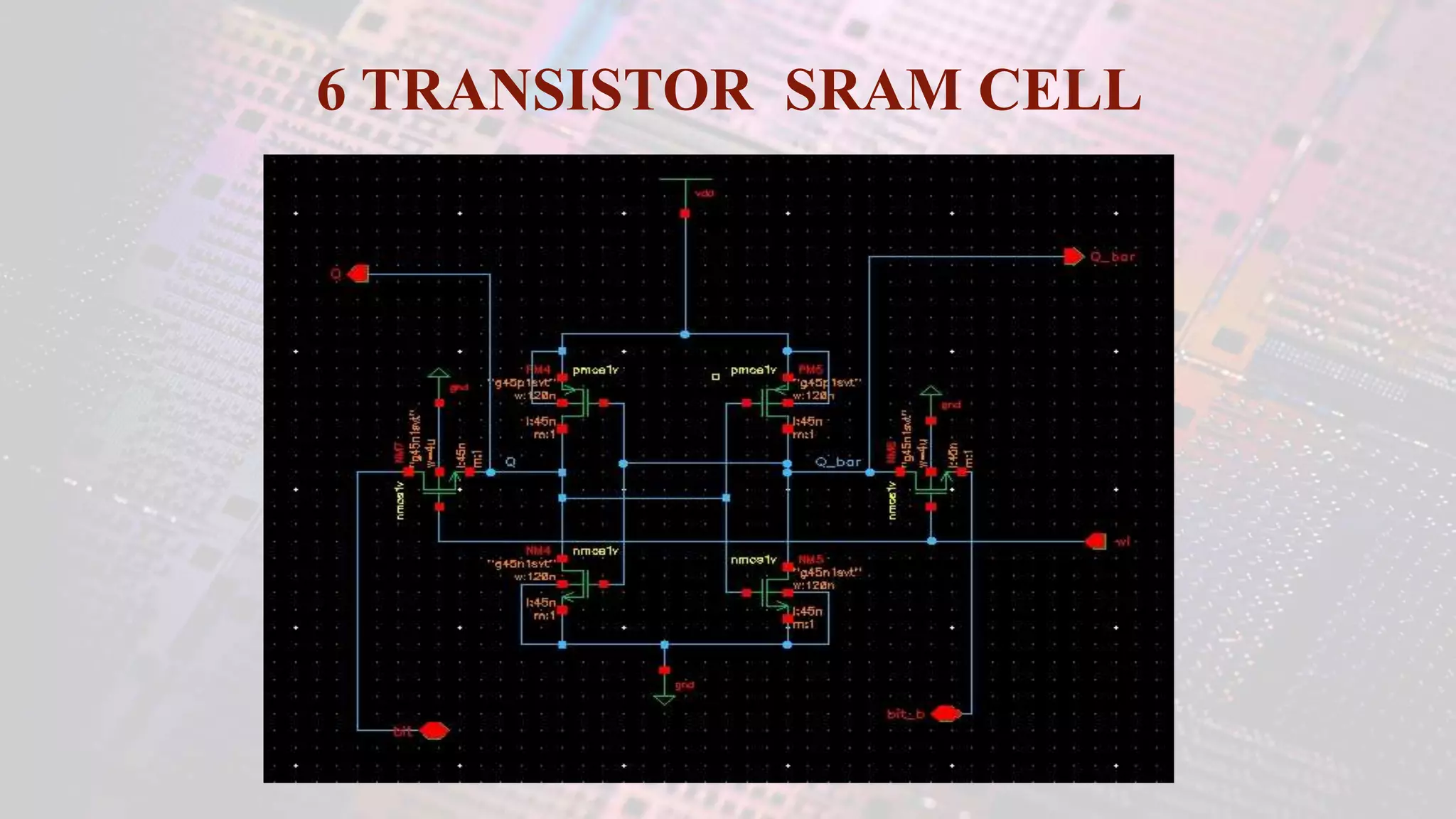
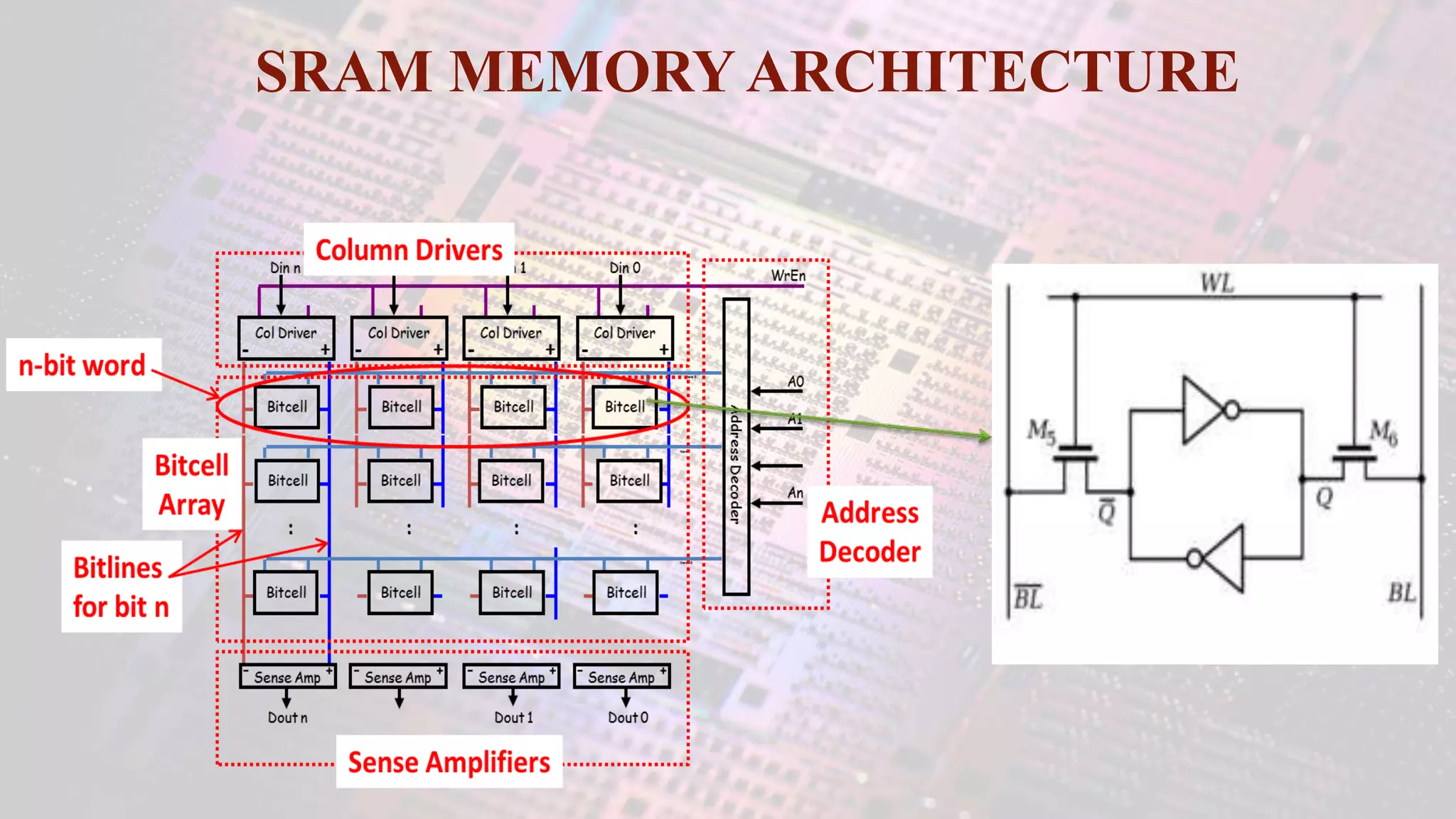
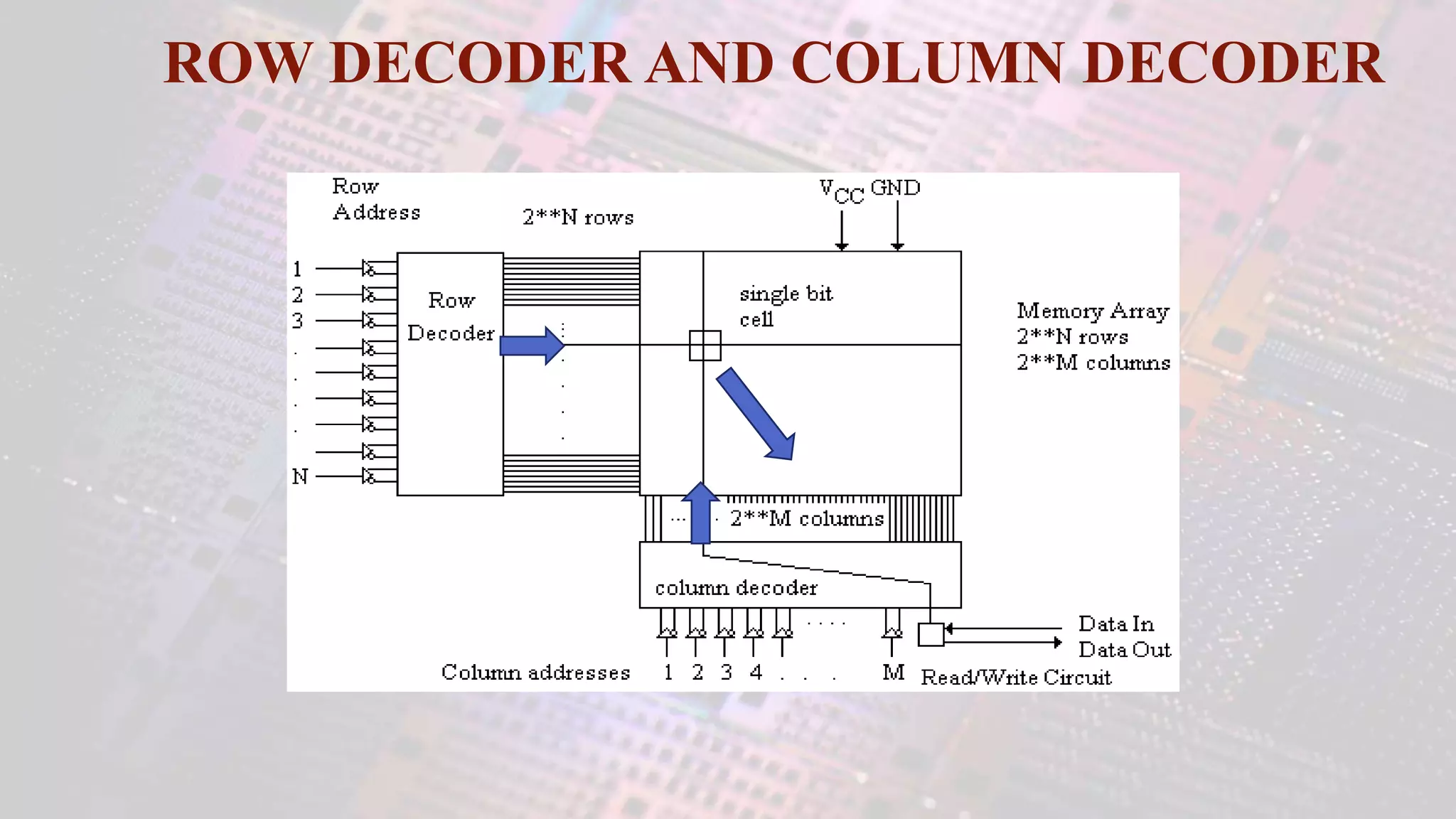
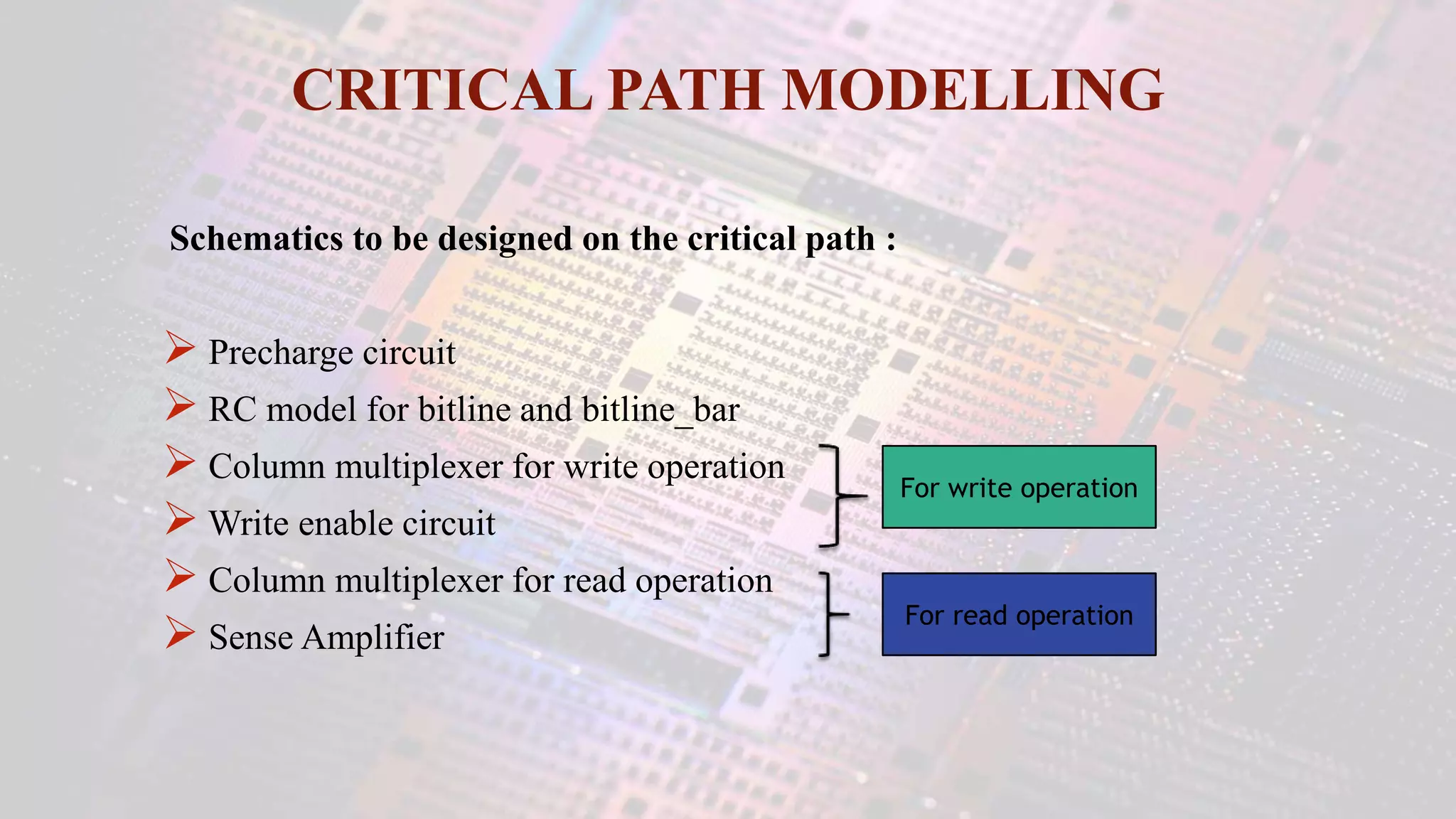
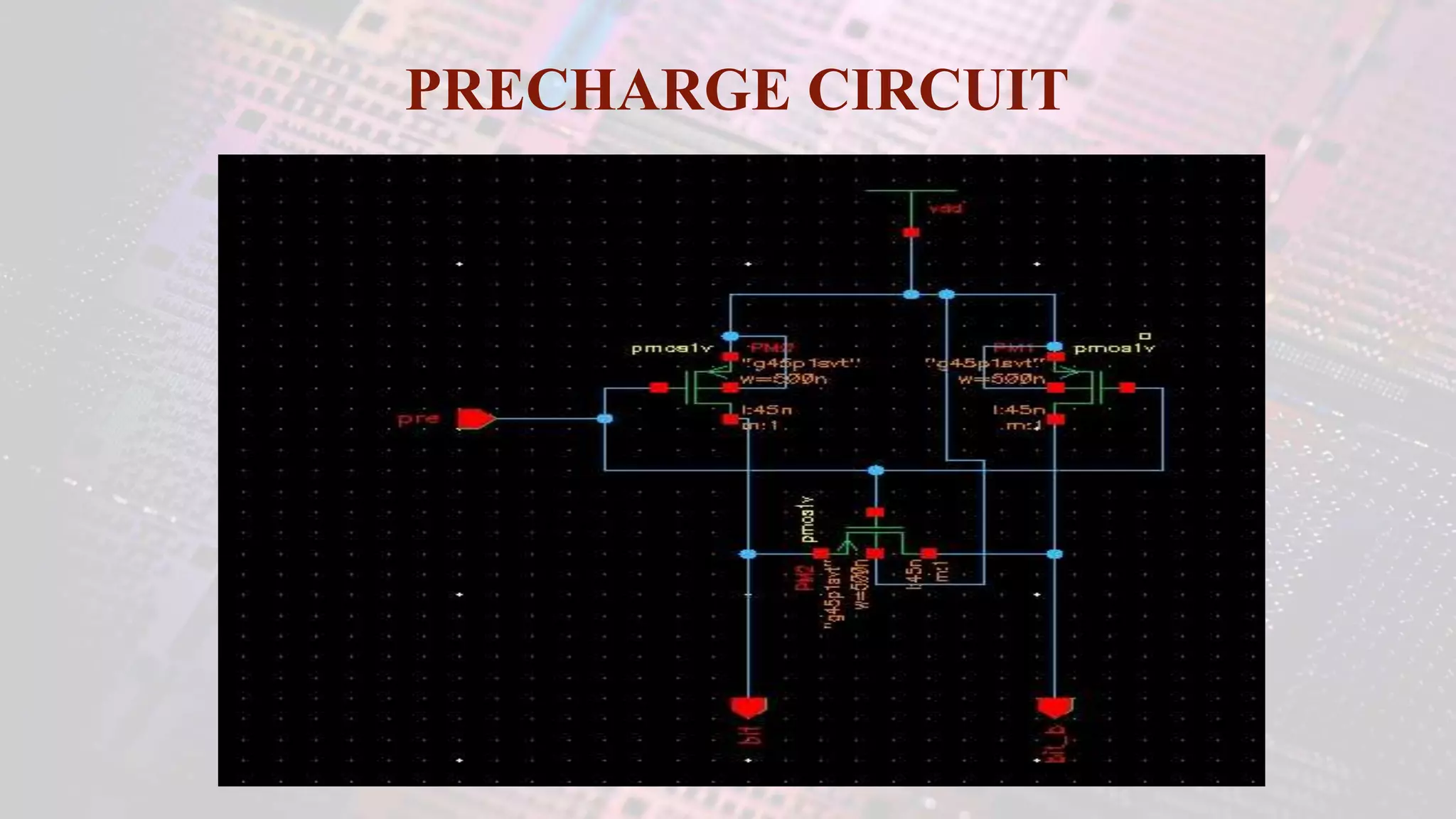
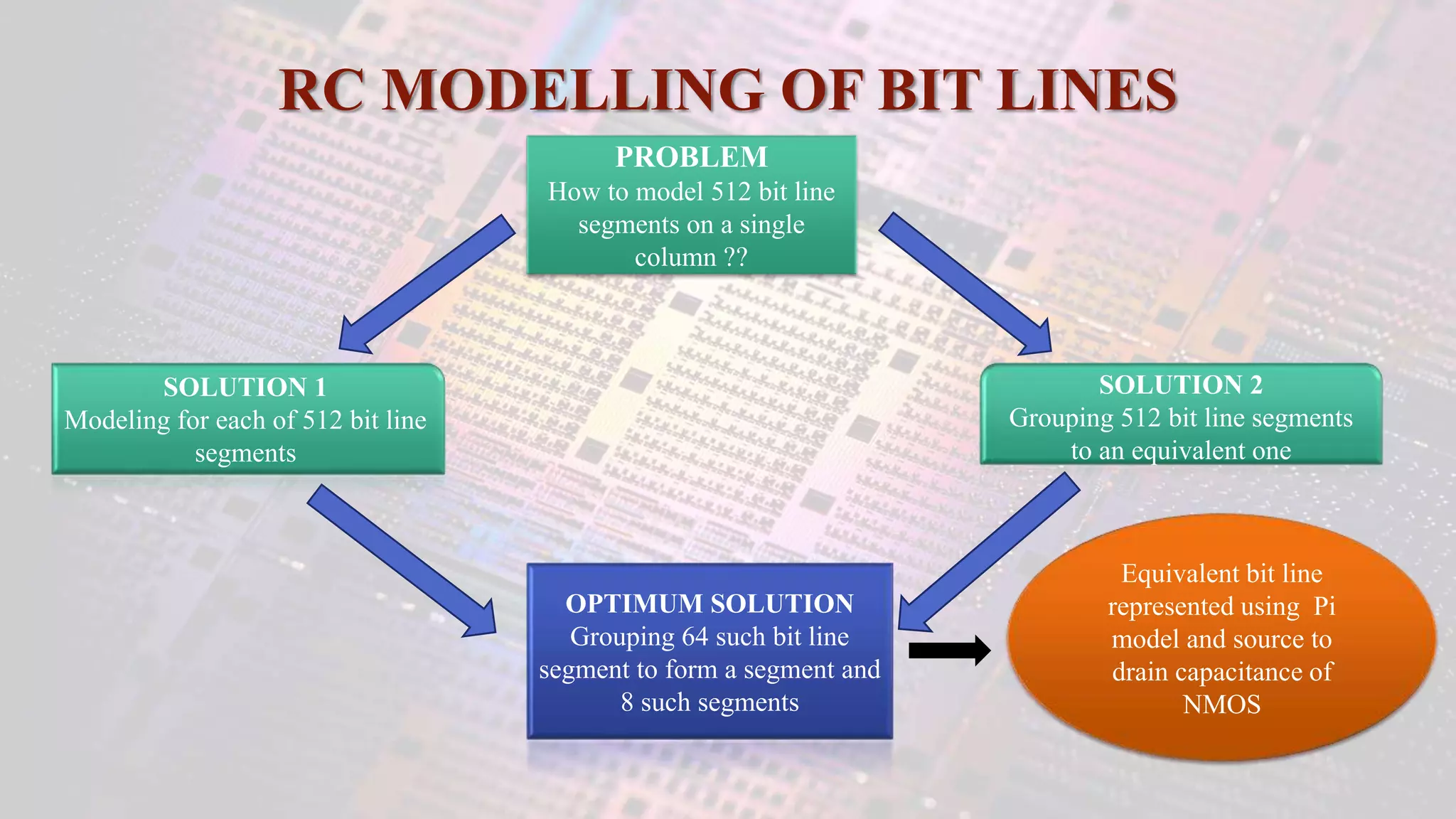
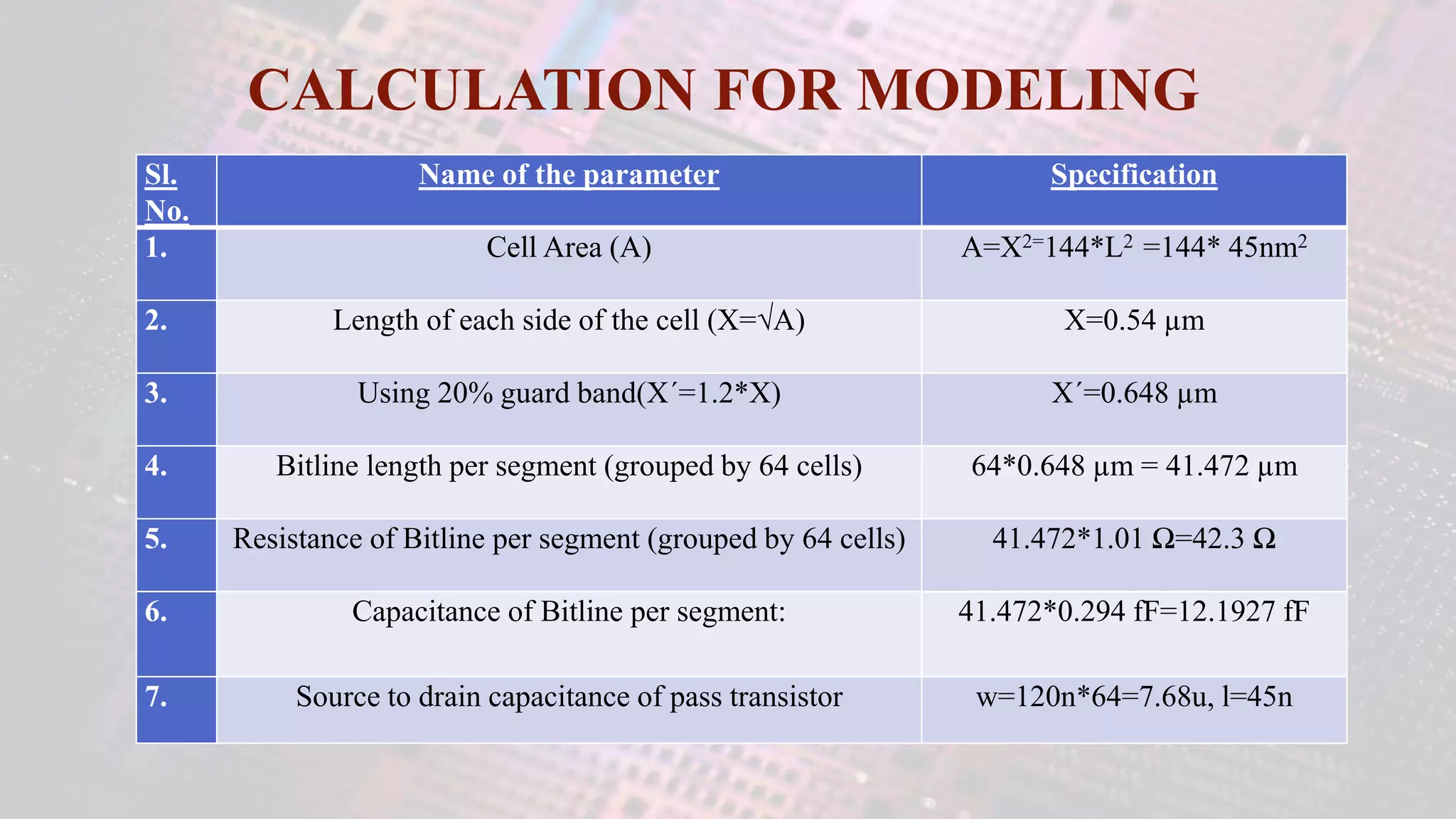
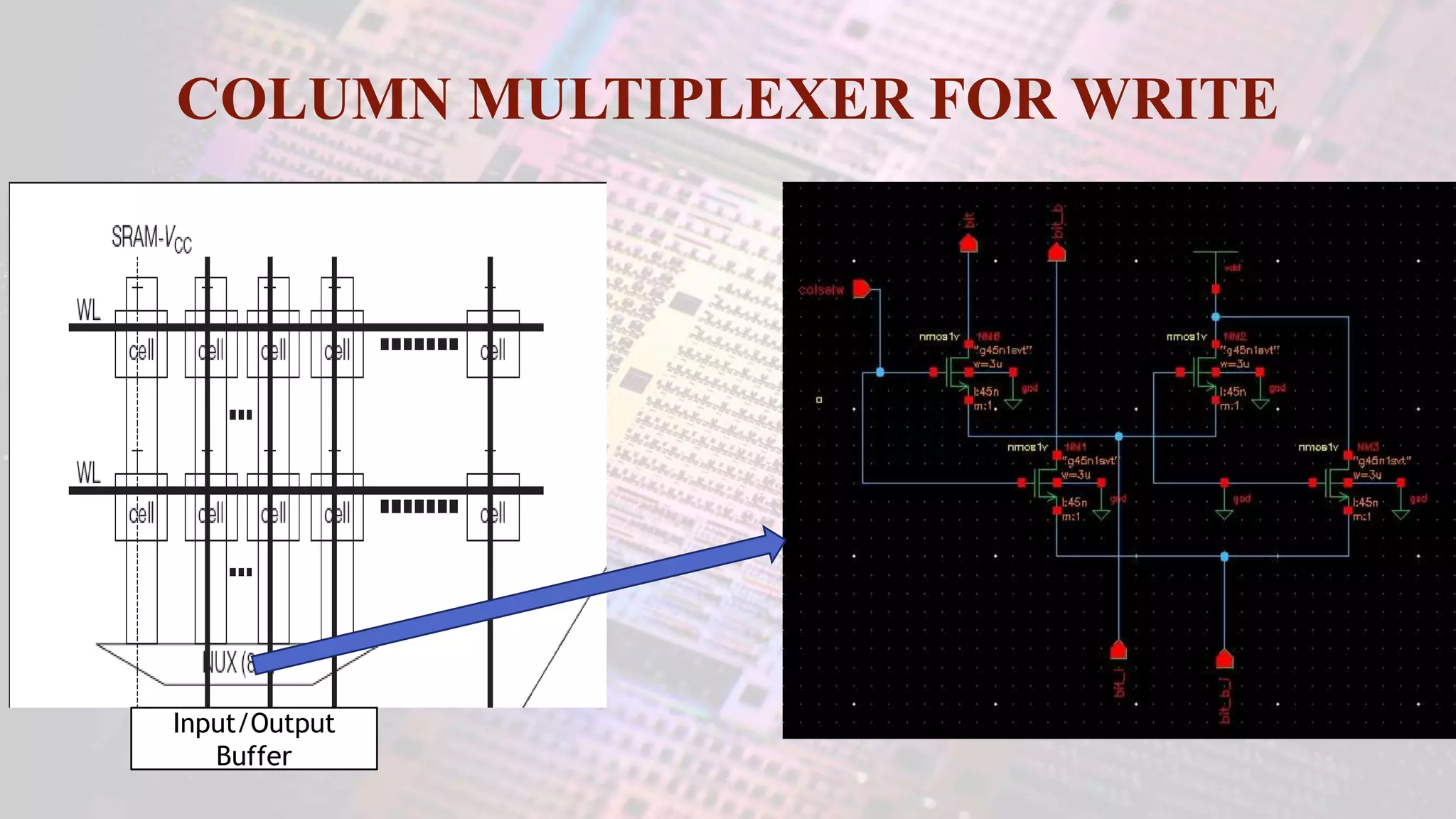
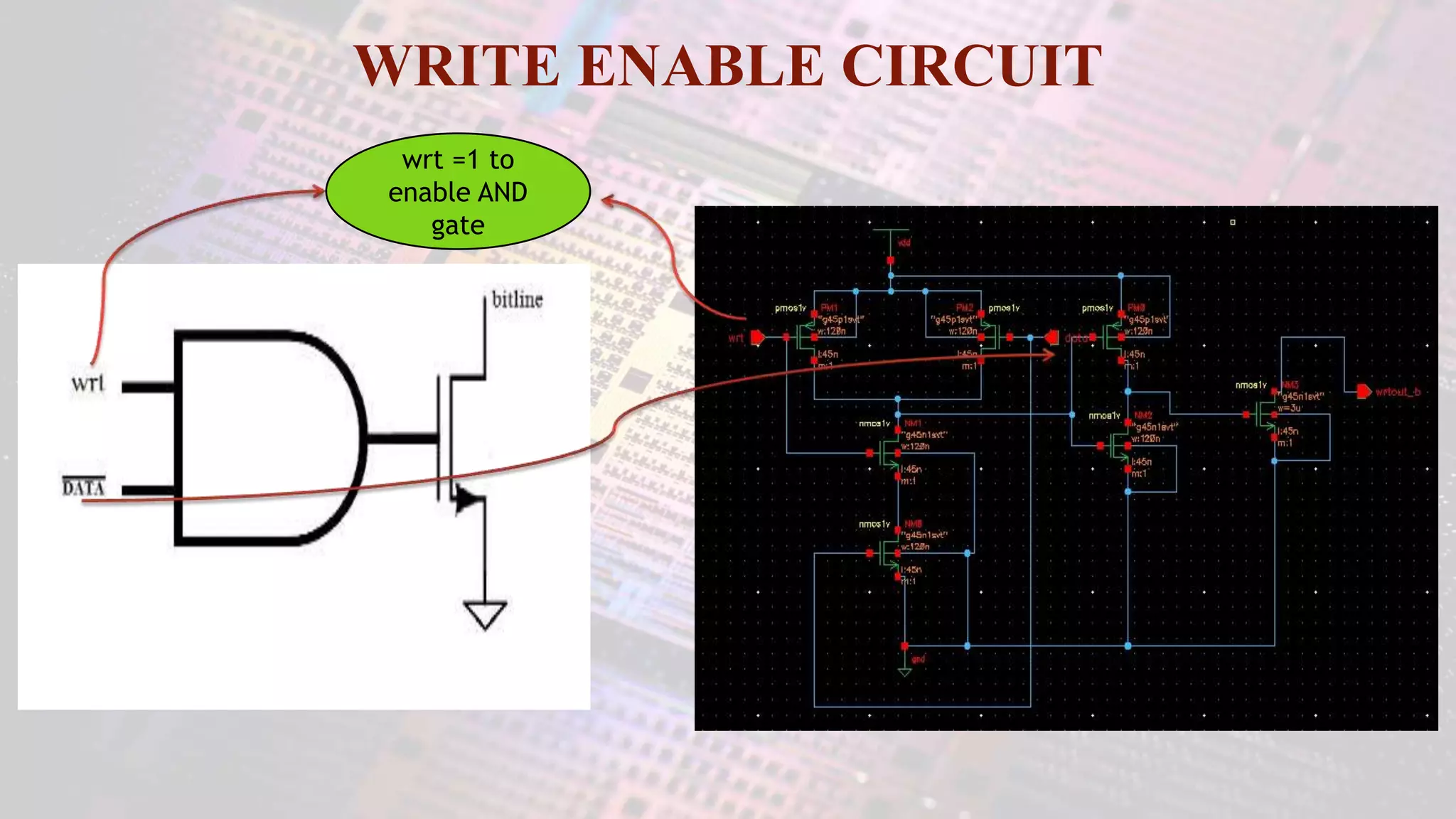
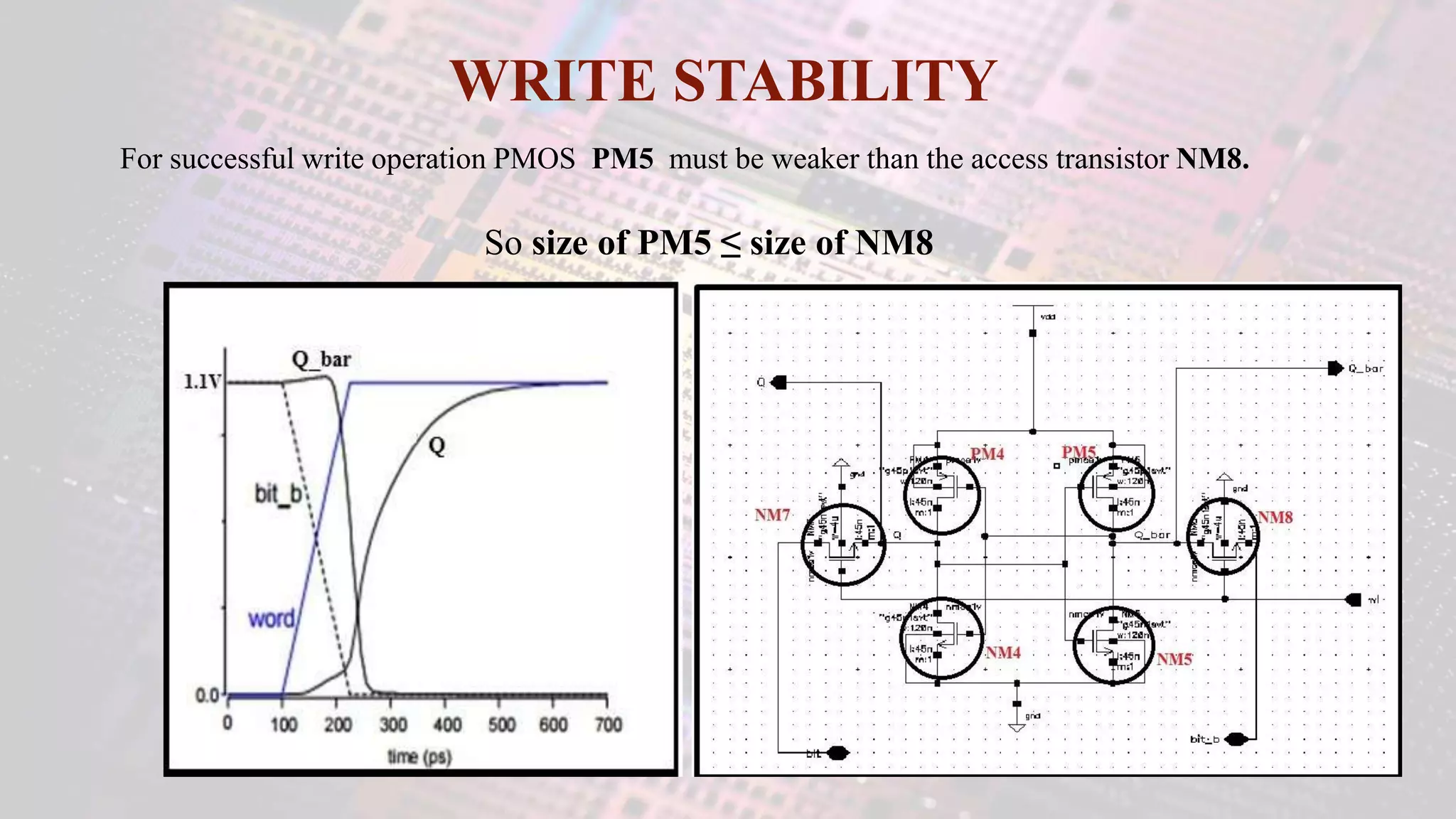
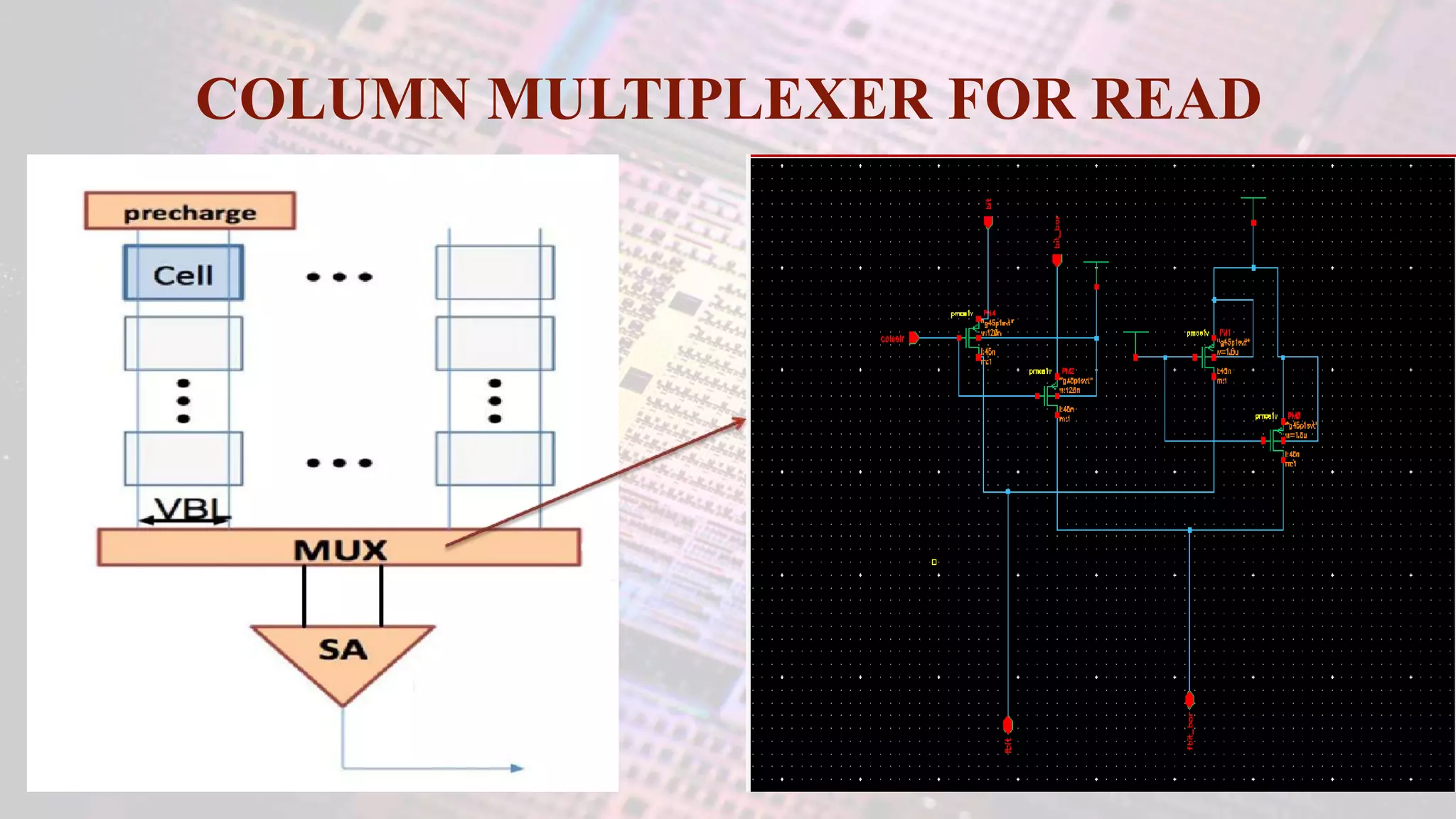
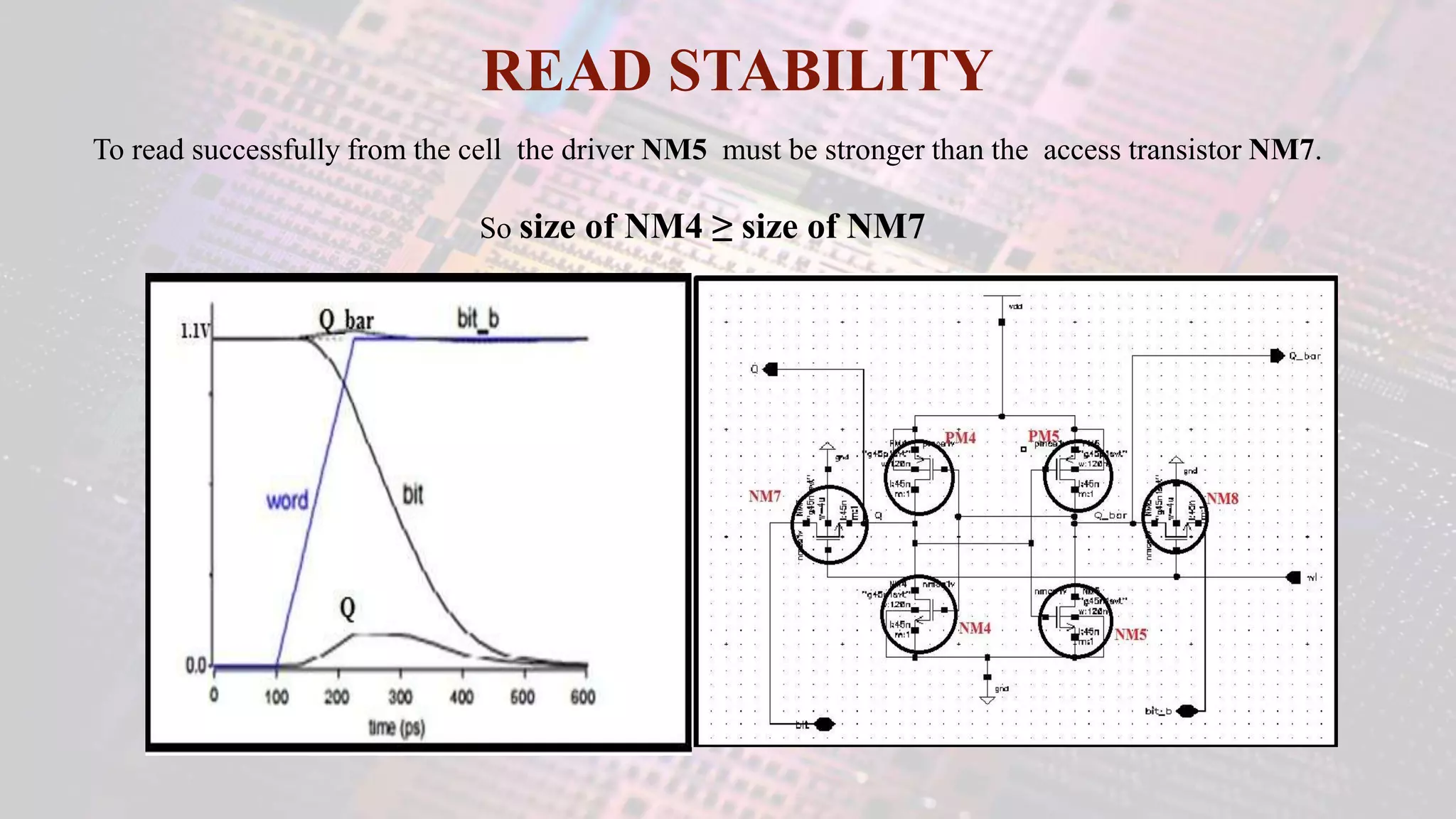
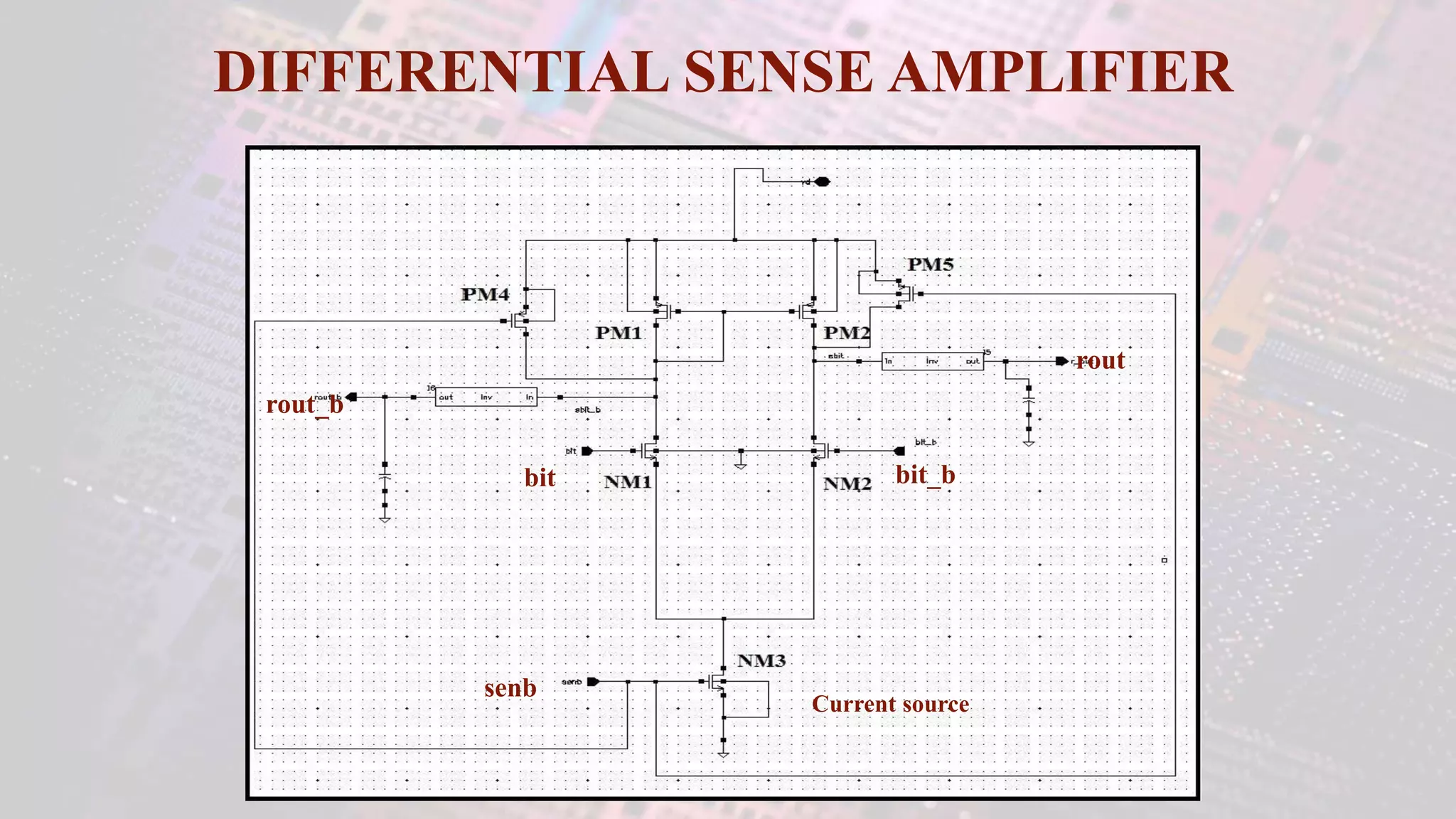
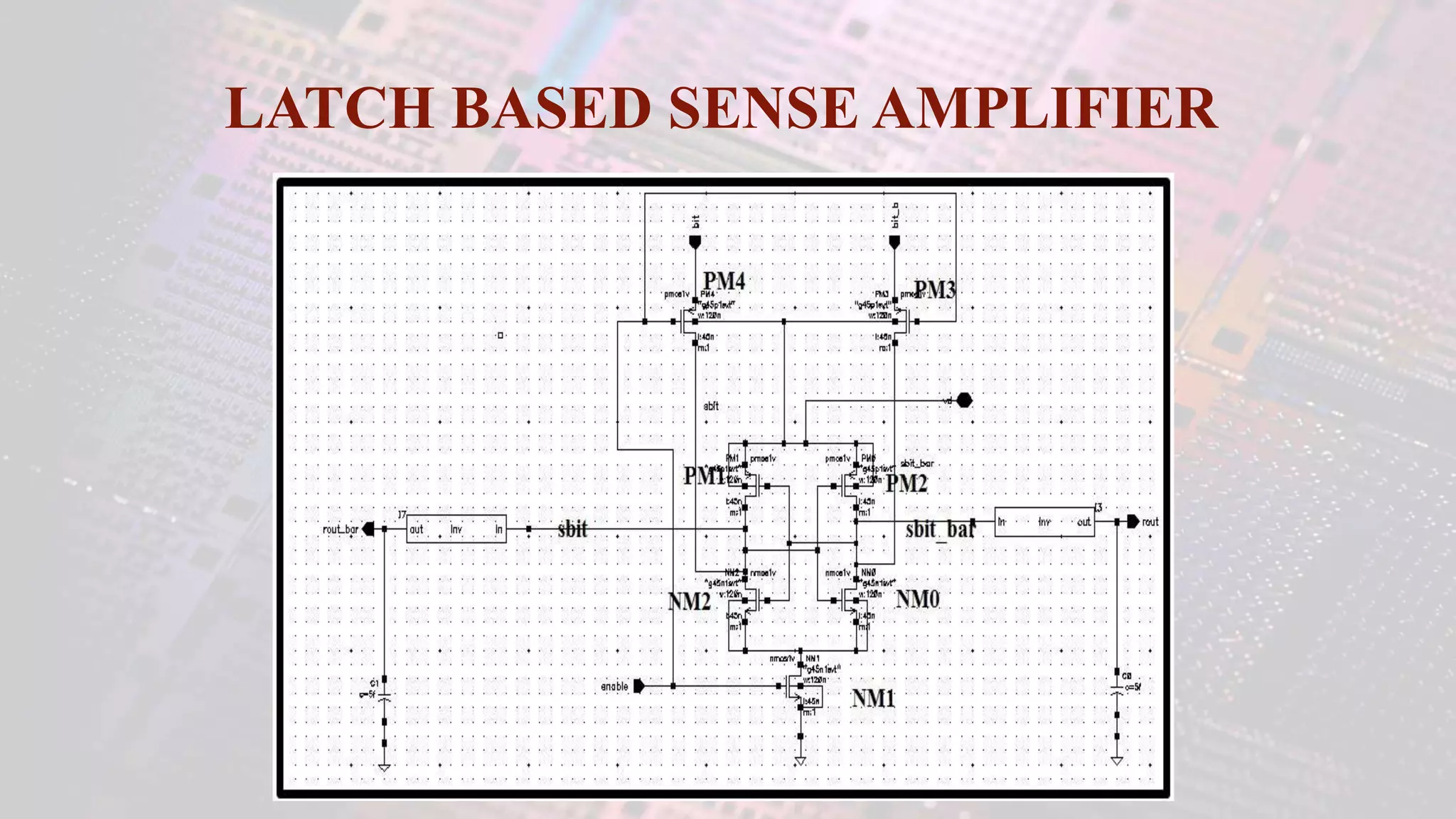
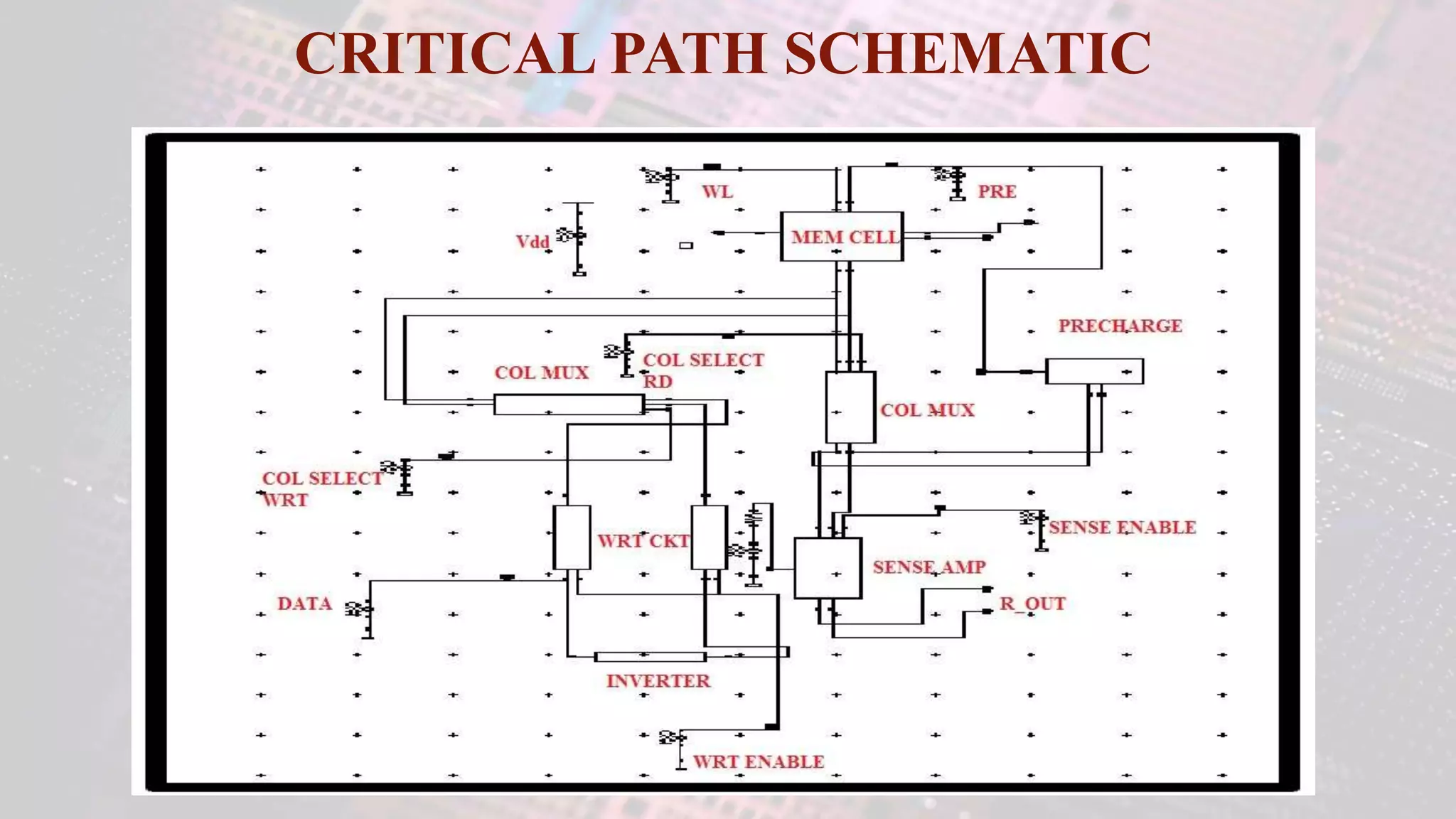
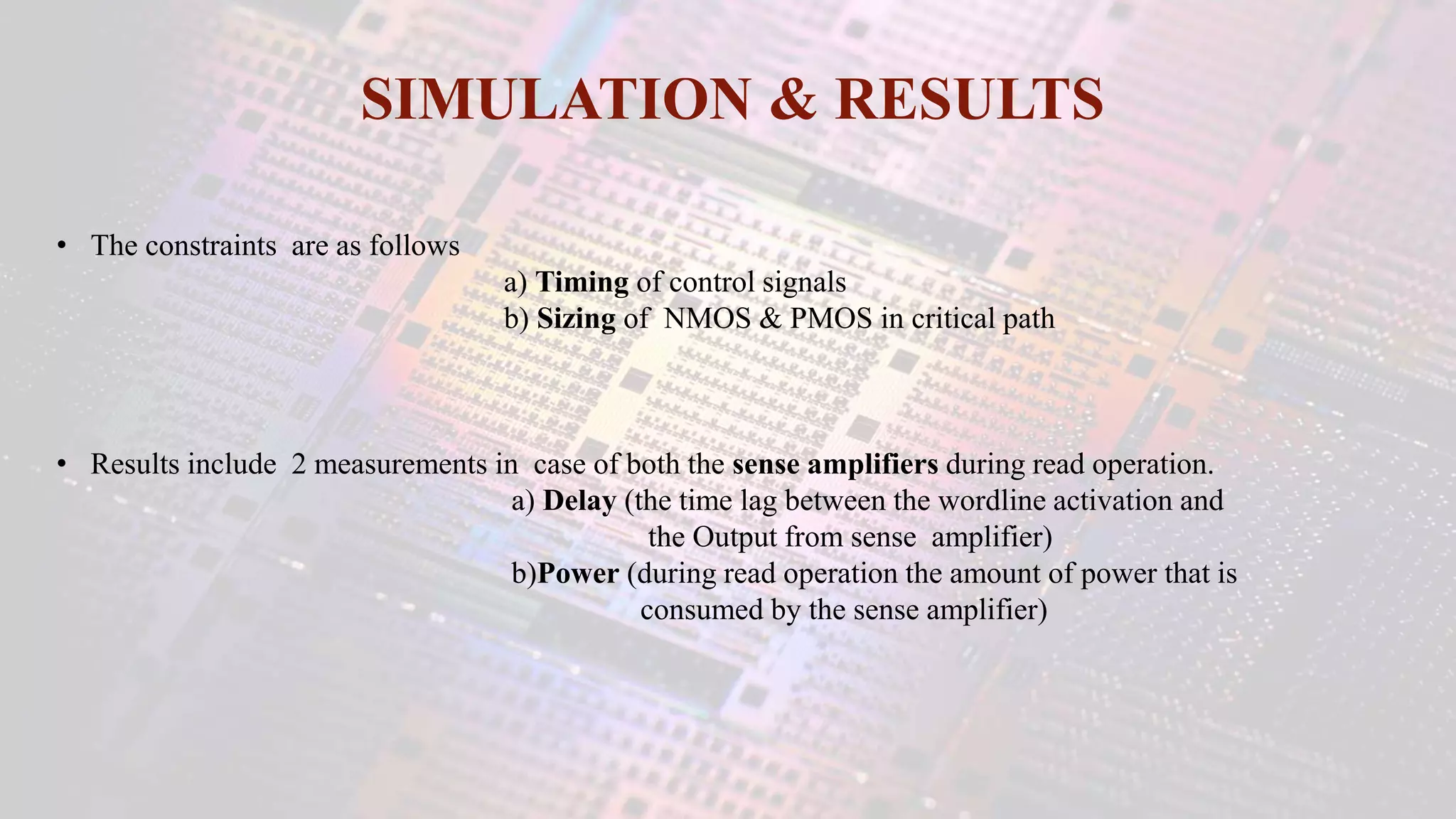
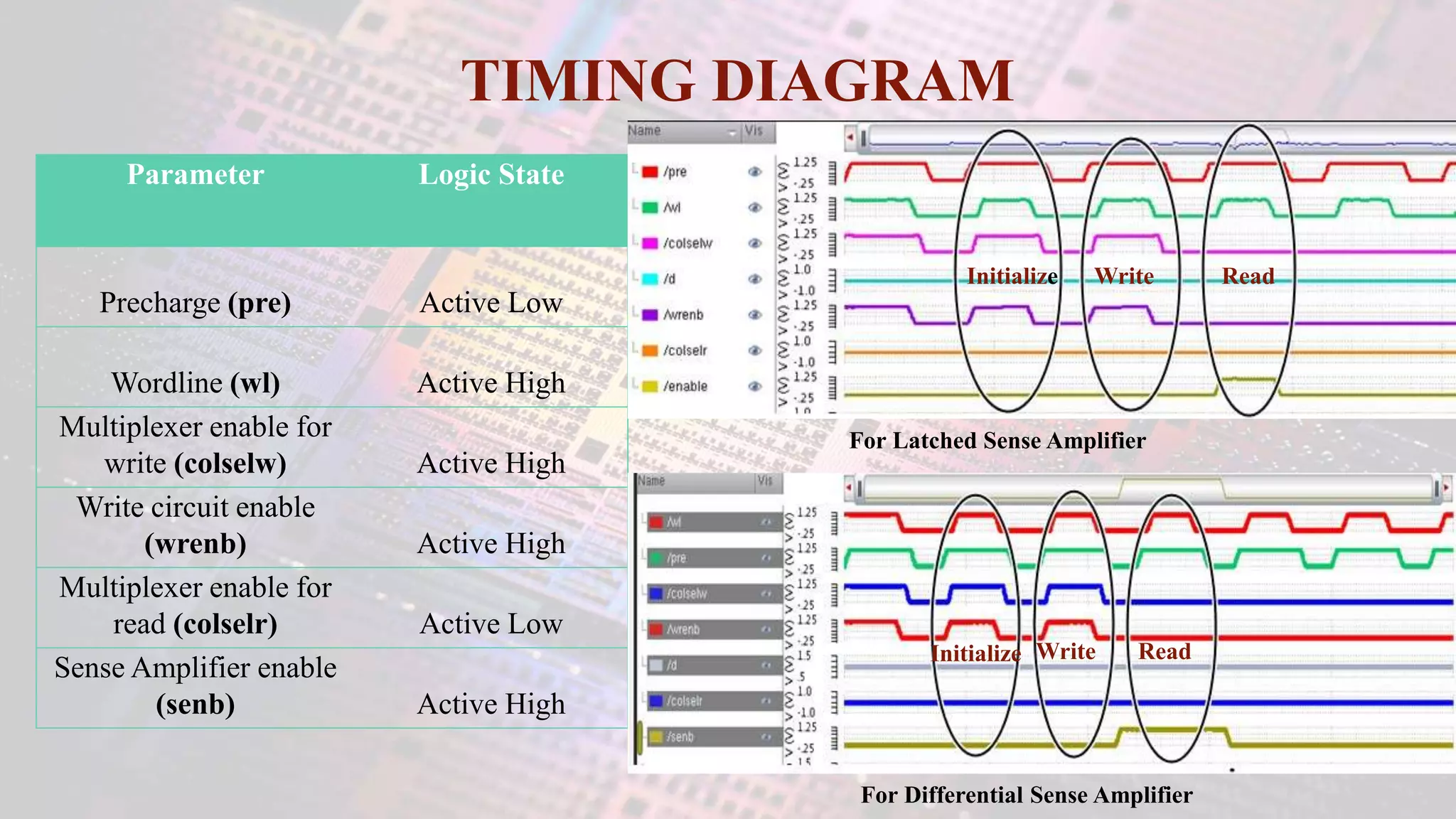
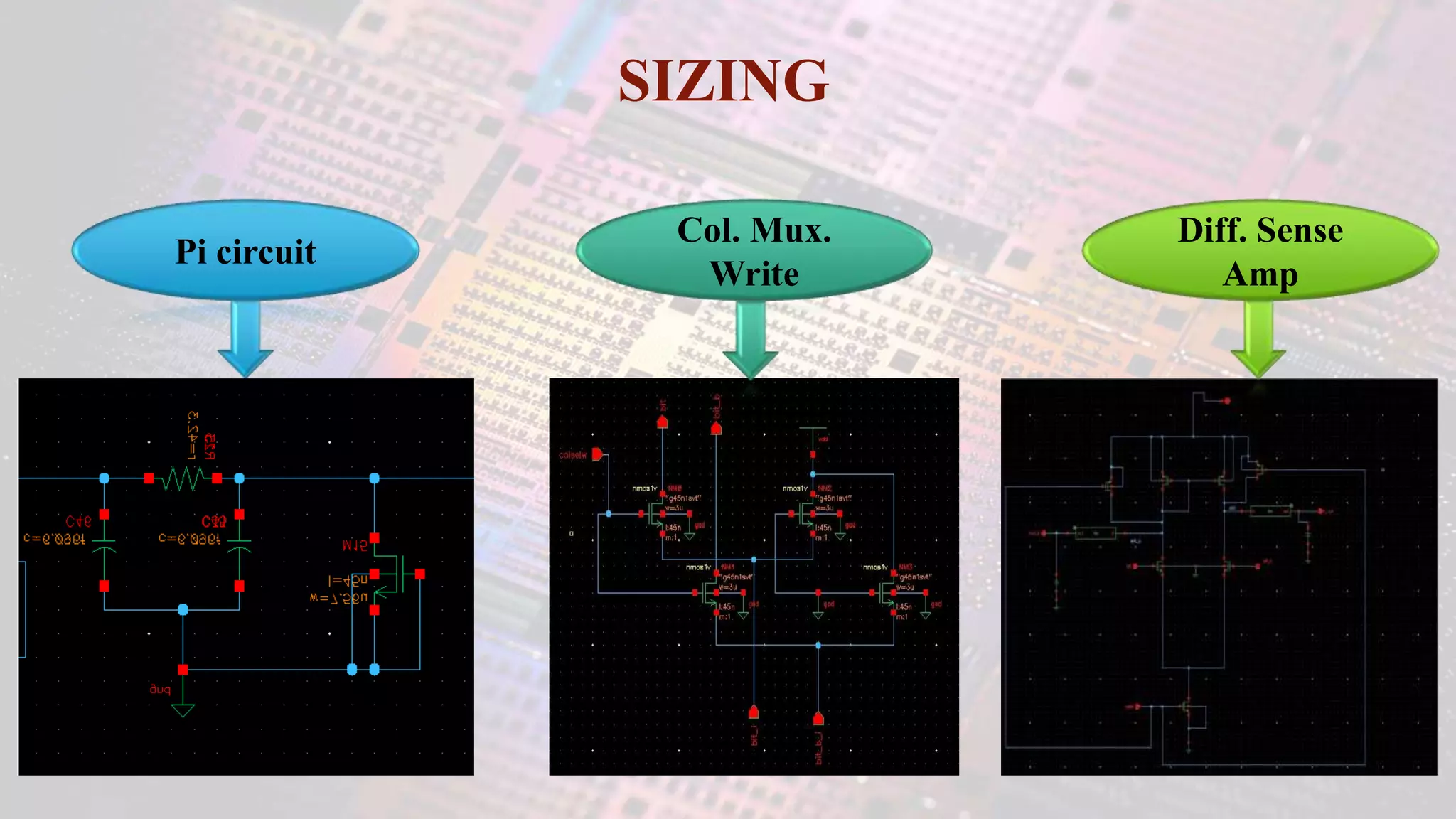
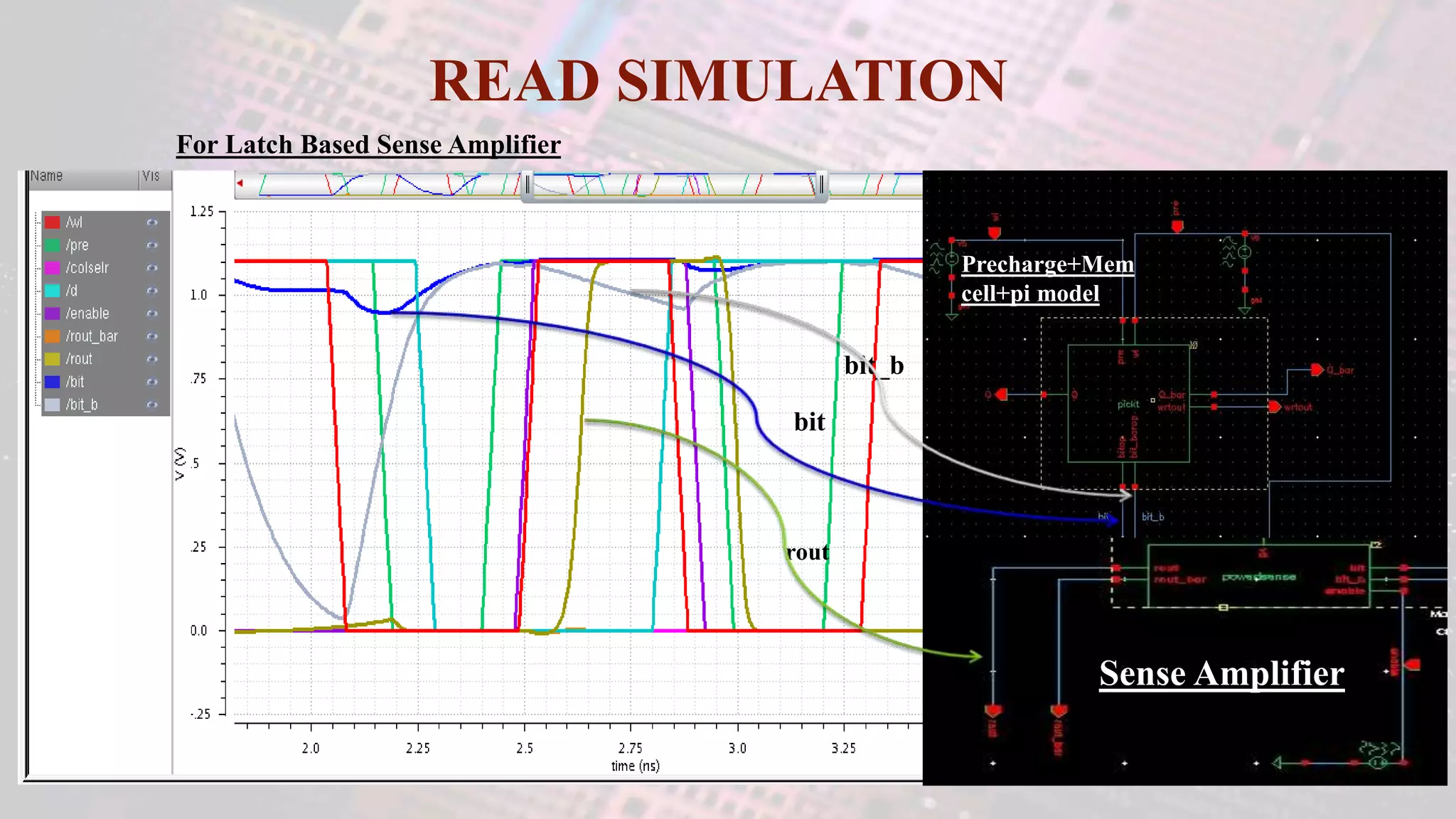
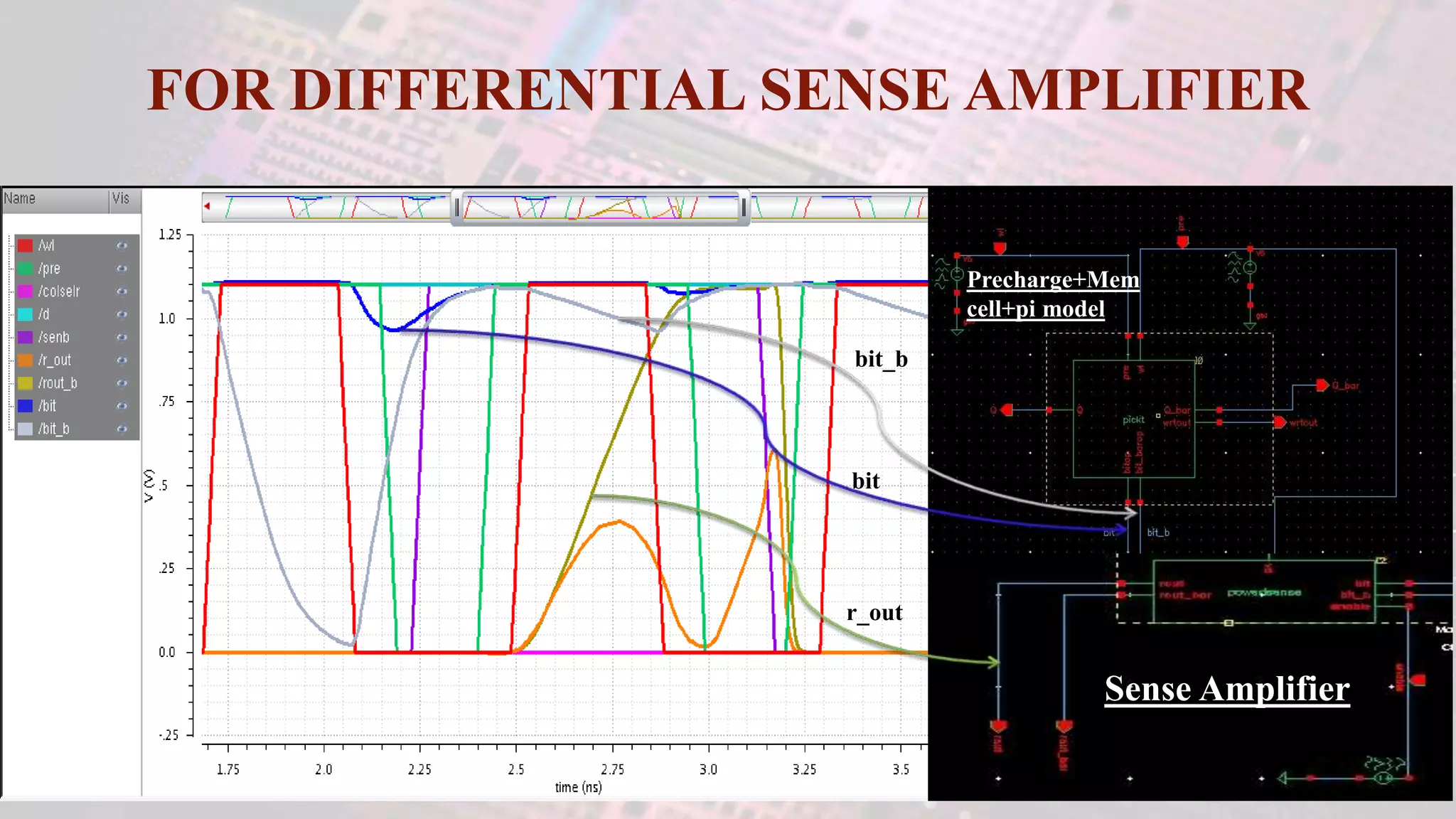
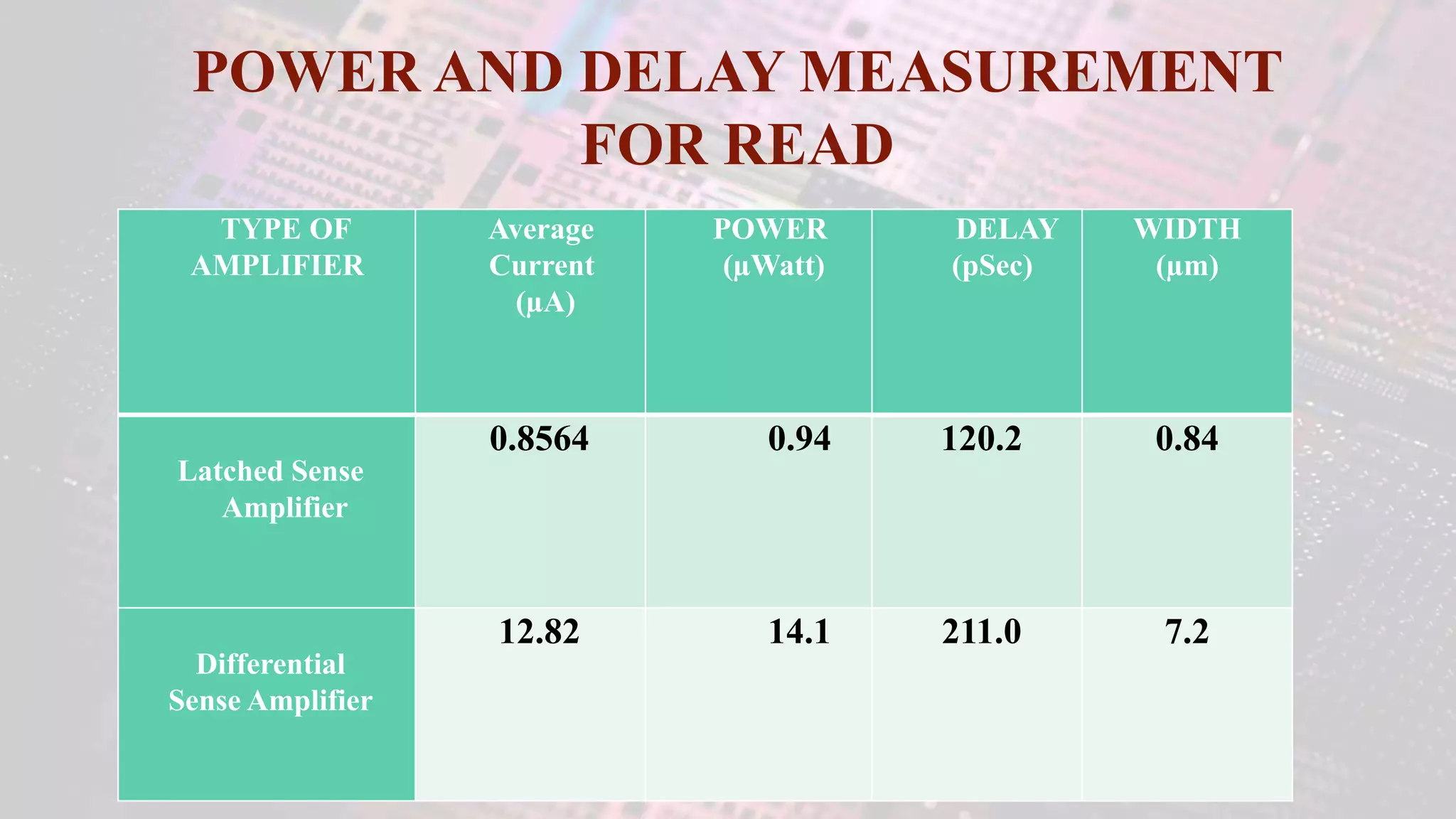
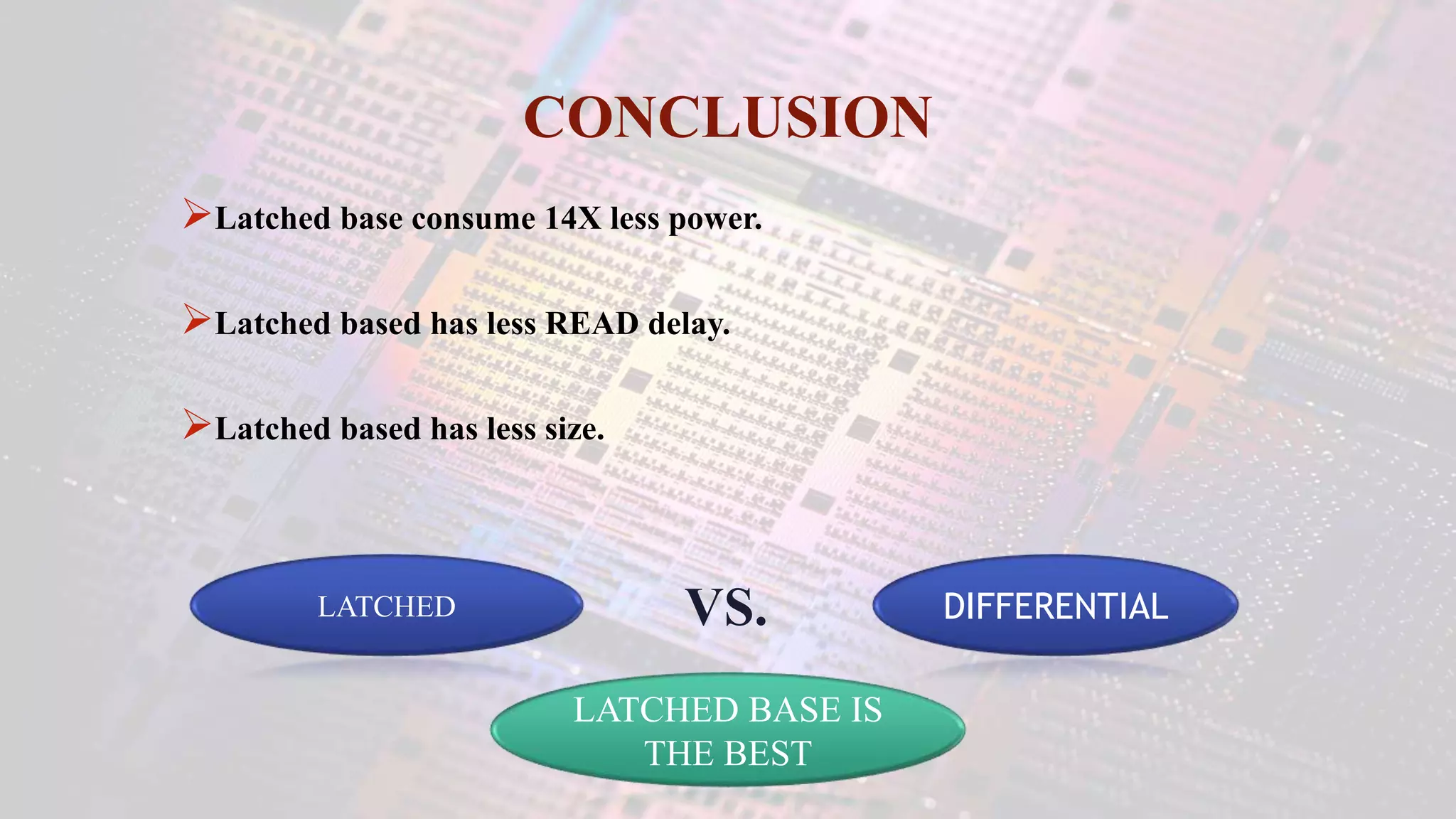
This document summarizes a student project to design a 32KB SRAM memory array using Cadence Virtuoso and a 45nm technology. It includes the design of a 6 transistor SRAM cell, row and column decoders, critical path components like the precharge circuit and sense amplifiers. Two types of sense amplifiers - differential and latched-based were modeled and their read delay, power consumption and sizing were compared through simulation. The results showed that the latched-based sense amplifier consumed 14x less power, had less read delay and size making it a better choice compared to the differential sense amplifier.