The document discusses the concept, meaning and importance of Information and Communication Technology (ICT). It defines ICT as the technology used to transmit and process information effectively between parties. ICT incorporates telecommunications, computers, software, storage and audiovisual systems. The document outlines how ICT is important in education by making the teaching-learning process simpler, more interactive and delivering content at lower costs. ICT allows for individualized learning and wide reach of education regardless of distance or climate.





![lwpuk laisz”k.k rduhdh izk;% lwpuk rduhdh ds
lekukFkhZ ds :i esa tkuk tkrk gSA ysfdu ;g vkSj
vf/kd fof’k”V in gS] tks ,dhd`r laizs”k.k ij vf/kd cy
nsrk gS vkSj nwjHkk”k rduhdh ¼nwjHkk”k
ykbZu]csrkj laosnu½ ,oadaI;wVj dslkFkvko’;d
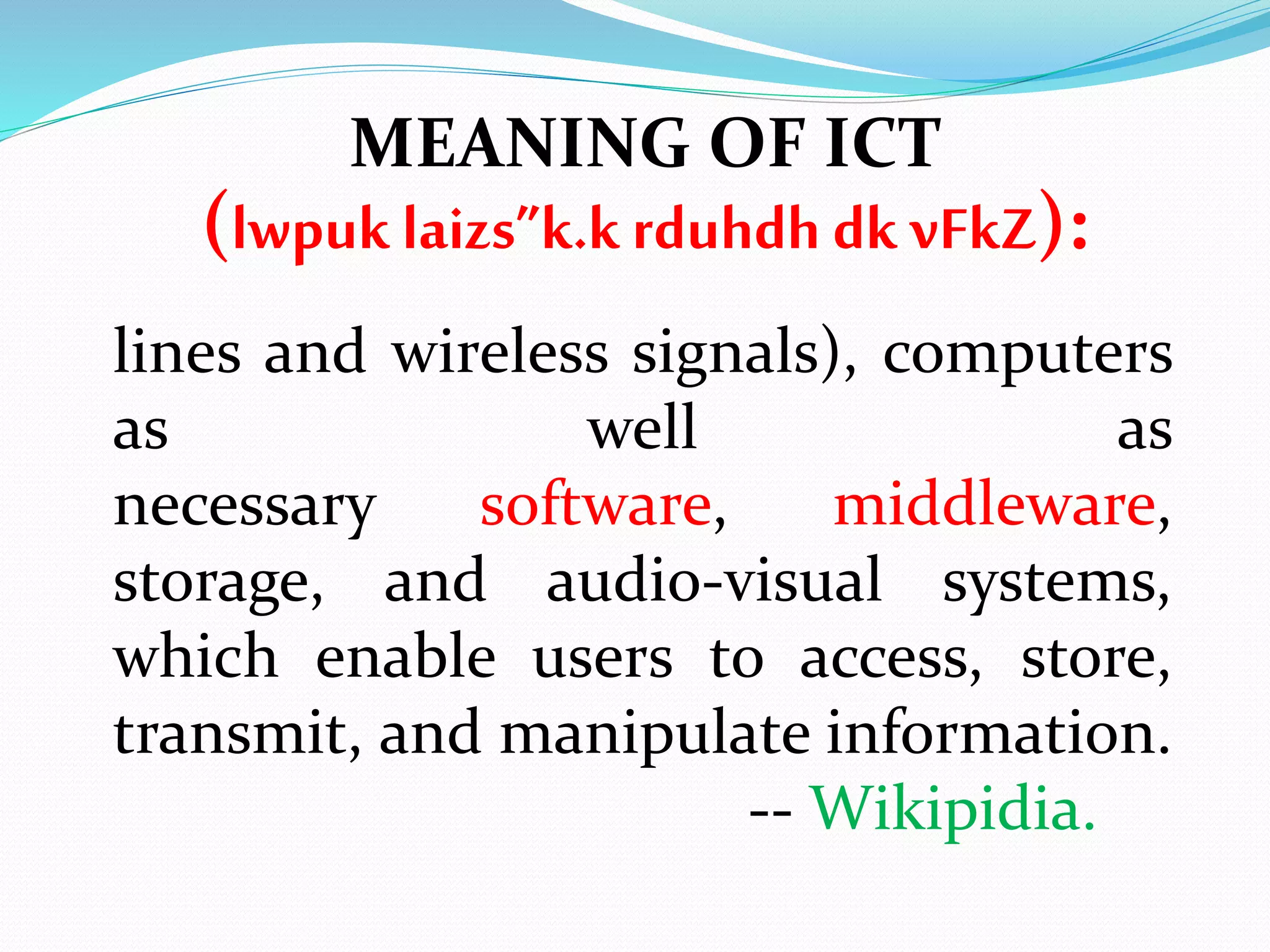
MEANING OF ICT
(lwpuk laizs”k.krduhdh dk vFkZ):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-7-2048.jpg)
![lkWQ~Vos;j] fefMyos;j] laxzg.k ;a= o JO;&n`’;
iz.kkfy;ksa dks ,d lkFk ykrk gS( tks mi;ksxdRrkZ
ds fy, lwpukvksa dks xE;] laxzg.k djus ;ksX;]
izlkfjrdjus;ksX; ,oaifjpkfyrdjus ;ksX;cukrkgS
&fofdihfM;k
MEANING OF ICT
(lwpuk laizs”k.krduhdh dk vFkZ):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-8-2048.jpg)




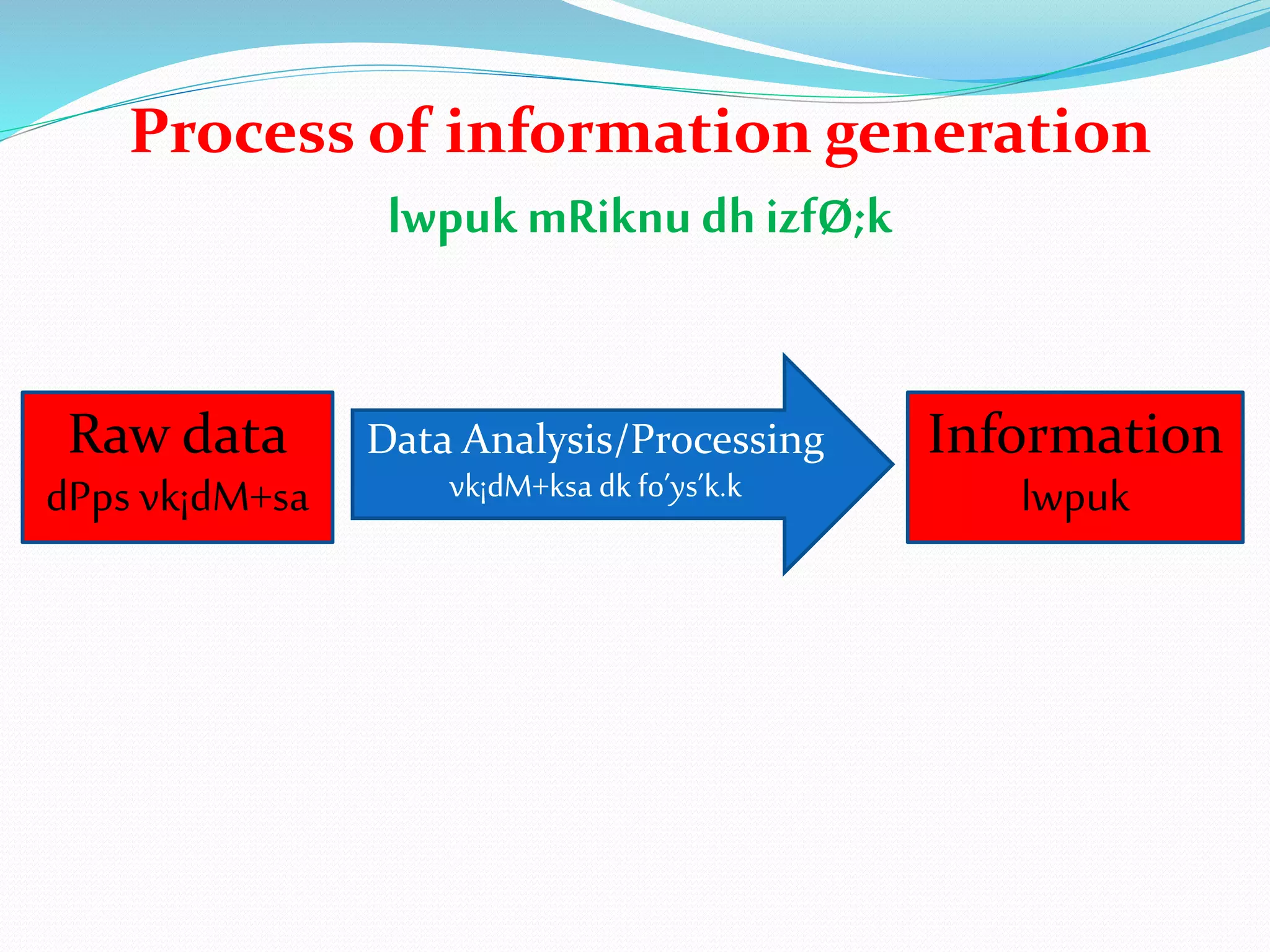
![Without analysis, the raw data
are meaningless. (fcukfo’ys”k.kds
dPps vk¡dM+sa vFkZghu gksrs gSaA)
After analyzing the raw data, we
can get the meaning from it.
(dPps vk¡dM+ksa ds fo’ys”k.kds i’pkr~]ge
mlls vFkZ fudkyldrs gSaA)
INFORMATION:(lwpuk)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-13-2048.jpg)


![(lwpuk dks vk¡dM+ksa ds bl rjg ds
fo’ys”k.k ds :i esa ifjHkkf”kr fd;k tk ldrk
gS] ftldk ifj.kke izkIrdÙkkZ ds fy,
vFkZiw.kZ gks vkSj tks orZeku ,oa
Hkfo”; ds fy,lkfRodewY;okykgksA)
DEFINITION OF INFORMATION
(lwpuk dh ifjHkk”kk)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-17-2048.jpg)
![Mutual exchange of facts, ideas,
opinions or emotions between
two or more persons is known as
‘communication’.(nks ;k nks ls vf/kd
O;fDr;ksa ds chp rF;ksa] fopkjksa] vuqekuksa
;k laoxksa ds ikjLifjd vknku&iznku dks
^laizs”k.k* dgrs gSaA)
COMMUNICATION (laizs”k.k)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-18-2048.jpg)
![MEANING OF WORD
COMMUNICATION(laisz”k.k‘kCn dk vFkZ):
The word communication is derived
from Latin word ‘communis’ which
means common.( vaxzth ‘kCn
communication dk fgUnh :ikarj.k laizs”k.k
gS] ftldh mRifÙk ySfVu Hkk”kk ds ‘kCn
‘communis’ ls gqbZ gS( ftldk vFkZ gS& lk>k ;k
lkekU;A)
COMMUNICATION (laizs”k.k)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-19-2048.jpg)

![According to ‘John Dewey’
“communication is a process of
sharing experience till it becomes a
common possession.” (tkWu Mhoh ds
vuqlkj] ^^ laizs”k.k vuqHkoksa ds rc rd
vknku&iznku dh izfØ;k gS] tc rd ;g ,d lk>h ;k
lkekU;laifÙku cutk,A**)
DEFINITION OF COMMUNITION
(Lakizs”k.k dh ifjHkk”kk)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-21-2048.jpg)
![Any group activity is impossible without
communication.(dksbZ Hkh lewg xfrfof/k fcuk laizs”k.k ds
vlaHko gSA)
Technology(rduhdh):
Technology can refer to material objects of
use to humanity, such as machines or
hardware, but it can also encompass broader
themes, including systems, methods of
organization and techniques.
(ekuo mi;ksx dh oLrq,¡] tSls& ;a= ;k e’khu vkSj gkMZos;j dks
rduhdh dgk tk ldrk gS( ysfdu blesa vkSj Hkh vf/kd foLr`r
fo”k;ksa tSls& iz.kkyh;ksa] laxBu dh fof/k;ksa vkSj rduhdksa
dks Hkhj[kk tk ldrk gSA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-22-2048.jpg)
![MEANING OF TECHNOLOGY( rduhdh dk vFkZ):
The word technology is derived from Greek
word ‘Tecnikos’ or ‘Techne’ Means Art or
Craft.(rduhdh ‘kCn xzhd ‘kCn ‘Tecnikos’ ;k ‘Techne’ ls fy;k
x;kgS] ftldk vFkZ gS&dyk ;k f’kYi)
DEFINITION OF TECHNOLOGY(rduhdhdh ifjHk”kk):
‘It is an application of science in Art.’
-Feish(1964)
fQ’k ds vuqlkj &^;g foKku dk dyk esa iz;ksxgSA*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-23-2048.jpg)
![‘Technology can be referred as a system having
various interrelated components arranged by
scientific method to obtain desire objectives.’
– Dr. Das
^dqN okafNr mÌs’;ksa dh izkfIr ds fy;s vo;oksa ls varlaZcaf/kr dksbZ
Hkh iz.kkyh oSKkfud jhfr ls lqO;ofLFkr fd;k x;k gks] mls ^rduhdh*
dgk ldrk gSA*
&MkW-nkl
DEFINITION OF ICT(lwpuklaizs”k.k rduhdhdh ifjHkk”kk):
The technology by which information can be
transmitted effectively in the same form to the receiver.
So, that the desire objectives can be realized, is called
ICT.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-24-2048.jpg)
![(og rduhdh] ftlds }kjk fdlh lwpuk dks
izkIrdÙkkZ rd mlh :i esa lapkfjr fd;k tk lds]
rkfd okafNr mÌs’;ksa dh iwfrZ gks( lwpuk
laisz”k.k rduhdh dgykrhgSA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-25-2048.jpg)



![(f”k{k.k vf/kxe izfØ;k dks ljy] lqxe] lgk;d ,oa
:fpdjcukus esa)
2. Individualization of
learning.(vf/kxeds oSfDrdj.k esa)
3. Making the learning more
lively interactive.(vf/kxedks vf/kd
thoar ,oavar%fØ;kRedcukus esa)
4. High speed delivery of
content.(fo’k;oLrq dks “kh/kzrk ls izLrqr
djus esa)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meaningandconceptofict-160827074802/75/Meaning-and-concept-of-ict-29-2048.jpg)



