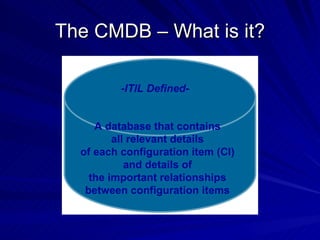
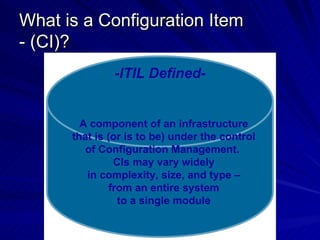
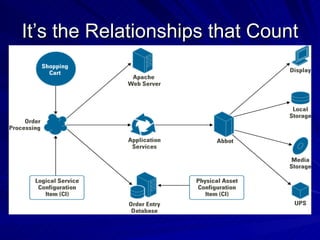
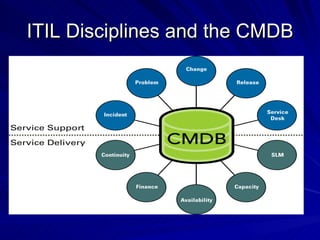
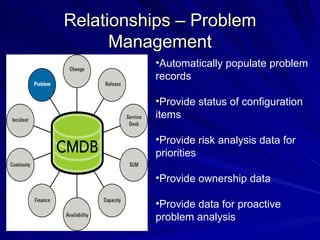
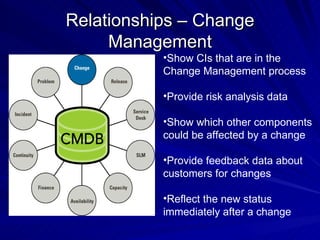
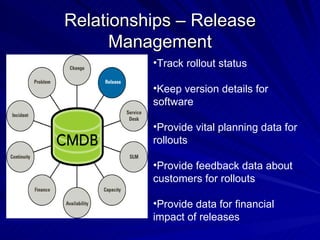
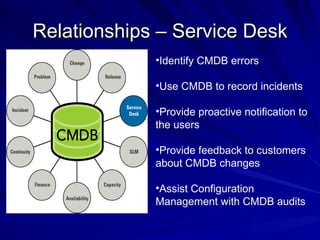
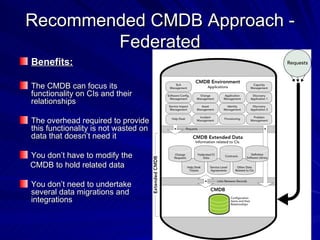
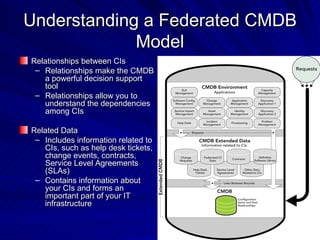
The document discusses the importance of a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) according to ITIL best practices. A CMDB is a central database that contains details of all configuration items (CIs) in an IT infrastructure and the relationships between them. It provides a single source of accurate information about the configuration of an organization's IT assets and services. This allows for effective incident management, problem management, change management, and other IT processes. Maintaining accurate relationships between CIs in a CMDB provides benefits like control, integration, and improved decision-making across an organization's IT operations.