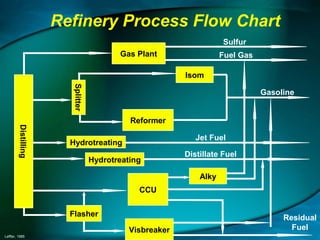
Refineries process crude oil through distillation and other separation processes to produce fuels and other products. Crude oil is separated into components like gasoline, jet fuel, diesel, and residual fuel through units like atmospheric distillers, vacuum distillers, reformers, crackers, and hydrotreaters. Refineries also have utilities like hydrogen plants, sulfur recovery units, wastewater treatment, and power generation. Hazards in refineries include fires and explosions from flammable liquids and gases, exposure to toxic chemicals, and physical hazards from high pressures and temperatures.