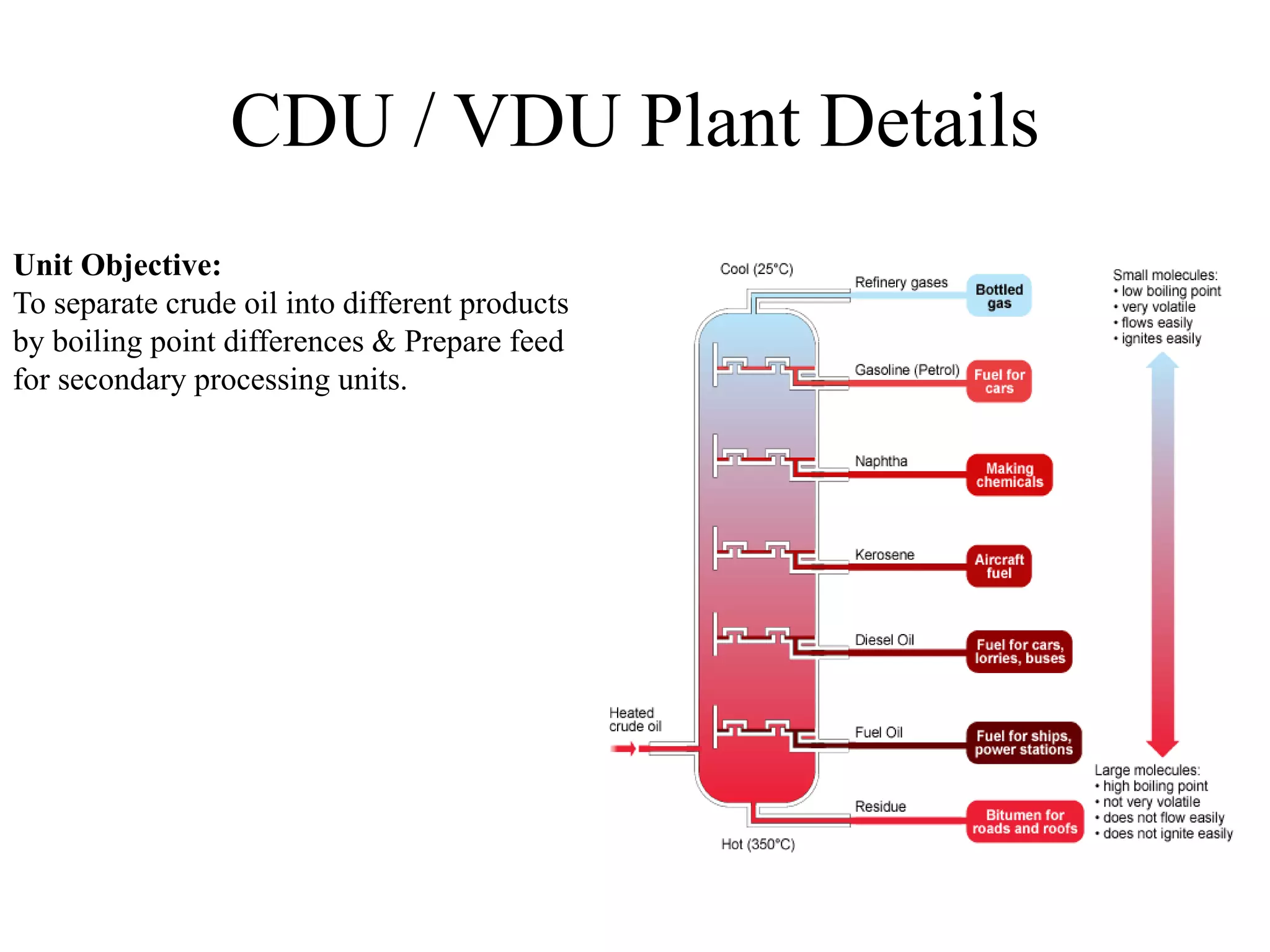
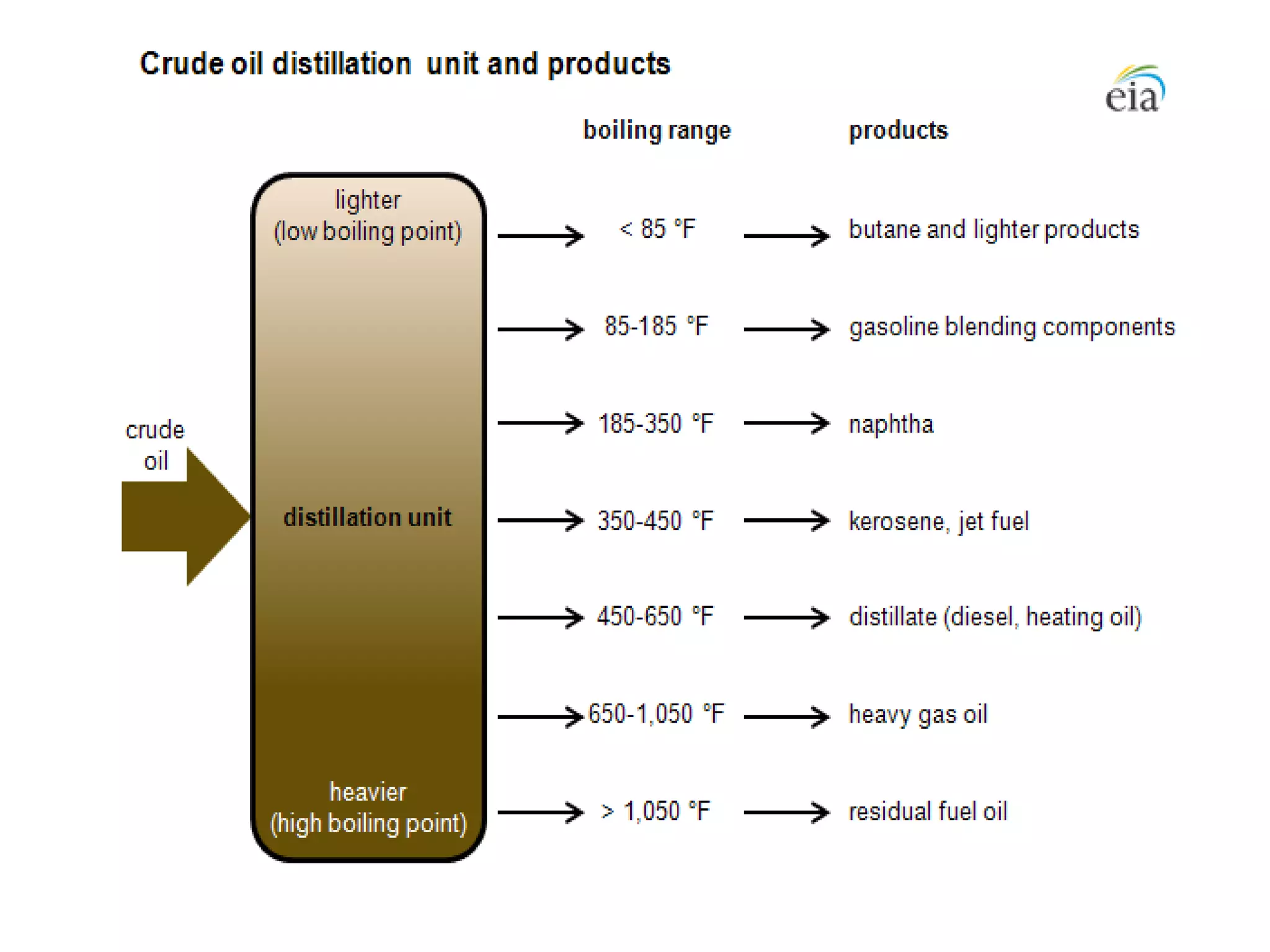
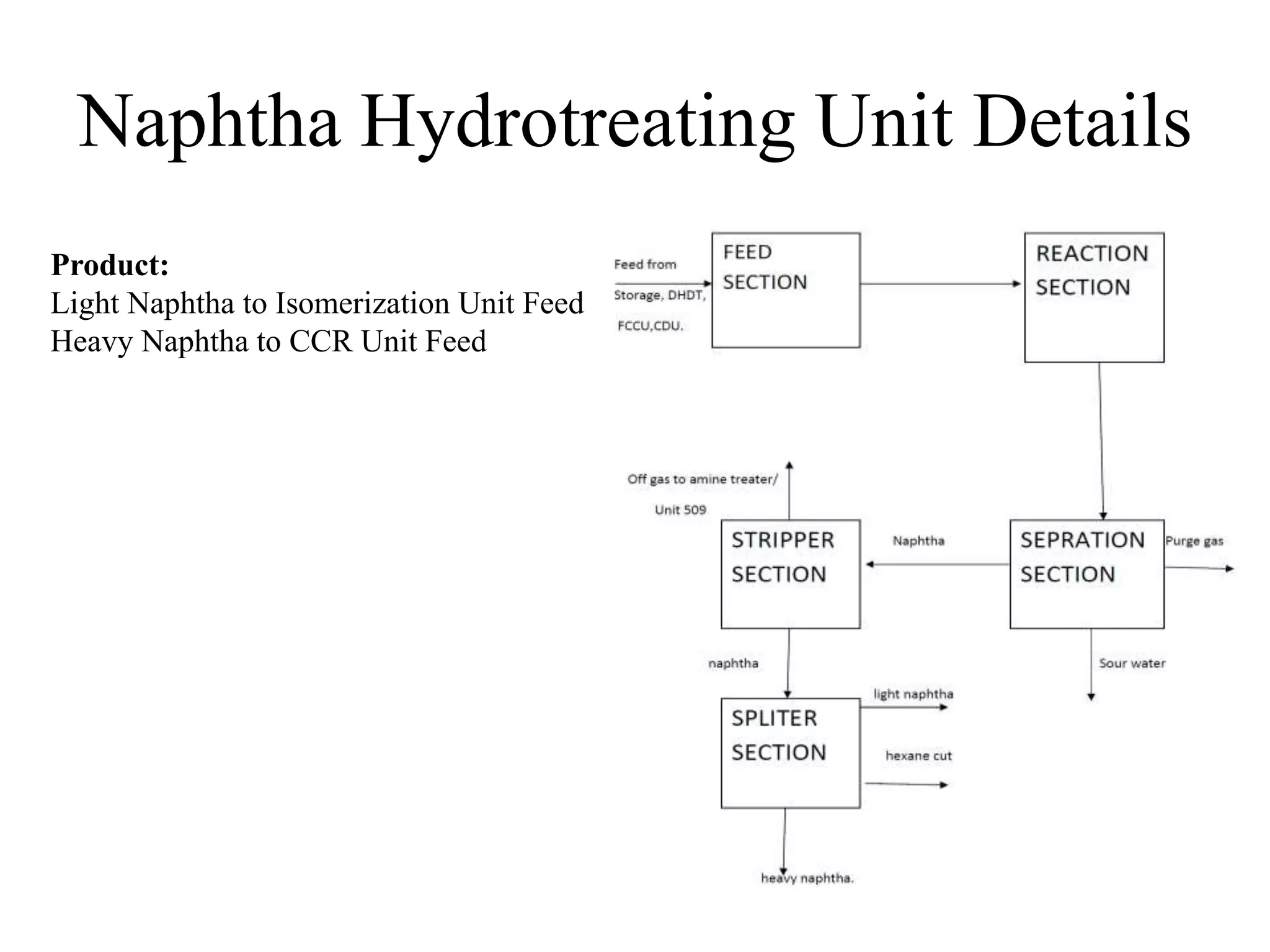
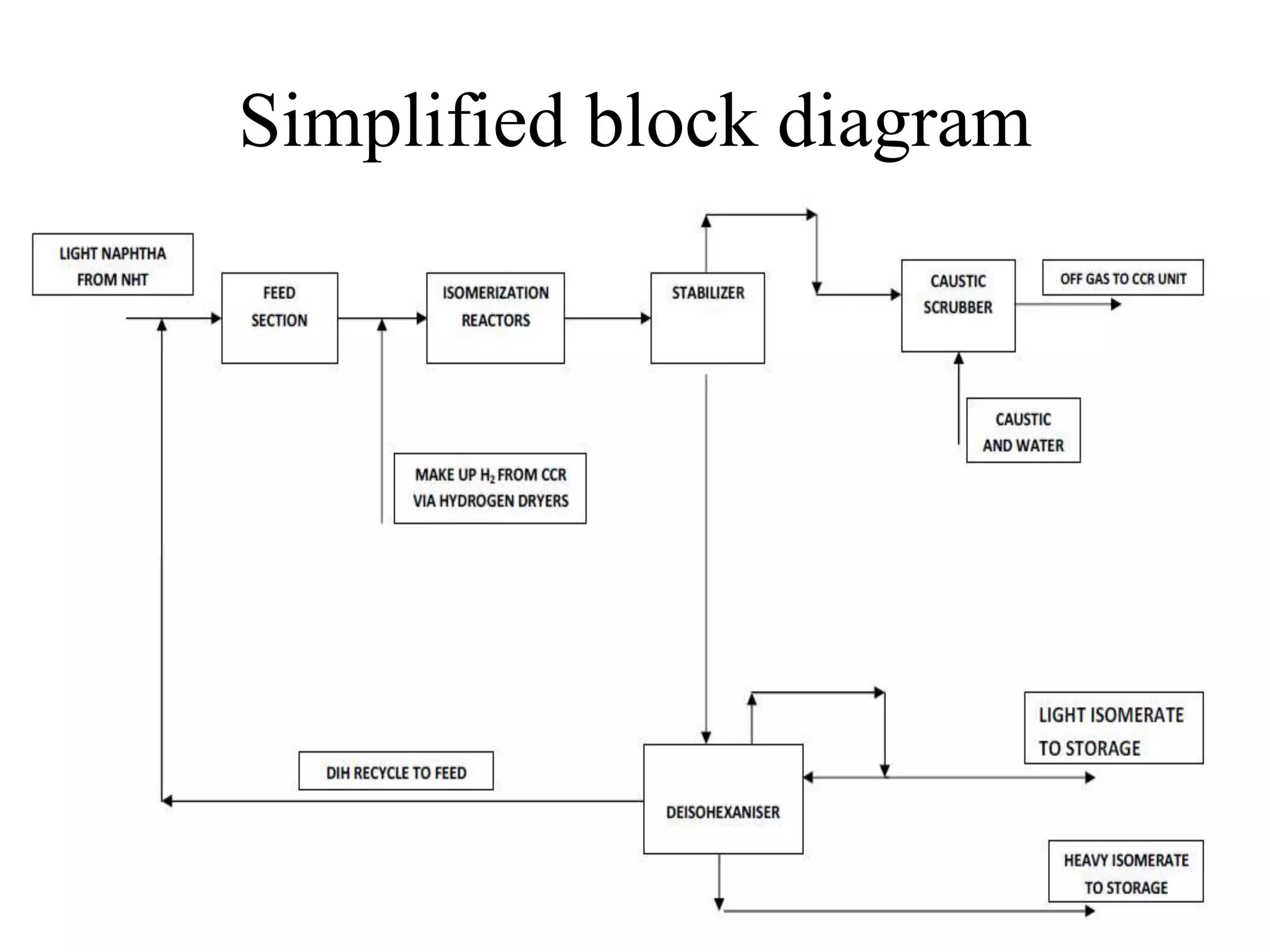
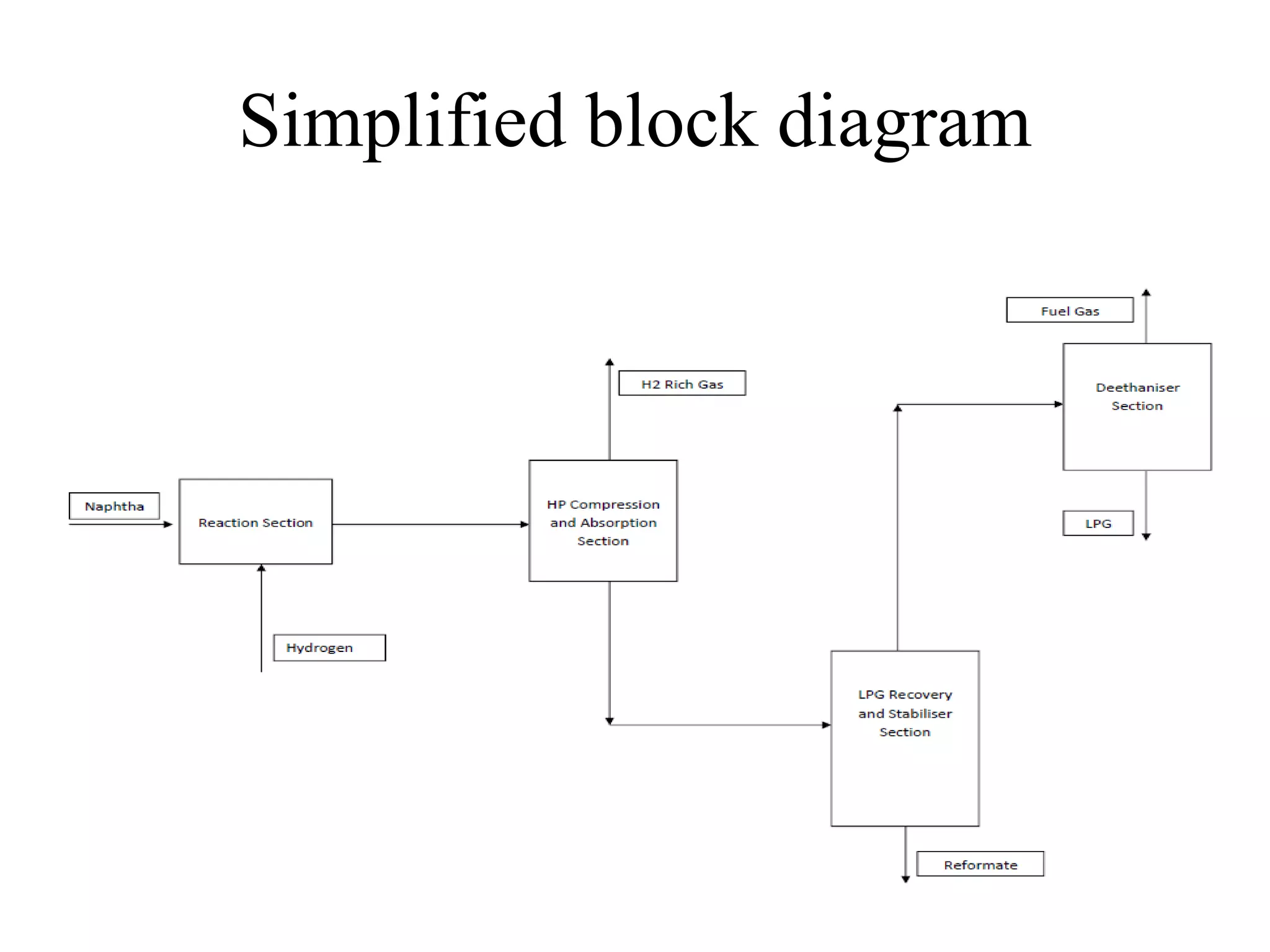
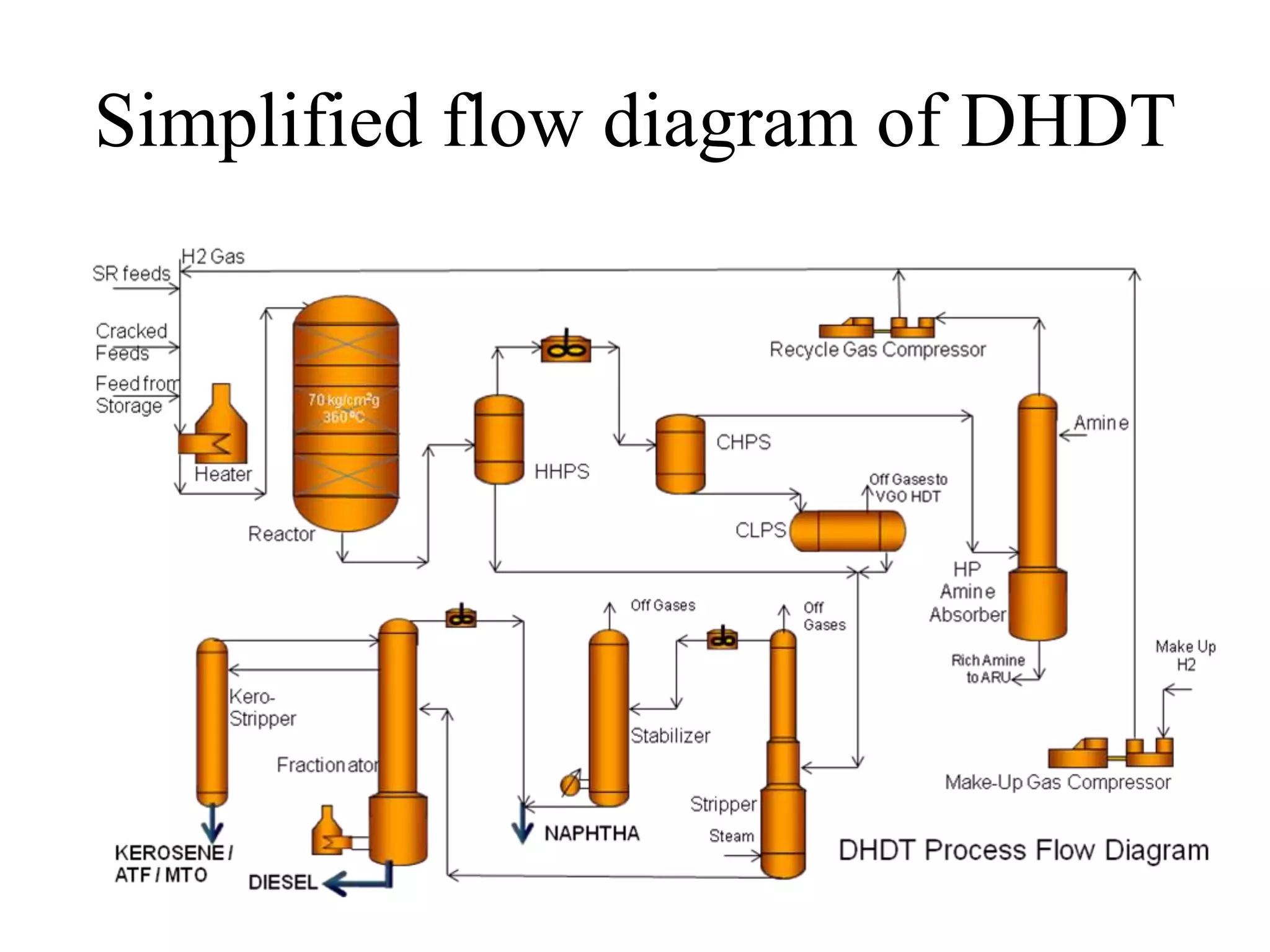
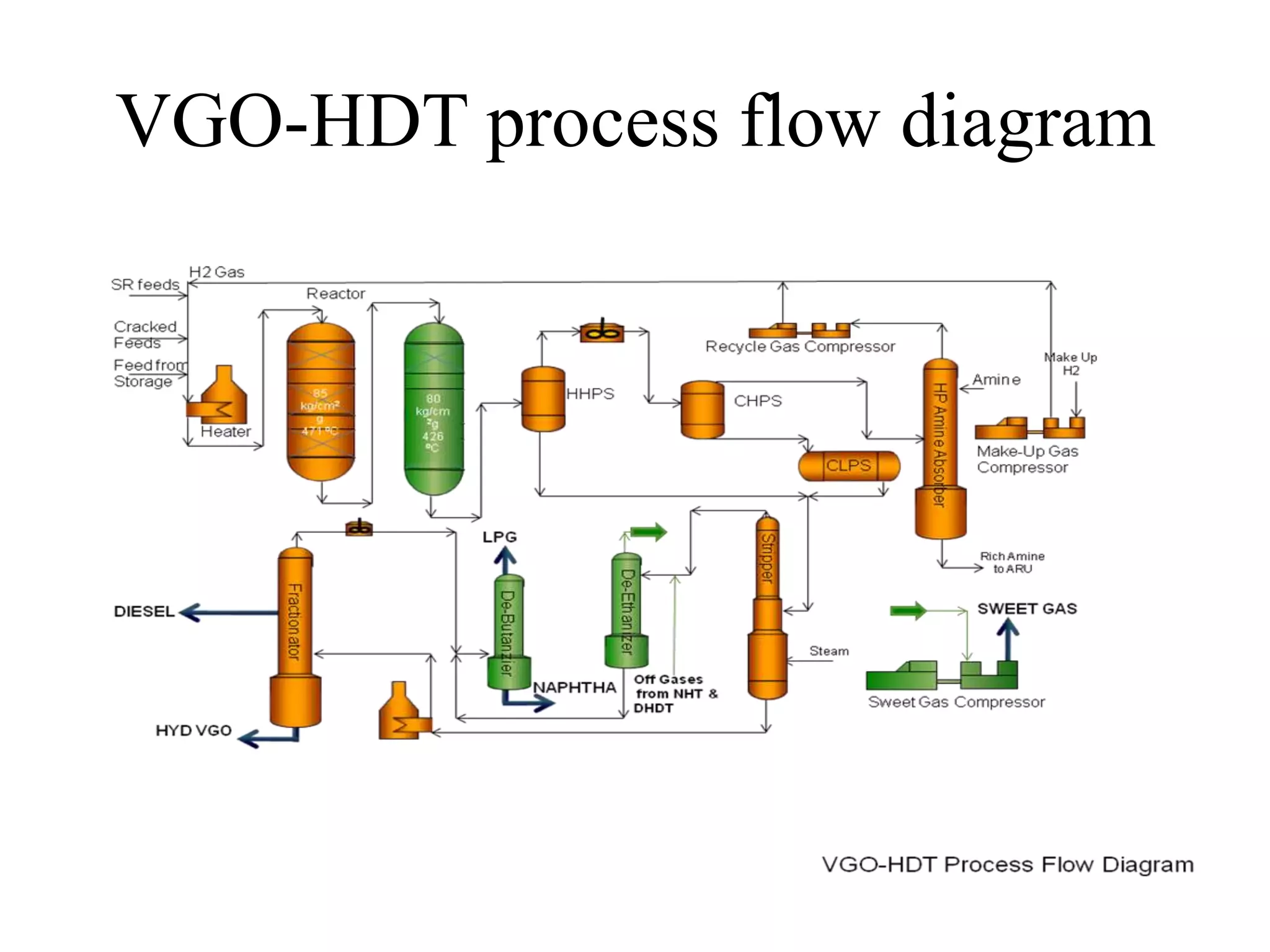
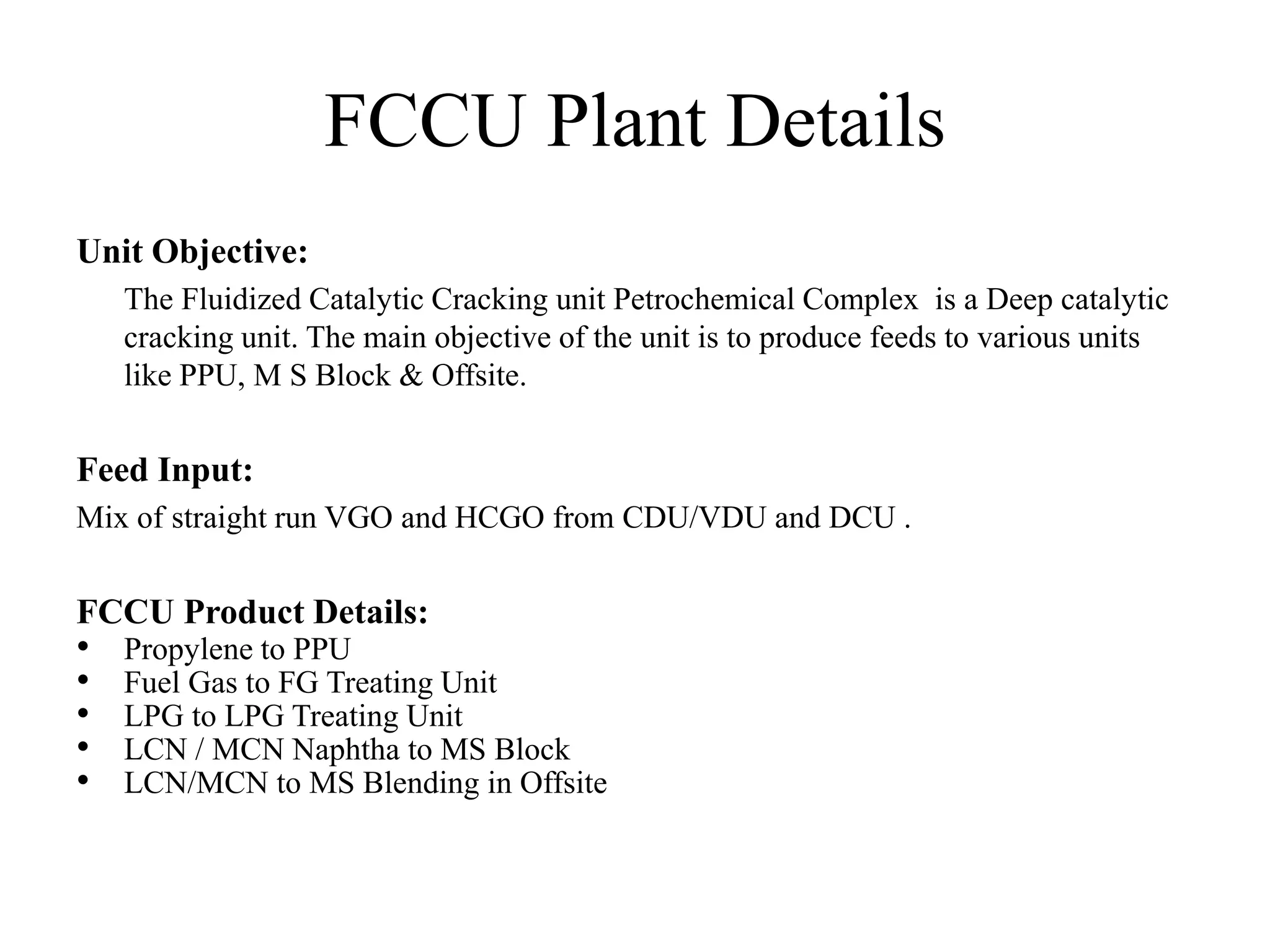
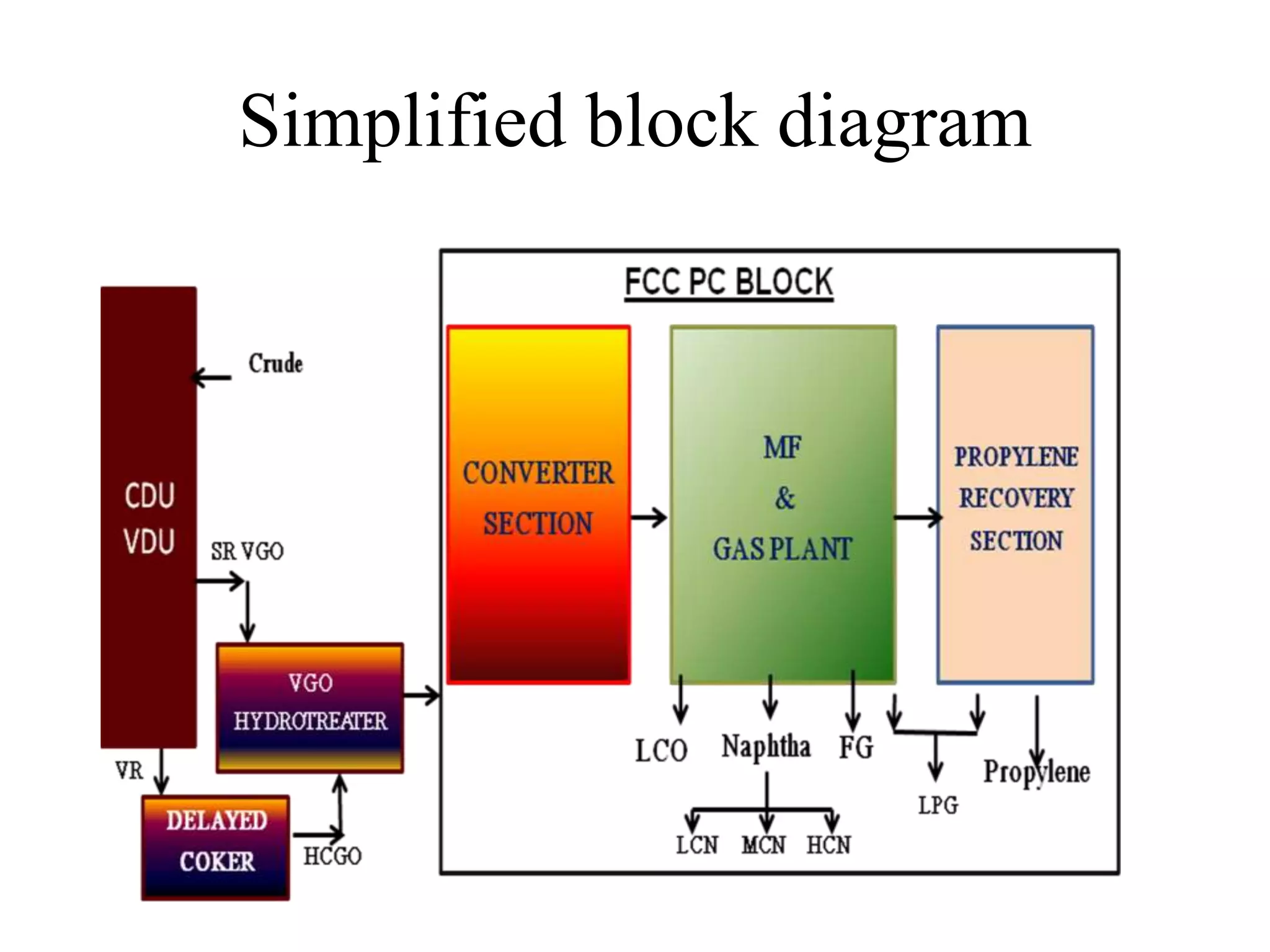
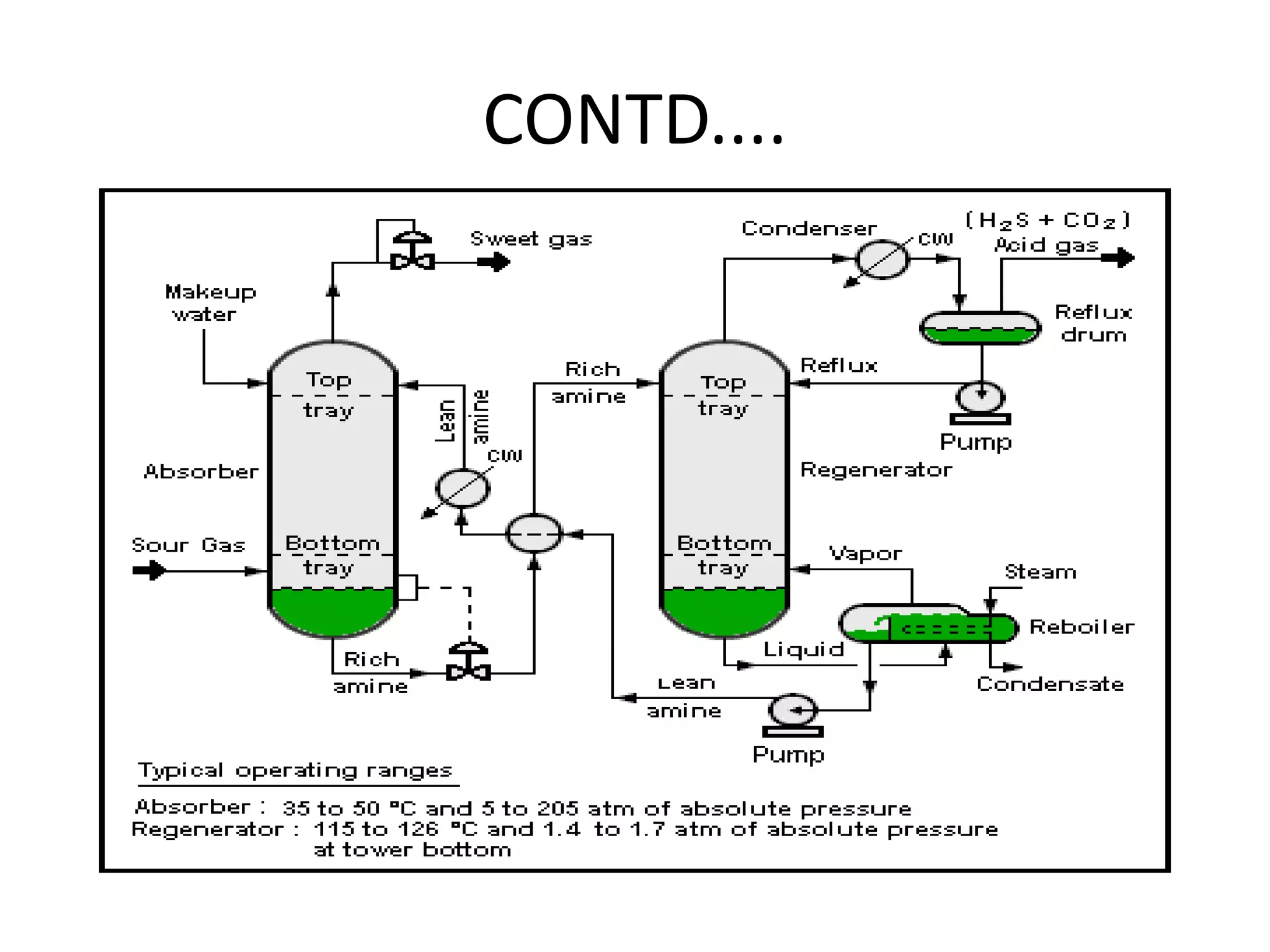
The document provides details about various refinery units including:
- Crude Distillation Unit (CDU), Naphtha Hydrotreating Unit (NHT), Isomerization Unit, Continuous Catalytic Reformer (CCR) Unit, Diesel Hydrotreating (DHDT) Unit, Vacuum Gas Oil Hydrotreating (VGO HDT) Unit, Fluidized Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit, Hydrogen Generation Unit (HGU), Polypropylene Unit (PPU), Sour Water Stripping (SWS) Unit, and Amine Regeneration Unit.
It describes the objectives, key inputs and outputs of each unit.

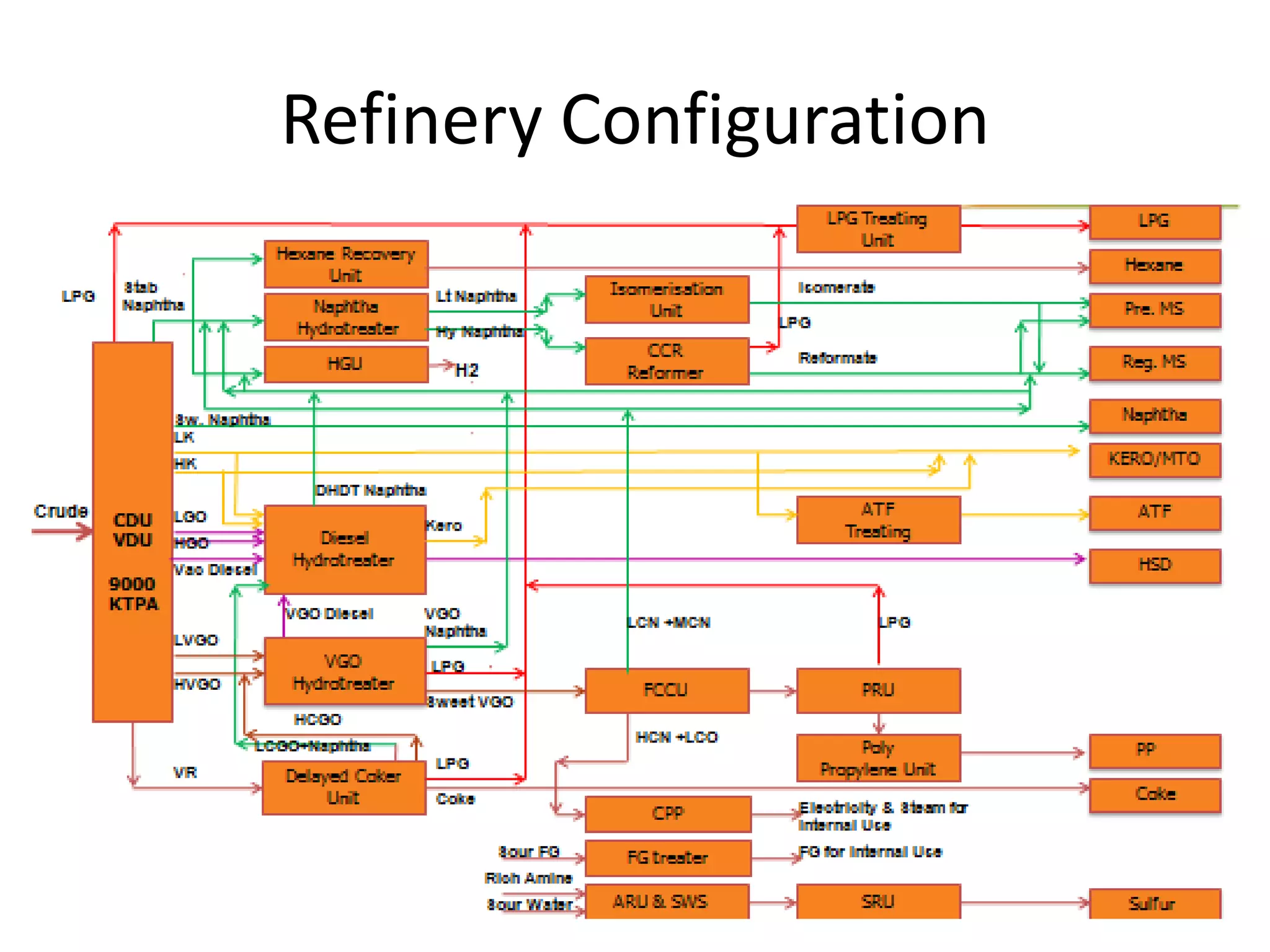
![Refinery Units
• CDU / VDU/ NSU(Naph. Stablizn Unit)
• NHT, CCR, Isomerization [MS Block]
• DHDT
• VGO-HDT
• FCC-PC, PRU & FCC
• LPG/FG/Naphtha Treaters
• Delayed Coker Unit
• Polypropylene Unit
• Sulphur Block
• HRU
• HGU
• ATF Merox](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refinerybasics-150228120237-conversion-gate02/75/Refinery-basics-3-2048.jpg)