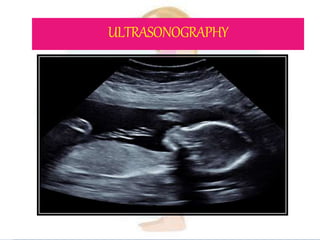
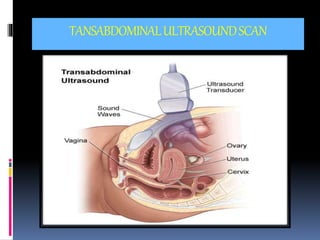
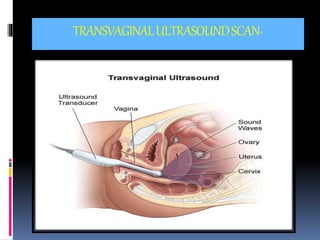
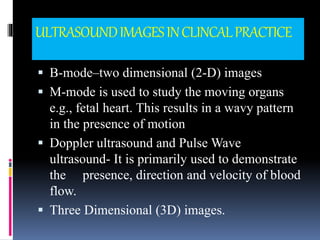
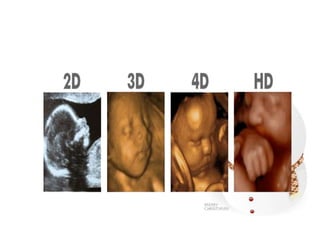
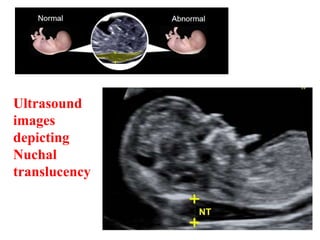
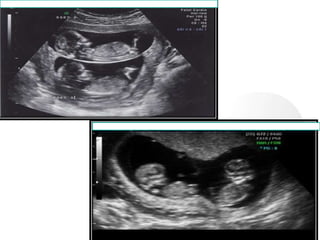
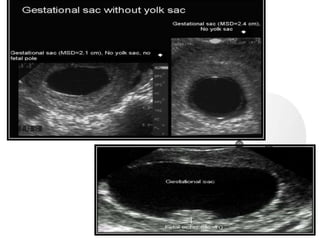
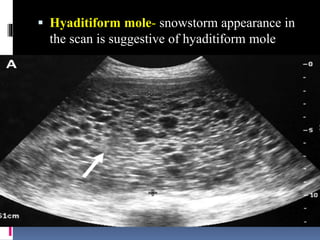
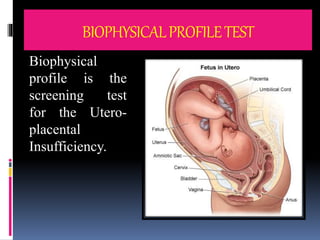
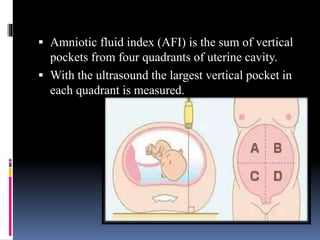
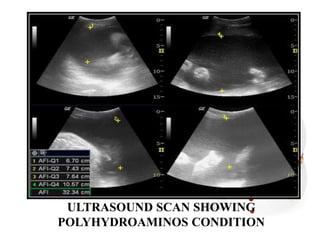
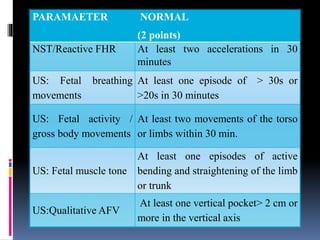
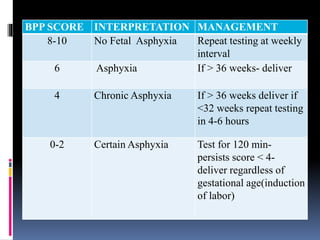
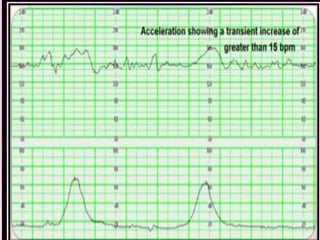
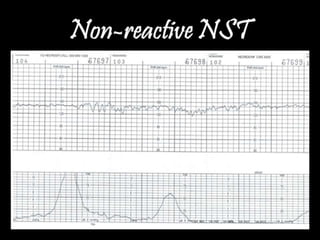
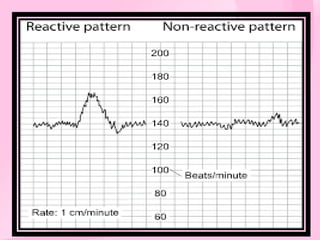
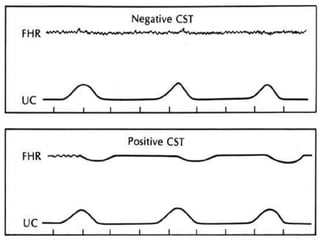
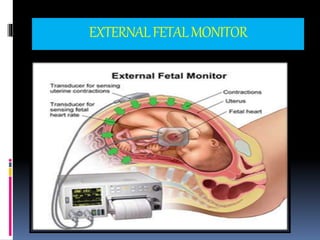
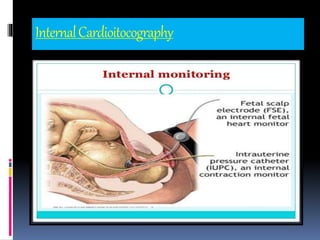
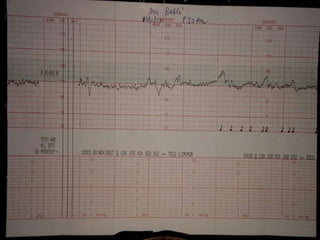
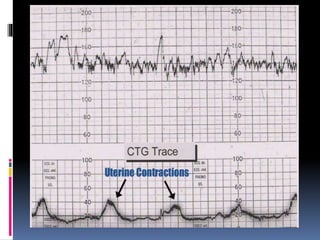
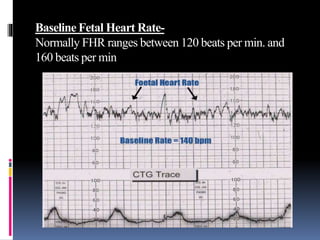
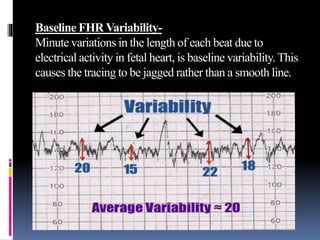
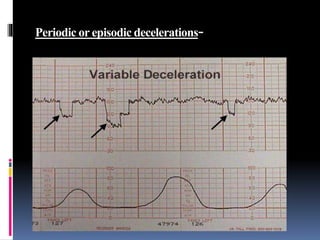
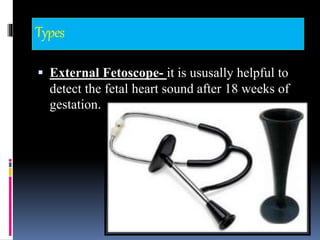
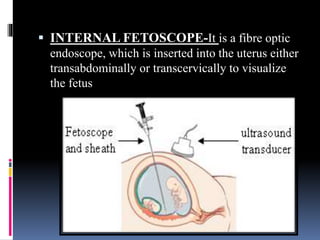
This document provides information on various biophysical tests used to assess maternal and fetal health during pregnancy. It discusses ultrasound screening which can detect fetal anomalies and assess growth. The biophysical profile test evaluates 5 parameters - fetal movement, tone, breathing, heart rate and amniotic fluid - to detect signs of fetal stress. A non-stress test monitors fetal heart rate in response to movement. Together these tests screen for placental insufficiency and fetal well-being during high-risk pregnancies.