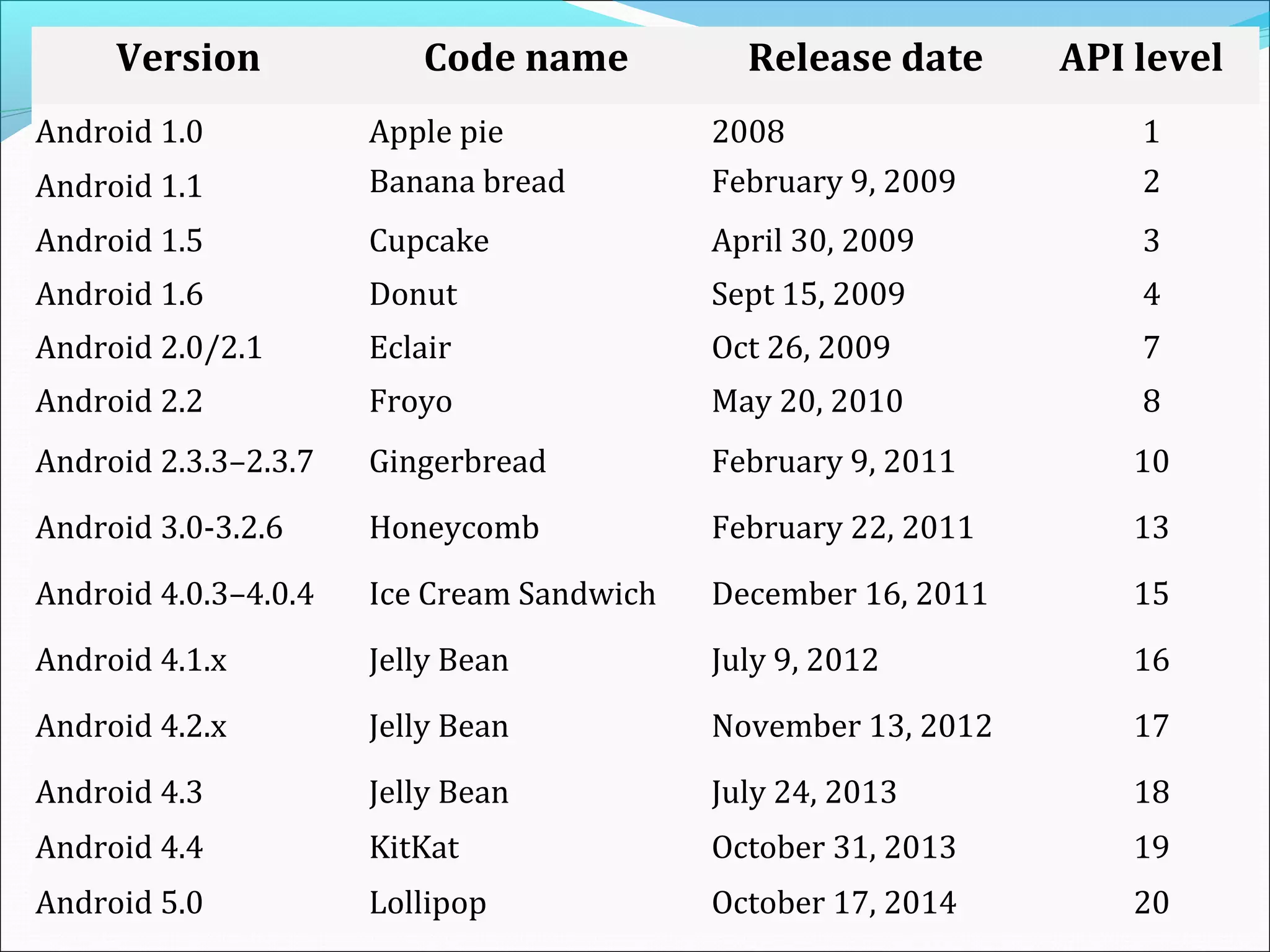
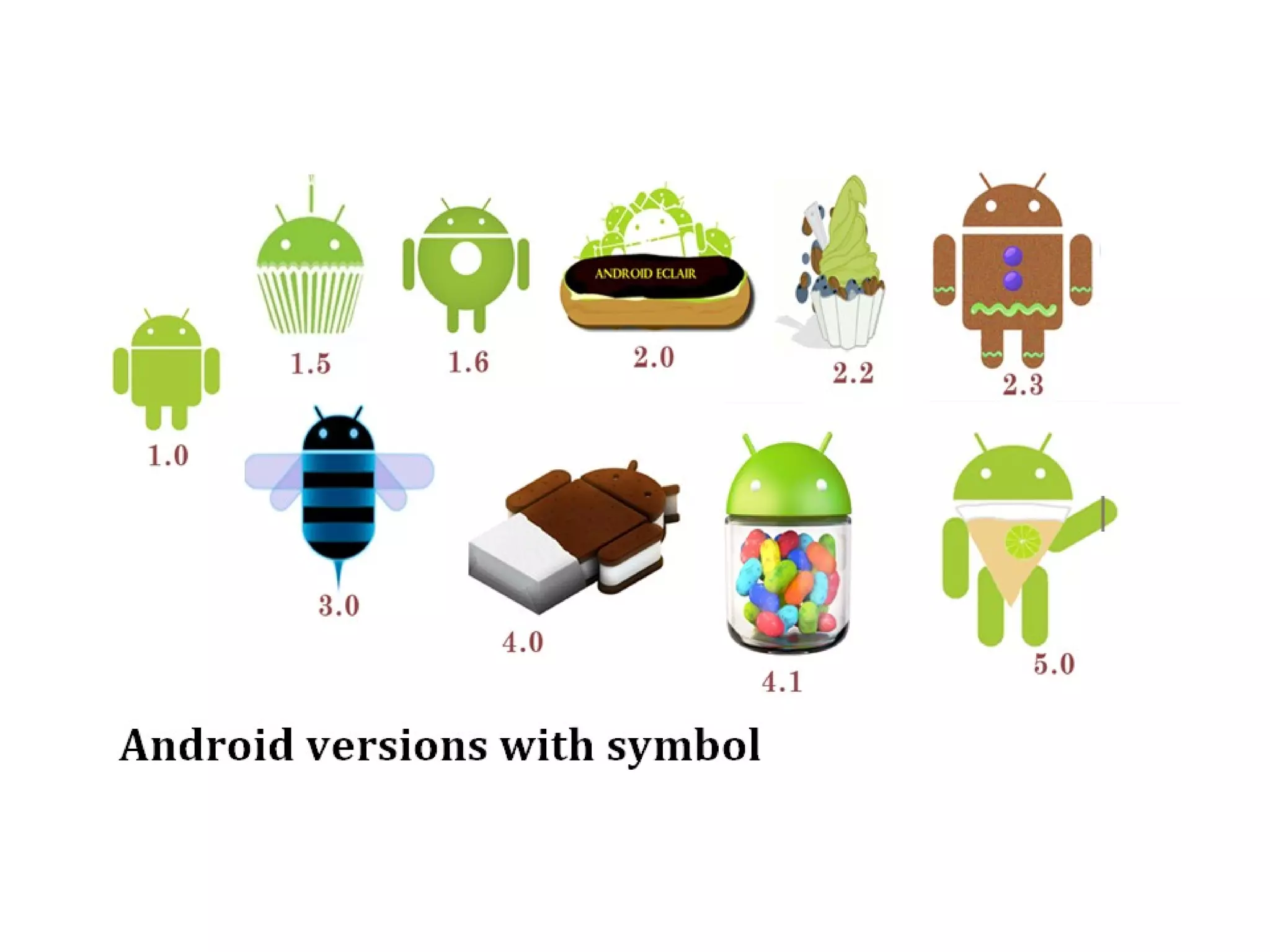
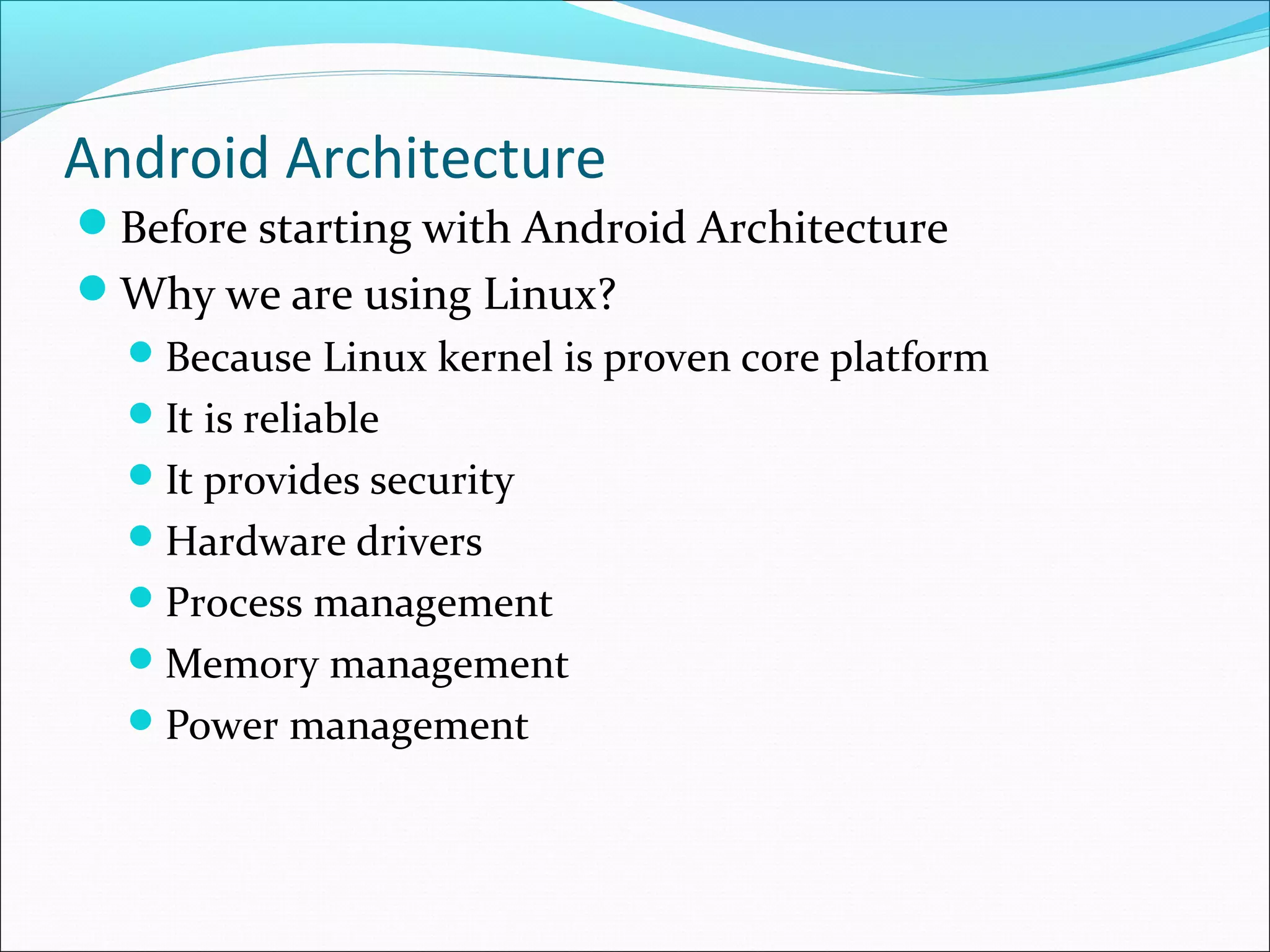
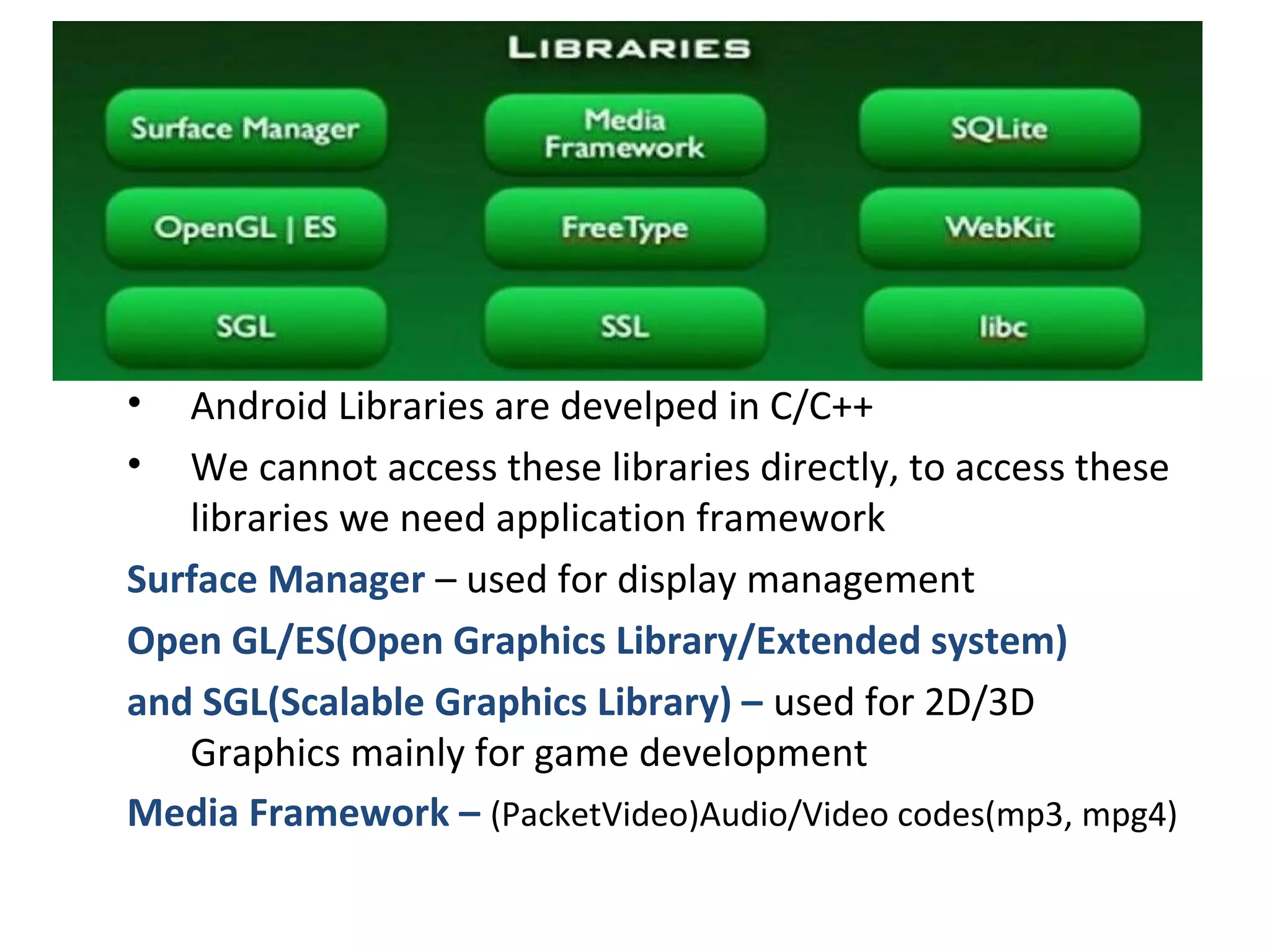
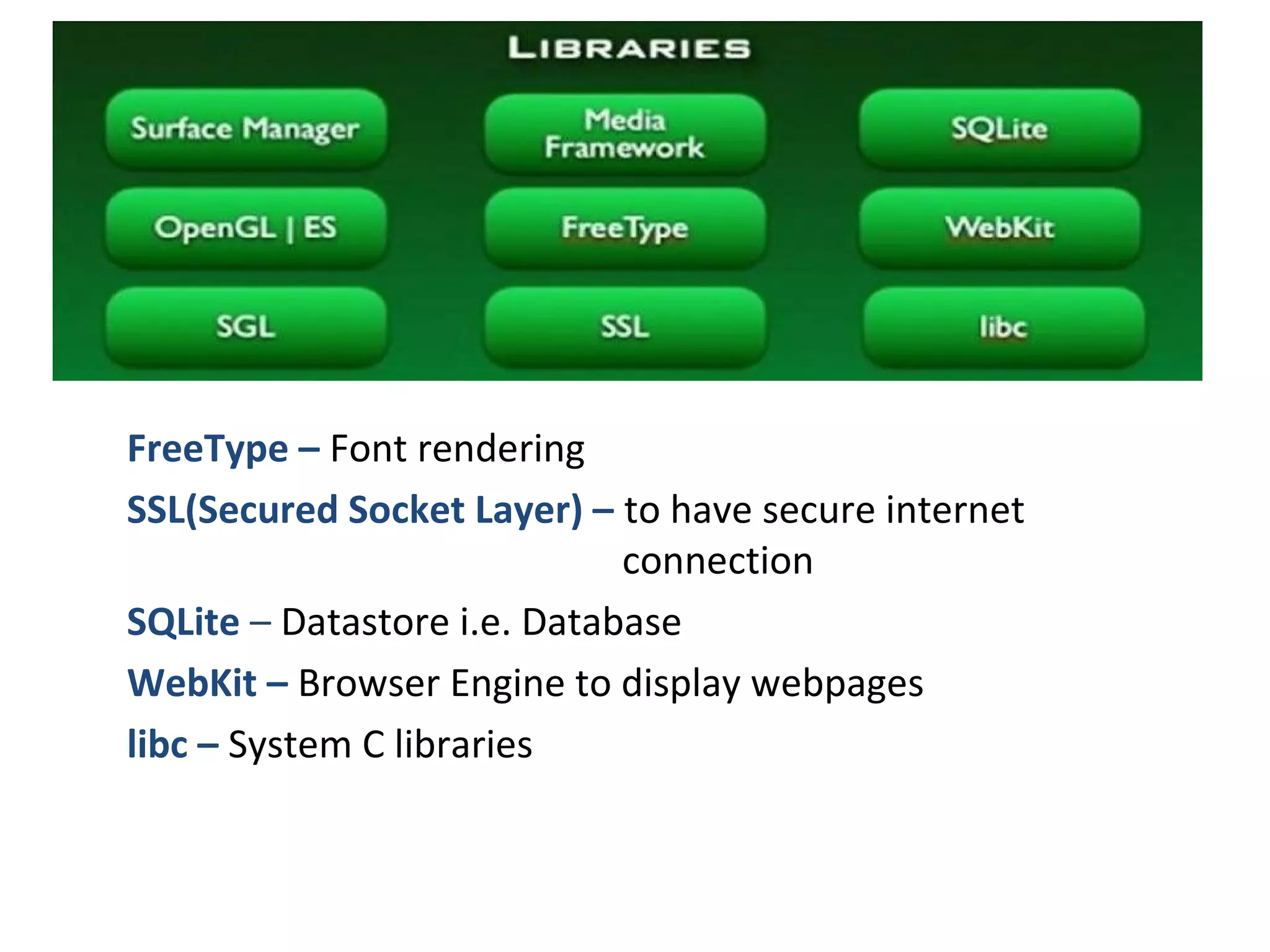
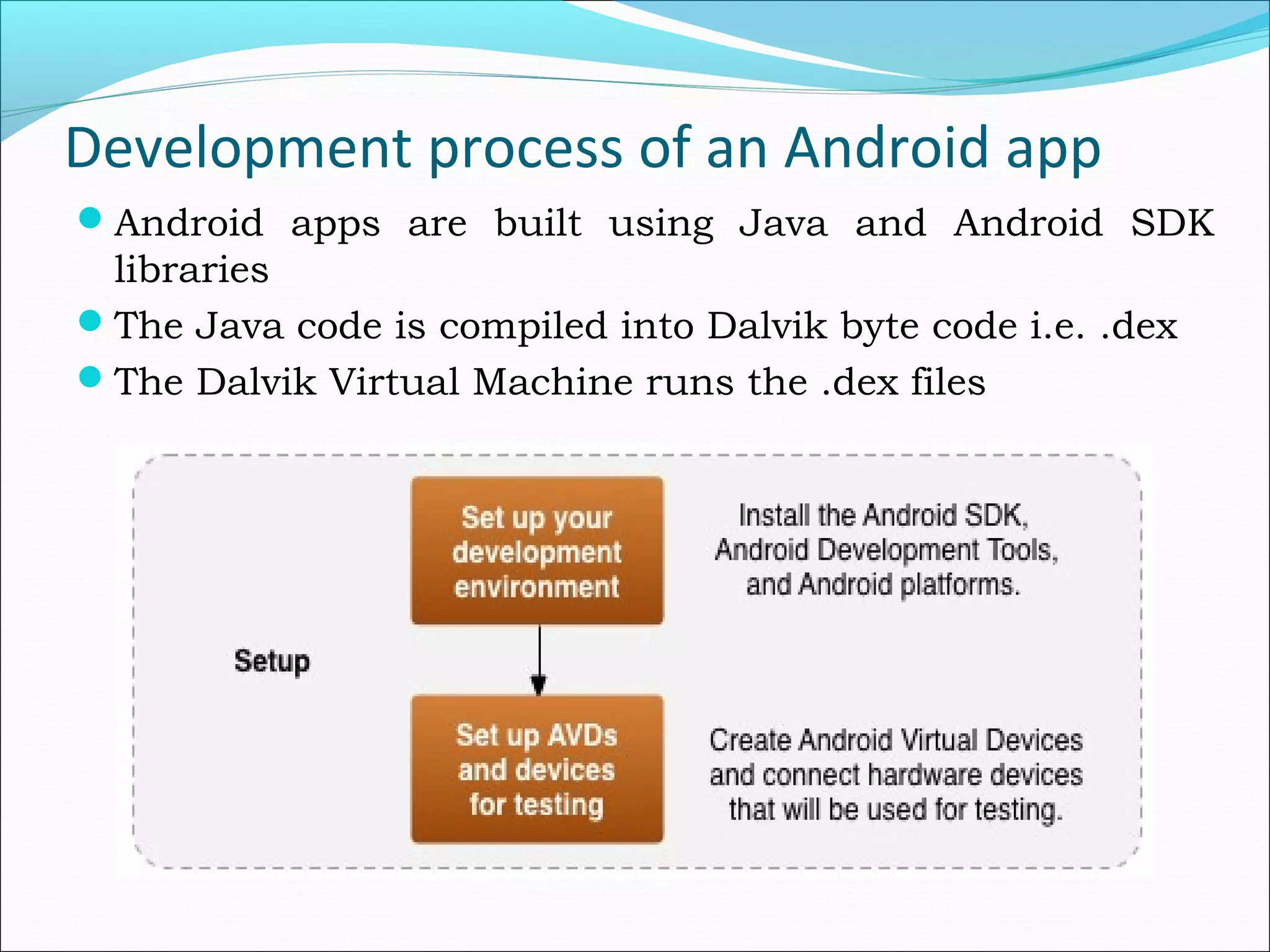
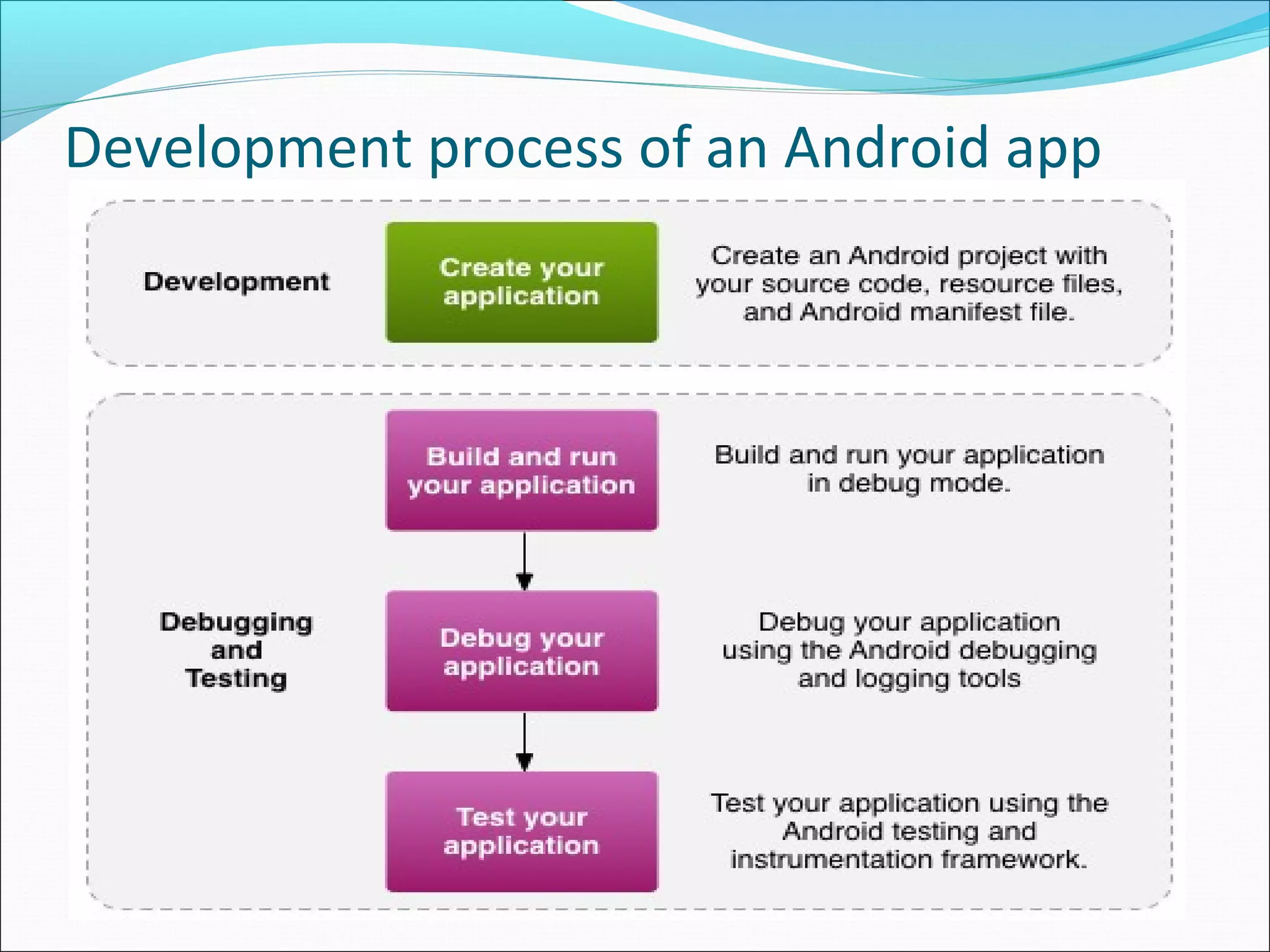
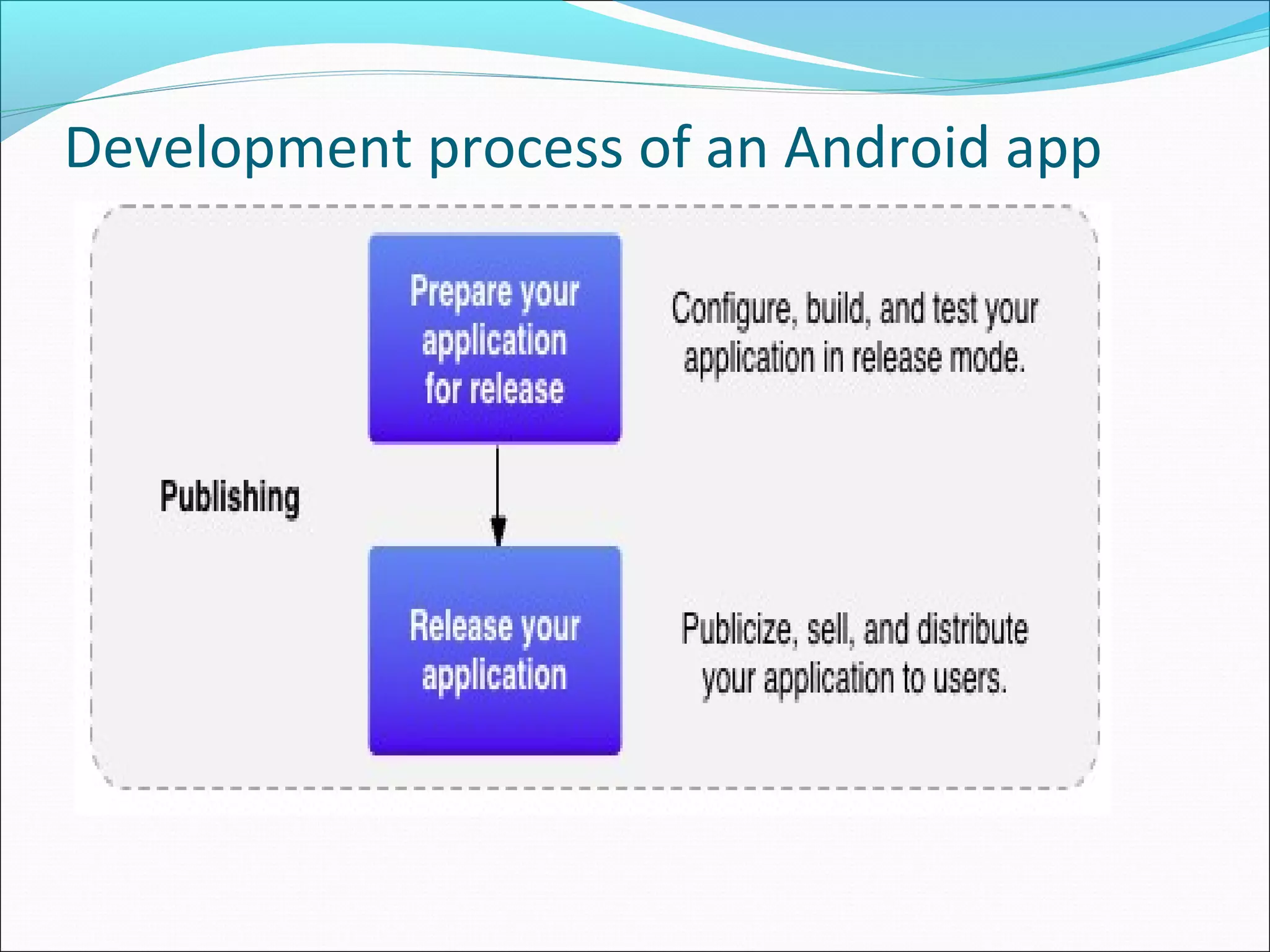
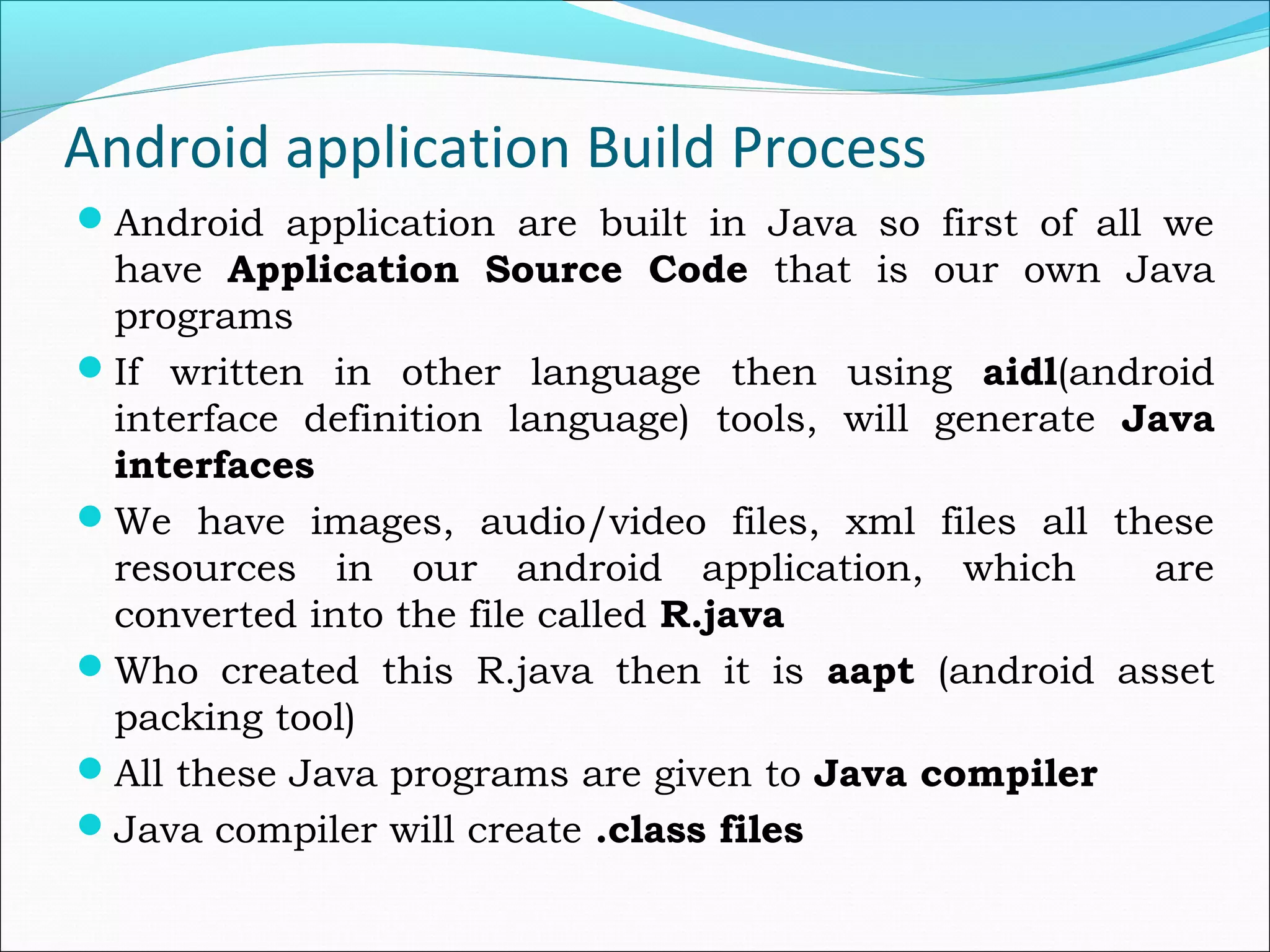
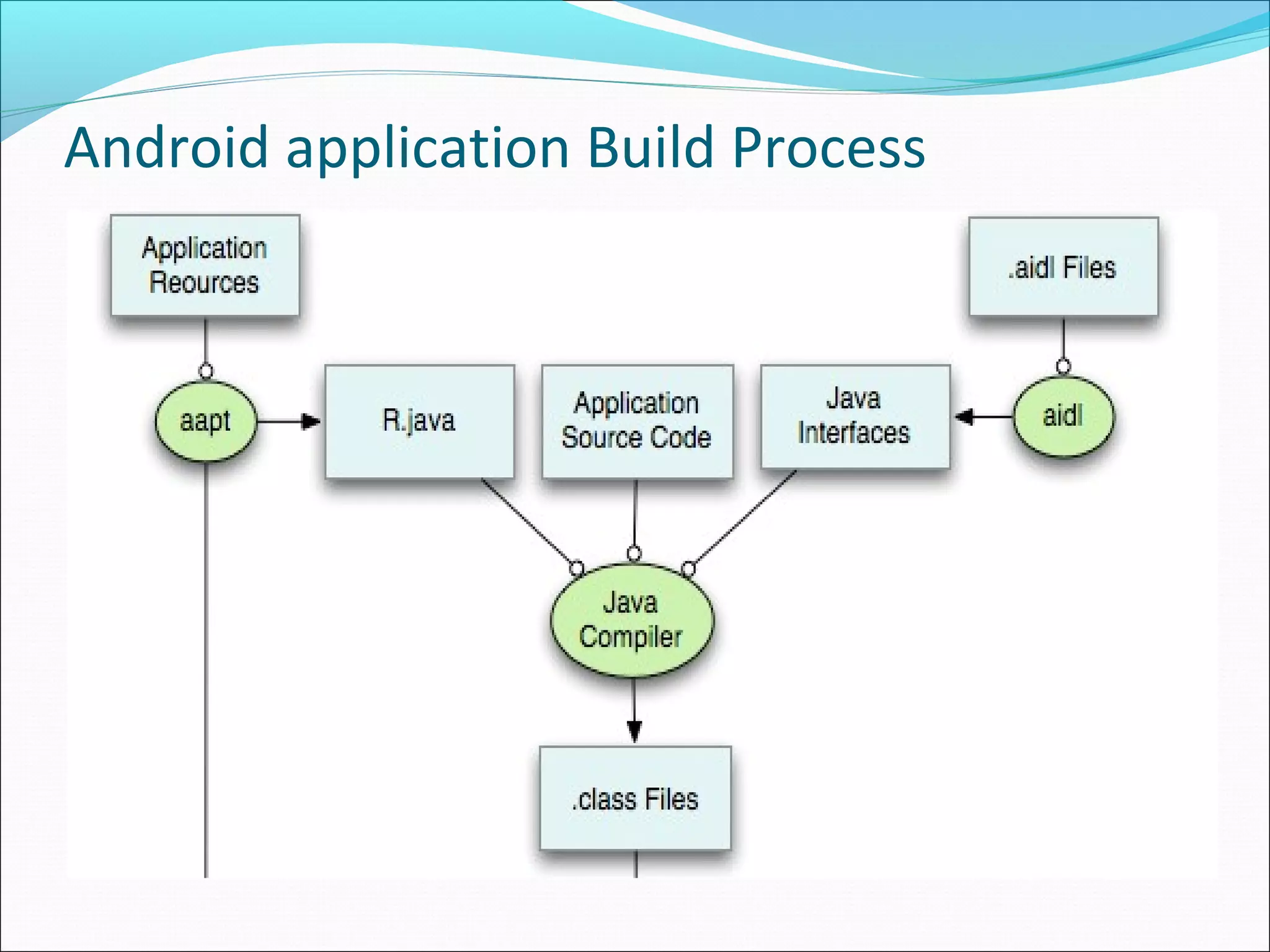
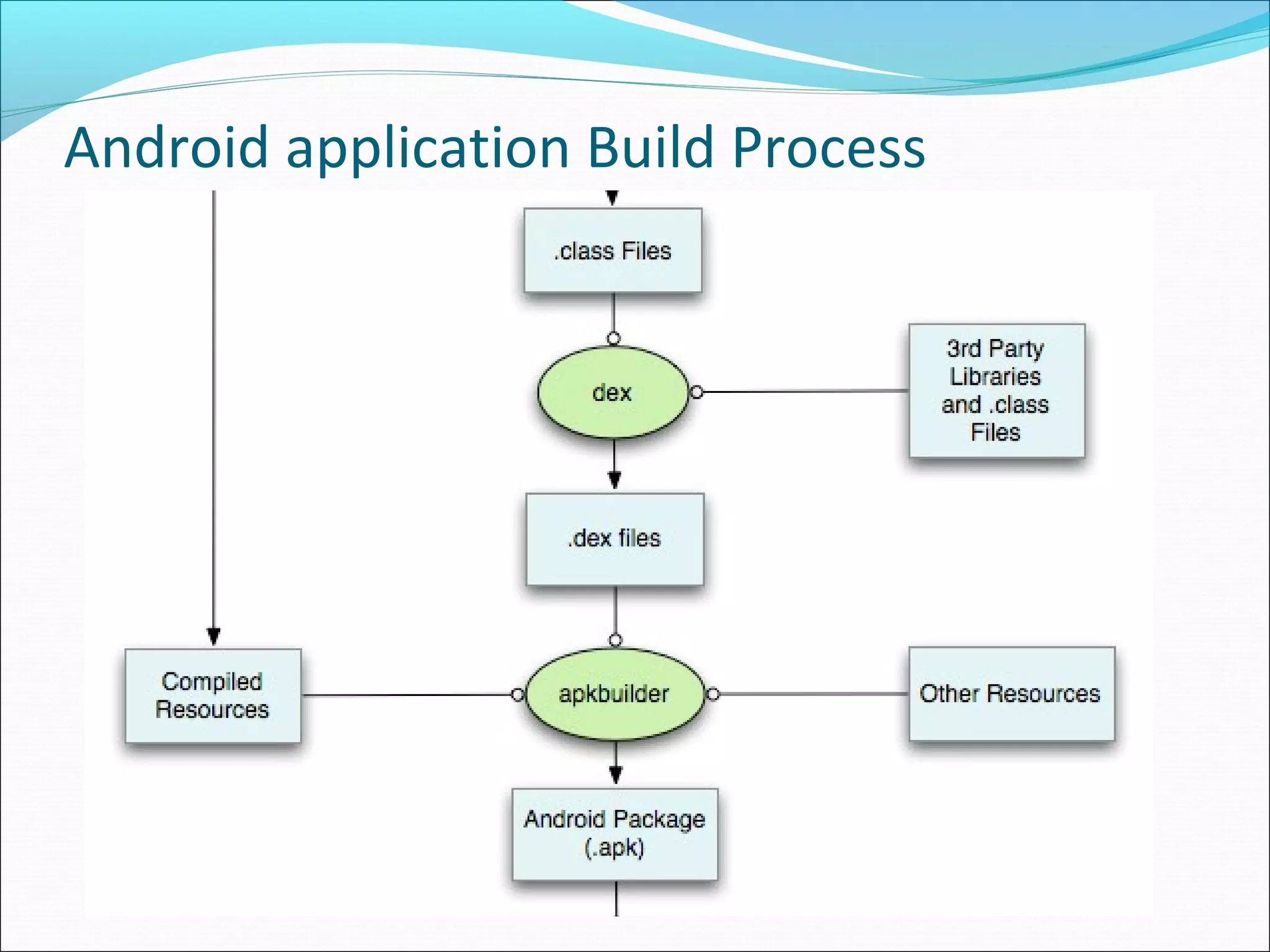
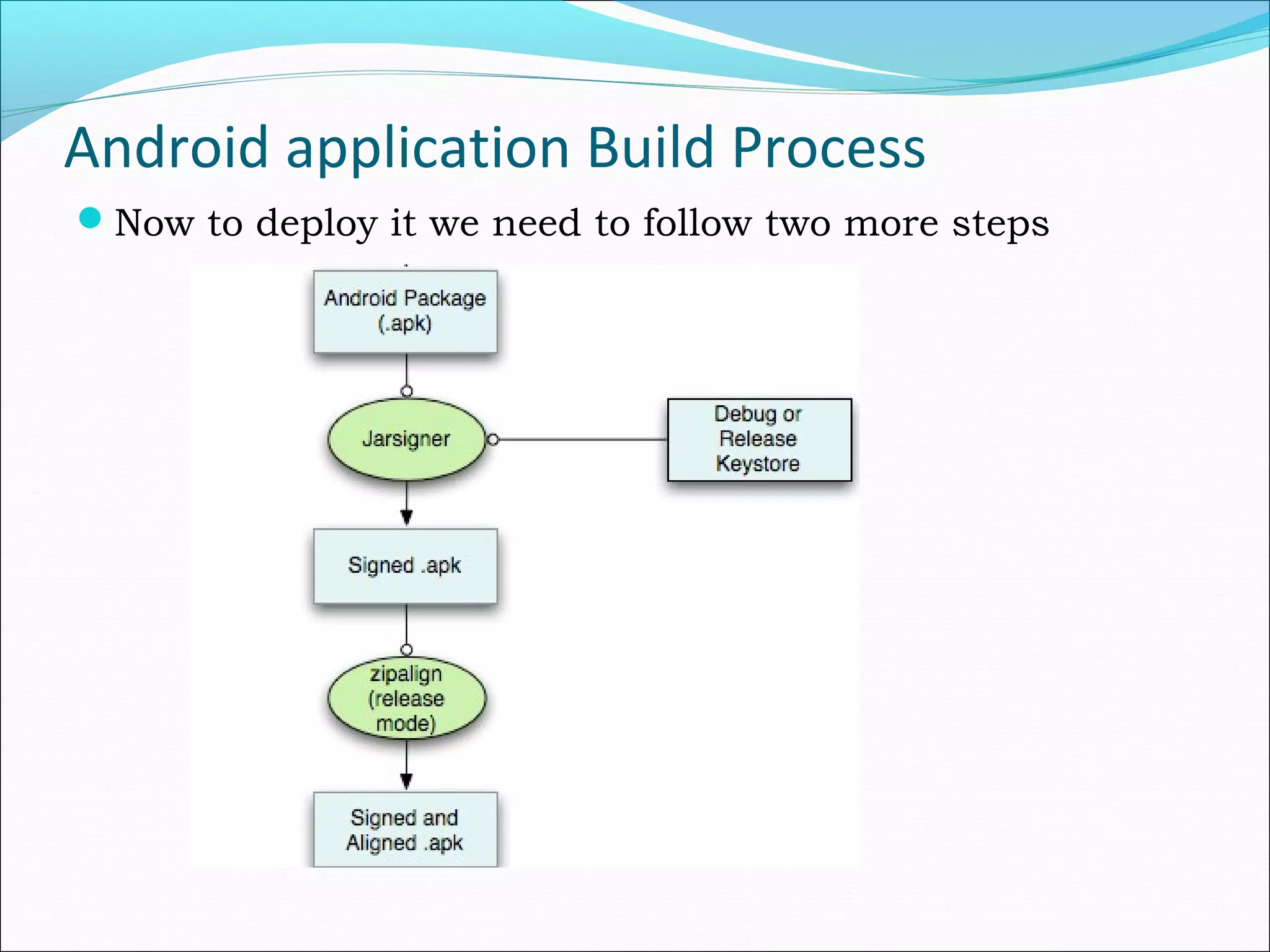
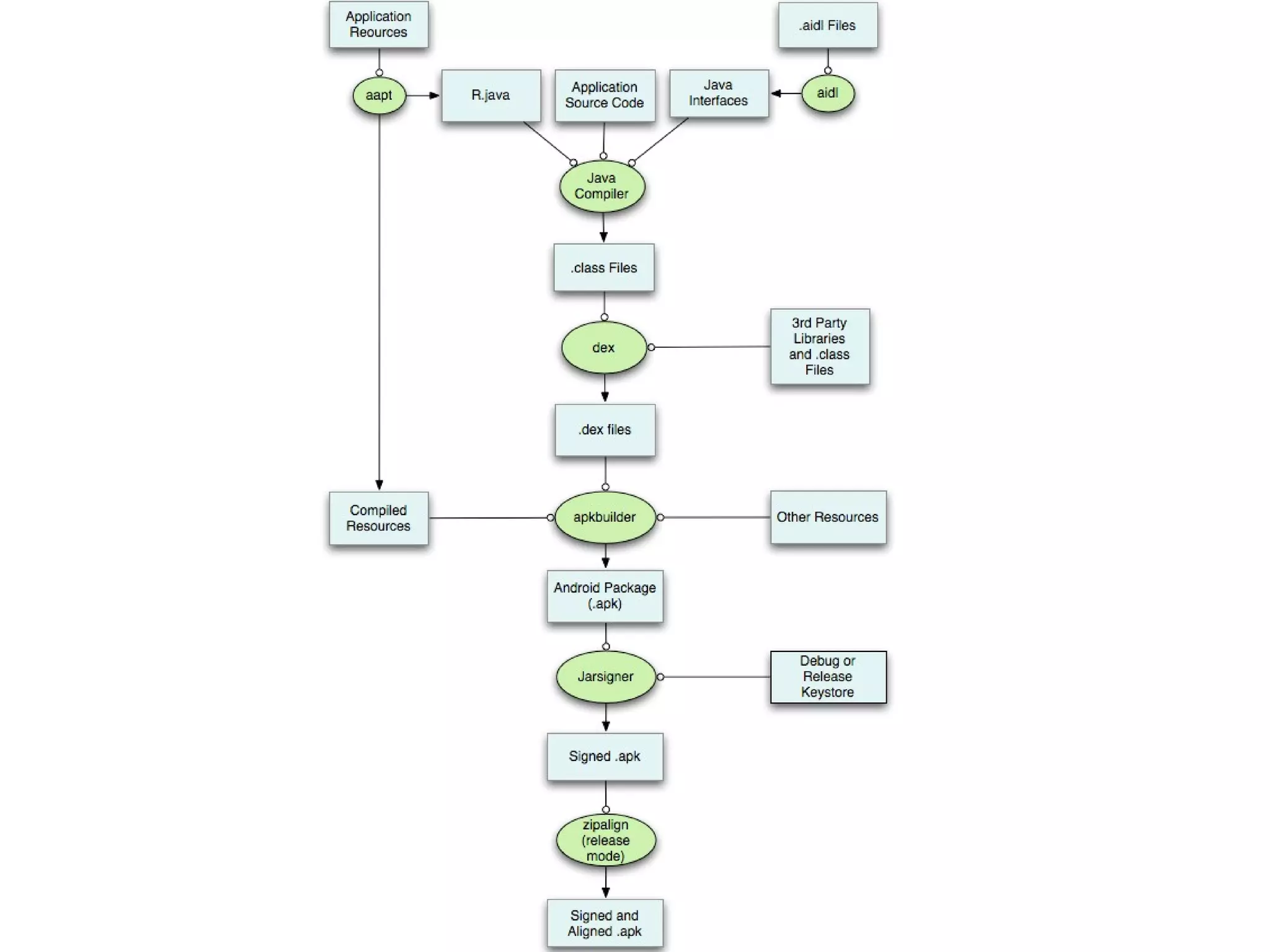
The document provides an overview of Android, covering its history, development, architecture, and the mobile app development process. It highlights Android as an open-source platform from Google and the Open Handset Alliance, showcasing its growth in the mobile market and various device applications. Key topics include Android versions, architecture layers, application development processes, and the tools and components involved in building Android applications.