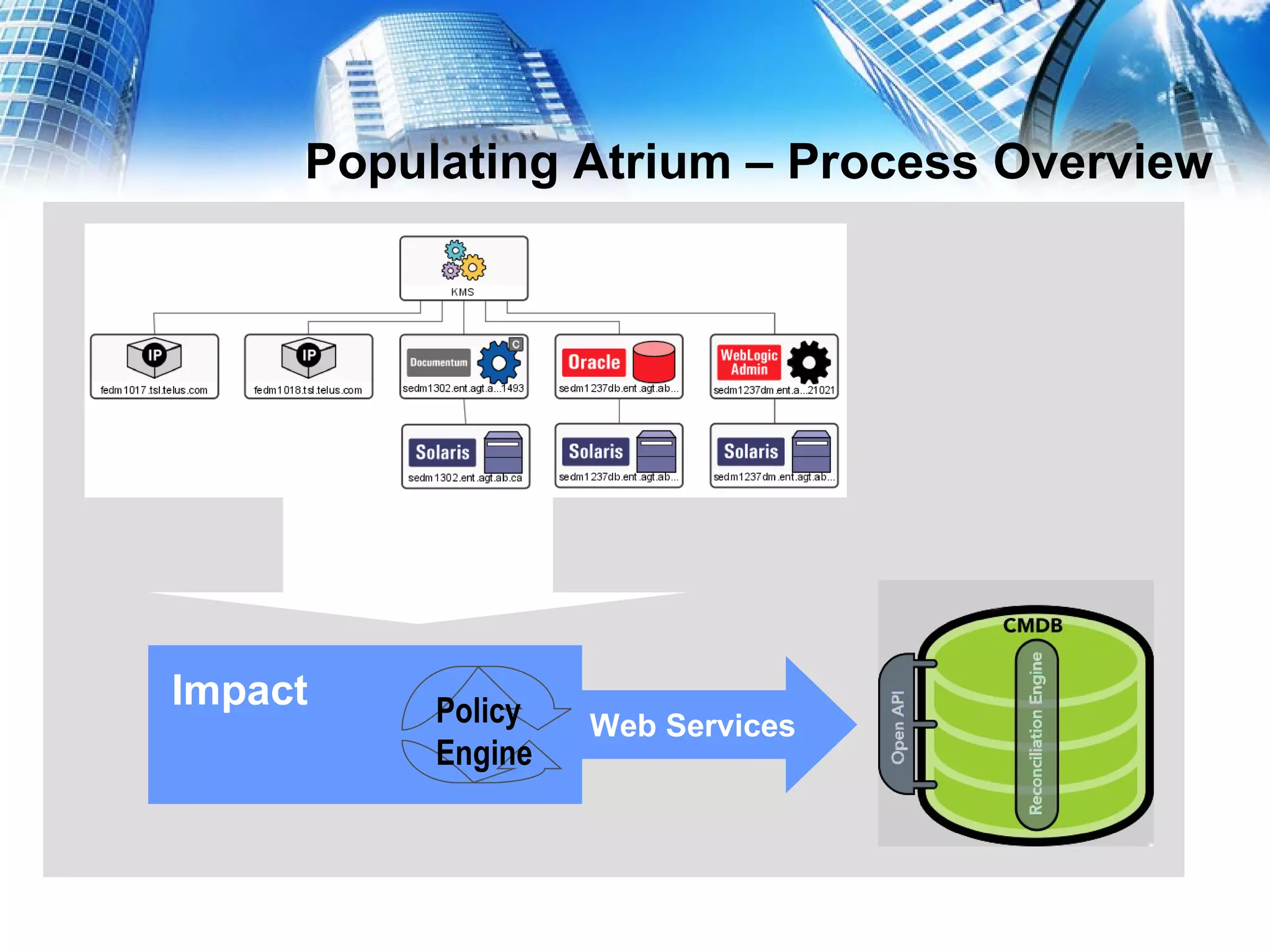
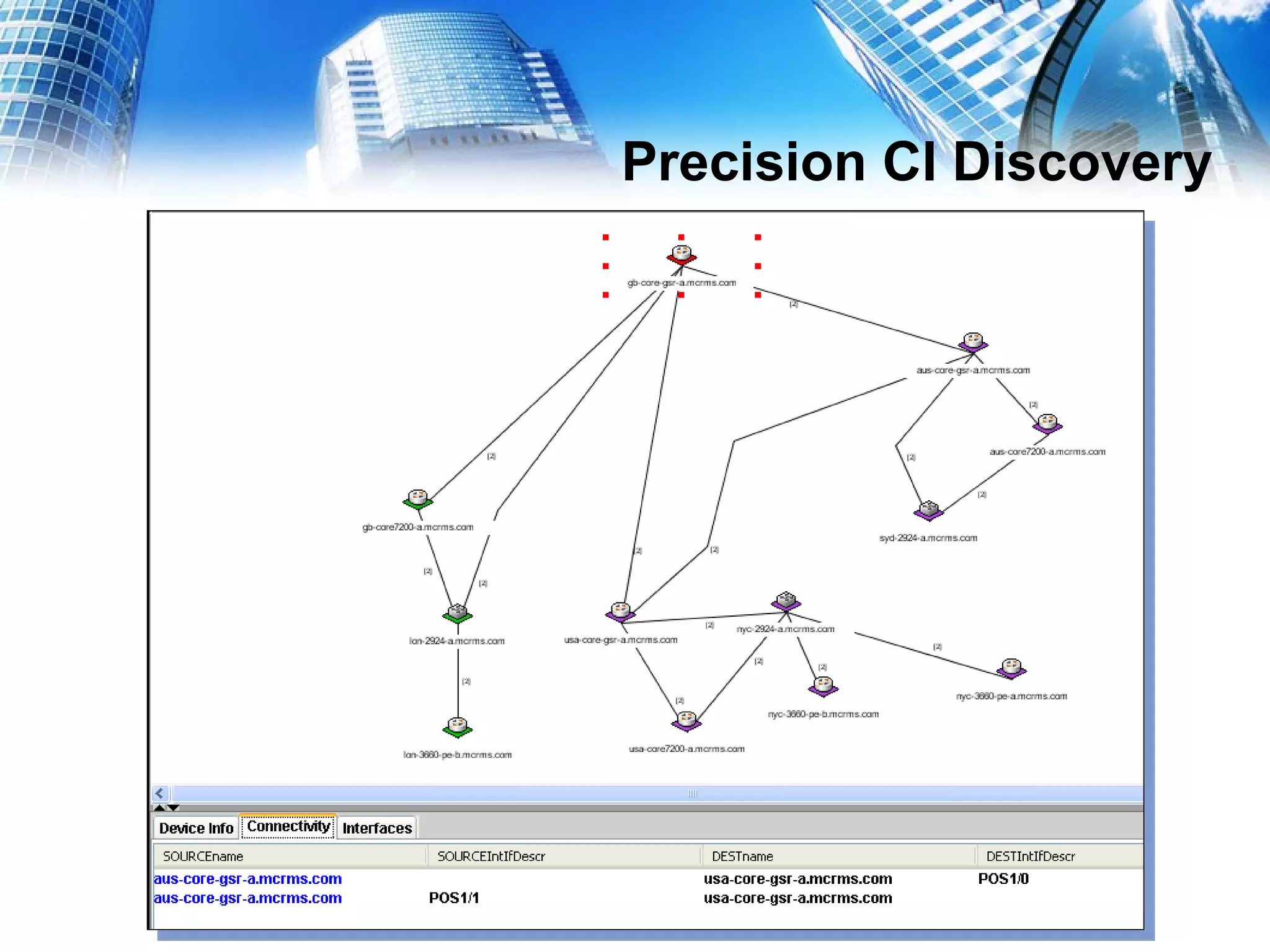
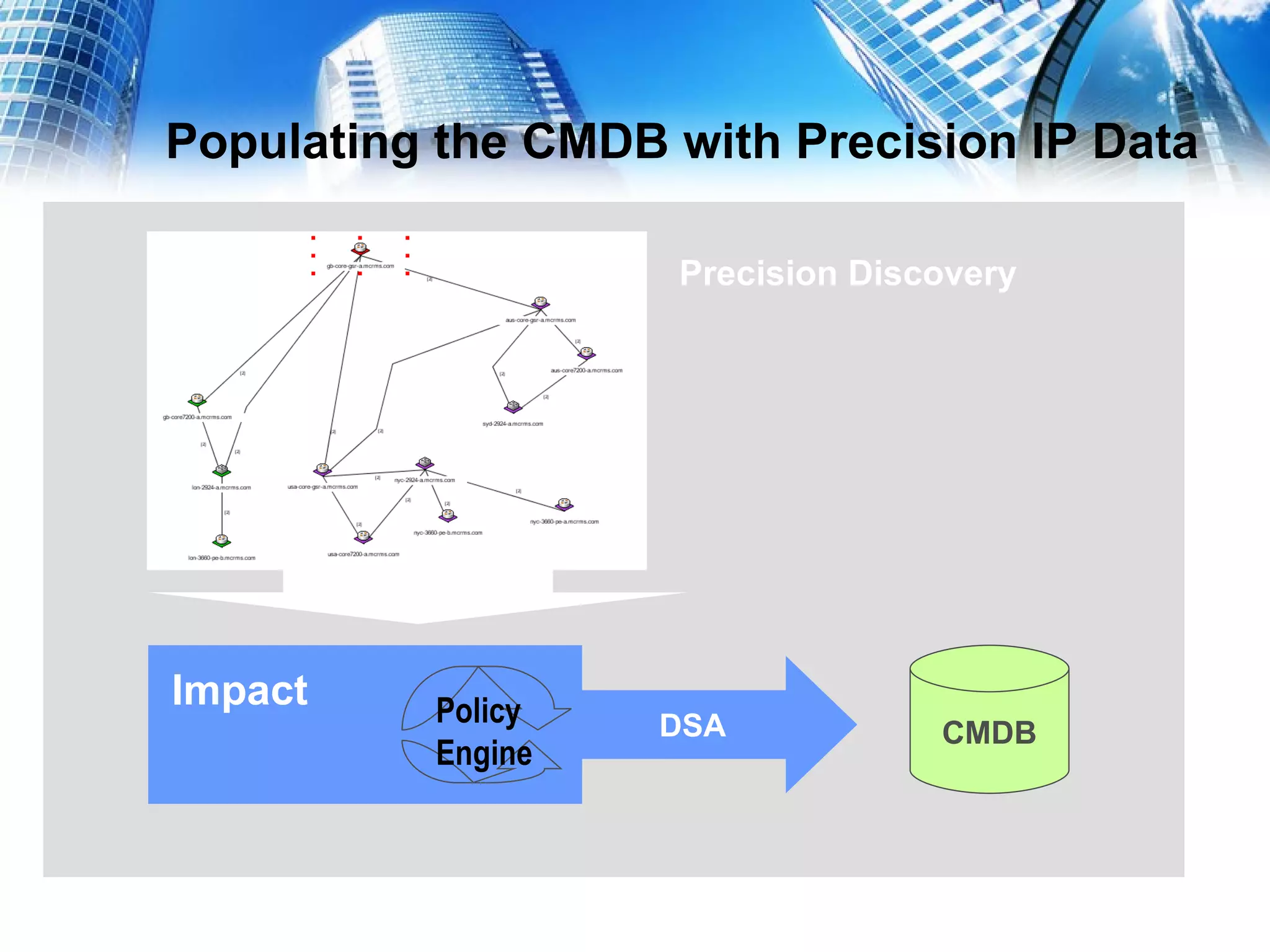
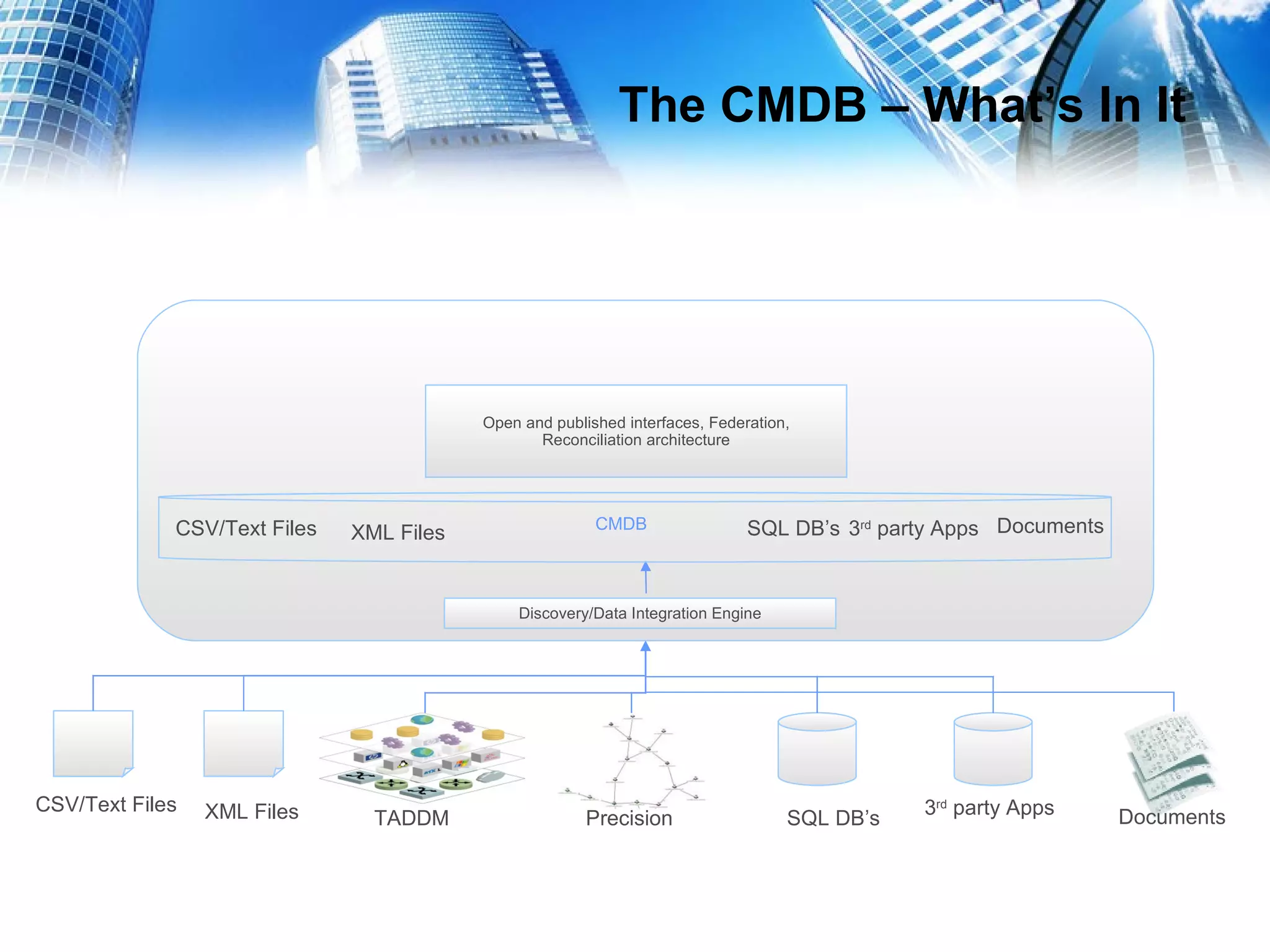
This document serves as a practical guide for deploying a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) in a Tivoli environment, emphasizing its significance for business service continuity. It outlines the stages of CMDB development, the population of CMDB with various data types, and the management of related processes using Tivoli products such as TADDM and TBSC. Additionally, the document discusses the benefits of ITIL best practices and business service management strategies in enhancing IT service delivery.


































































![Additional Discussion Antonio Rolle [email_address] http://www.generationetech.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ttuccmdb20070508final-12514764753638-phpapp02/75/A-Practical-Guide-to-CMDB-Deployment-in-a-Tivoli-Environment-75-2048.jpg)