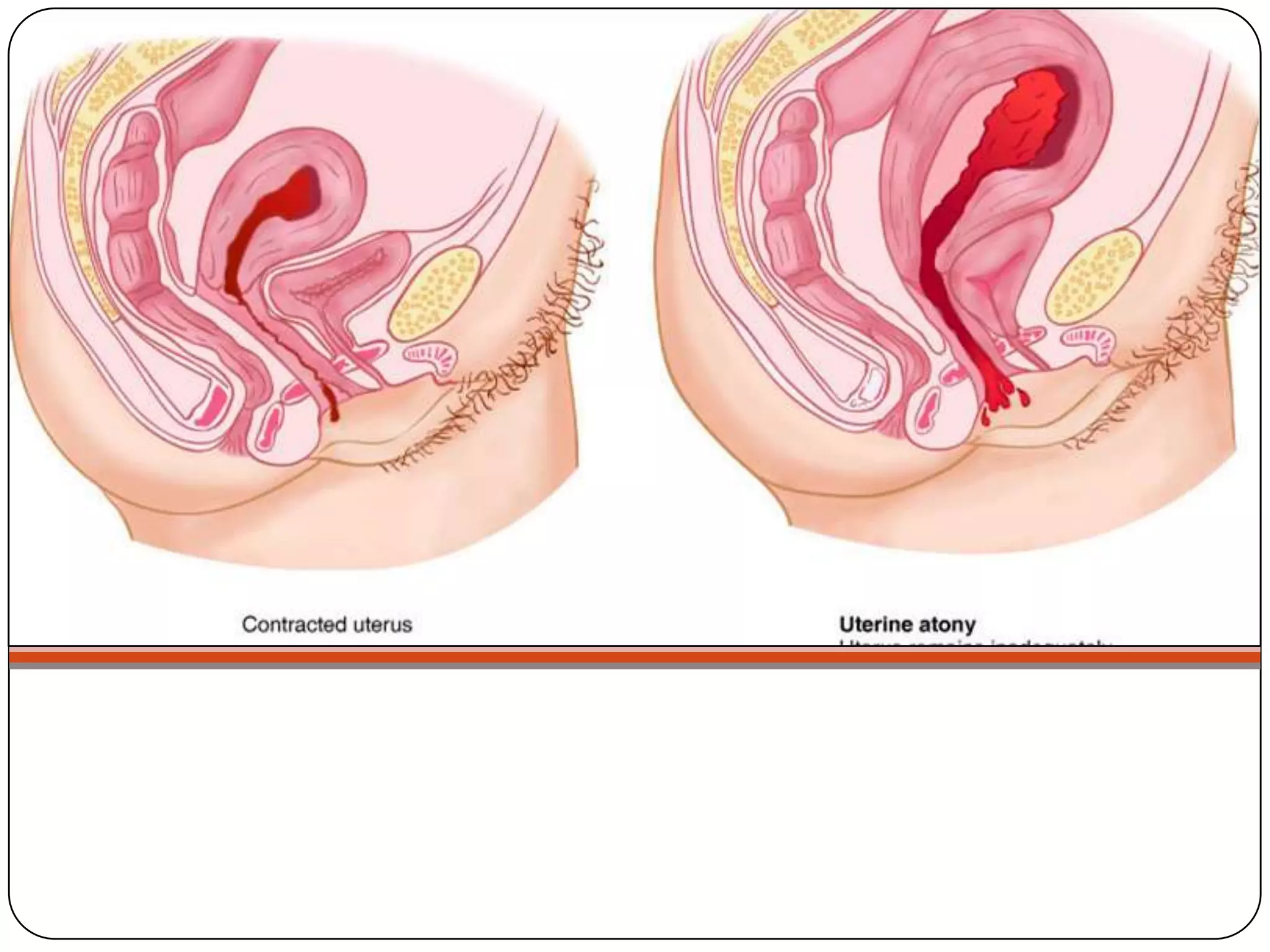
This document summarizes postpartum hemorrhage, its risk factors, etiologies, pathophysiology, nursing interventions, and other potential postpartum complications including infection, emotional disorders, thrombophlebitis, and domestic violence. It discusses postpartum hemorrhage definitions and causes such as uterine atony, retained tissues, and genital tract trauma. It also outlines nursing assessments and treatments for various postpartum complications.