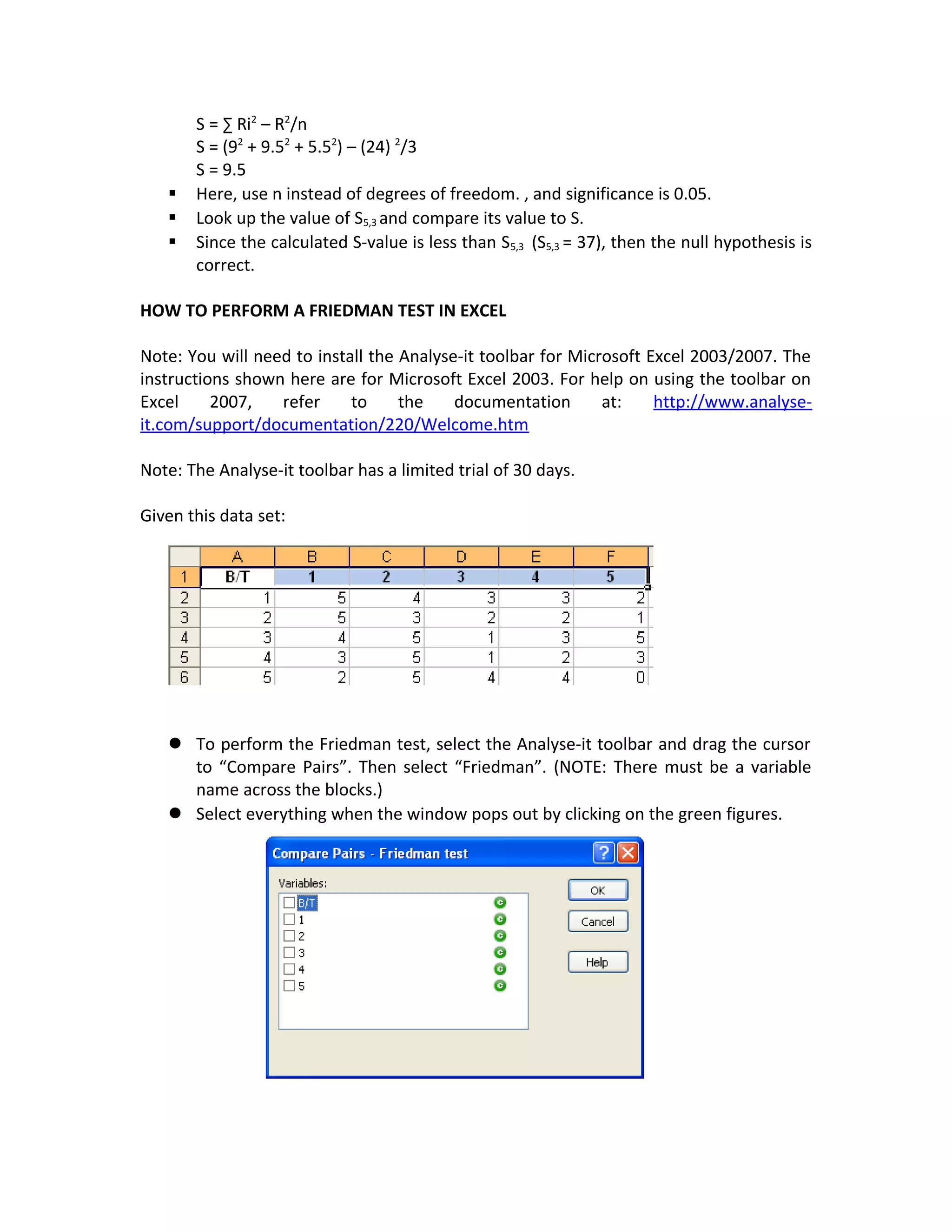
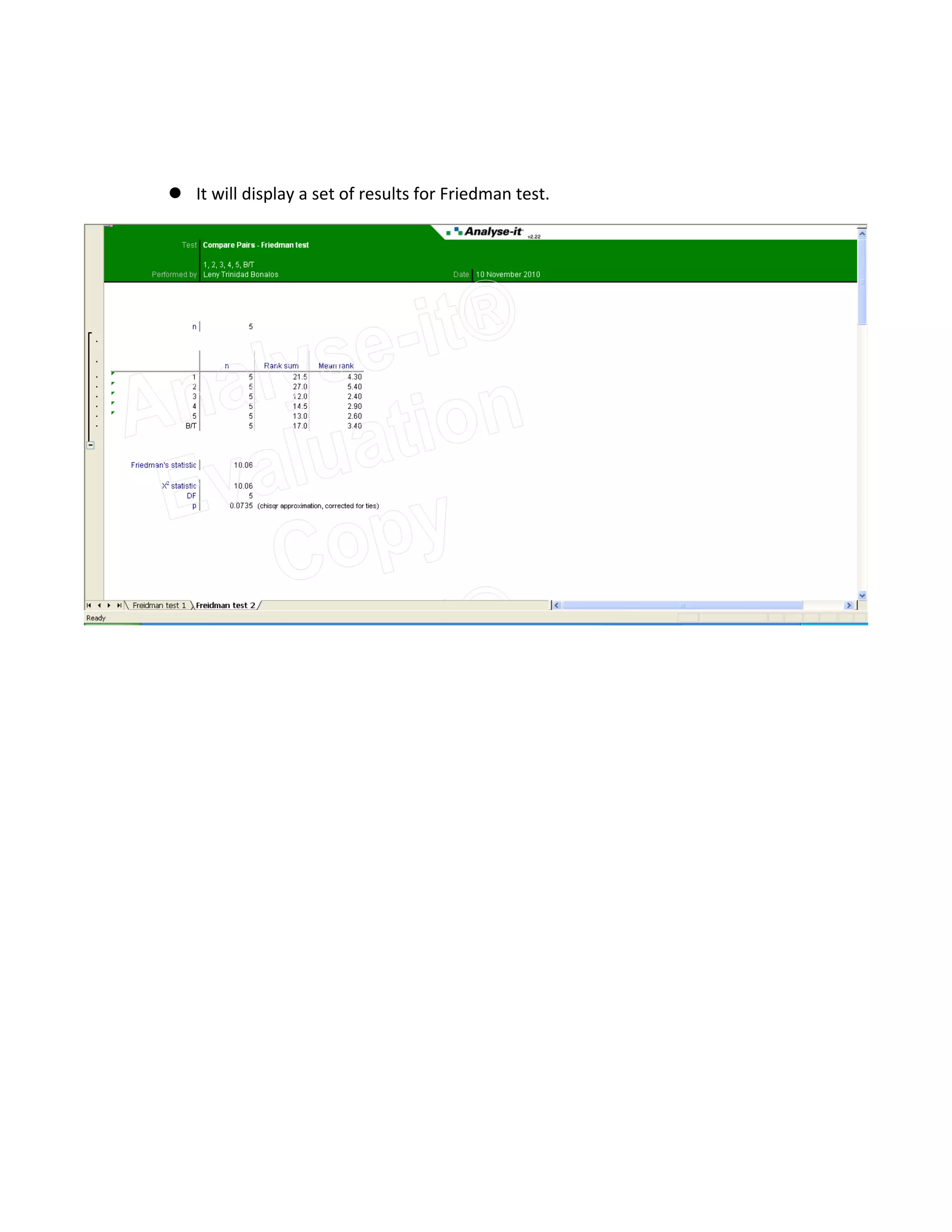
Friedman's test is a nonparametric test used to detect differences in treatments across multiple test blocks when using ordinal or ranked data. It involves ranking the data within each block, summing the ranks for each treatment, and calculating a Friedman test statistic that is compared to a chi-square critical value to determine if the null hypothesis that the treatments have identical effects can be rejected. An example demonstrates constructing a table with ranked data, calculating the Friedman statistic, determining the degrees of freedom, looking up the critical value, and comparing it to the statistic to evaluate the null hypothesis. The test can also be performed in Excel using the Analyse-it plugin.