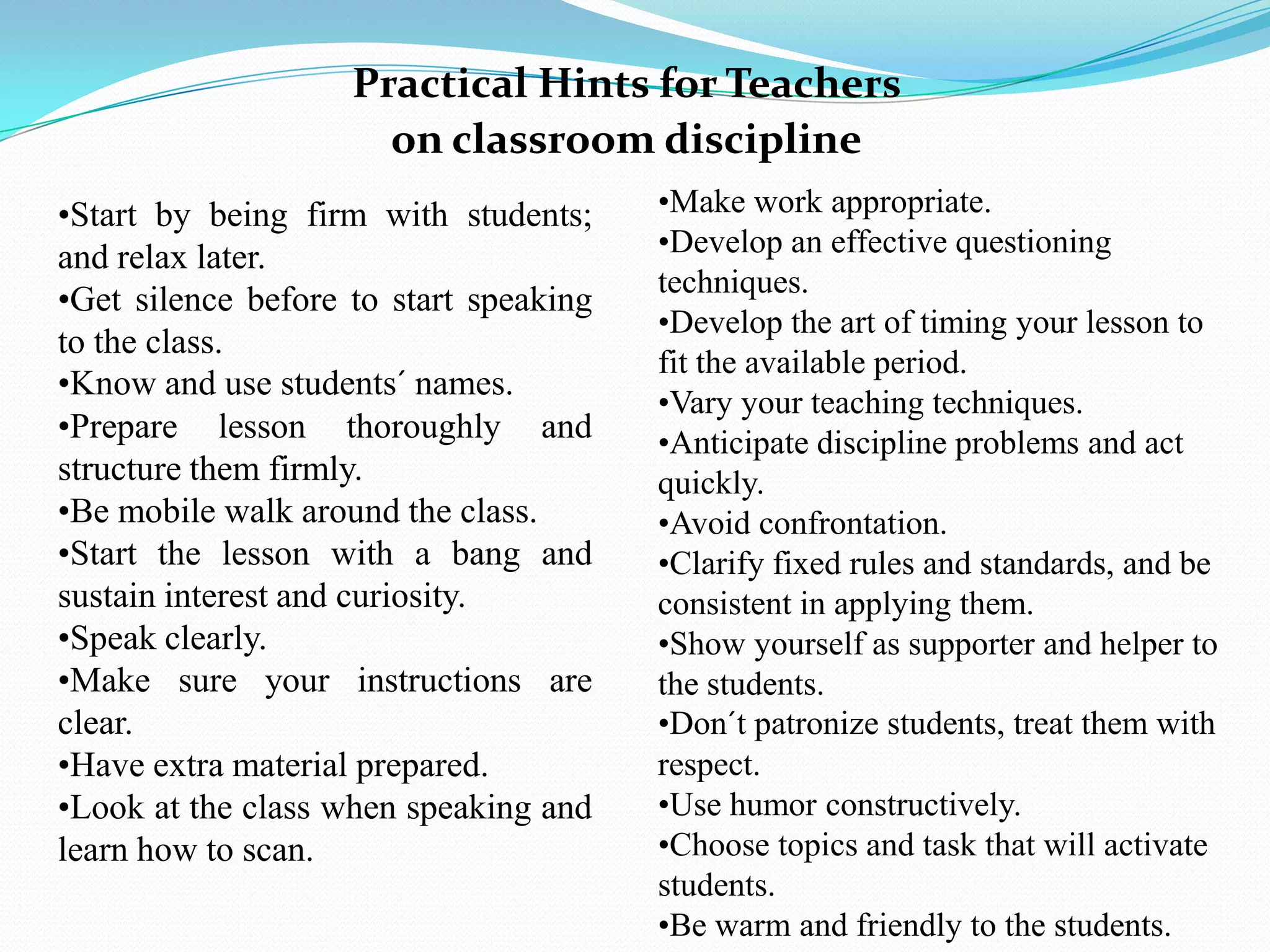
This document discusses classroom discipline from the perspectives of both teachers and students. It defines discipline as training imposed to improve self-control and obedience through regulations and authority. Effective classroom discipline involves promoting appropriate behavior, developing relationships, and establishing a productive learning environment. Factors that contribute to management include methodology, interpersonal skills, student motivation, and clear expectations. The document provides practical tips for teachers to maintain discipline such as being firm yet flexible, engaging students, anticipating issues, and treating students with respect.