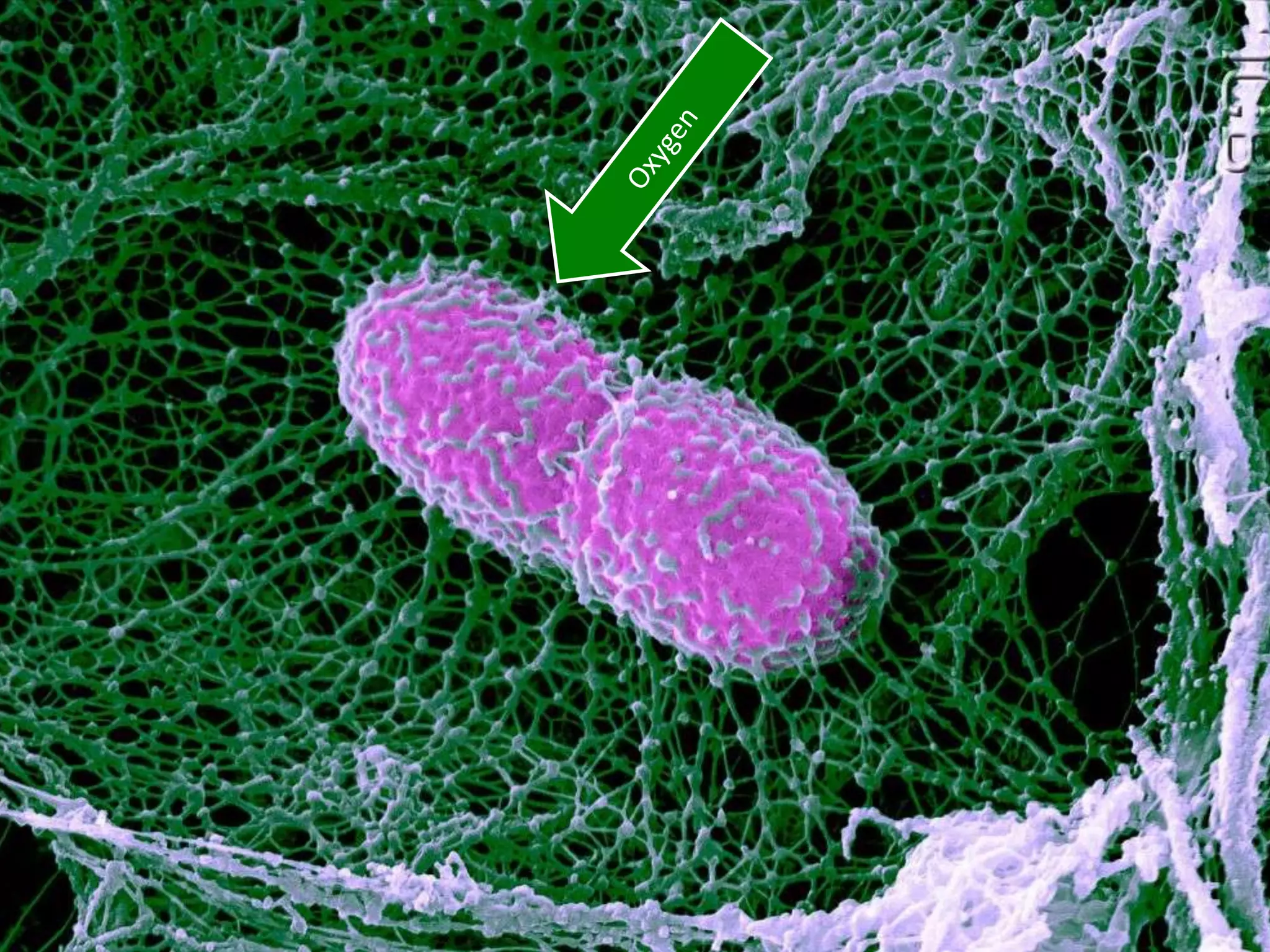
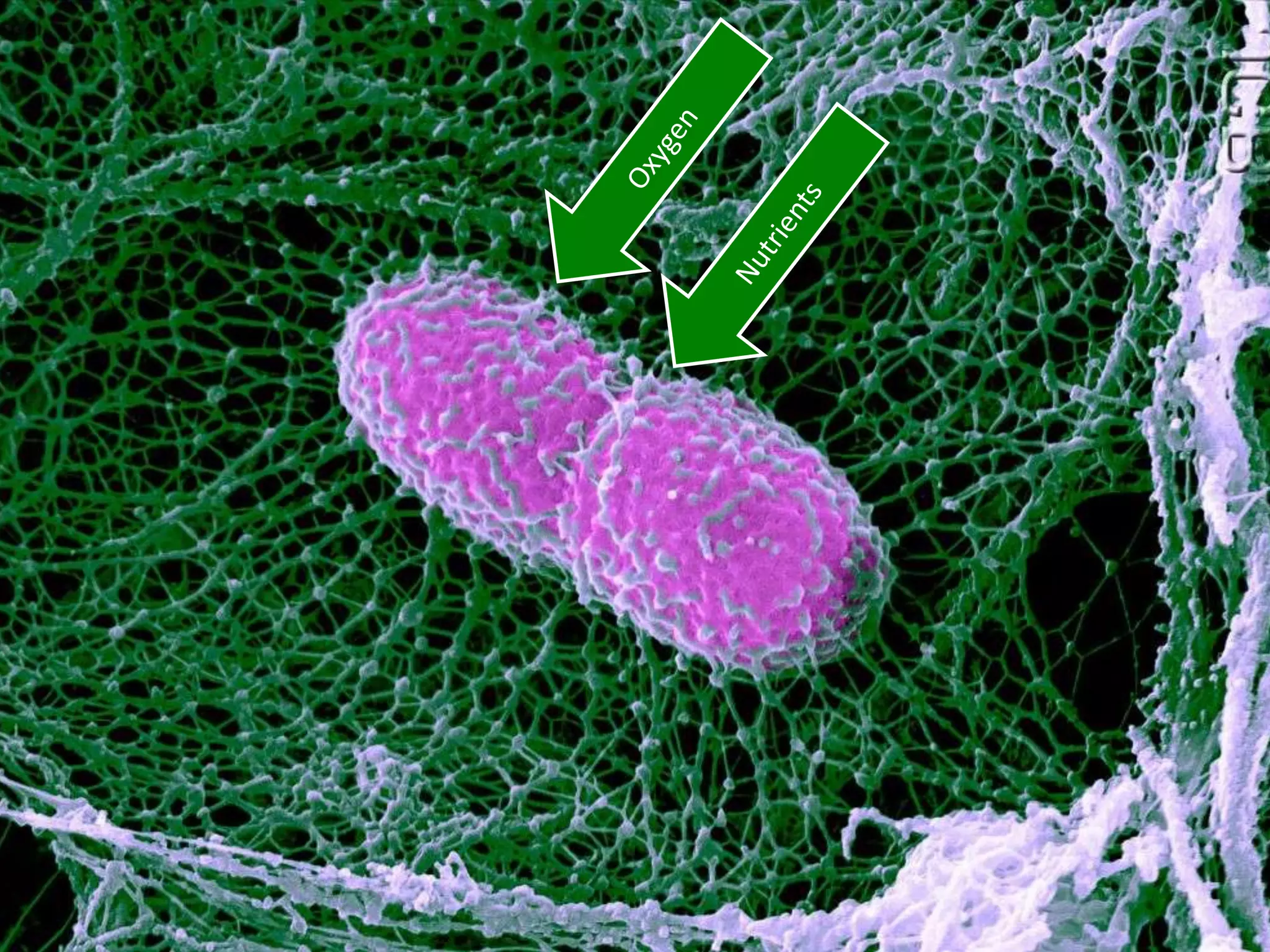
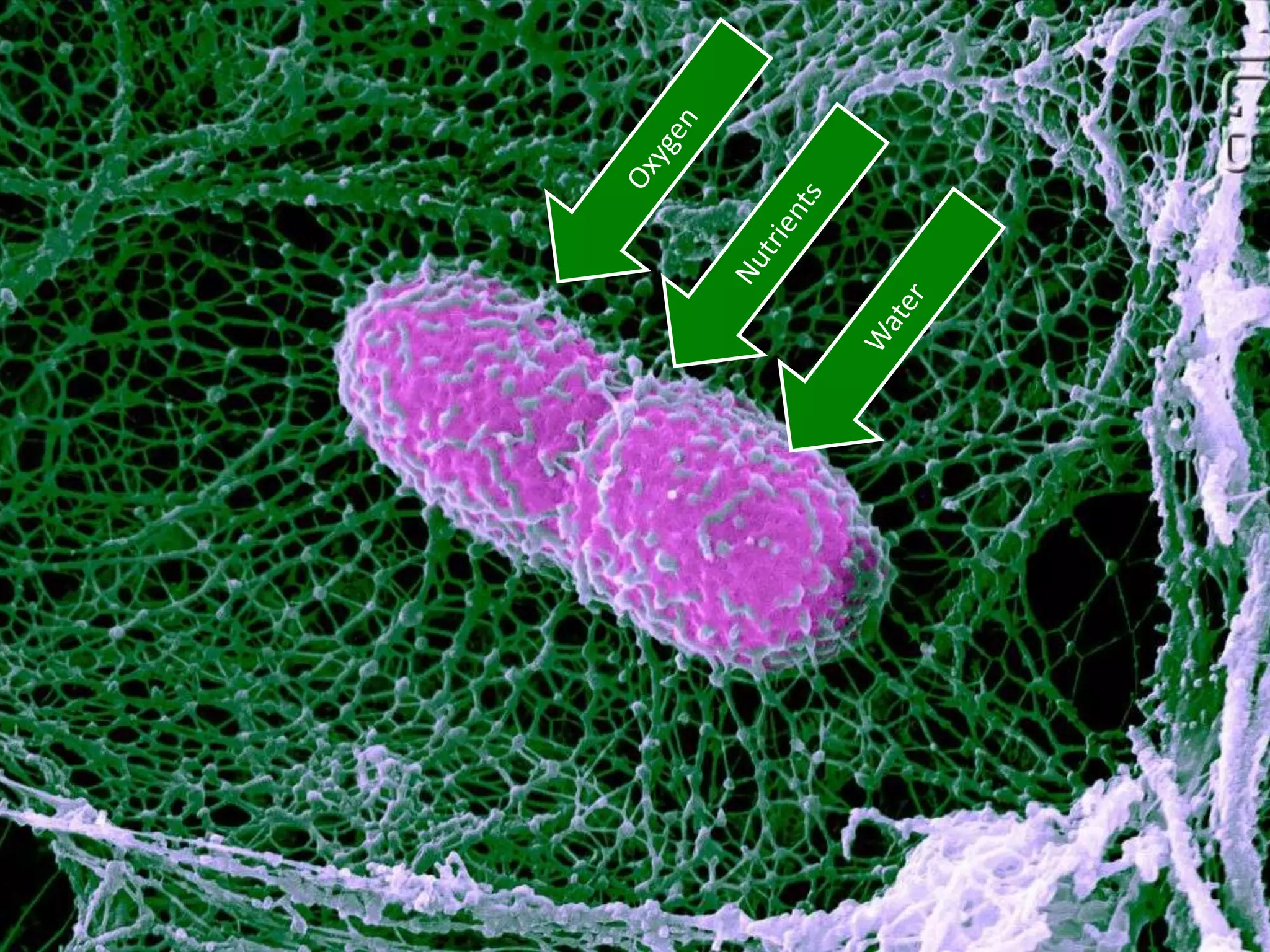
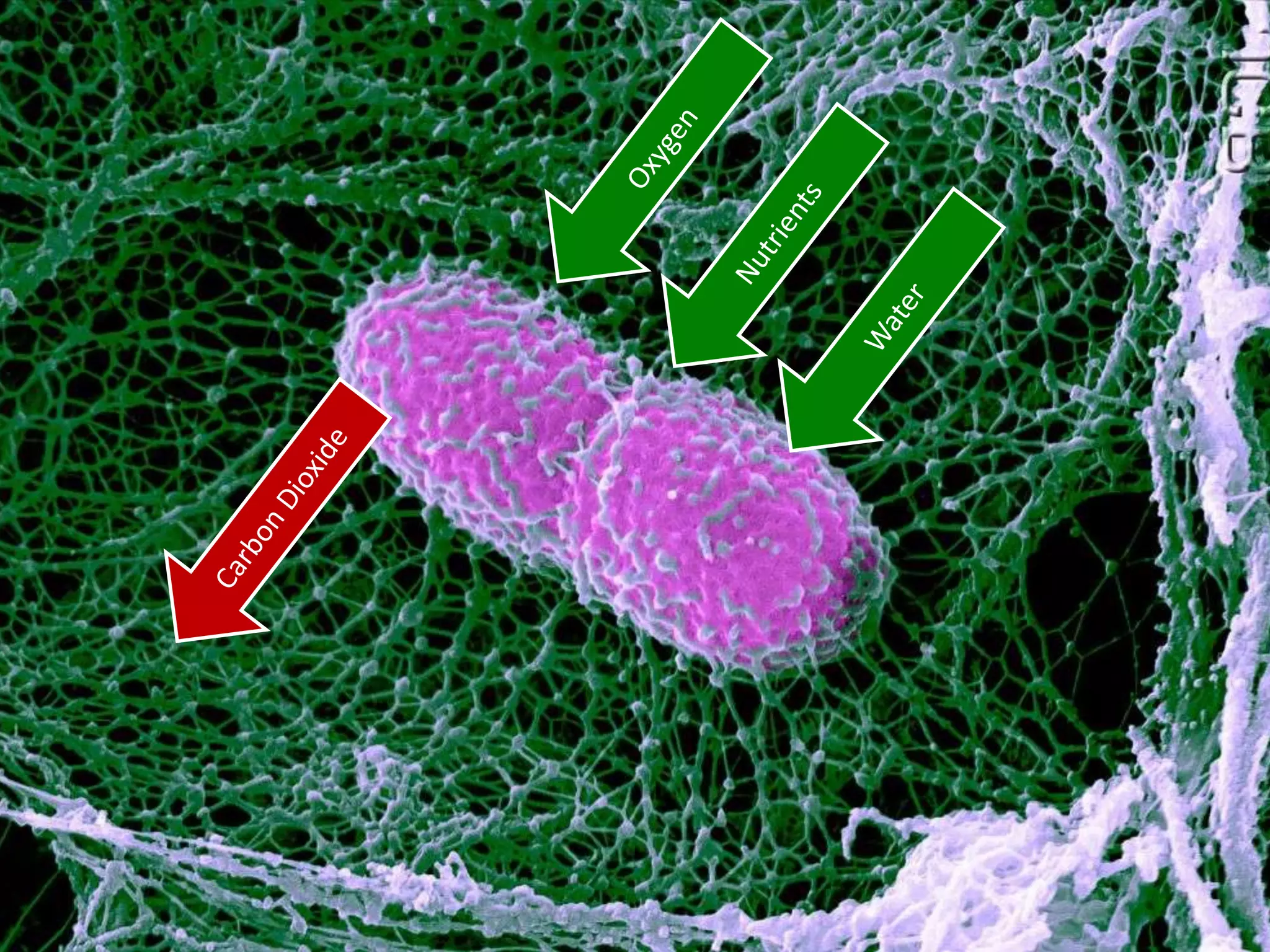
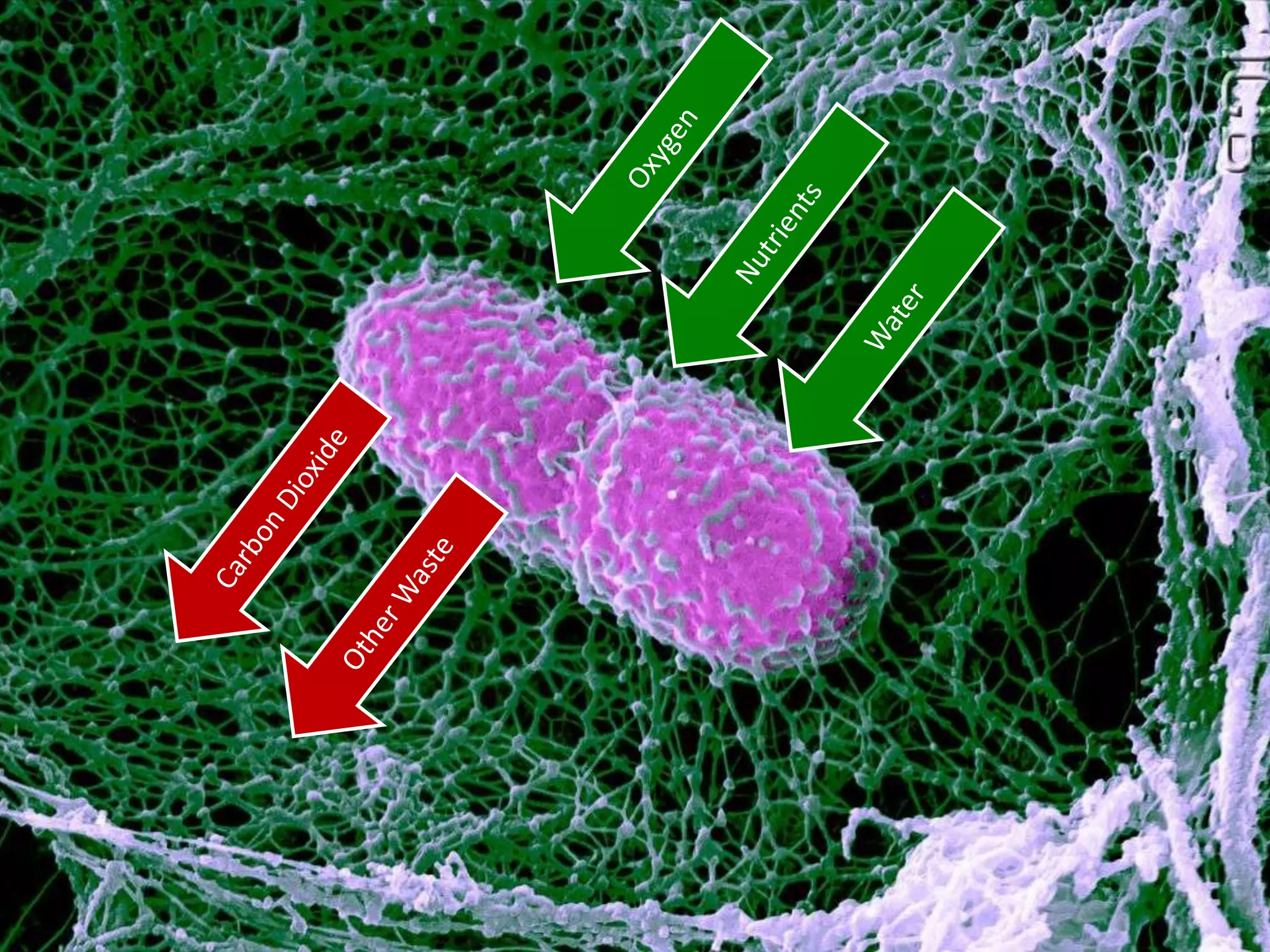
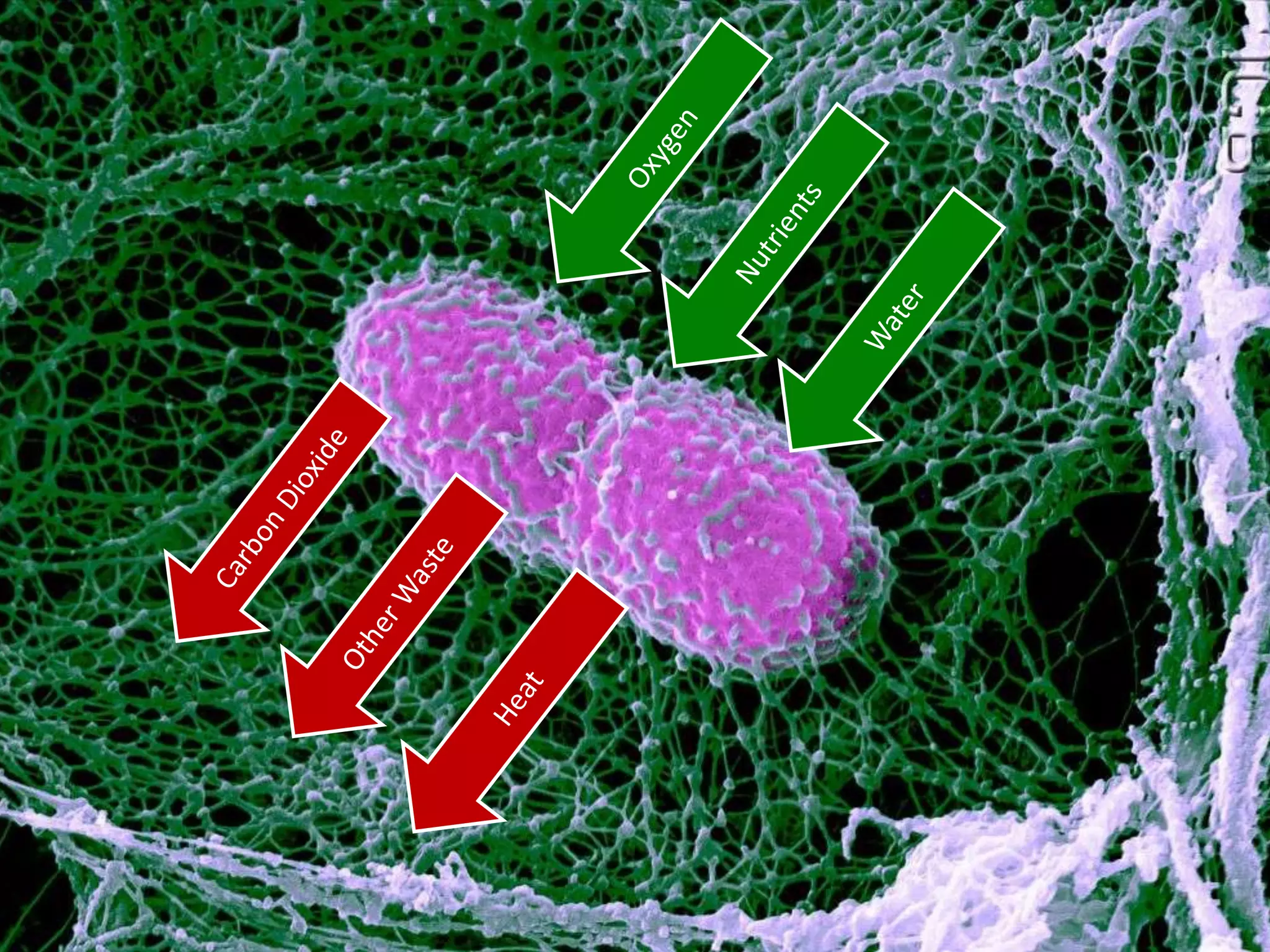
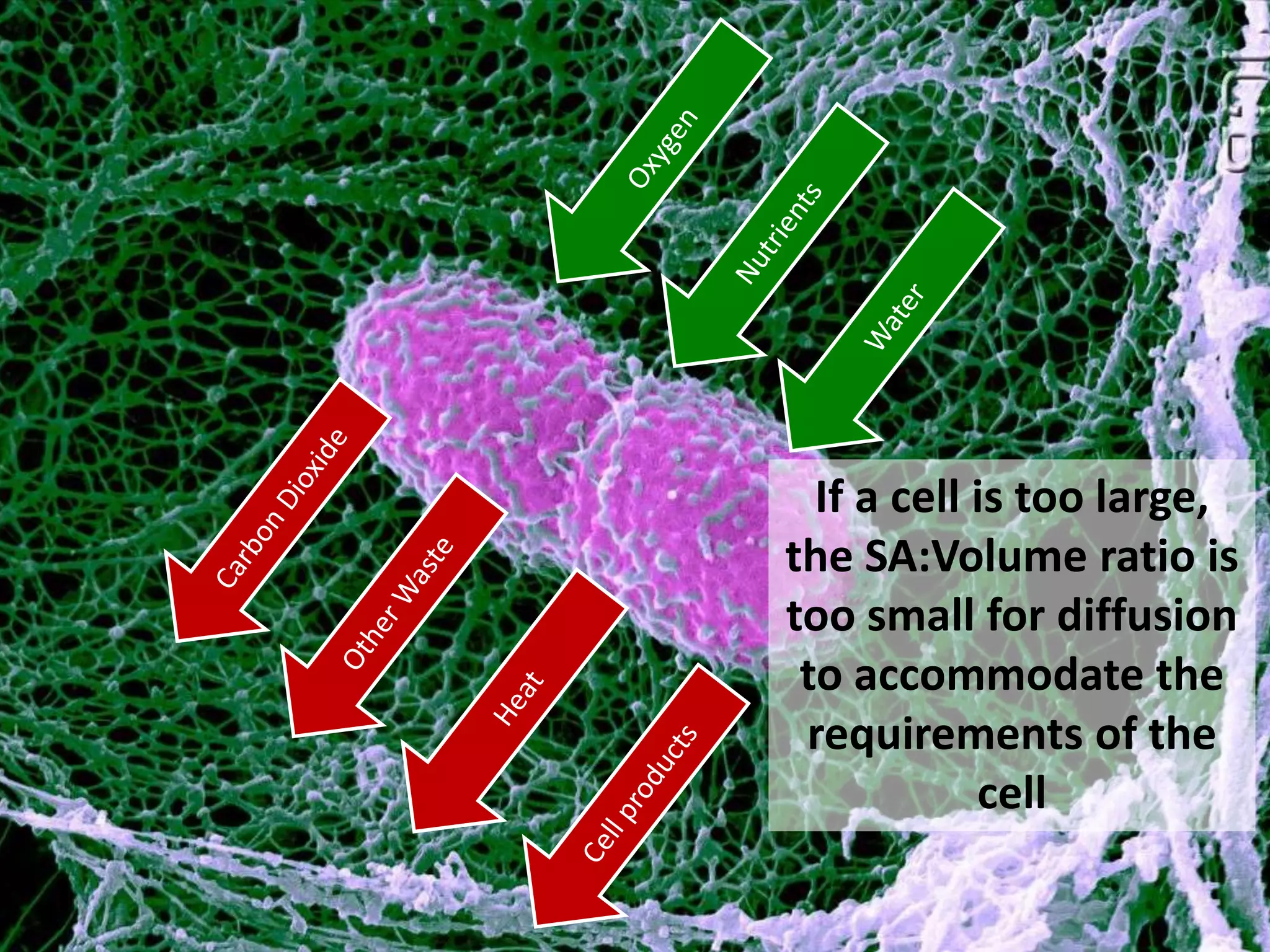
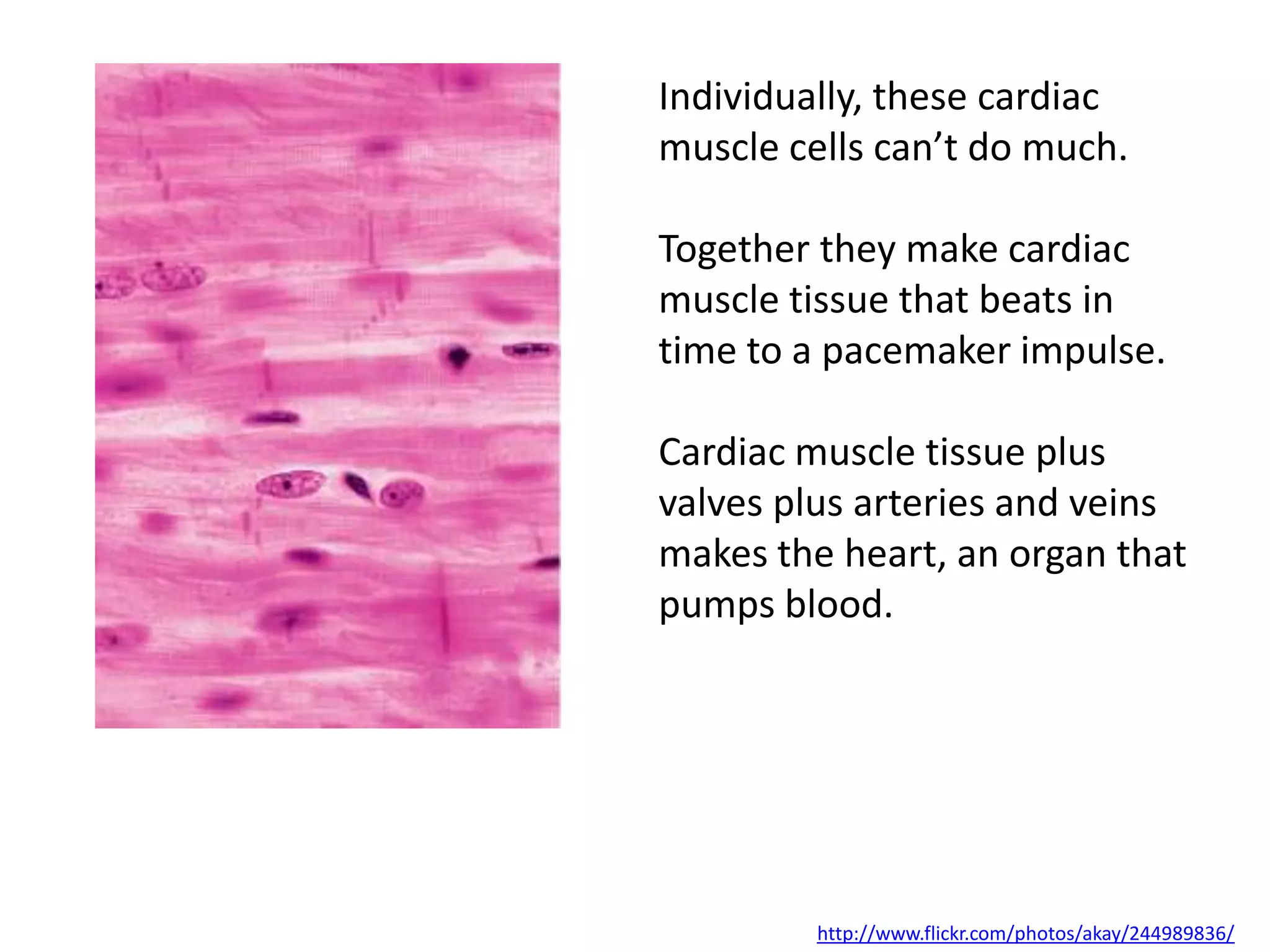
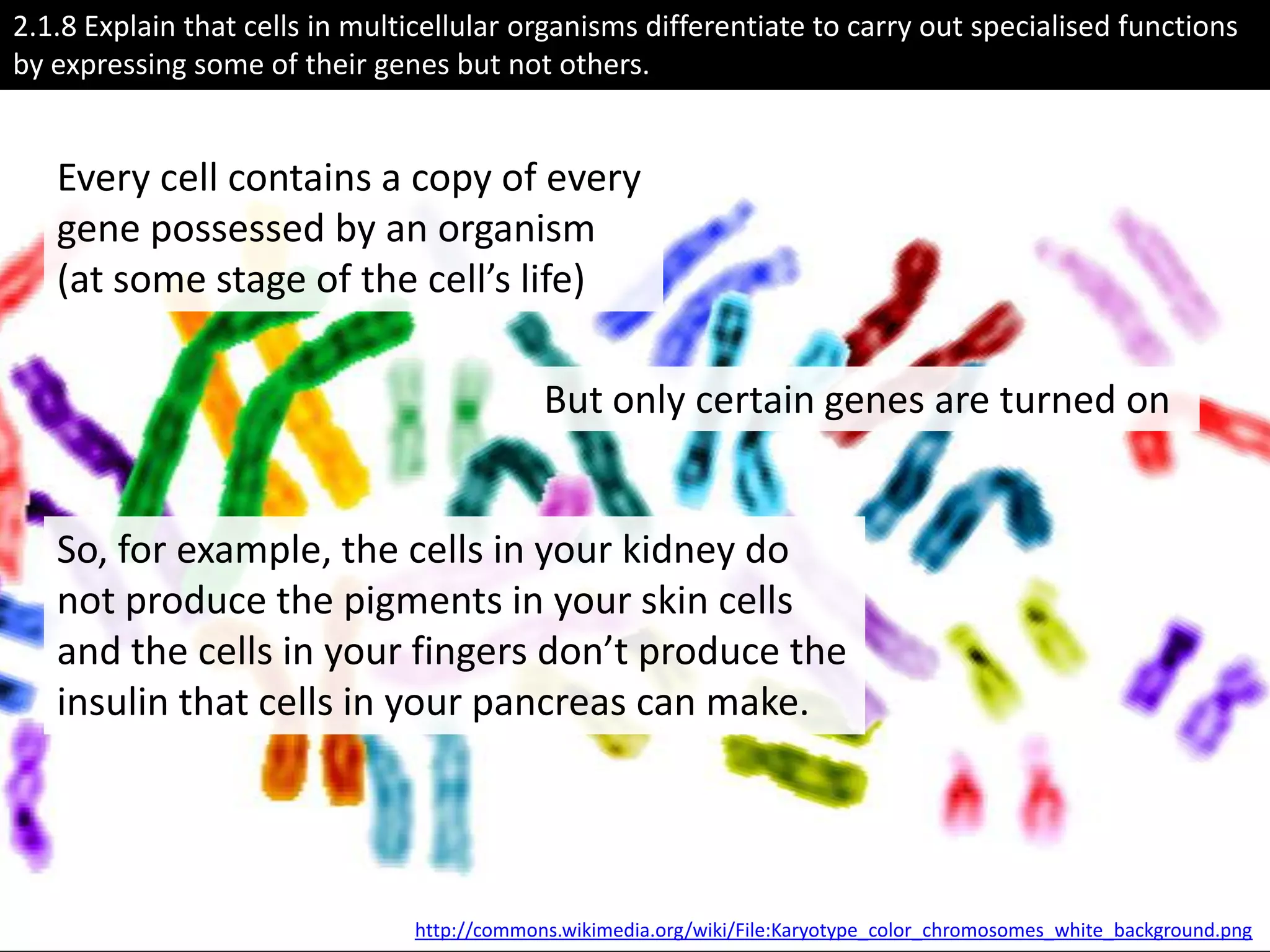
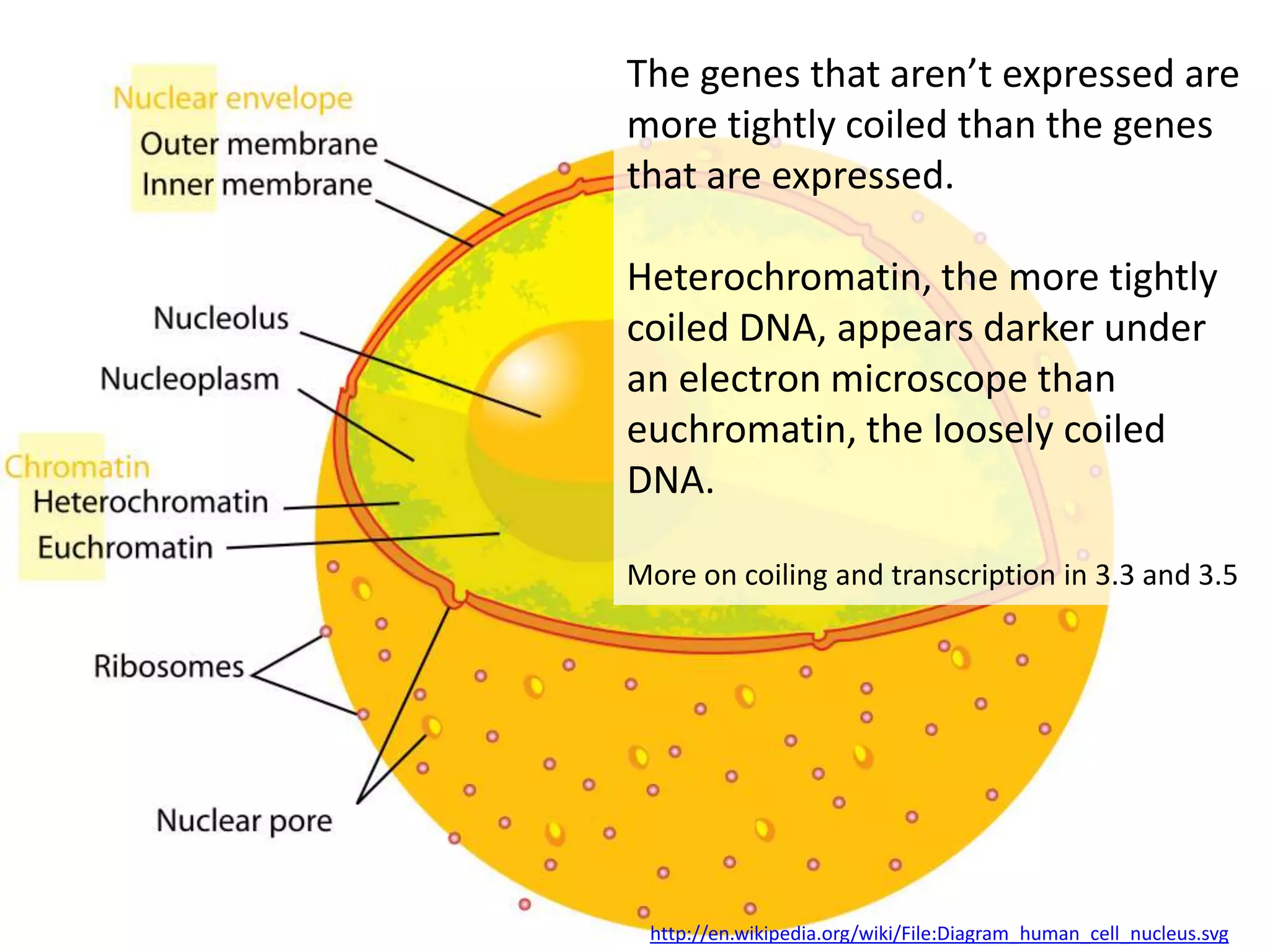
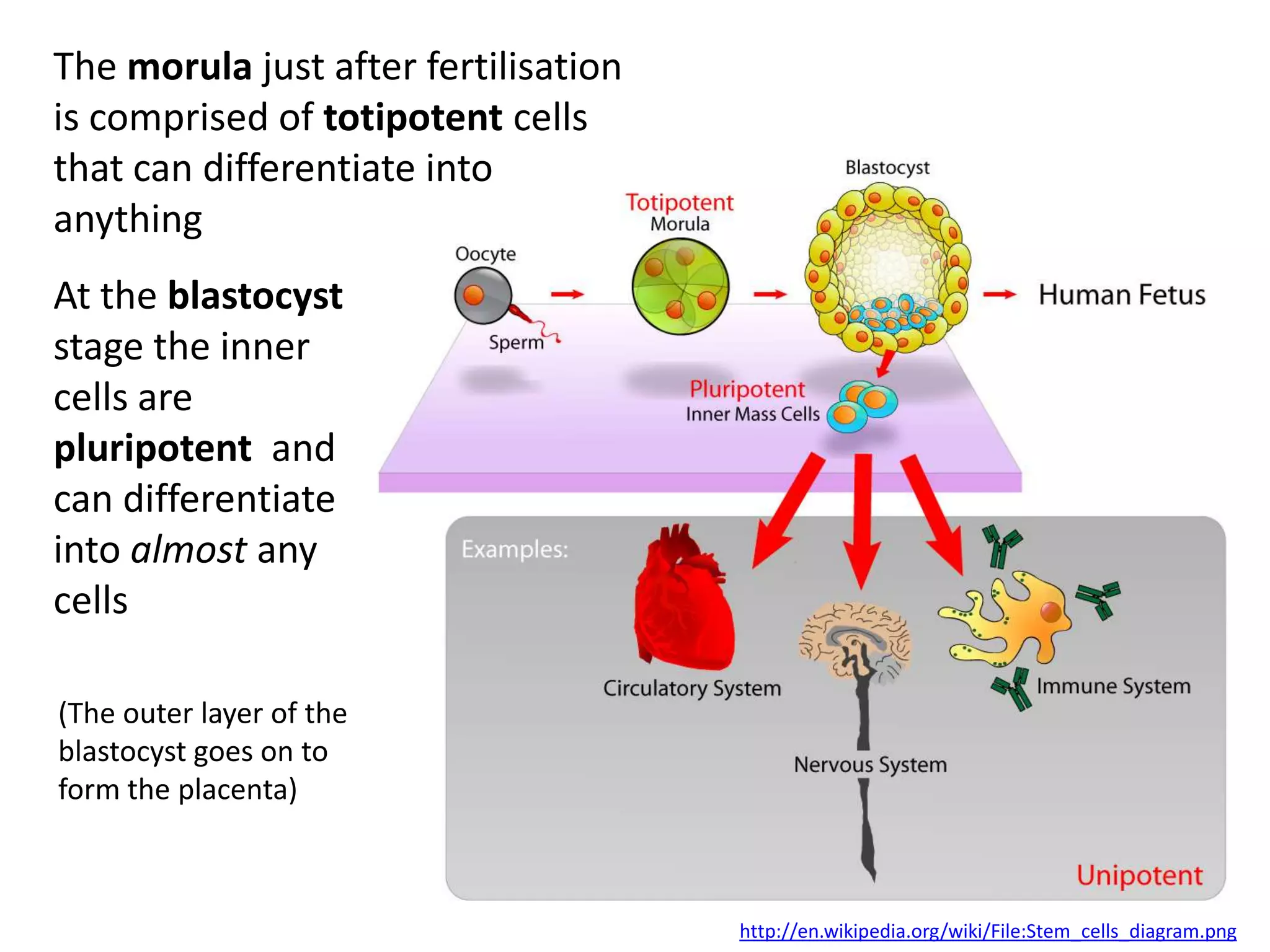
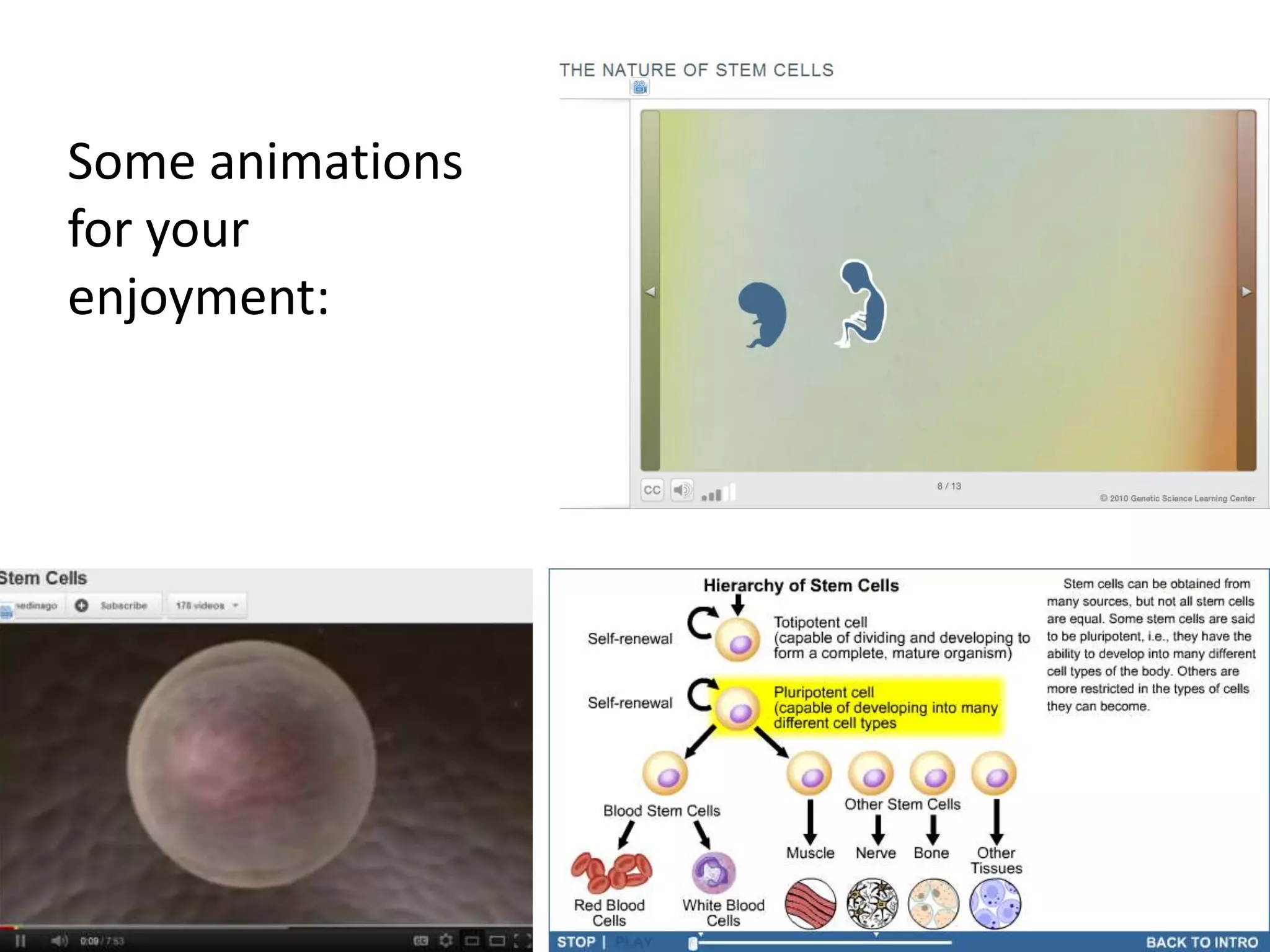
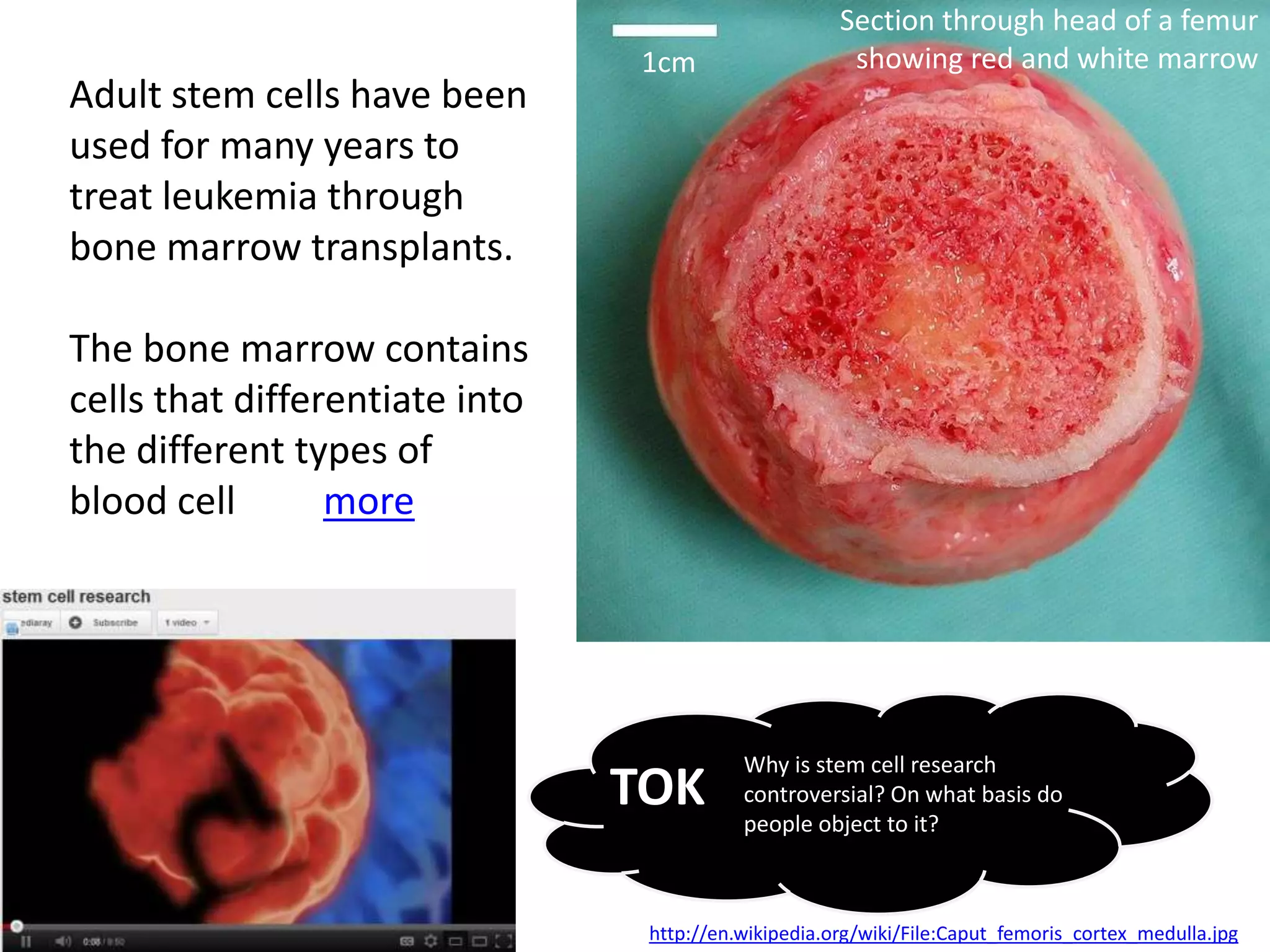
The cell theory states that cells are the basic unit of life, new cells are formed from existing cells, and cells and their products make up living organisms. Evidence for the cell theory came from early microscope observations by Hooke, van Leeuwenhoek, and others showing the presence of cells. Schleiden and Schwann combined these observations with their own work to propose the first two principles of the cell theory. Virchow later added the third principle that cells only arise from pre-existing cells. Unicellular organisms carry out all the functions of life, while multicellular organisms show emergent properties and cell differentiation allows specialization of function.