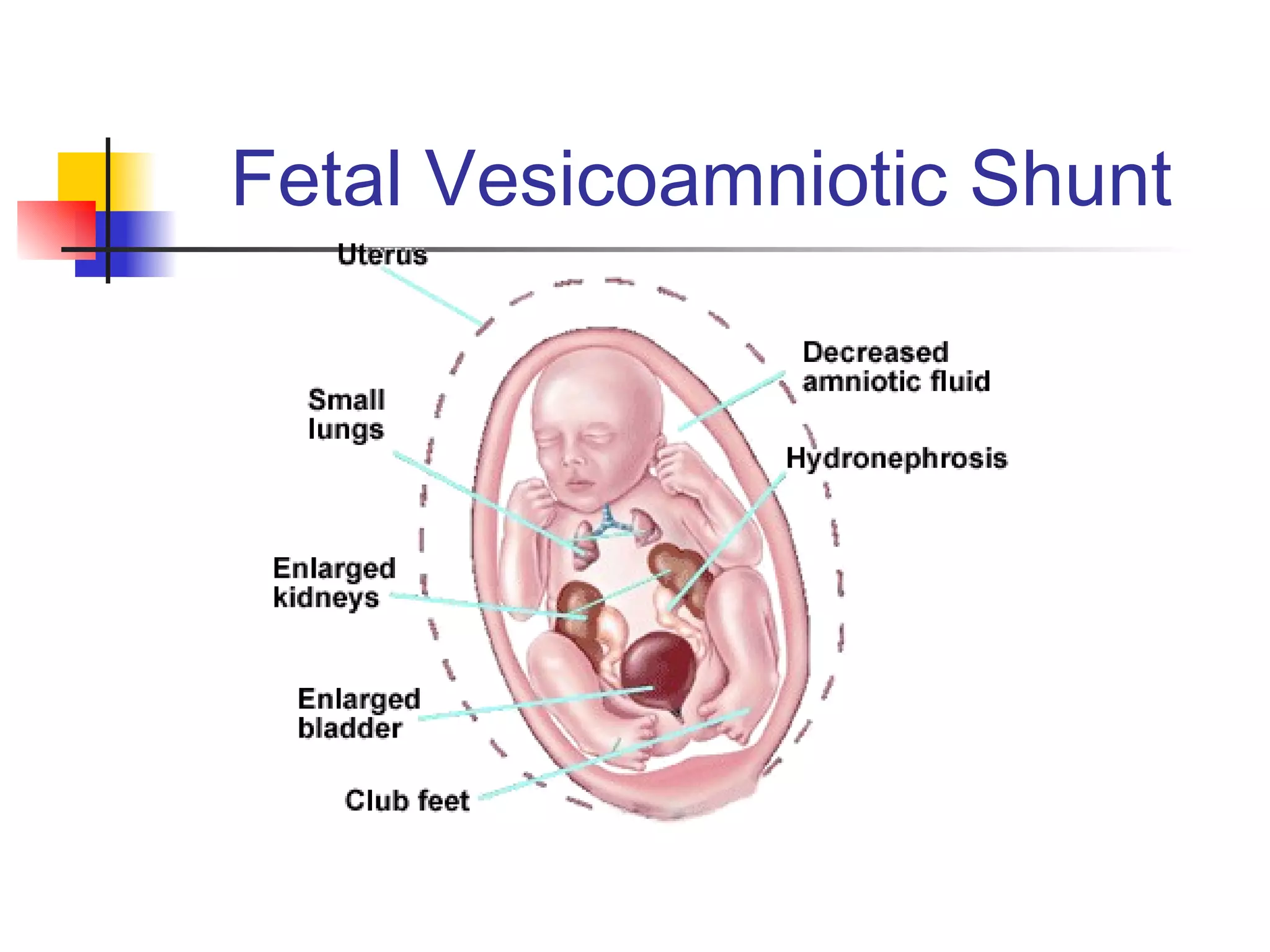
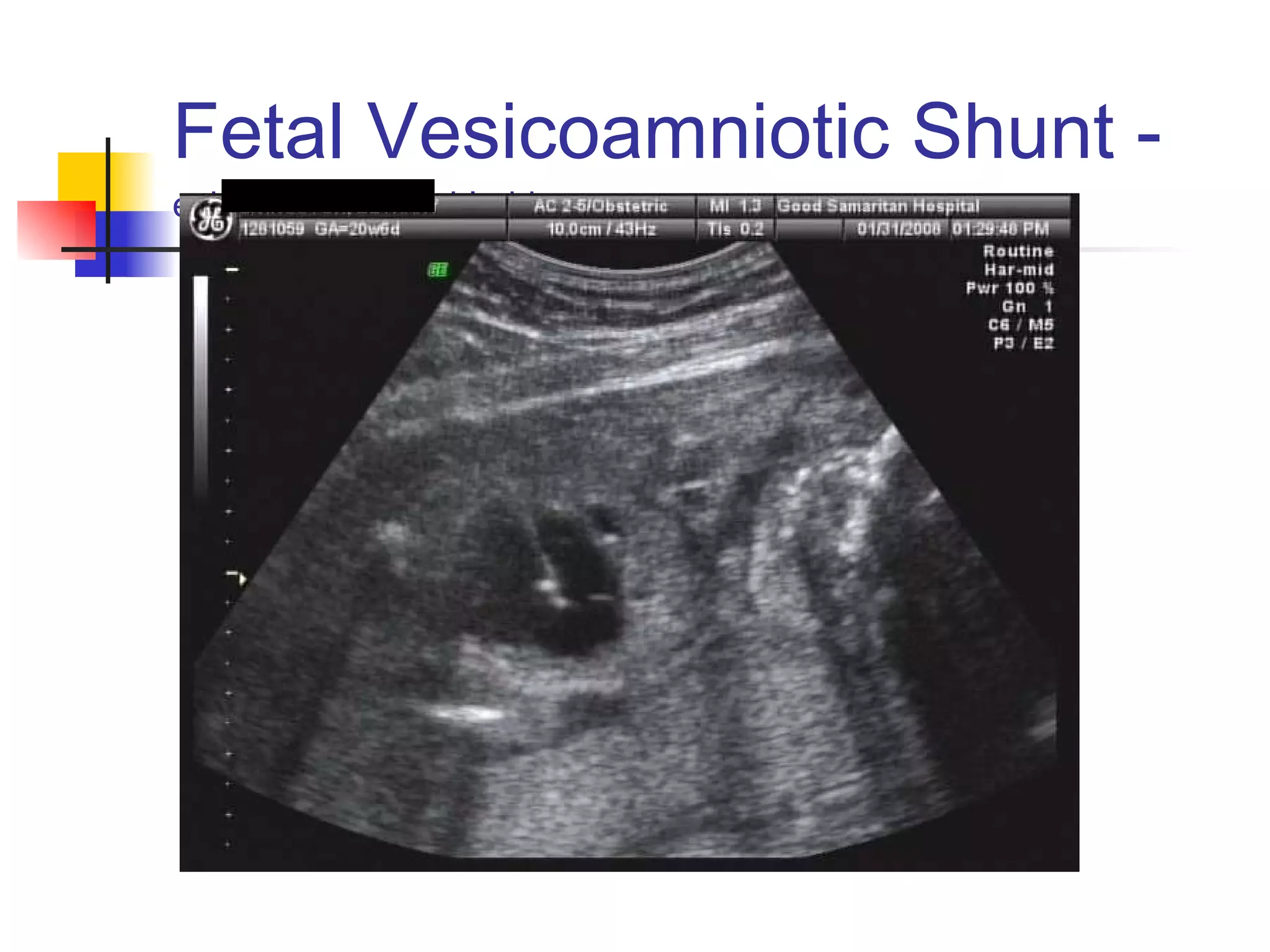
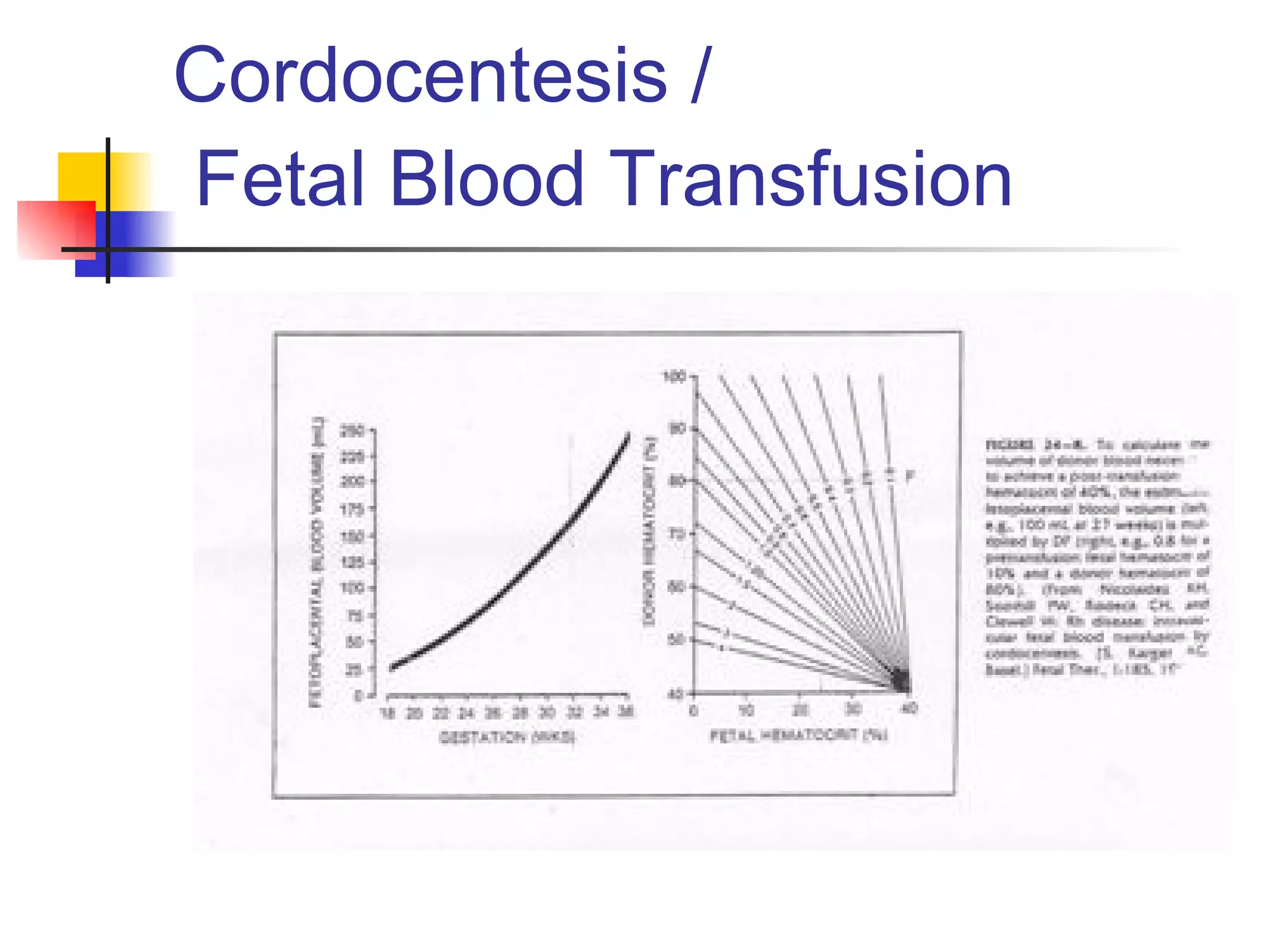
The document discusses various diagnostic tests used in fetal monitoring including:
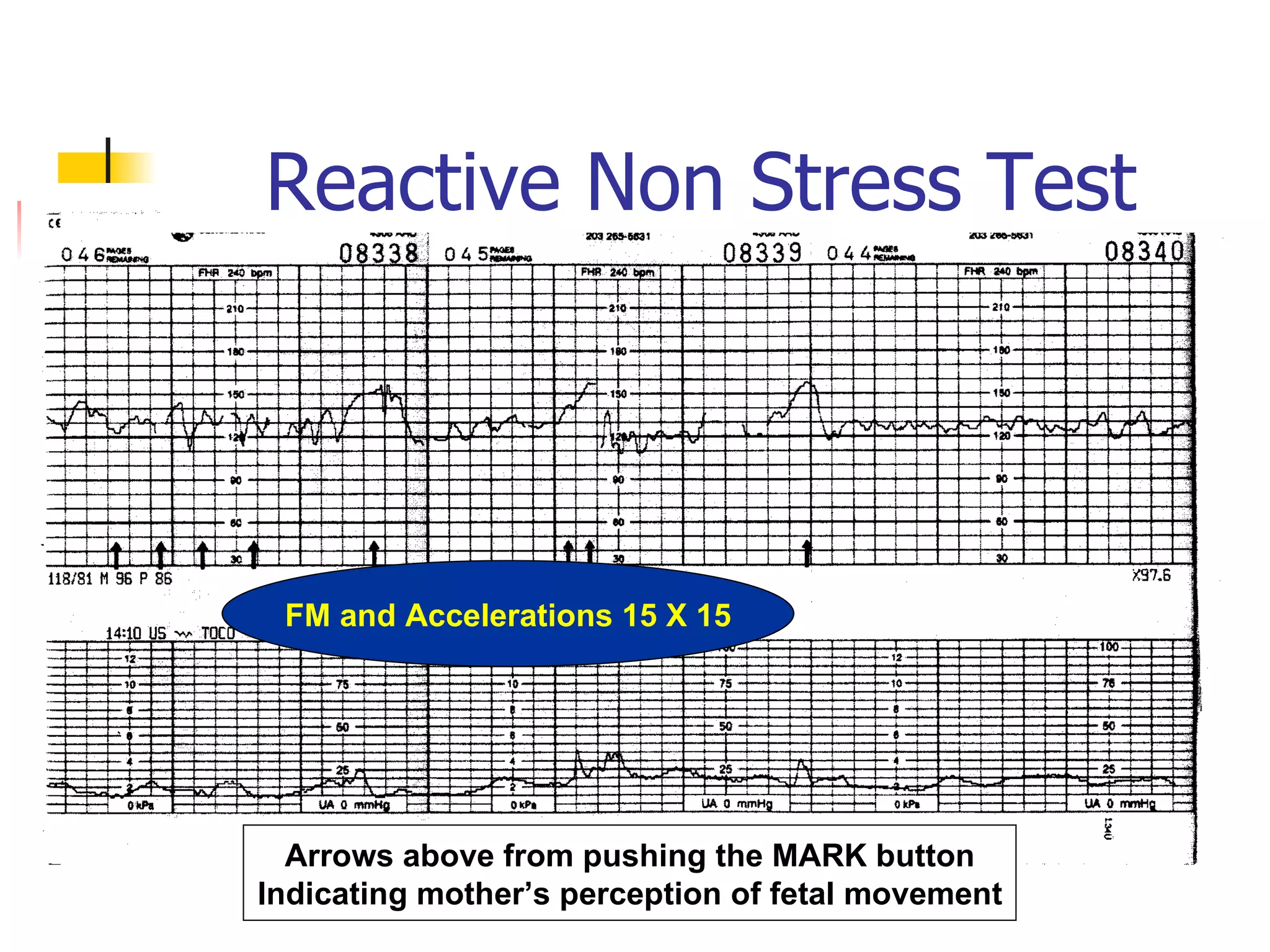
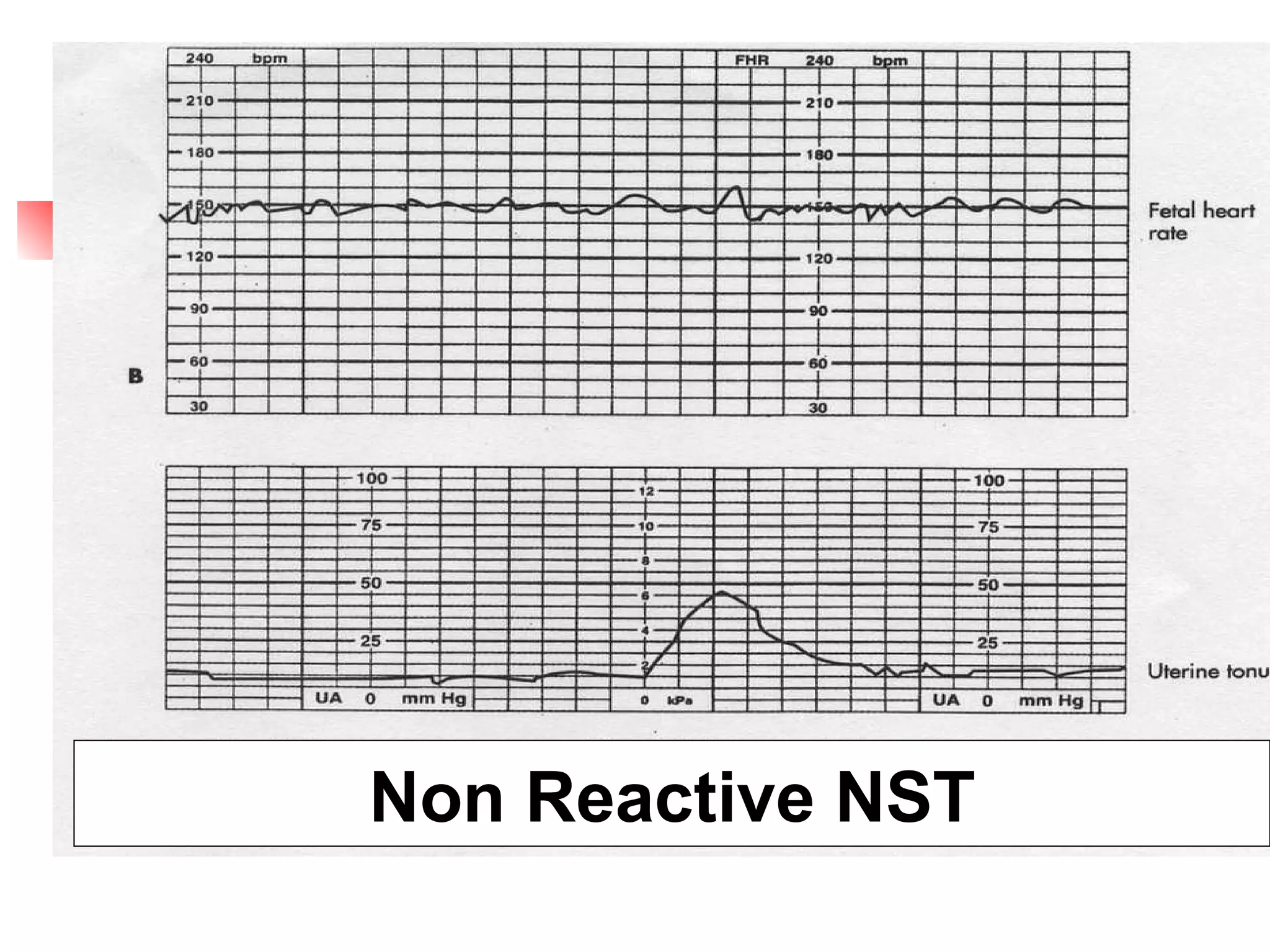
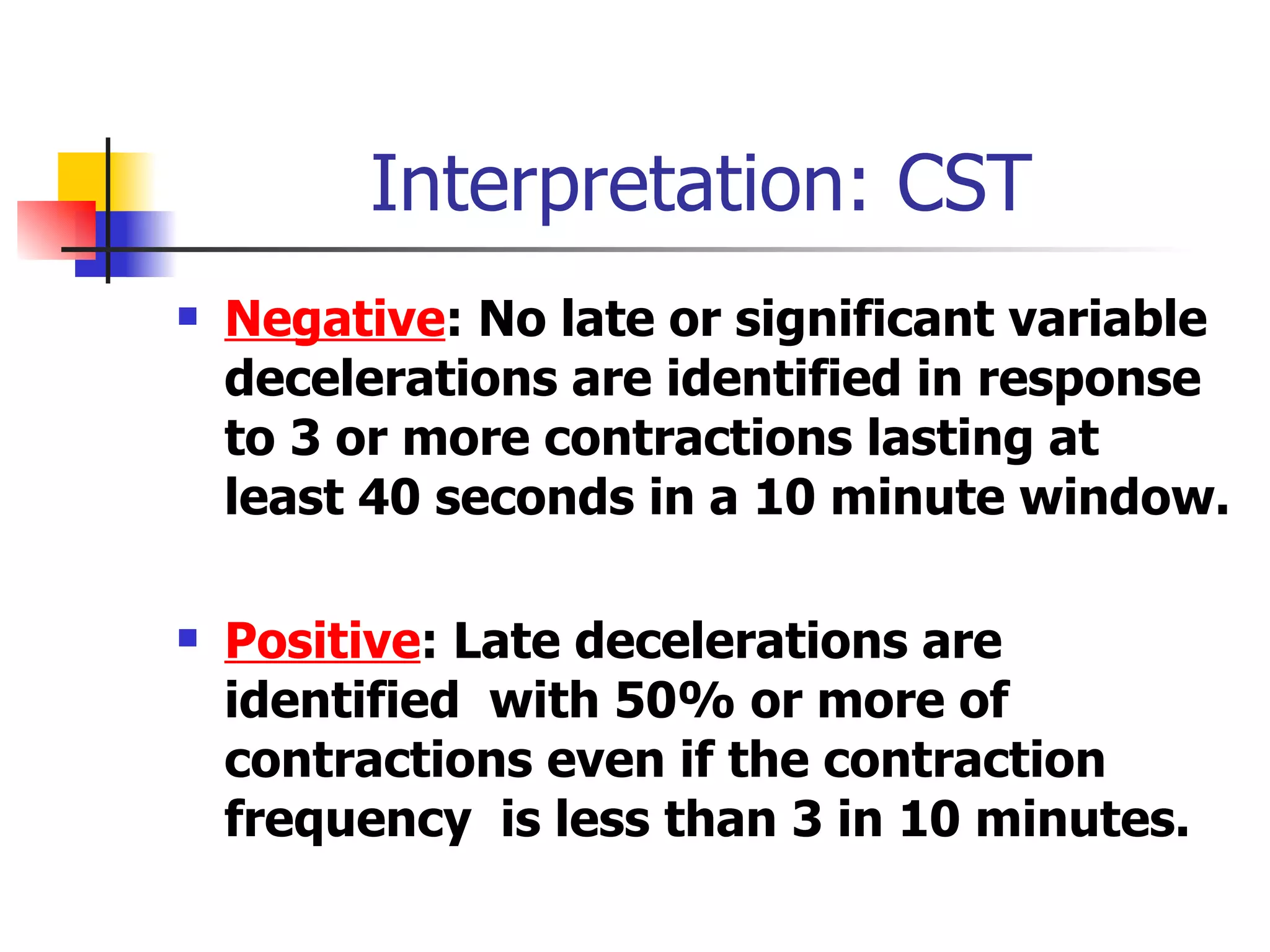
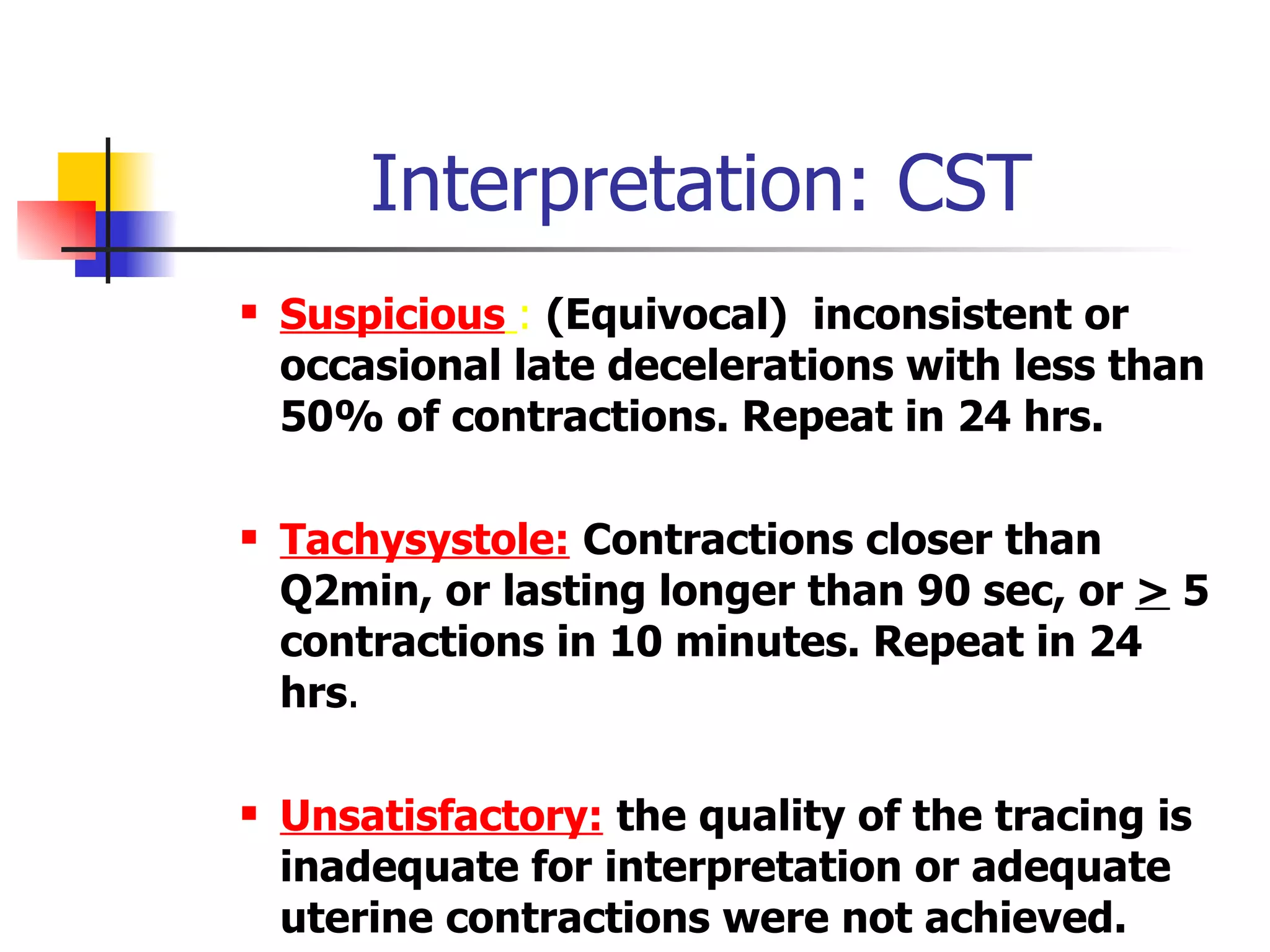
1. Non-stress tests (NST) which evaluate fetal heart rate patterns to assess oxygenation, neurological, and cardiac function. A reactive pattern indicates intact fetal well-being.
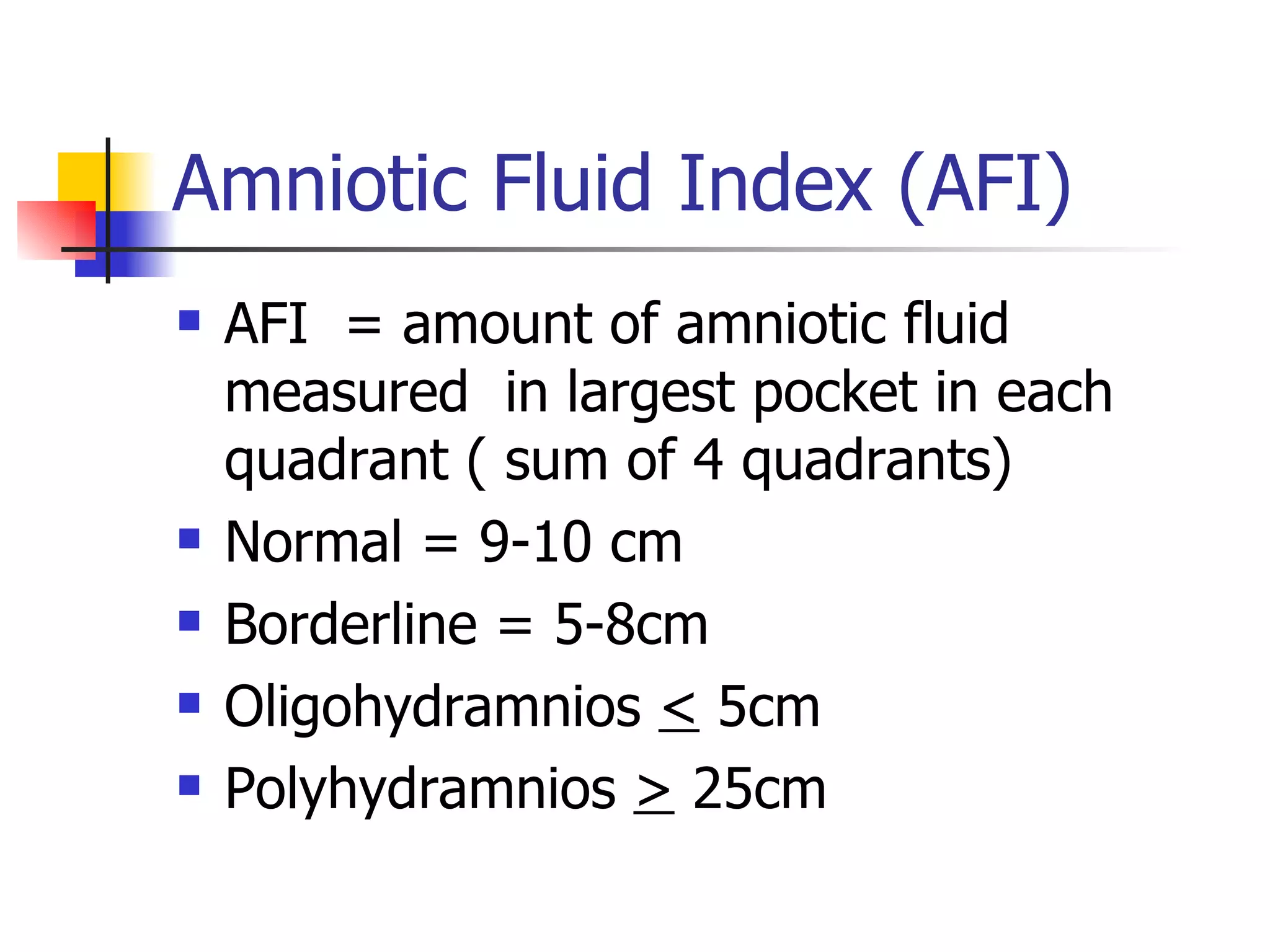
2. Biophysical profiles (BPP) which combine NST and ultrasound to assess fetal movements, tone, breathing and amniotic fluid in a standardized scoring system.
3. Doppler studies analyze umbilical and cerebral blood flow to identify compromised fetuses before problems occur. Reverse diastolic flow in the umbilical artery is ominous.
4. Amniocentesis tests amniotic fluid for genetic/infection screening or lung maturity