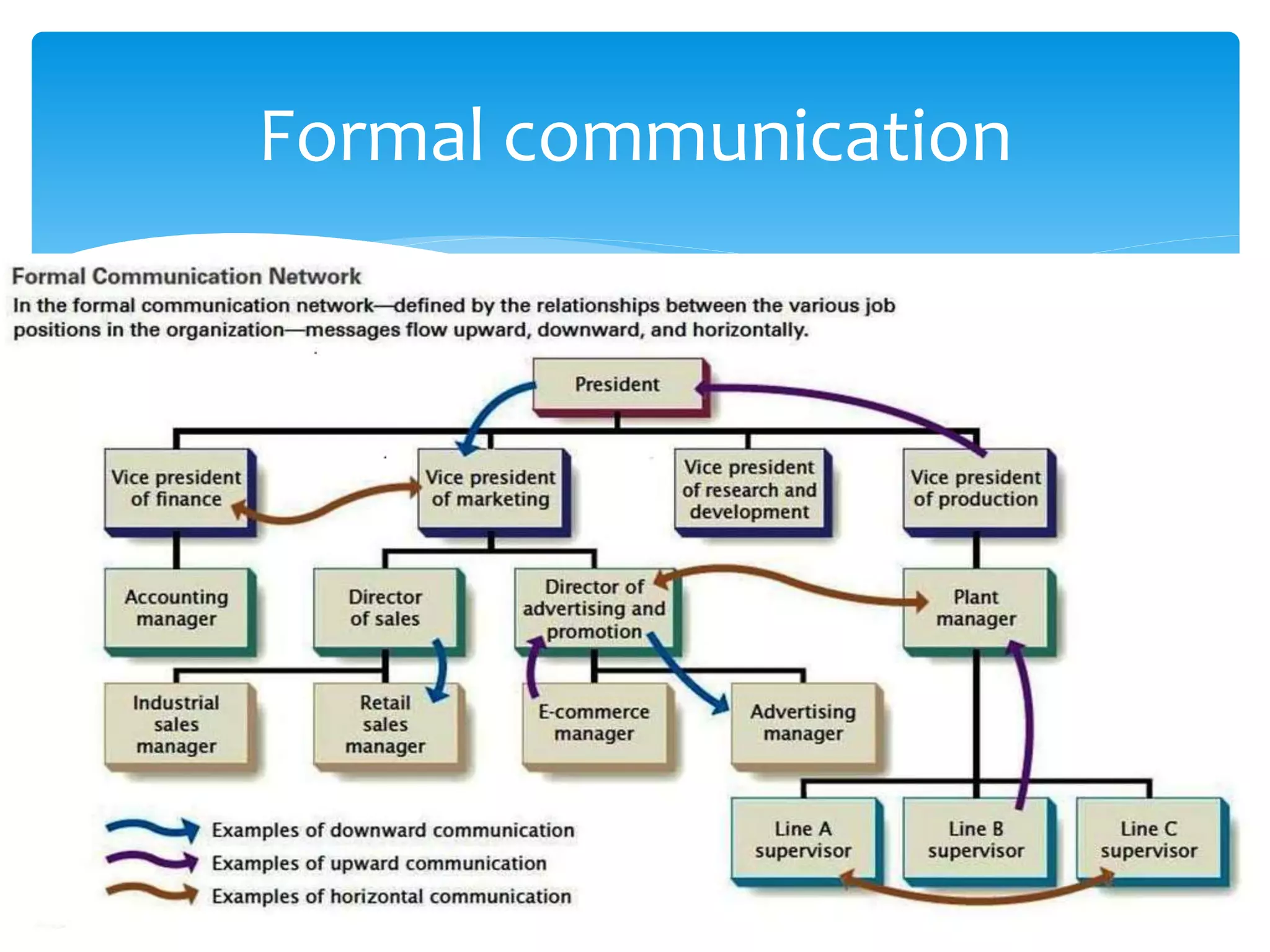
This document discusses various aspects of business communication. It defines business communication as communicating for business transactions to ensure mutual understanding. Most business communication is transactional and involves an exchange between sender and receiver. Good communication is important for business operations, sales, and profits. Internal communication occurs within an organization while external communication is between a business and outside world. The components of business communication include the source/sender, encoding, channel, decoding, receiver, and feedback. The document also discusses formal communication networks like single chain, wheel, circular, free flow, and inverted V.