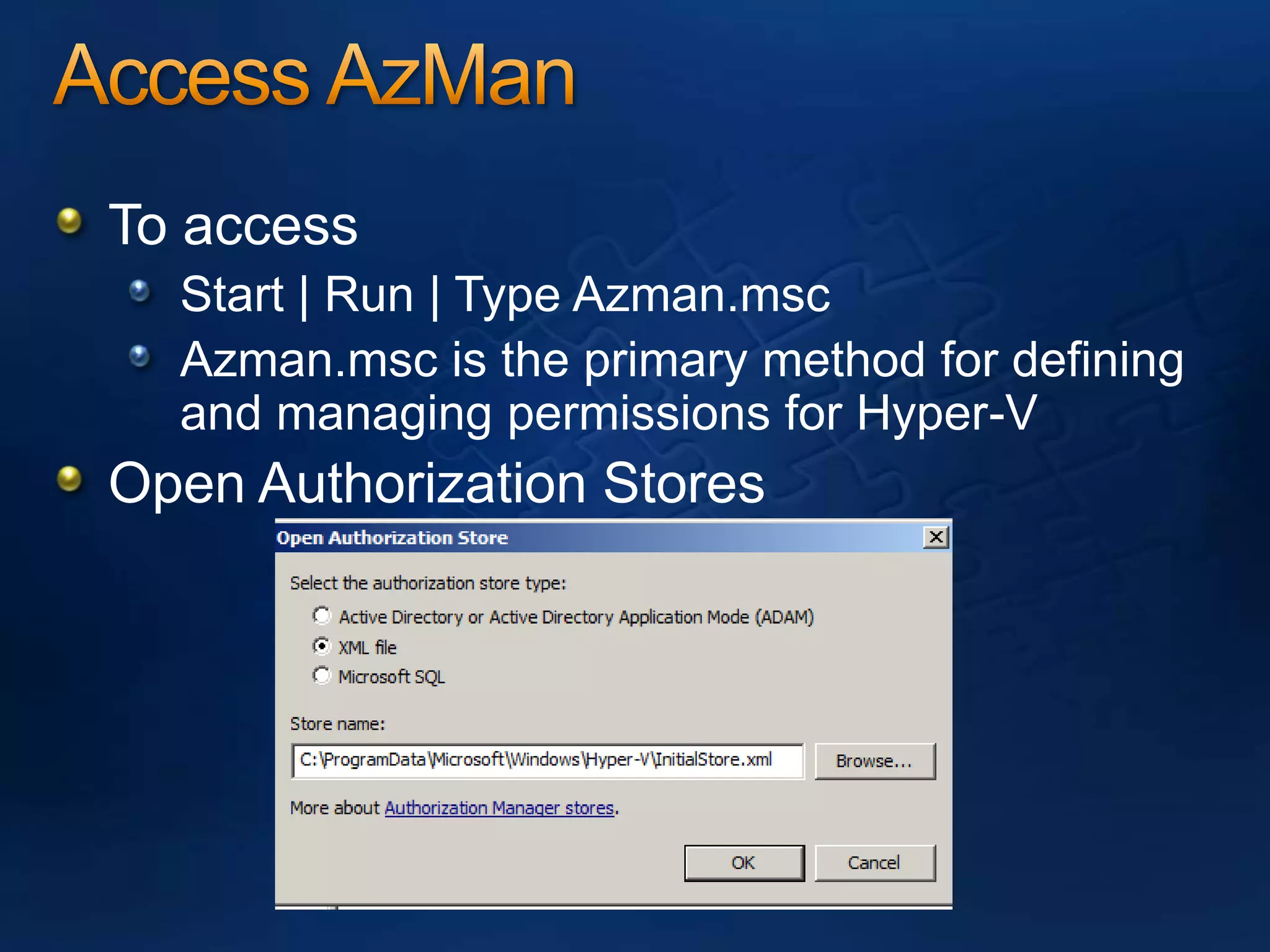
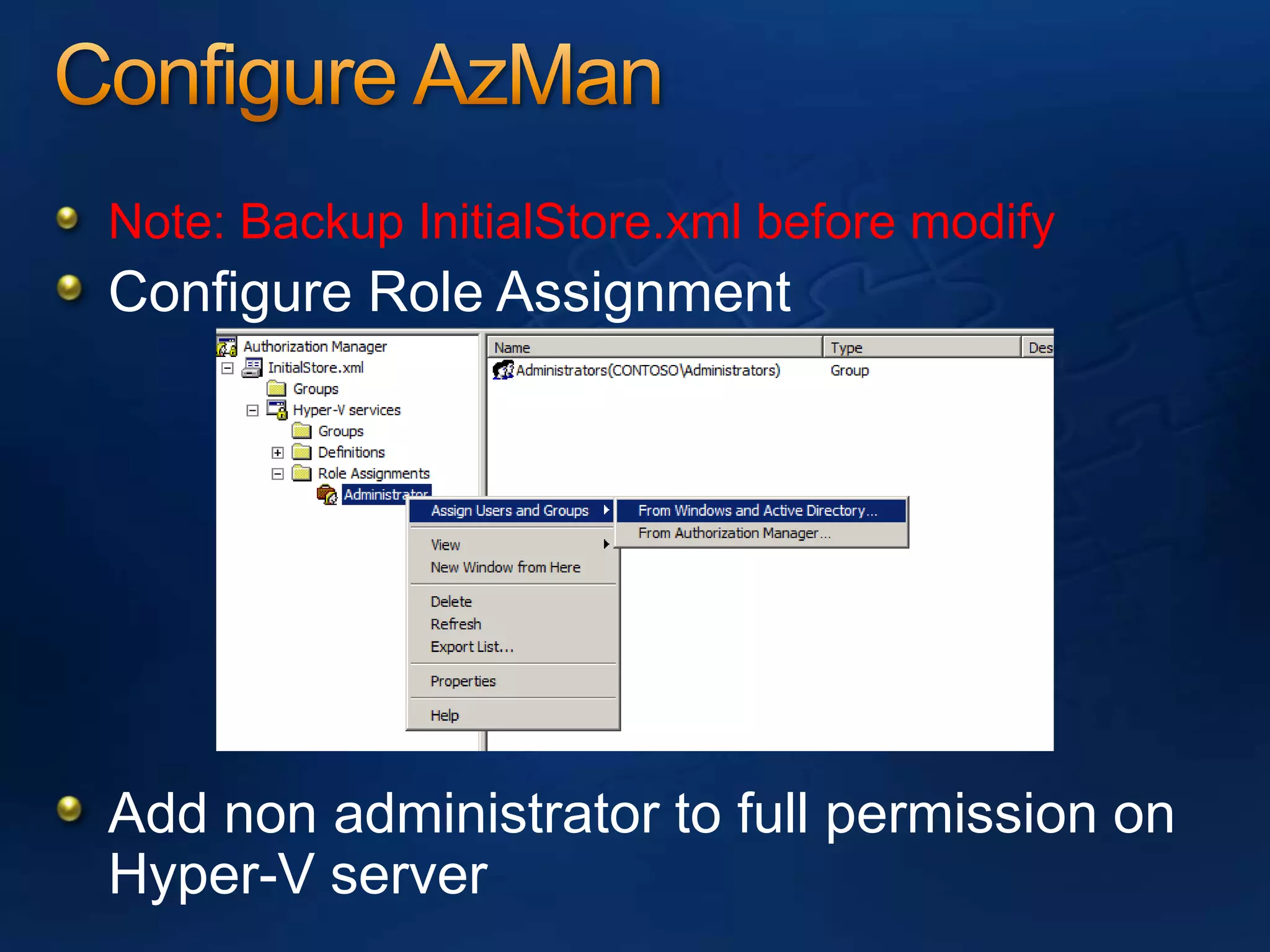
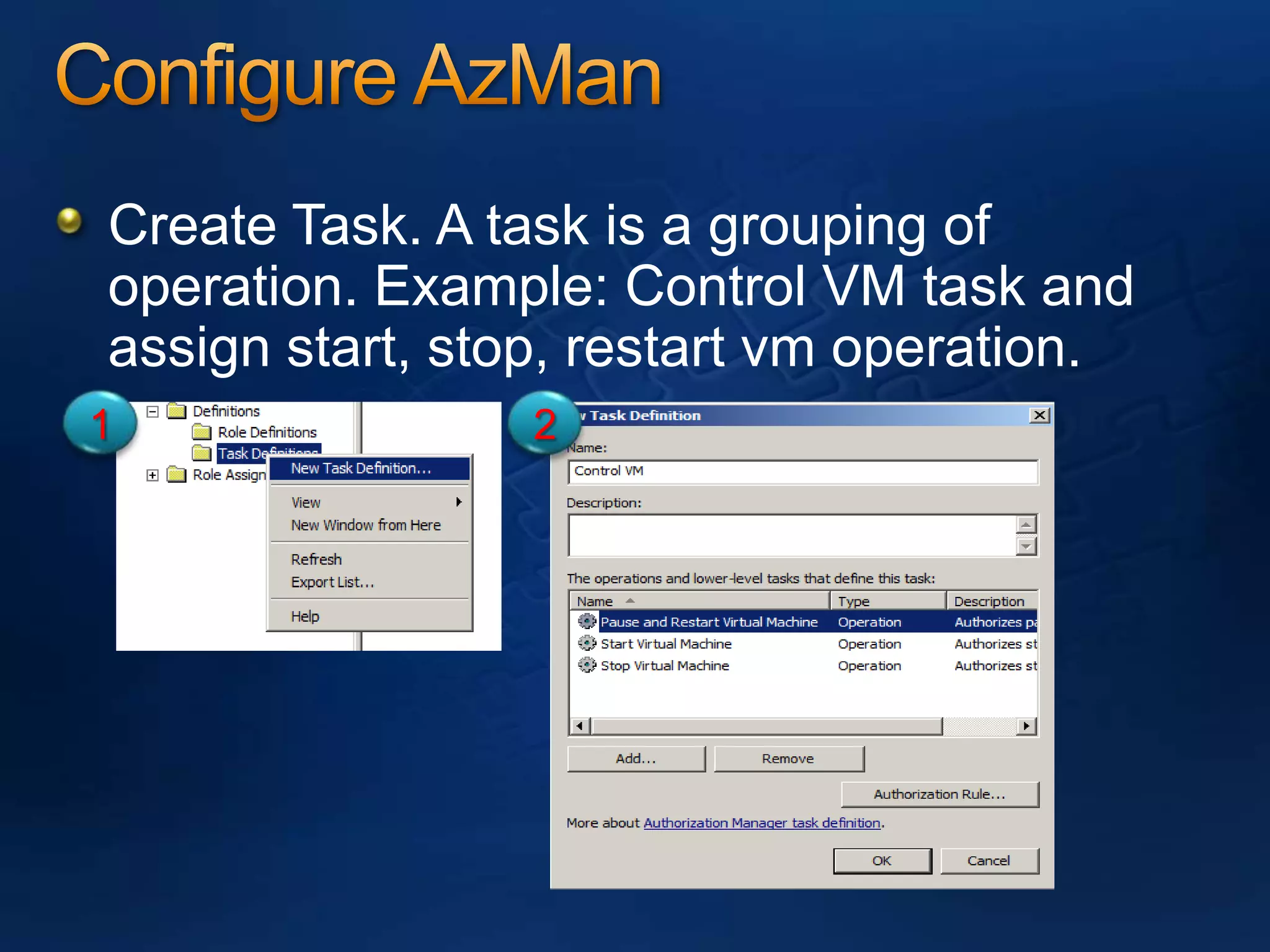
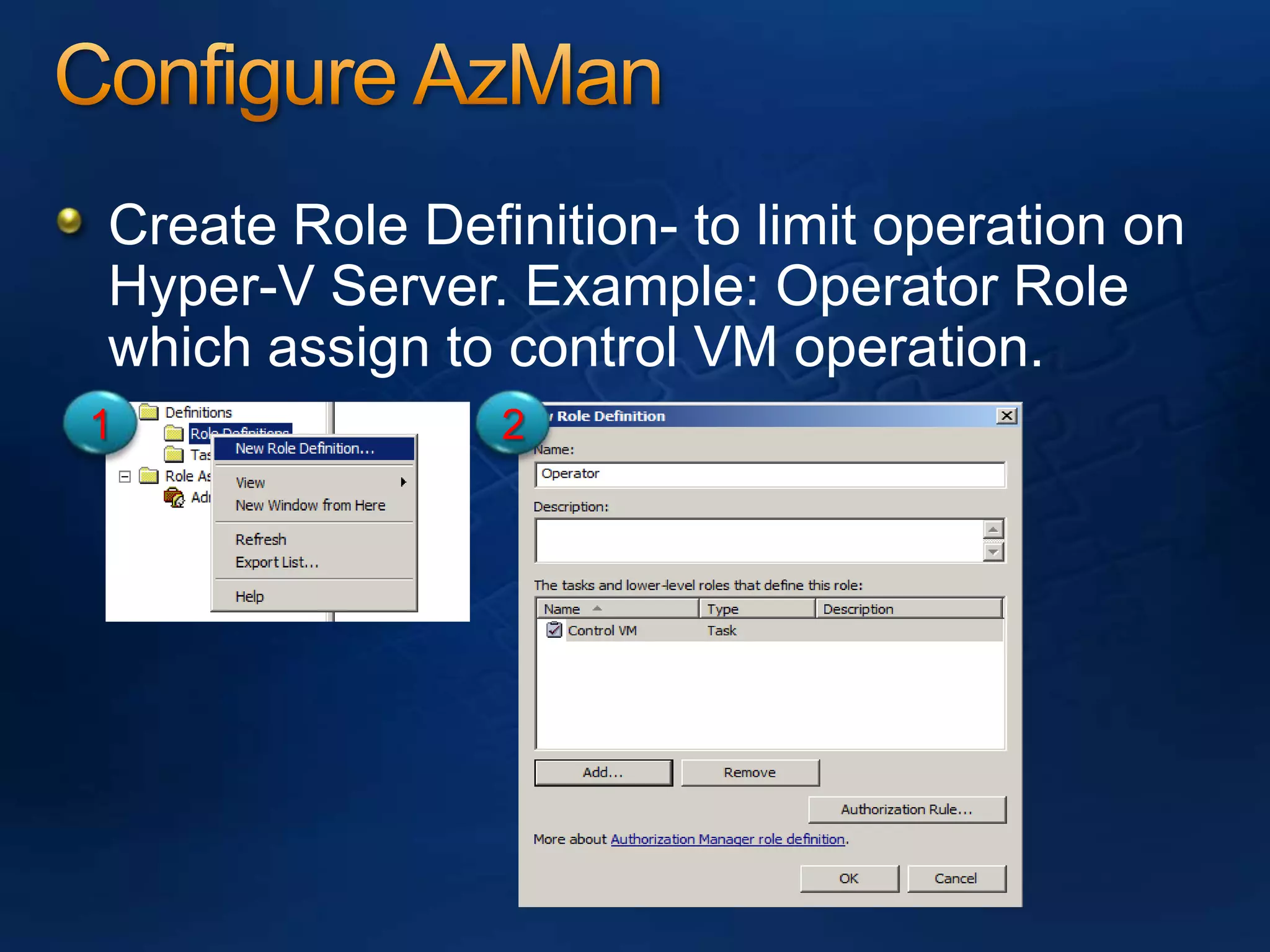
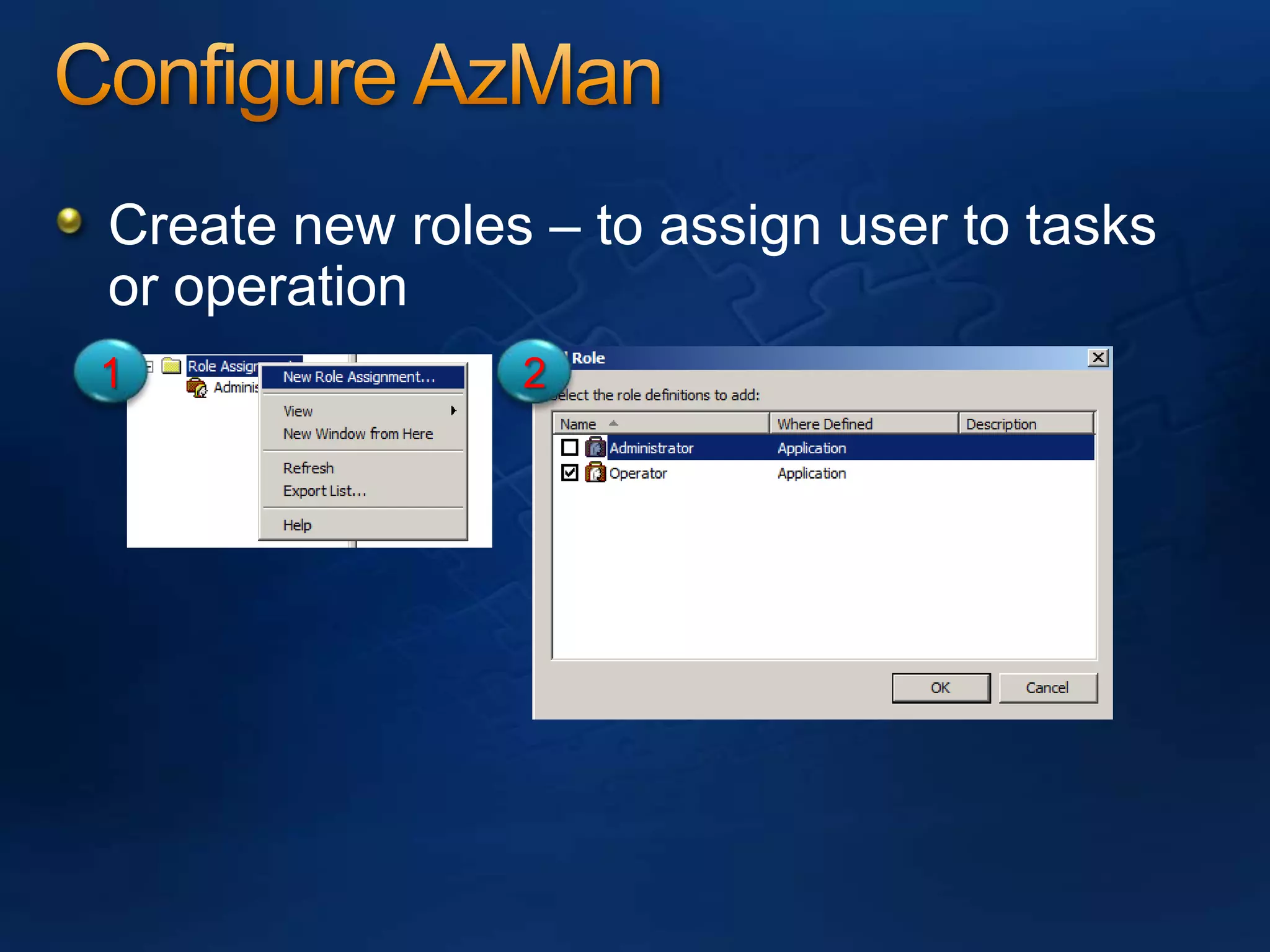
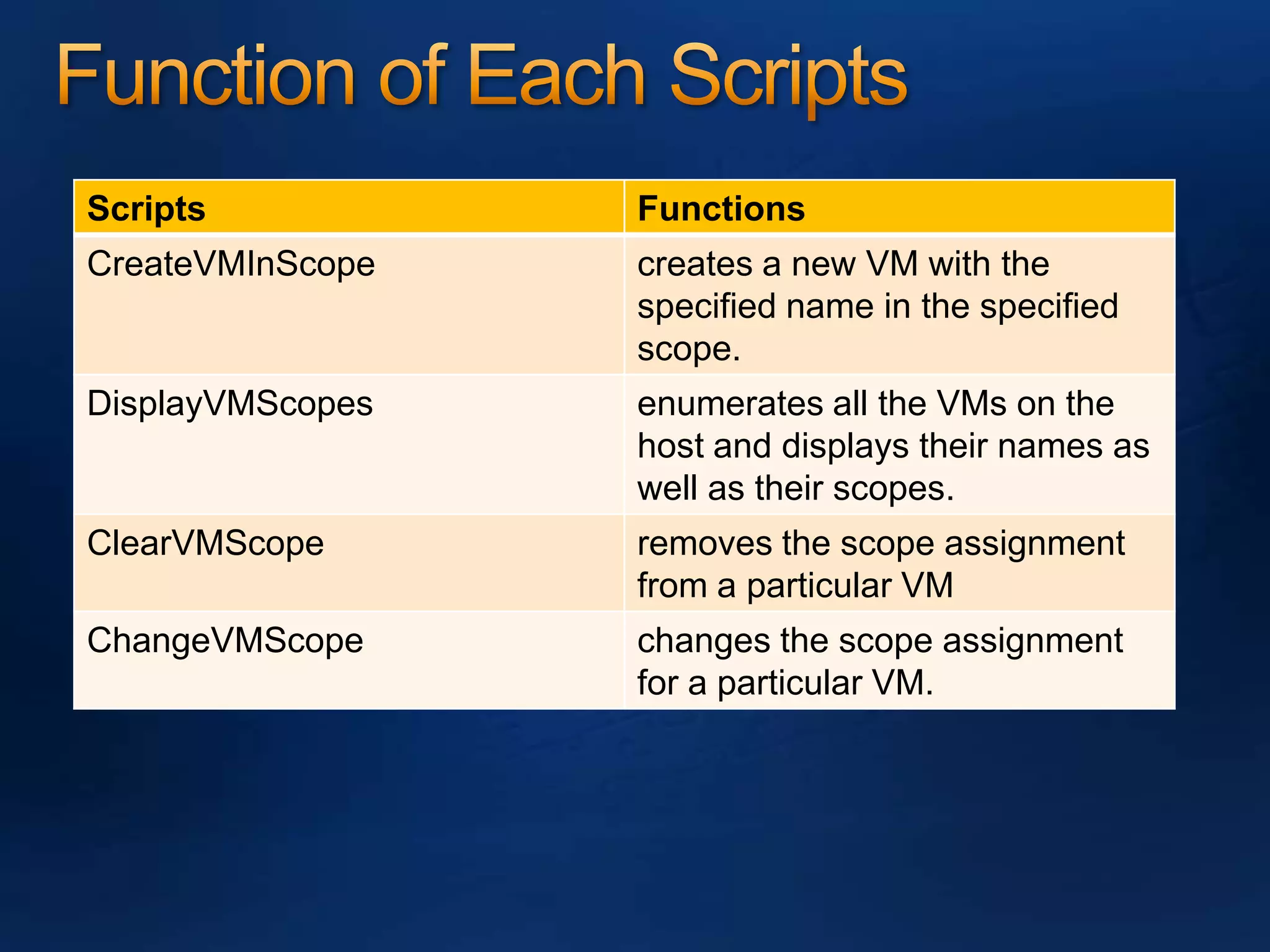
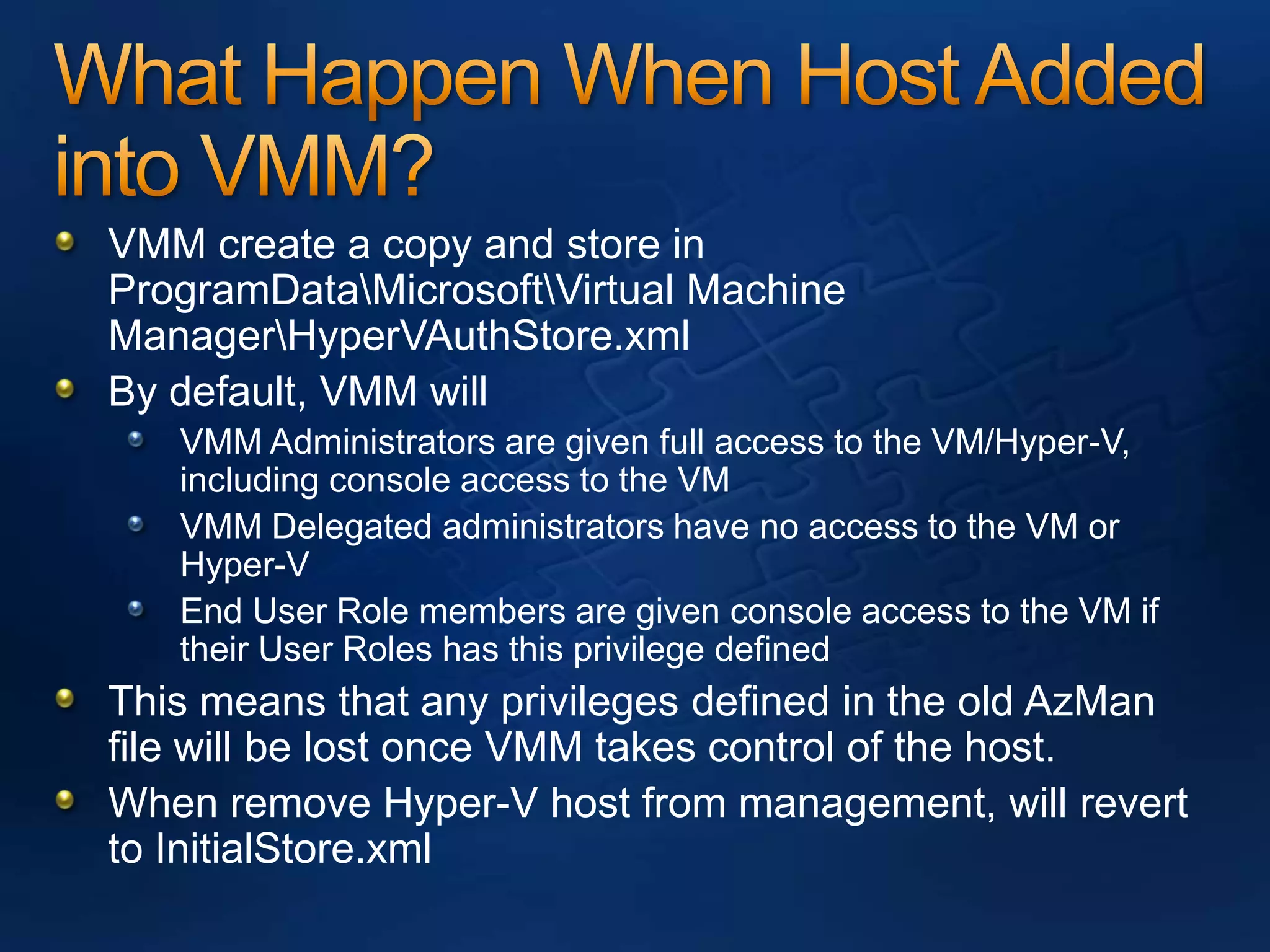
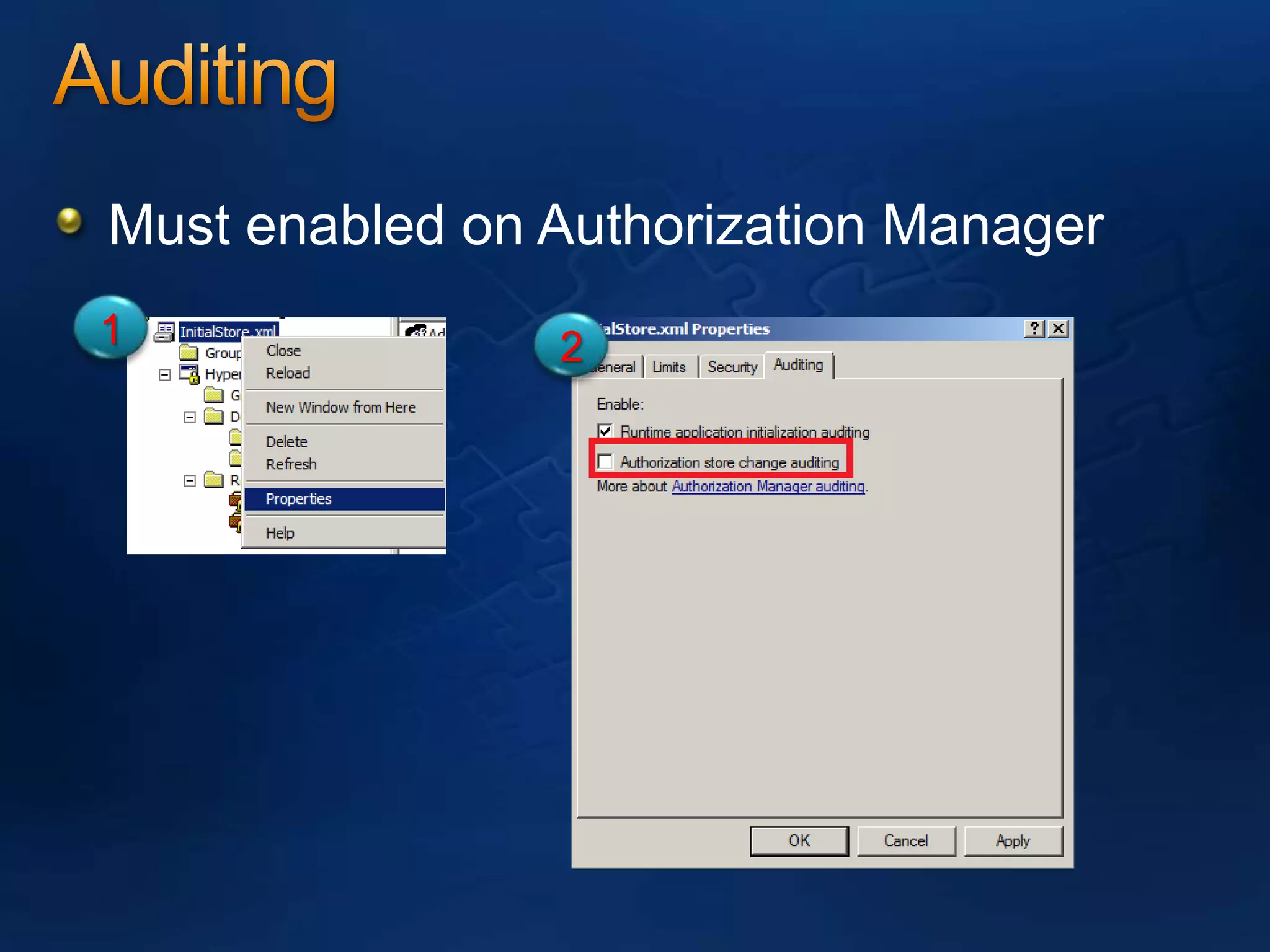
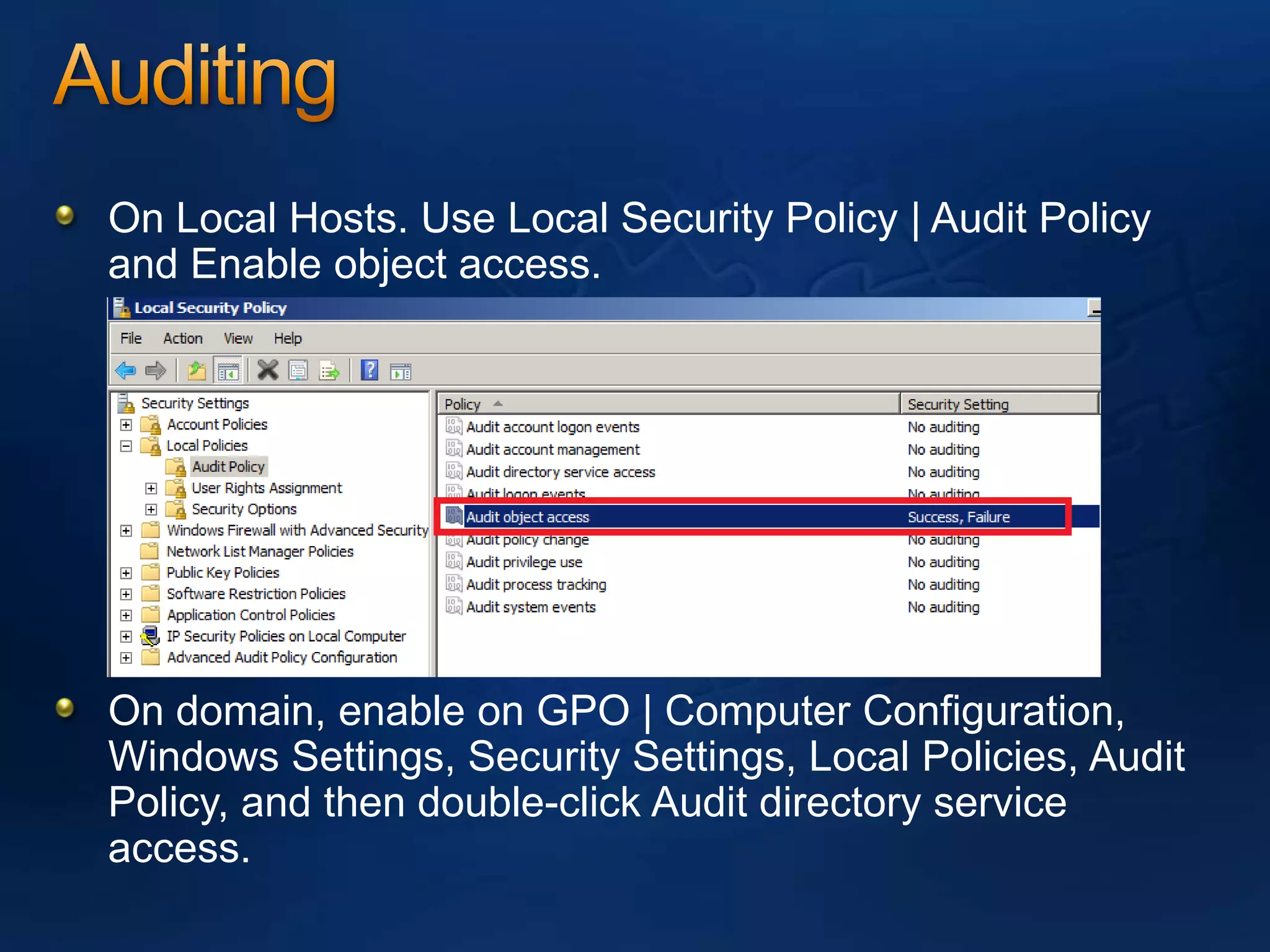
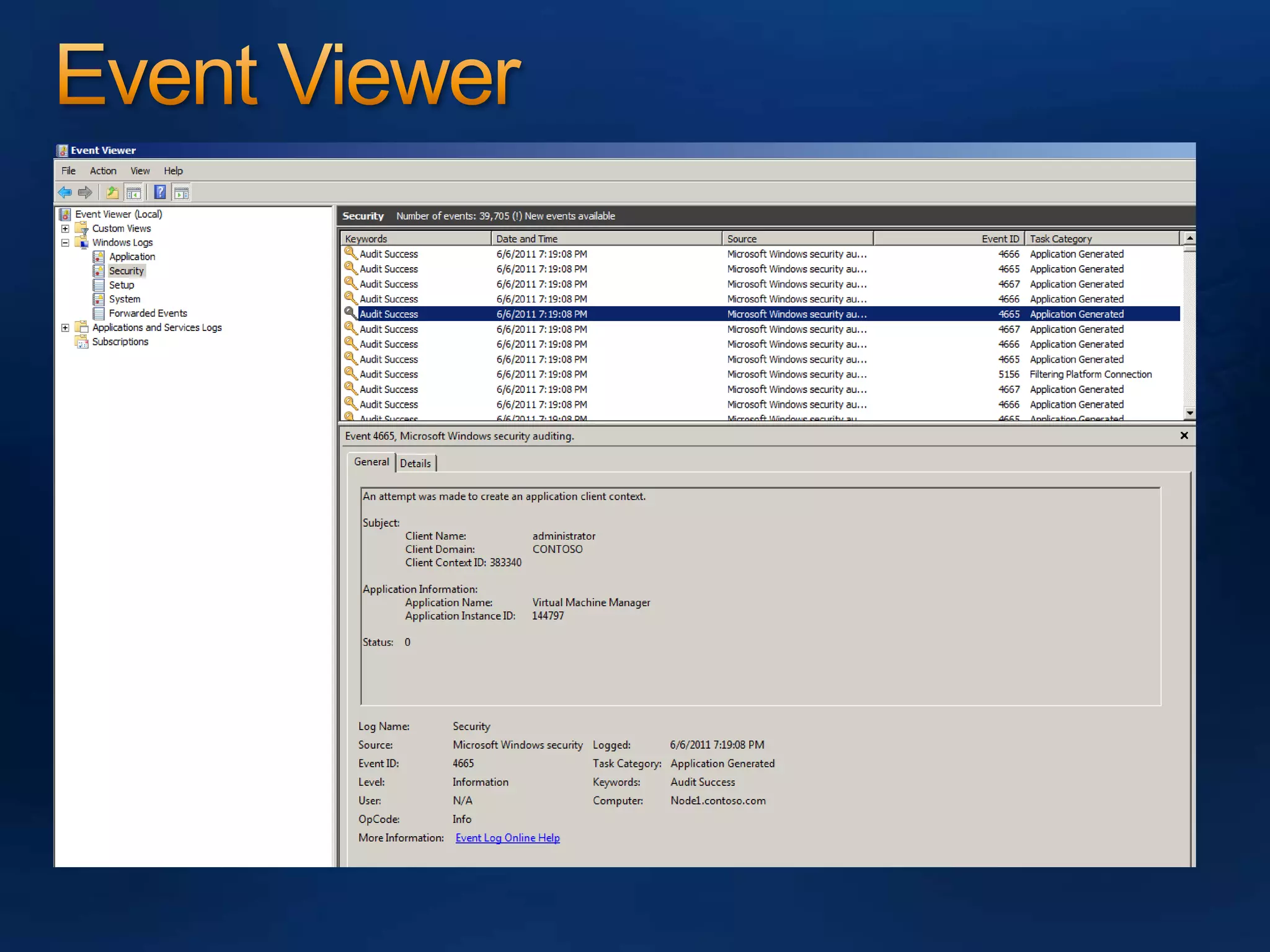
AzMan is the authorization manager that controls role-based access in Hyper-V. It uses role definitions and assignments to determine which tasks and operations each user role is allowed to perform. AzMan can be used to securely configure access at the hypervisor or individual VM level. It is configured through the Azman.msc interface by creating roles, tasks, and assigning users and groups to roles. When a Hyper-V host joins a domain or is managed by VMM, AzMan permissions may be overwritten and default to provide full access to domain admins or VMM administrators.