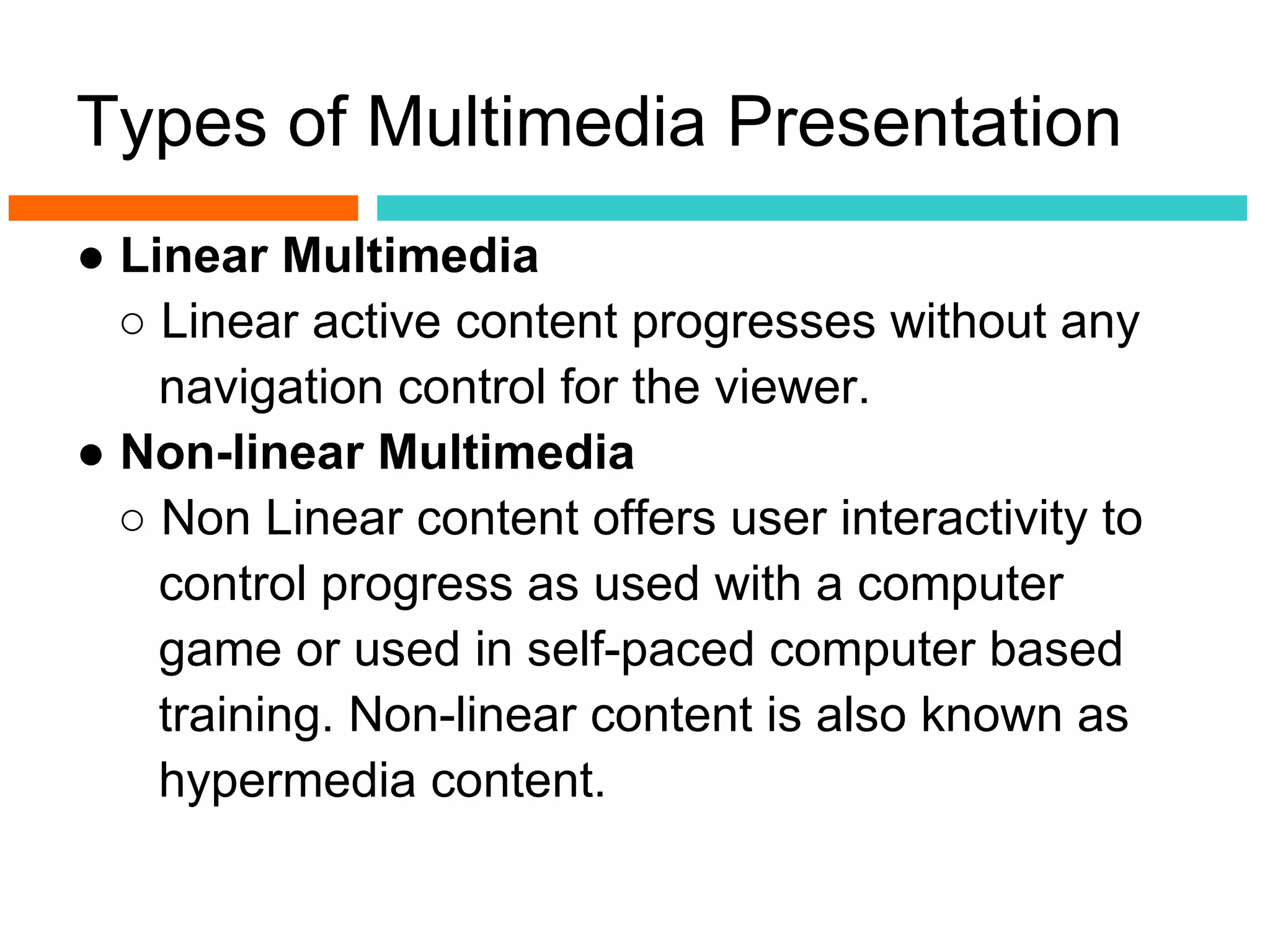
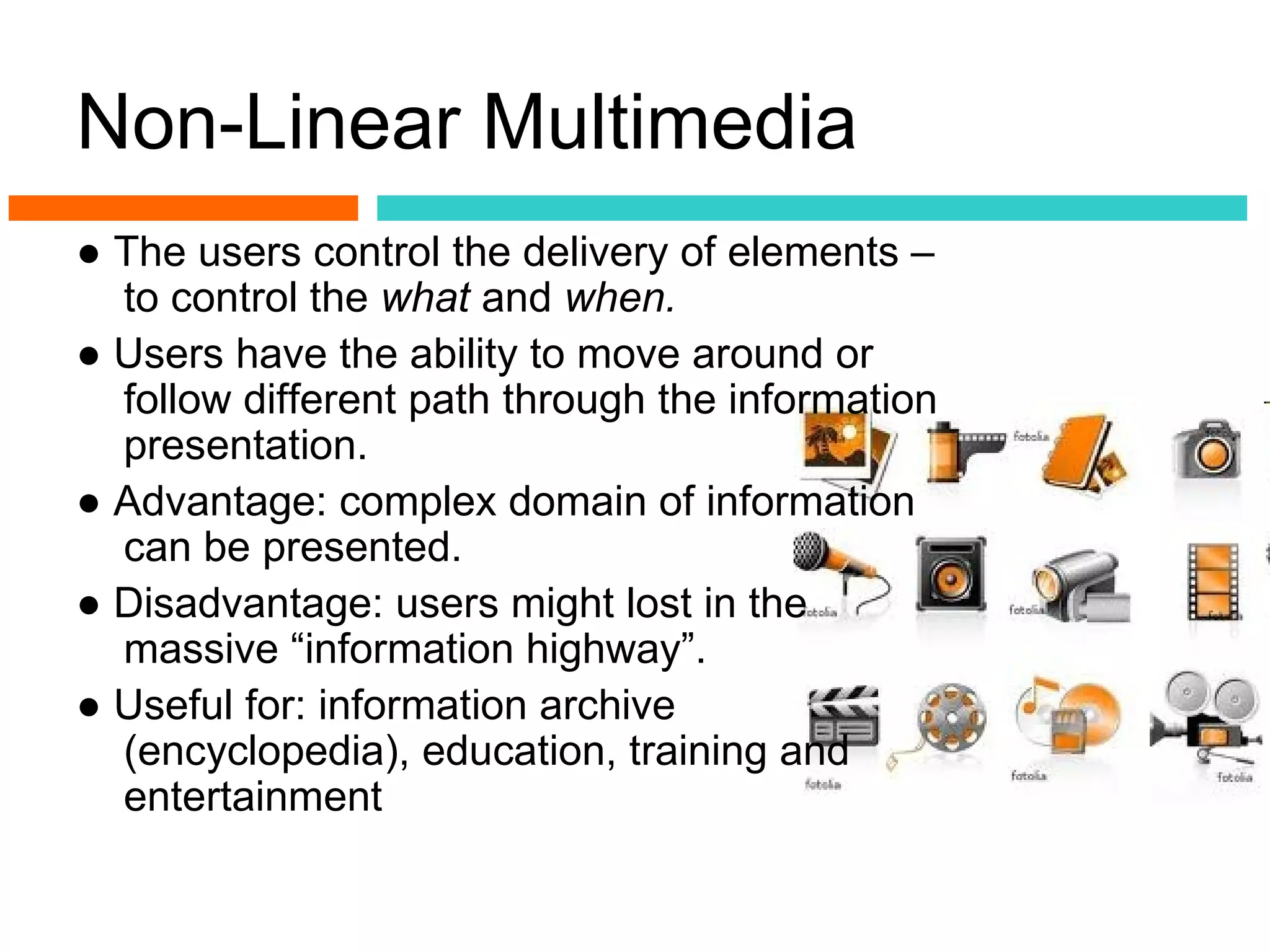
This document introduces multimedia and its applications. It defines multimedia as a combination of text, graphics, sound, animation and video to effectively communicate ideas. It discusses two types of multimedia presentations: linear, which progresses without user control, and non-linear, which offers interactivity. It provides examples of linear and non-linear multimedia. It also outlines several applications of multimedia such as in creative industries, commerce, entertainment, engineering, science, medicine, education and more.