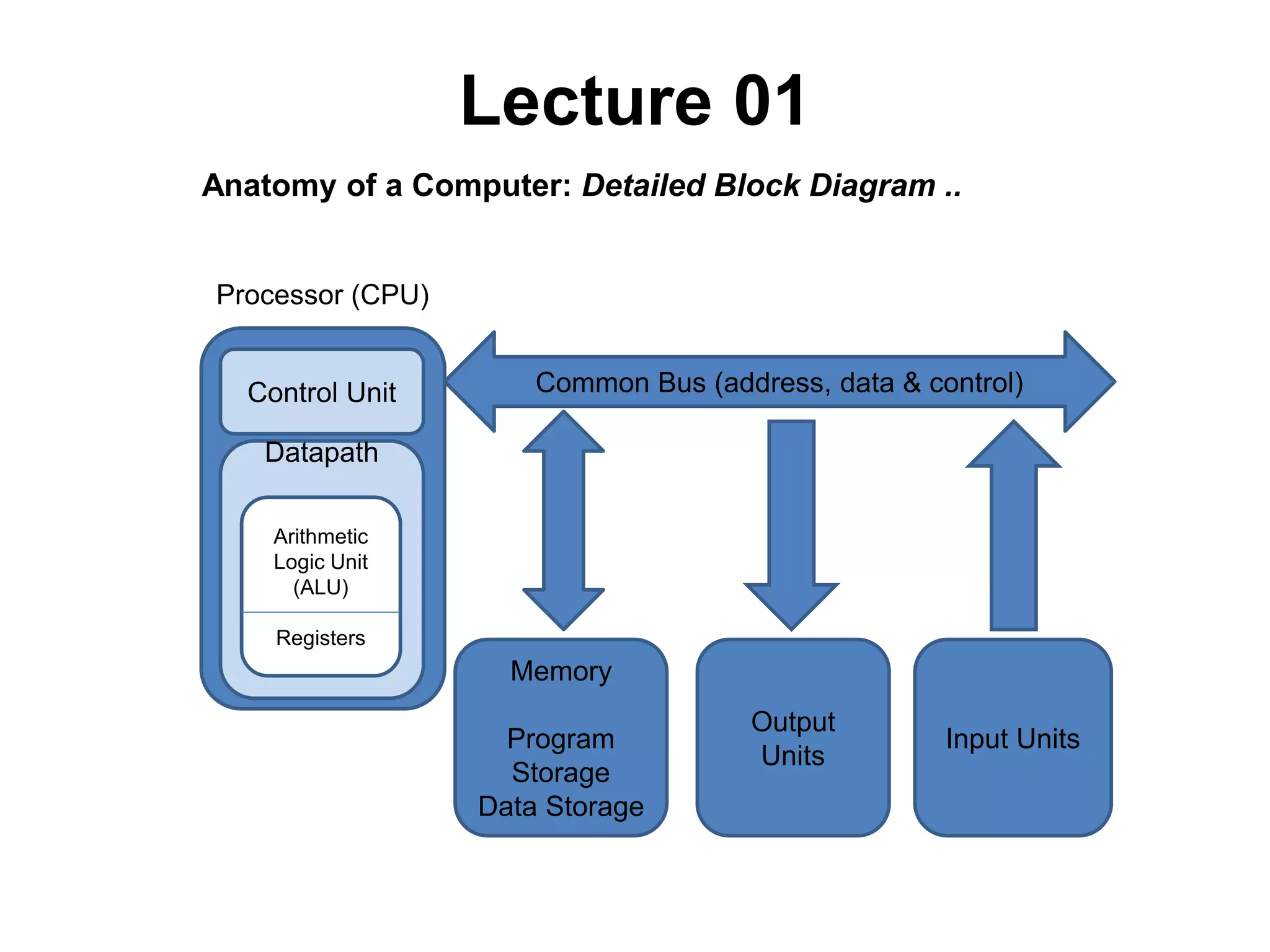
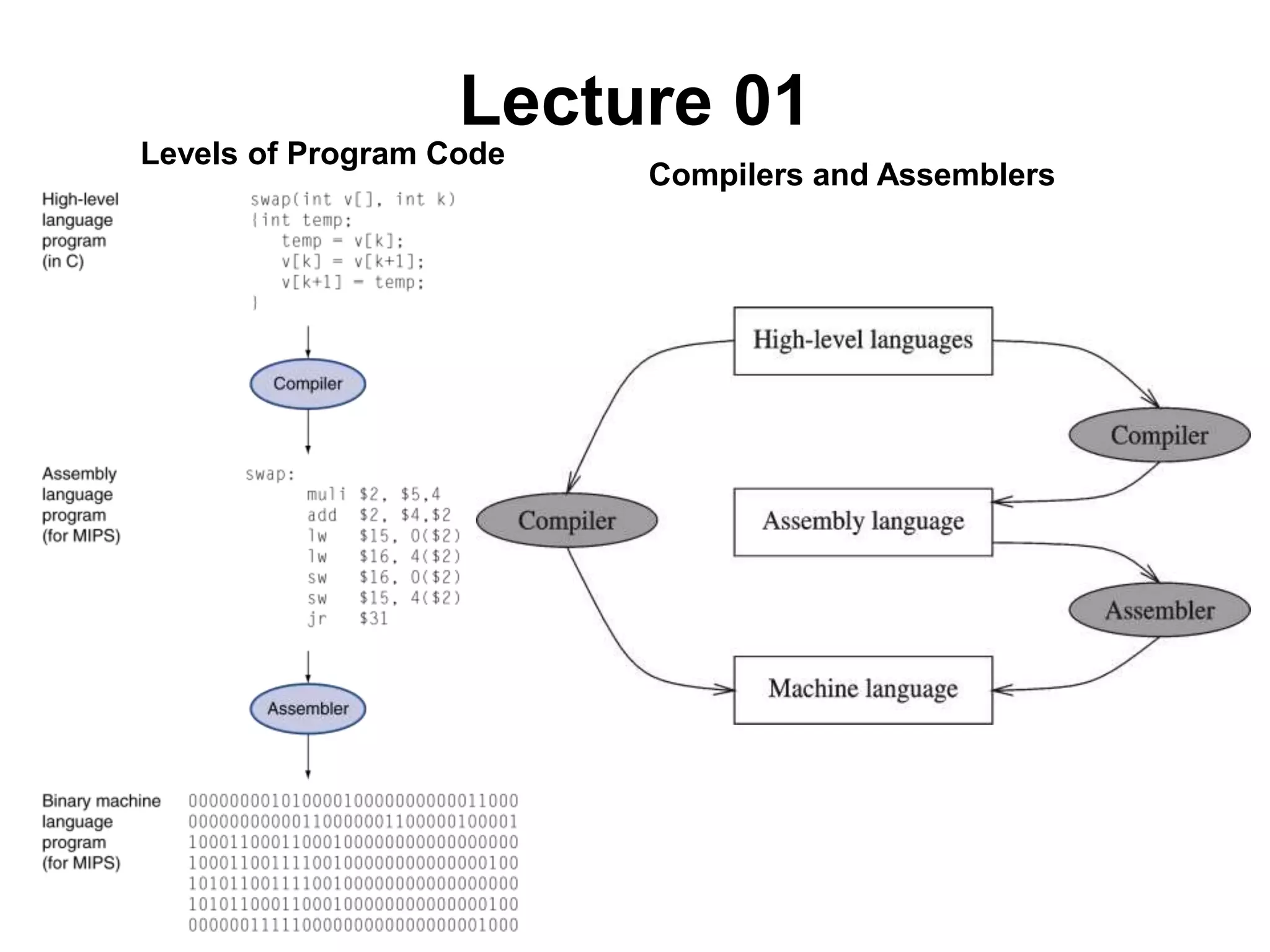
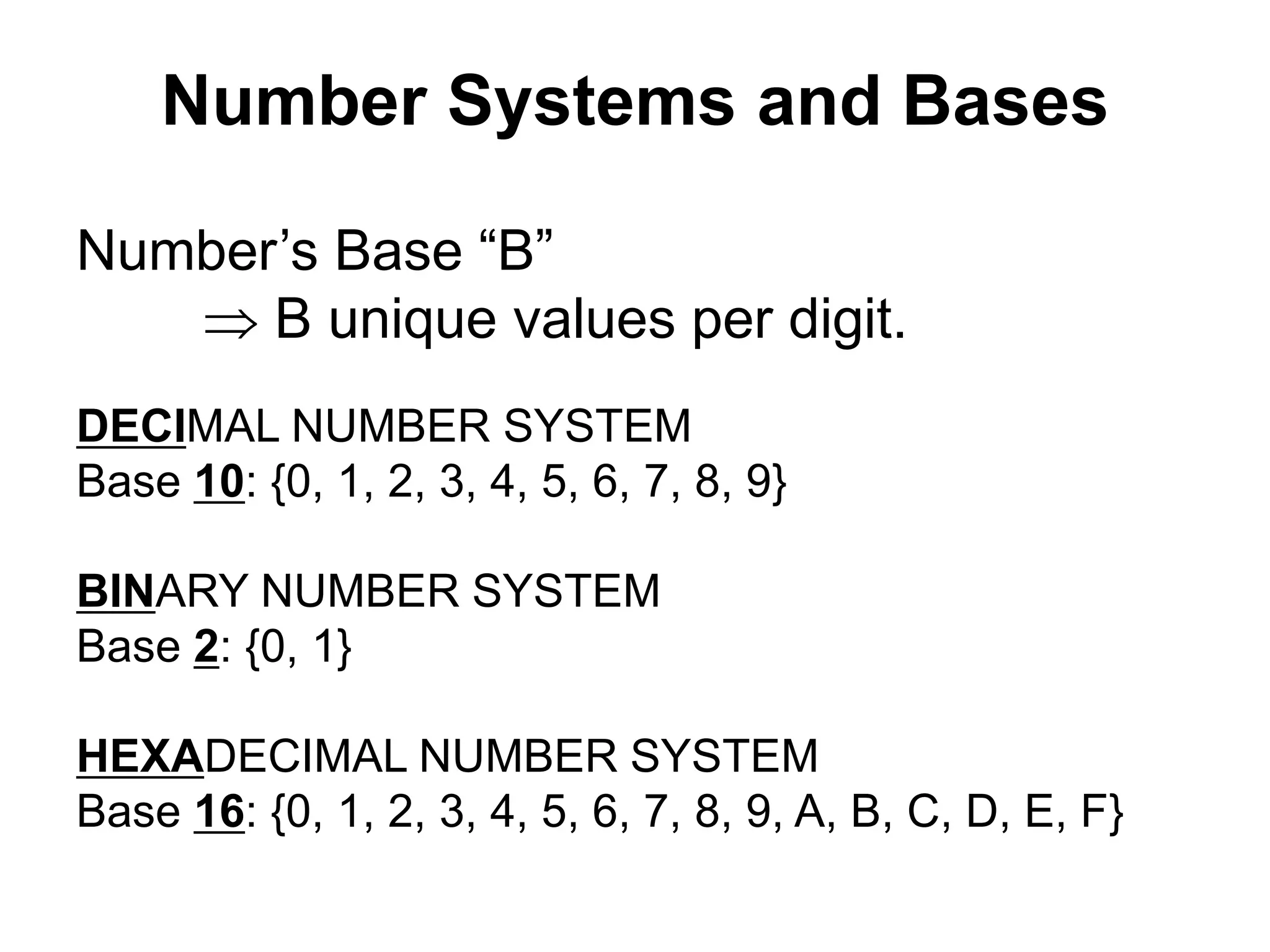
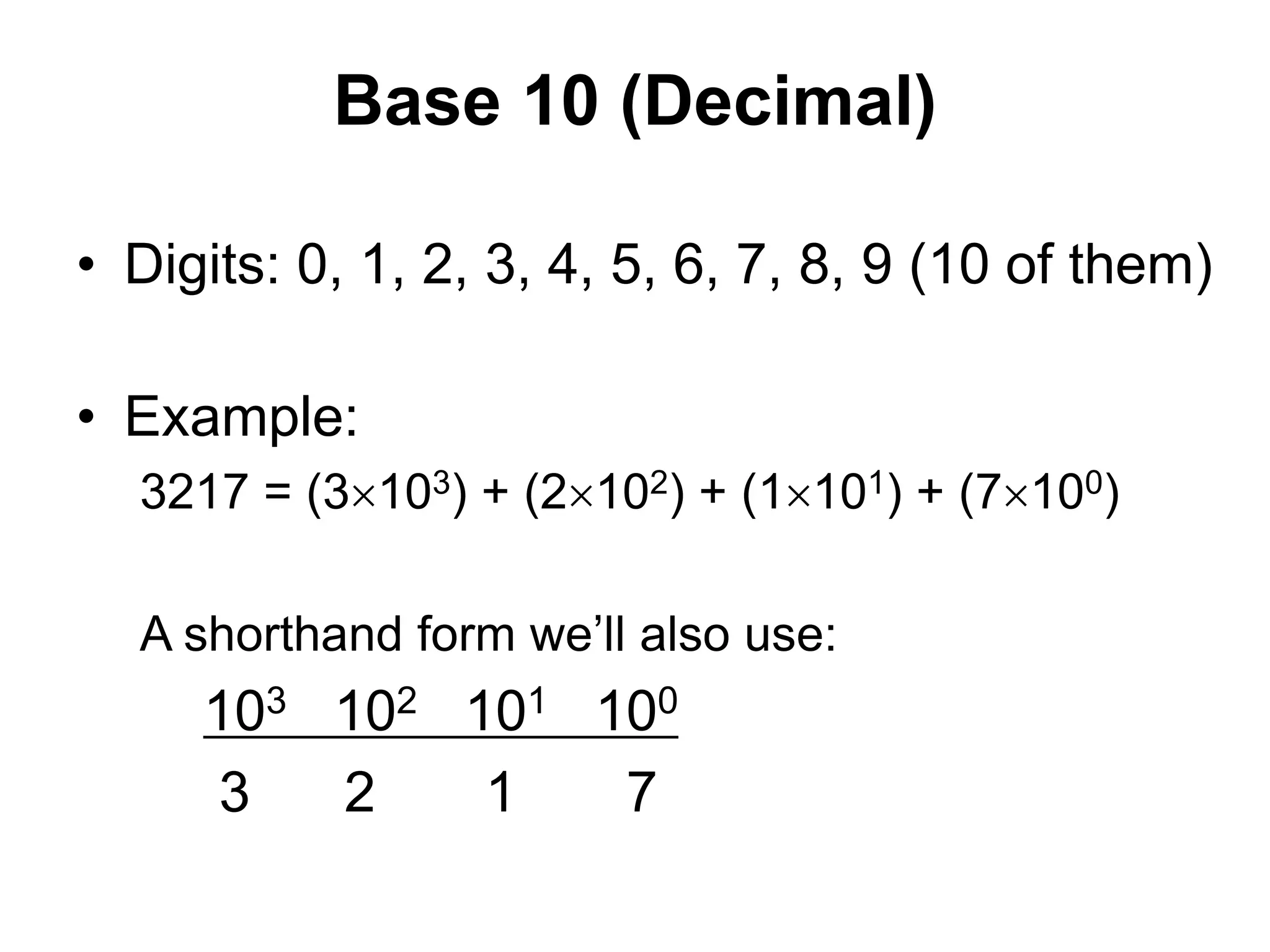
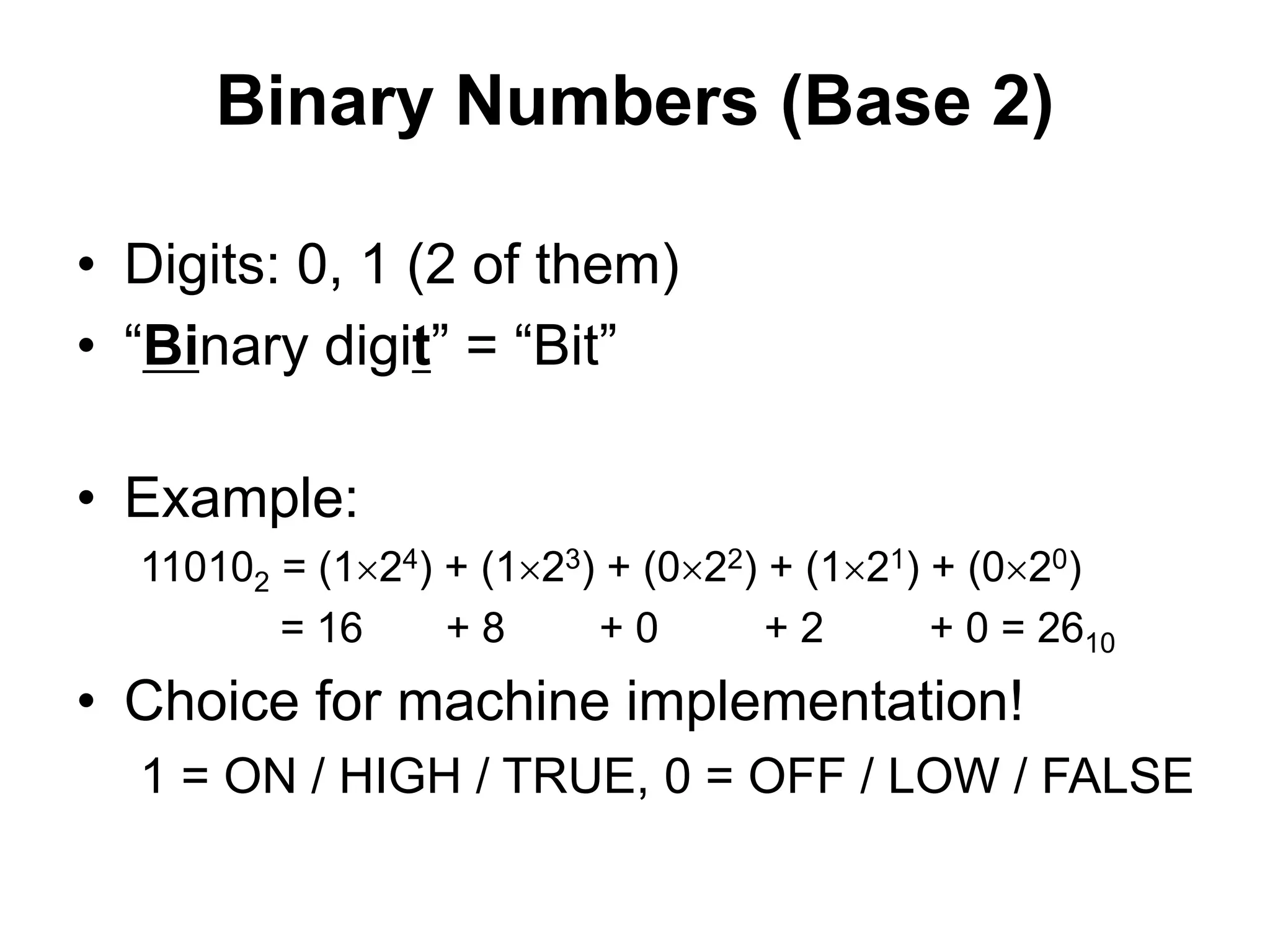
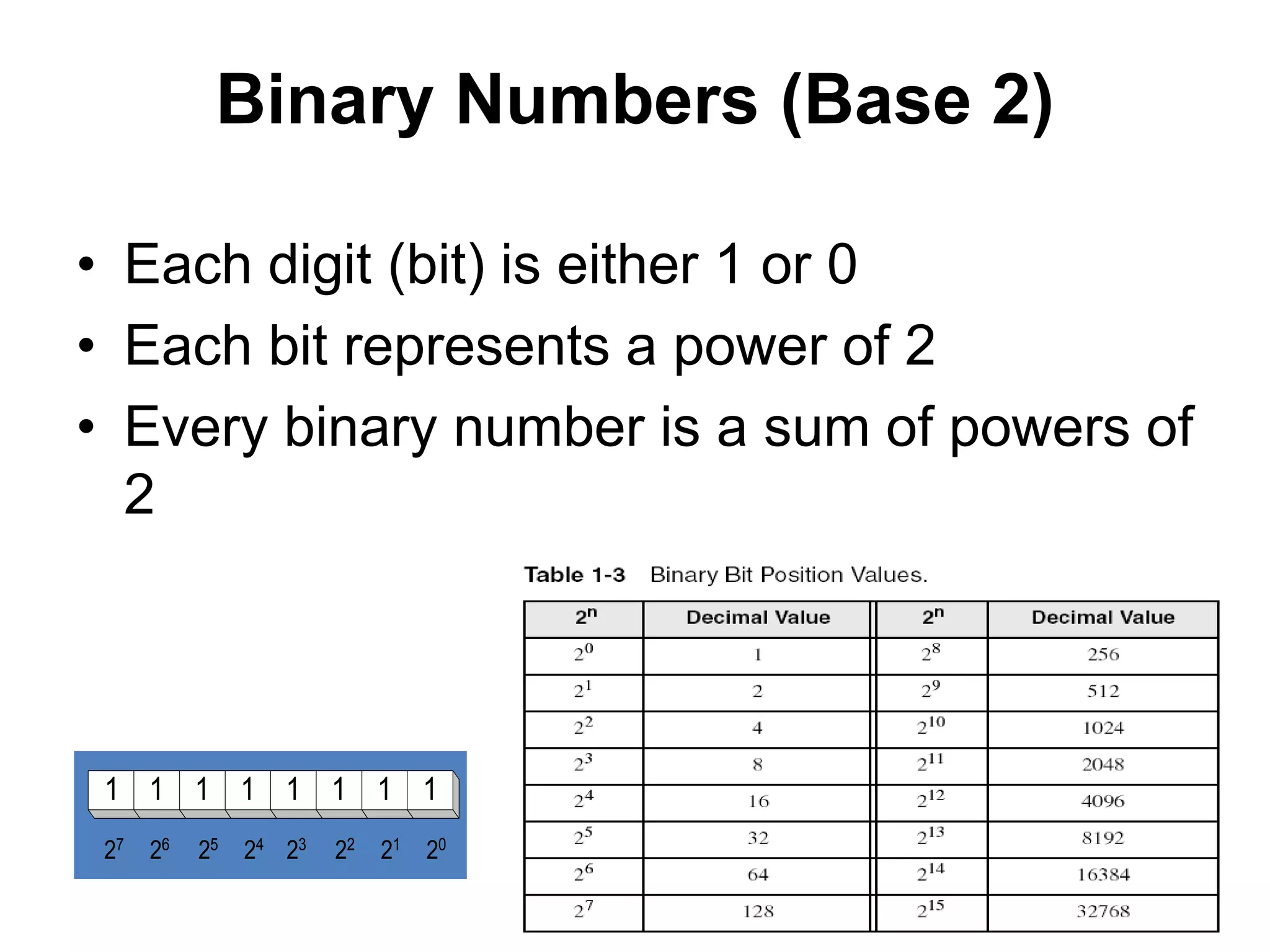
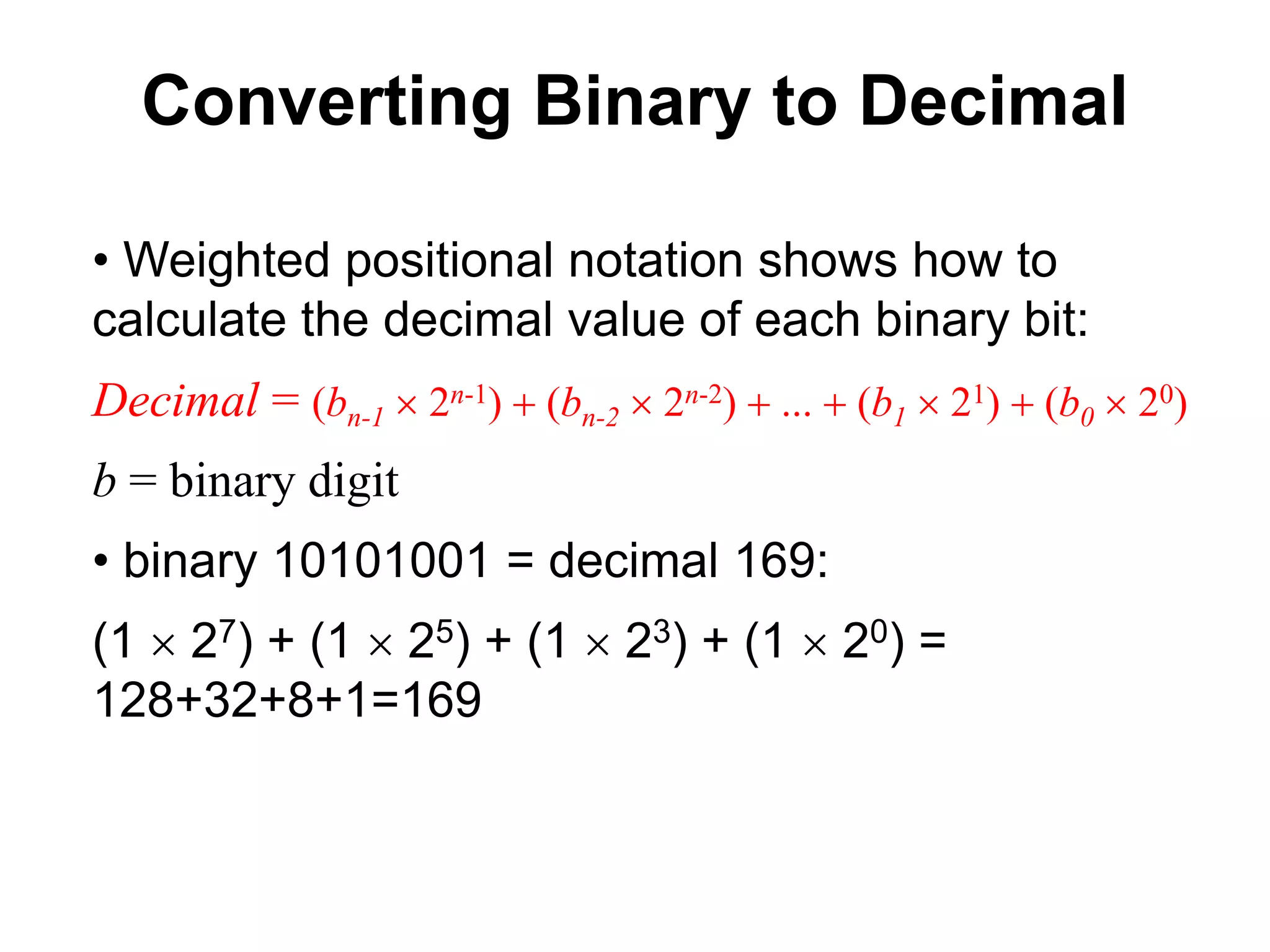
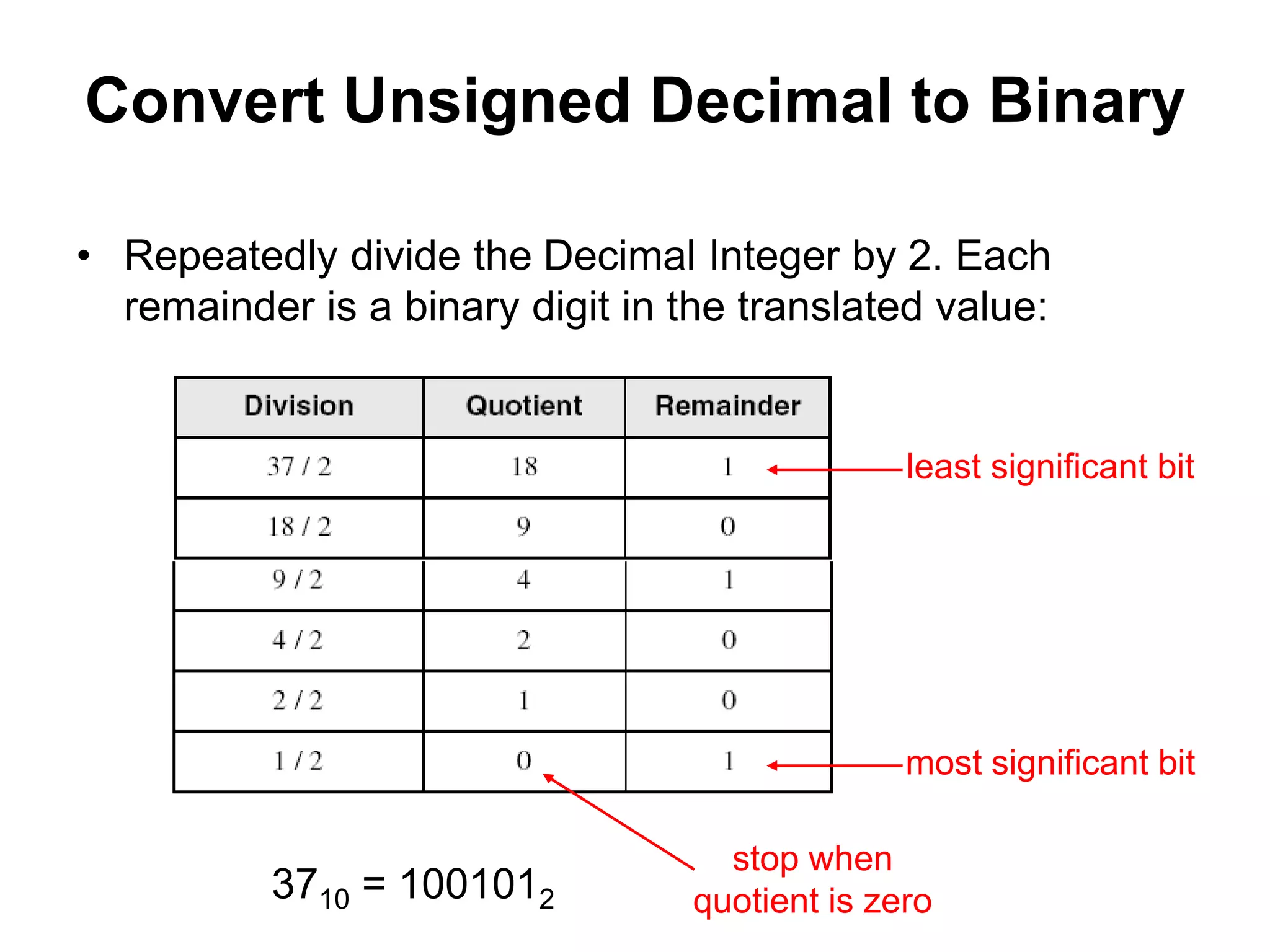
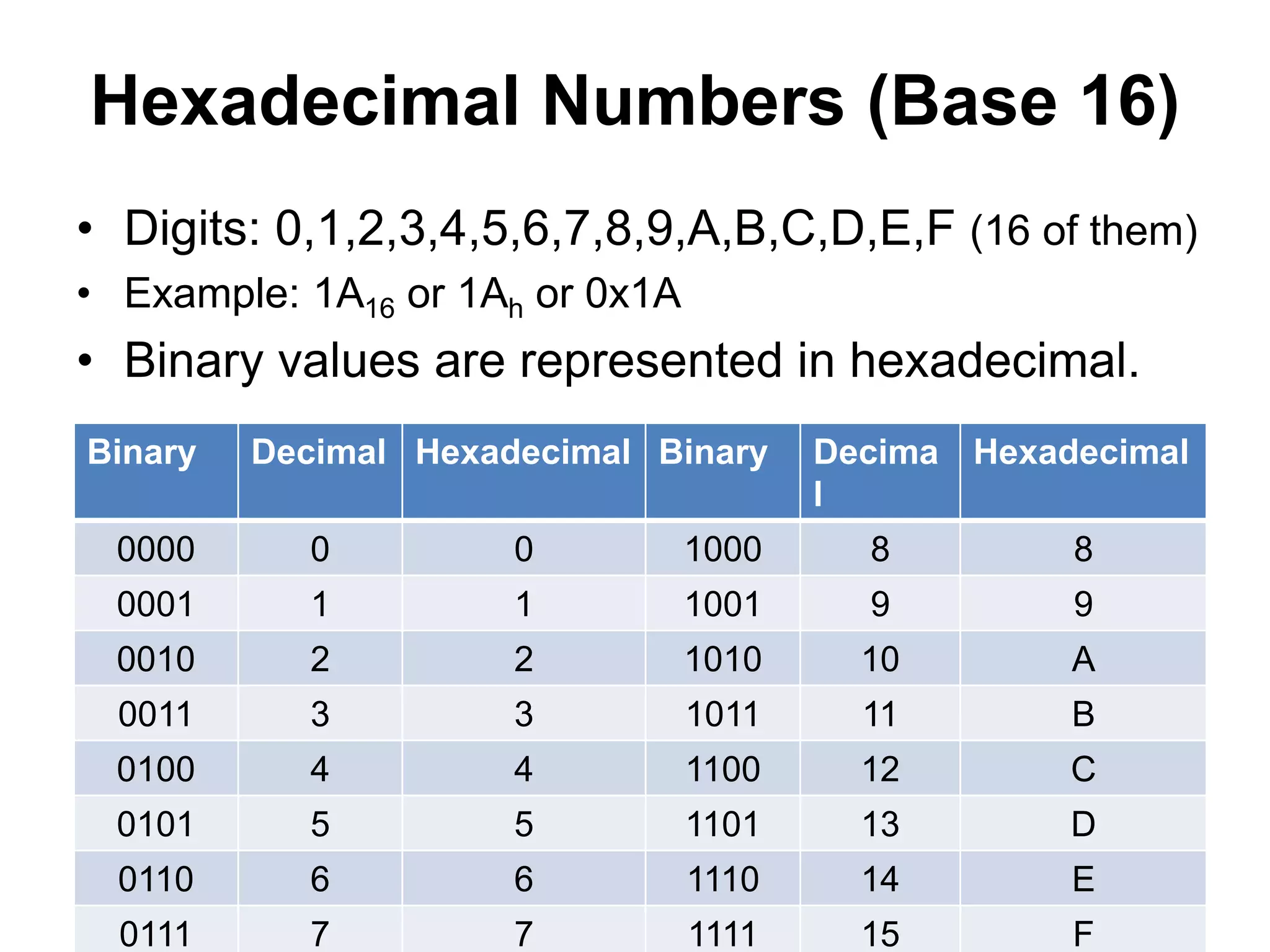
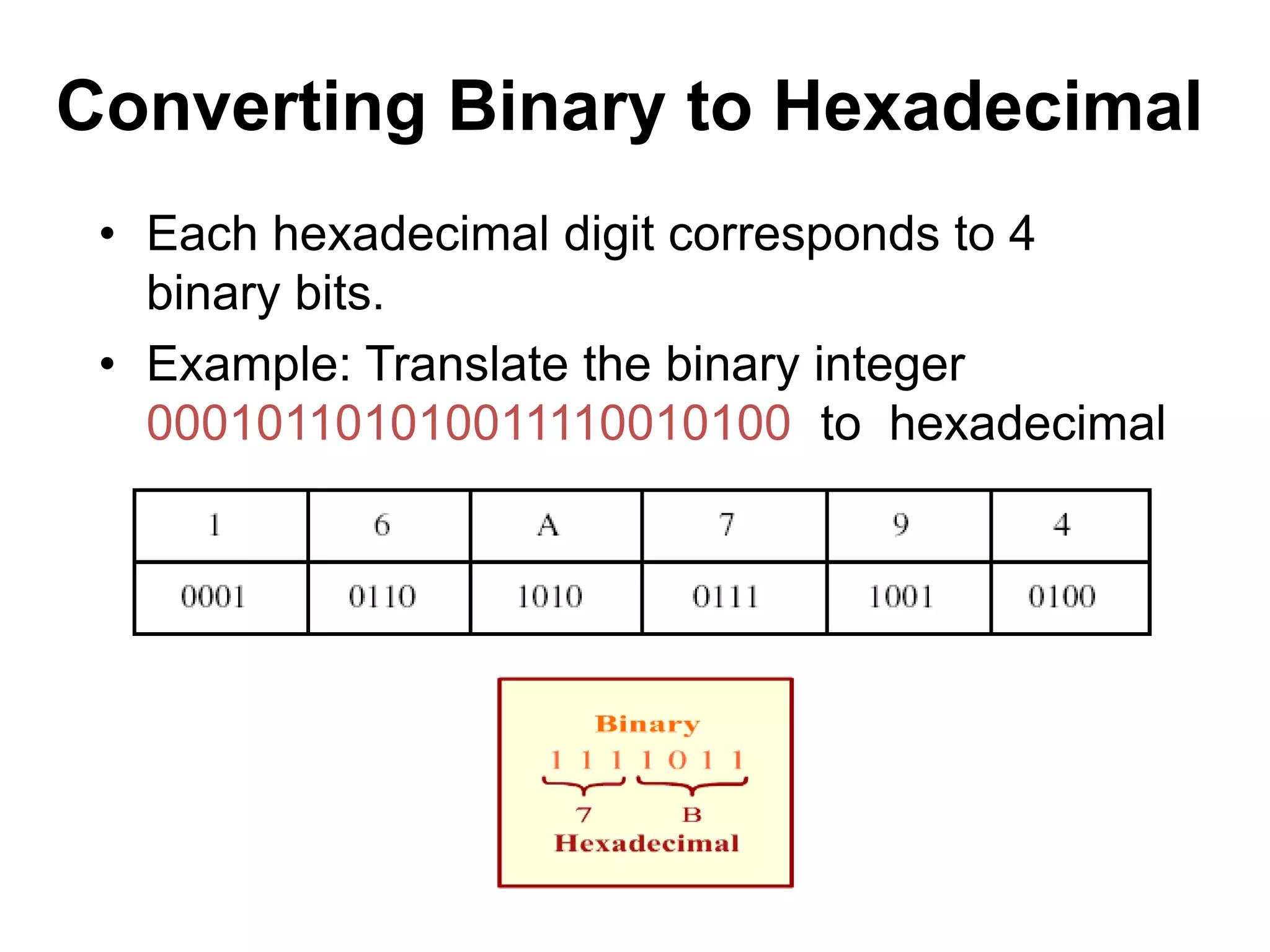
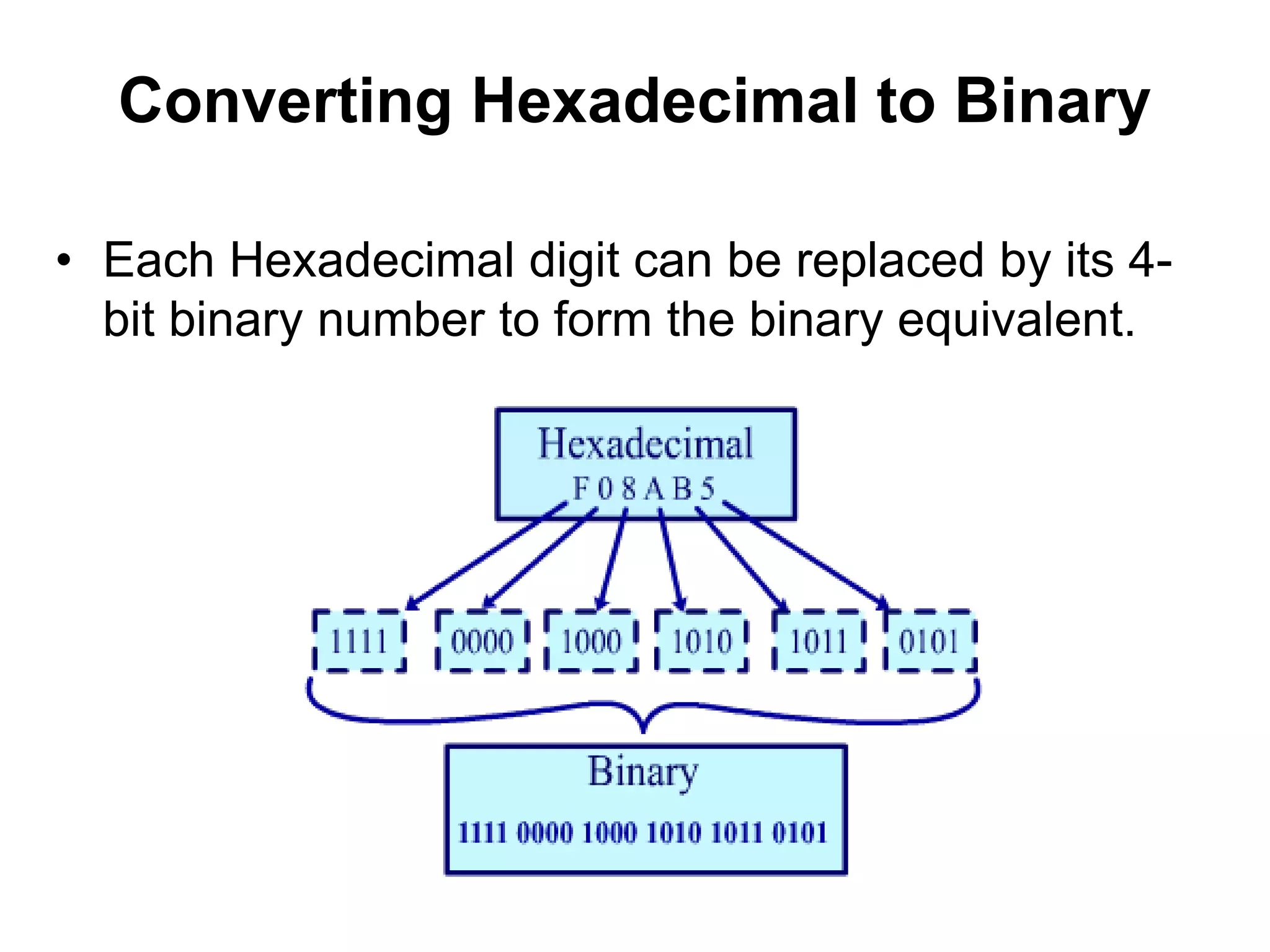
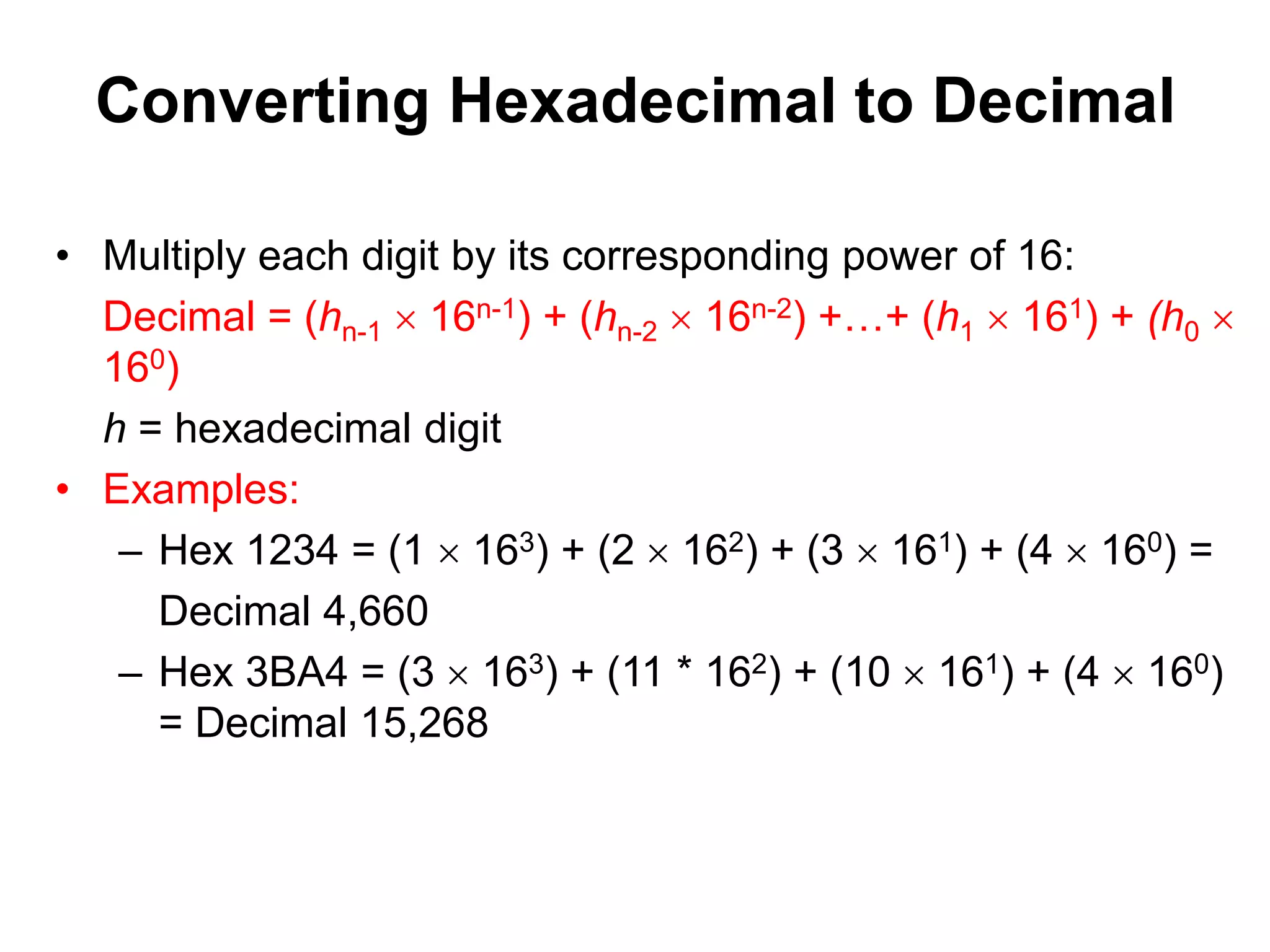
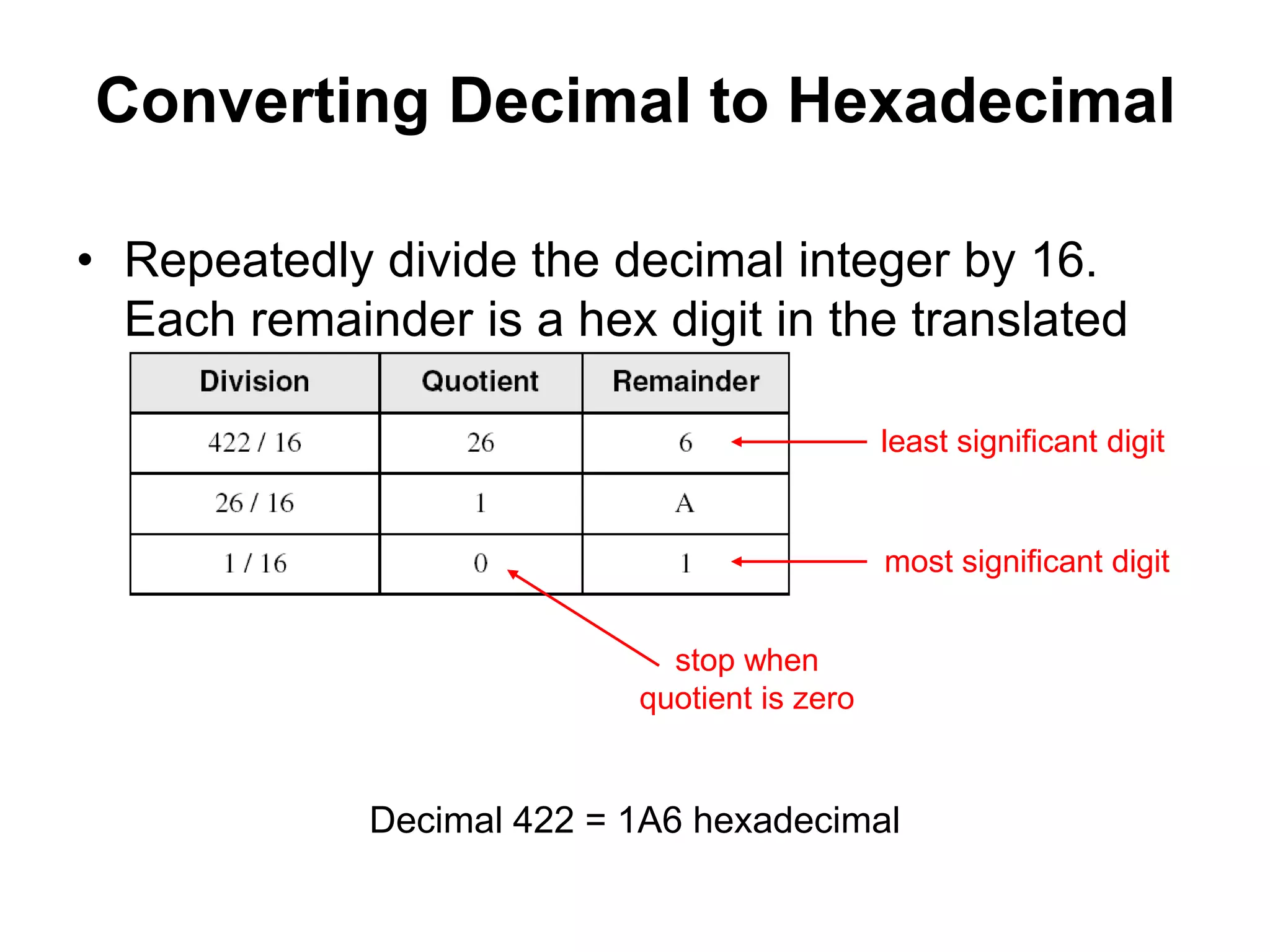
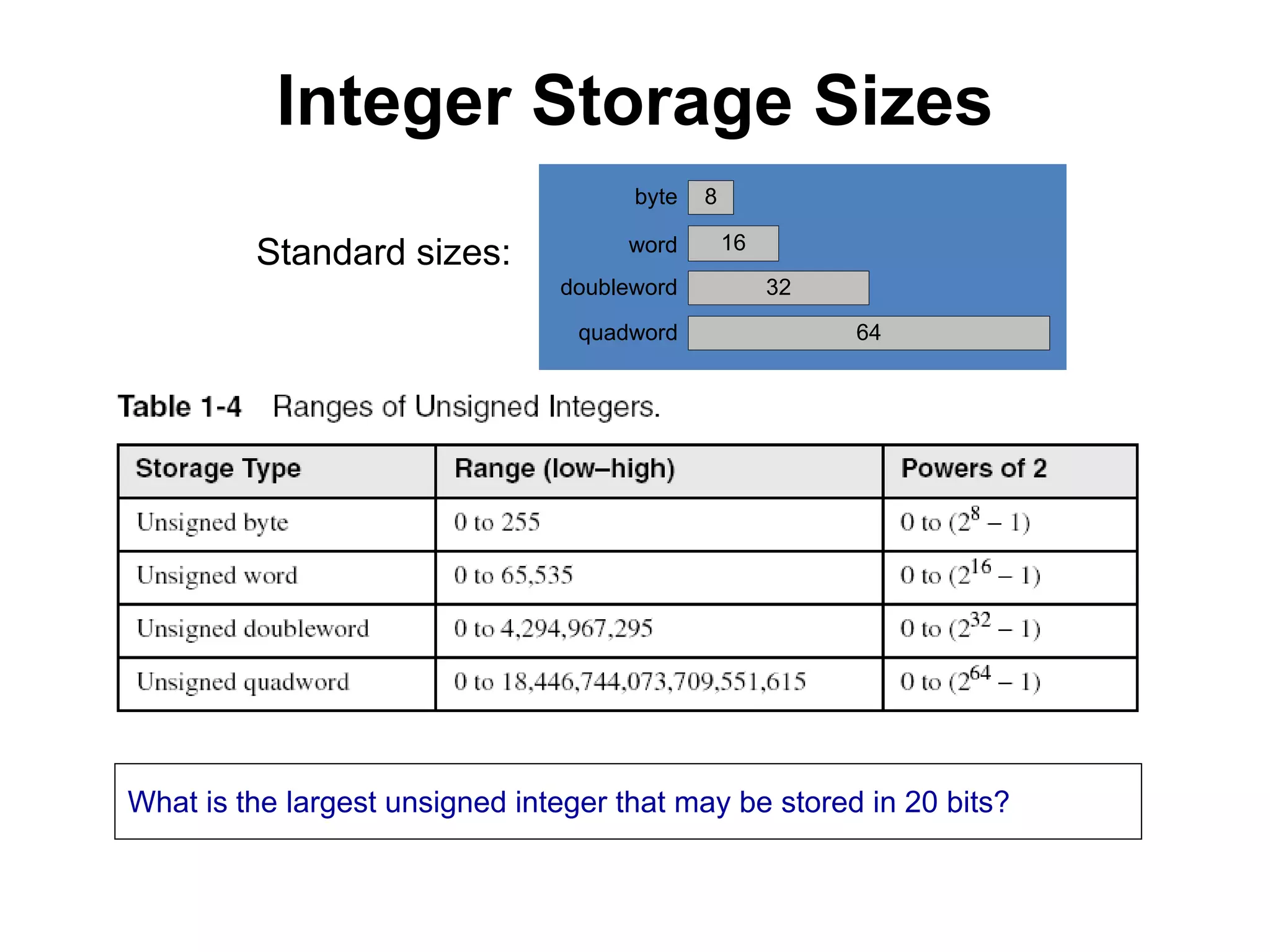
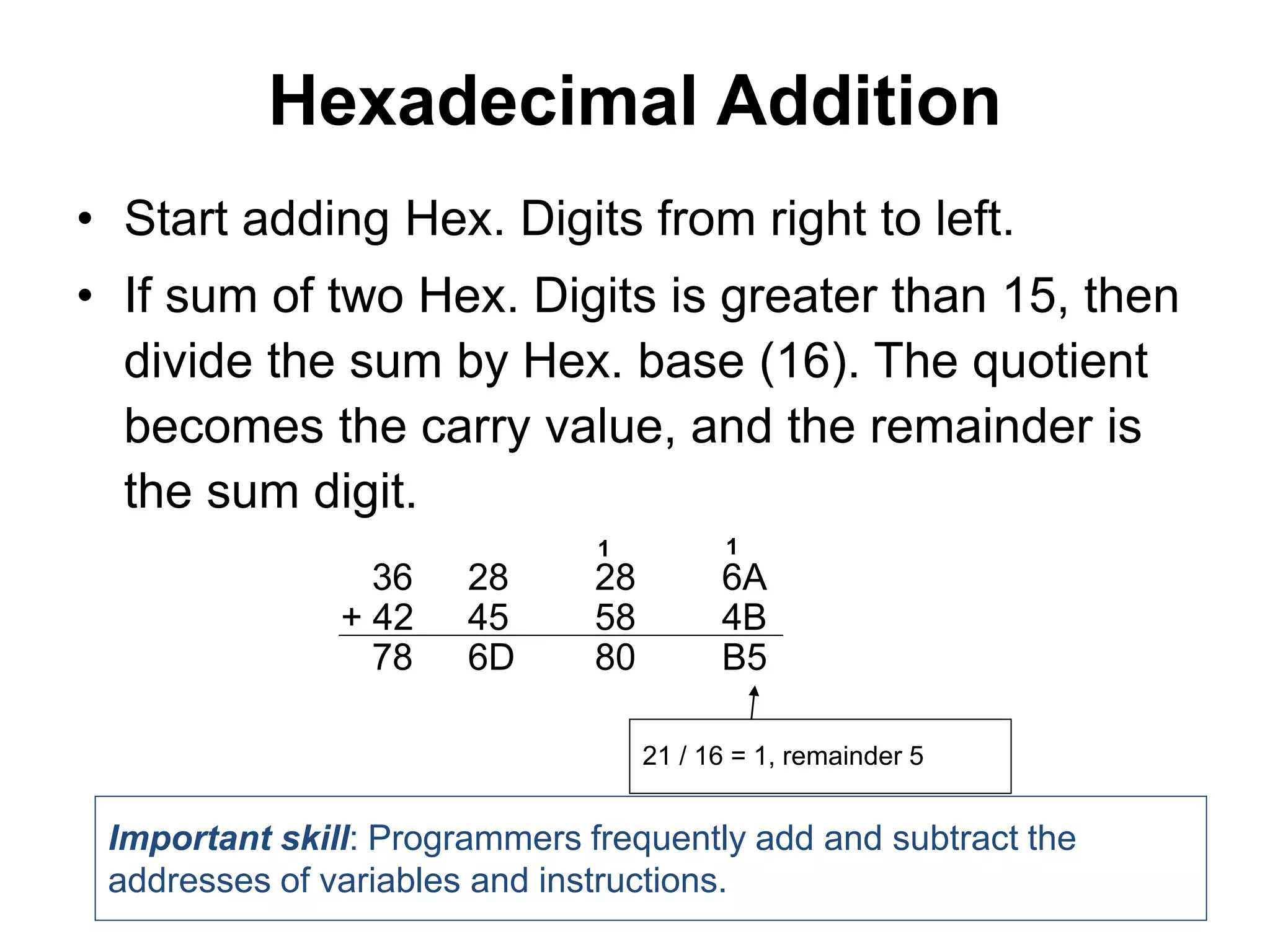
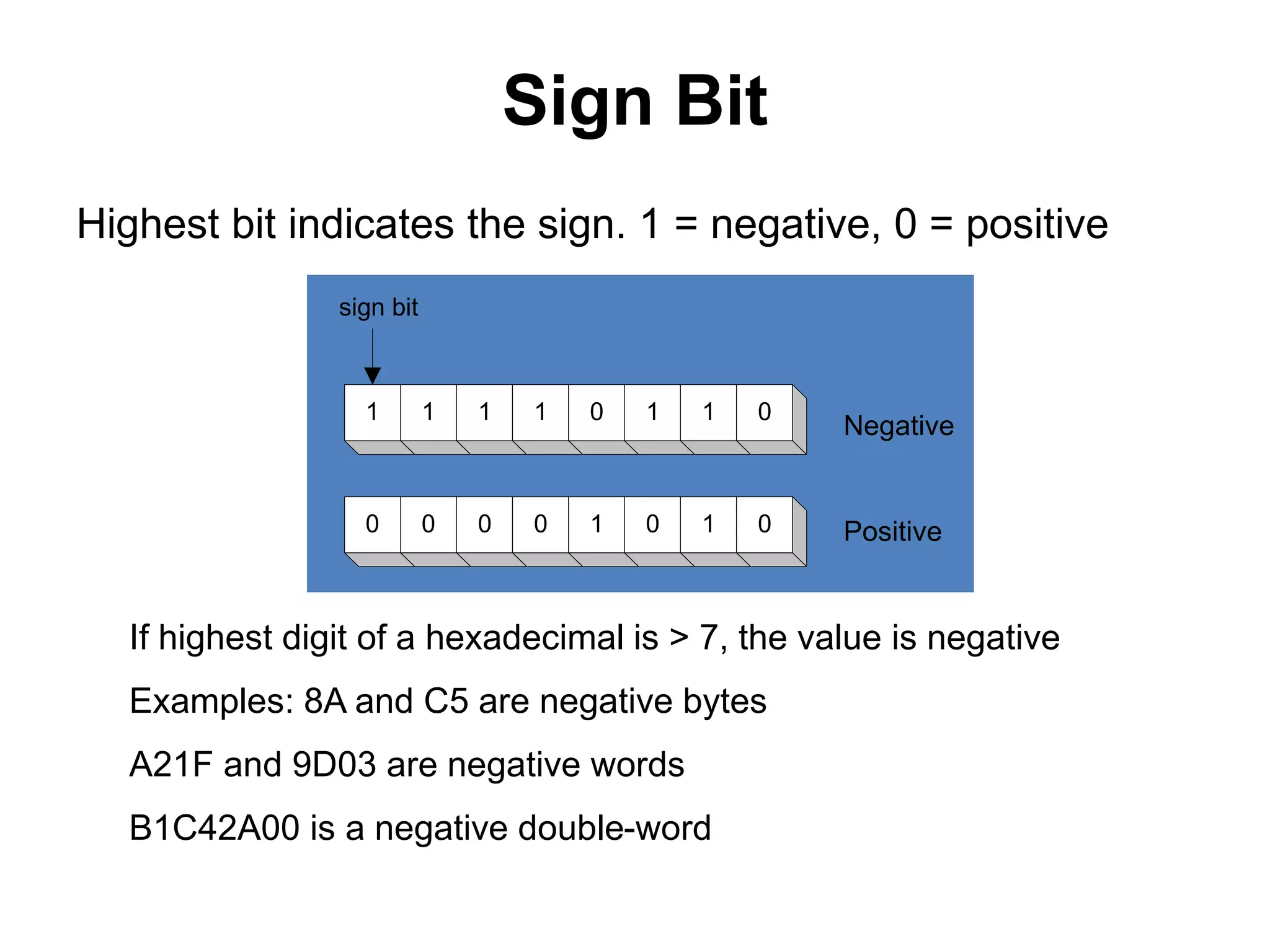
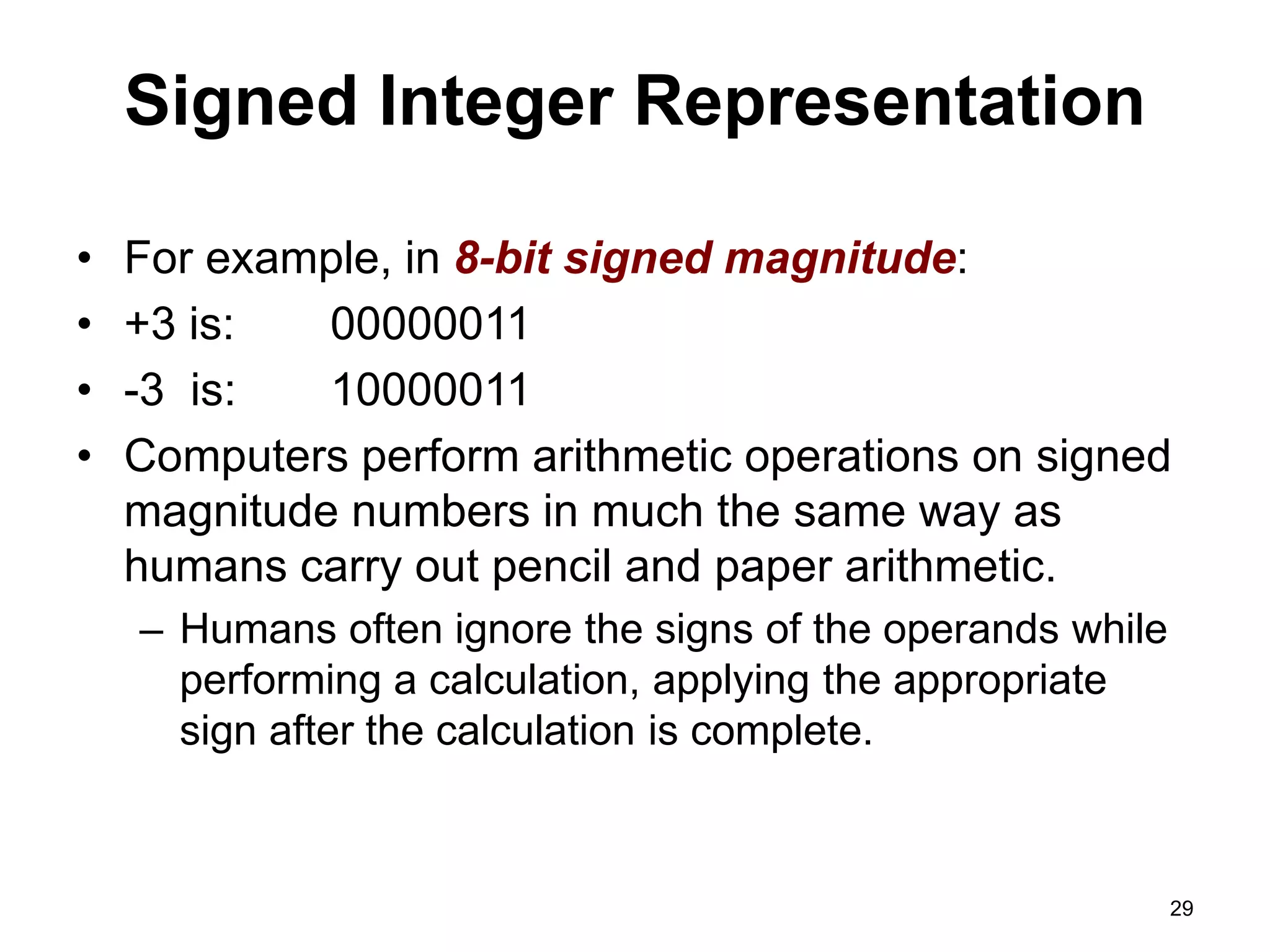
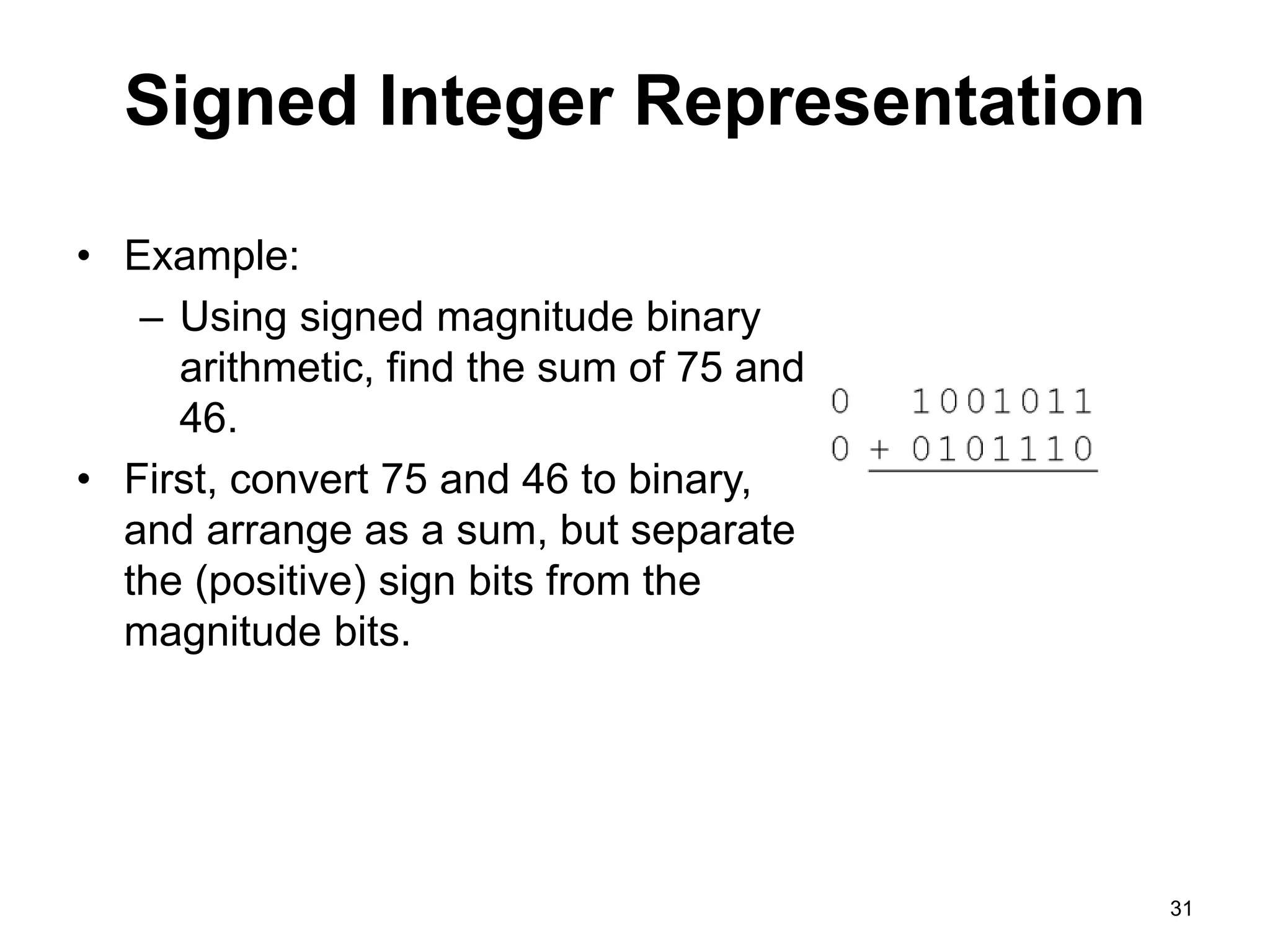
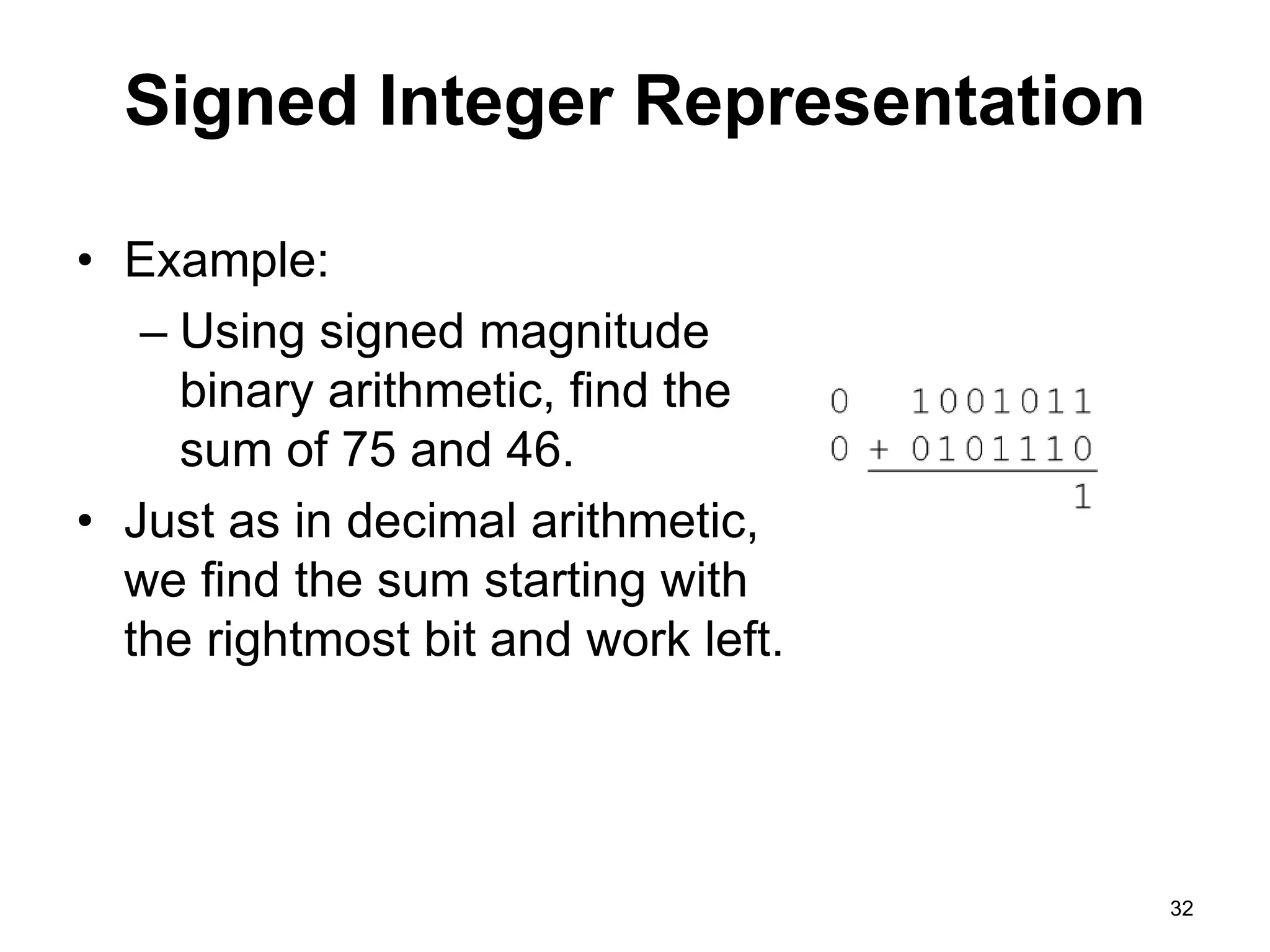
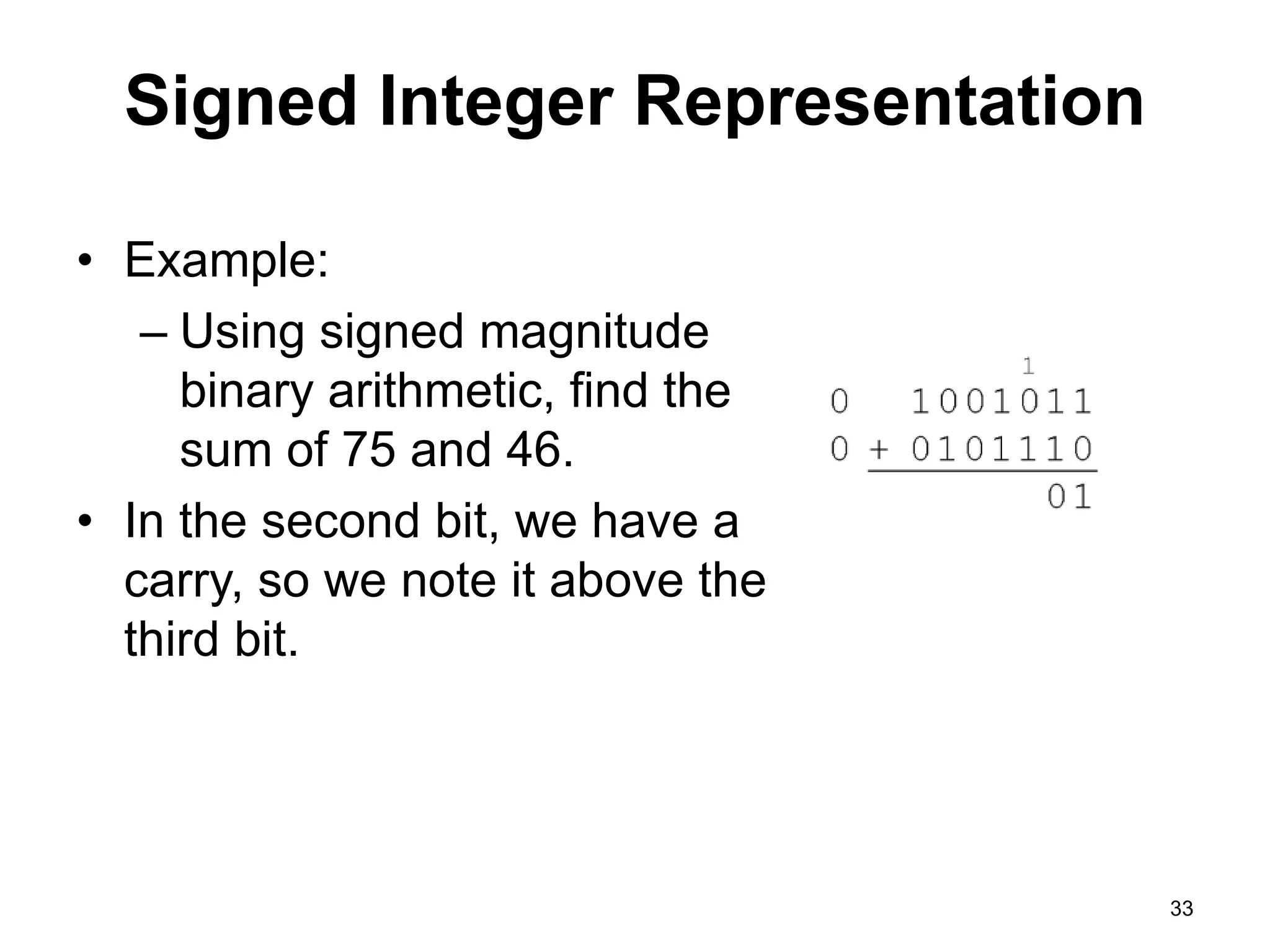
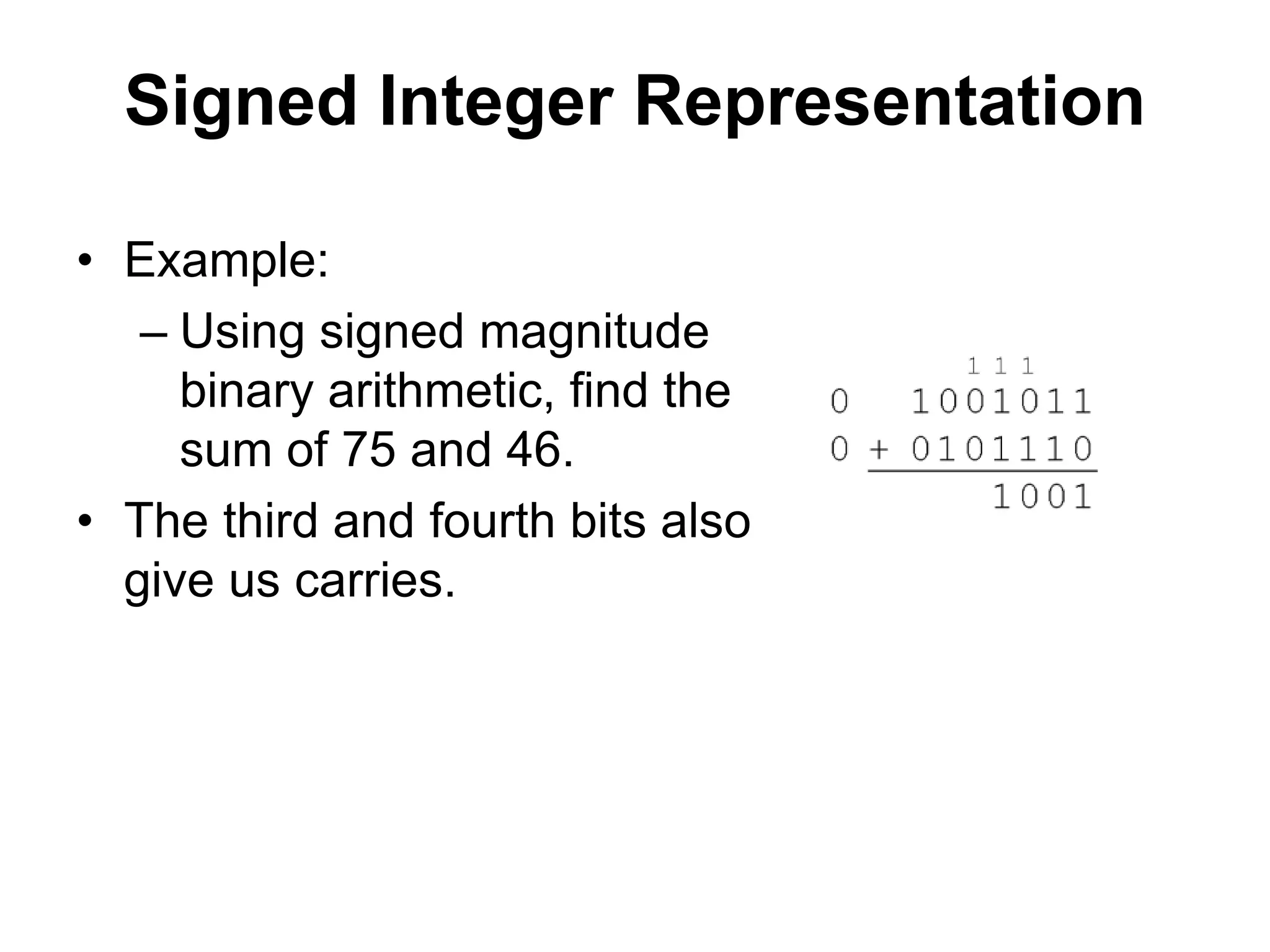
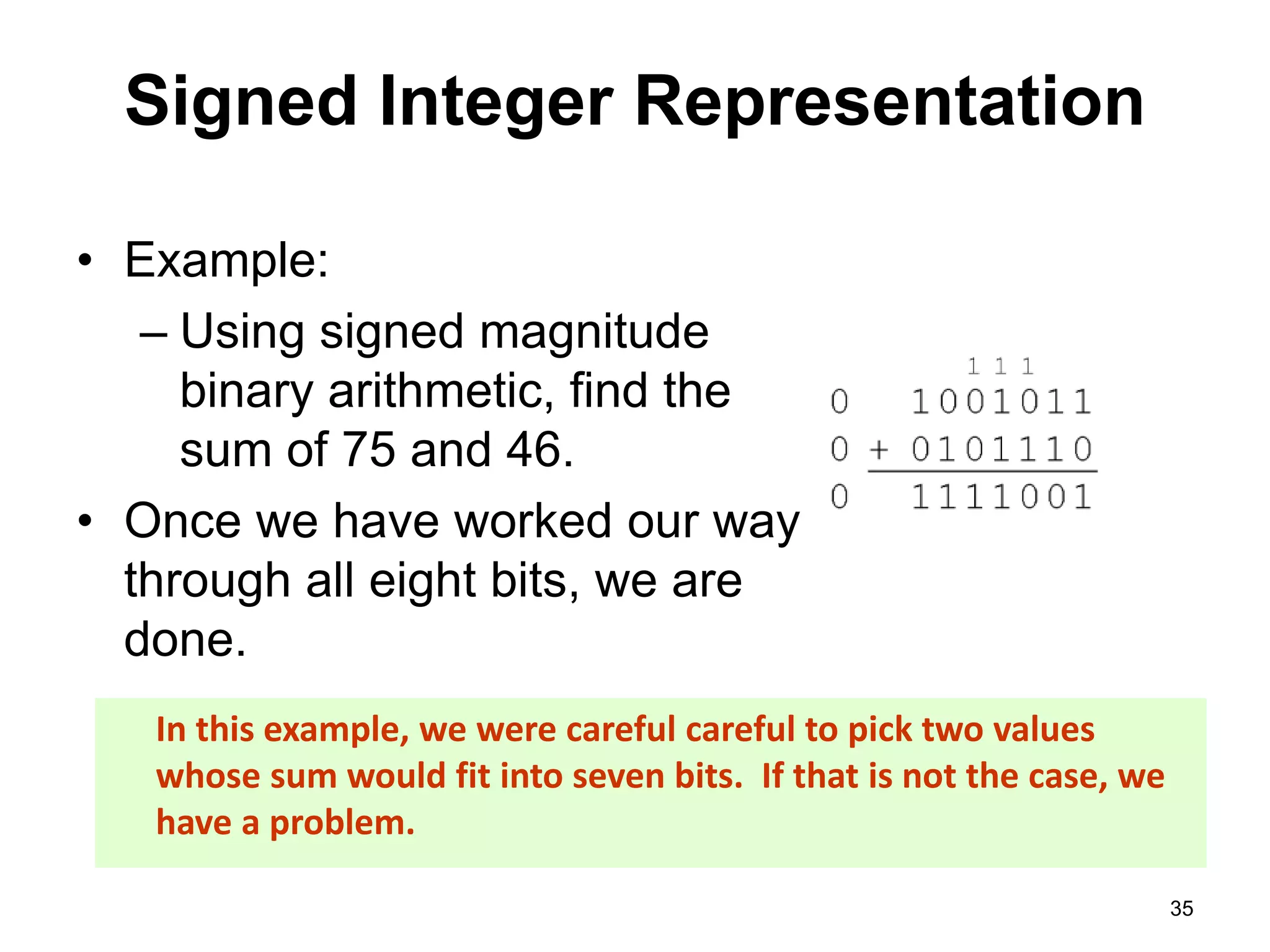
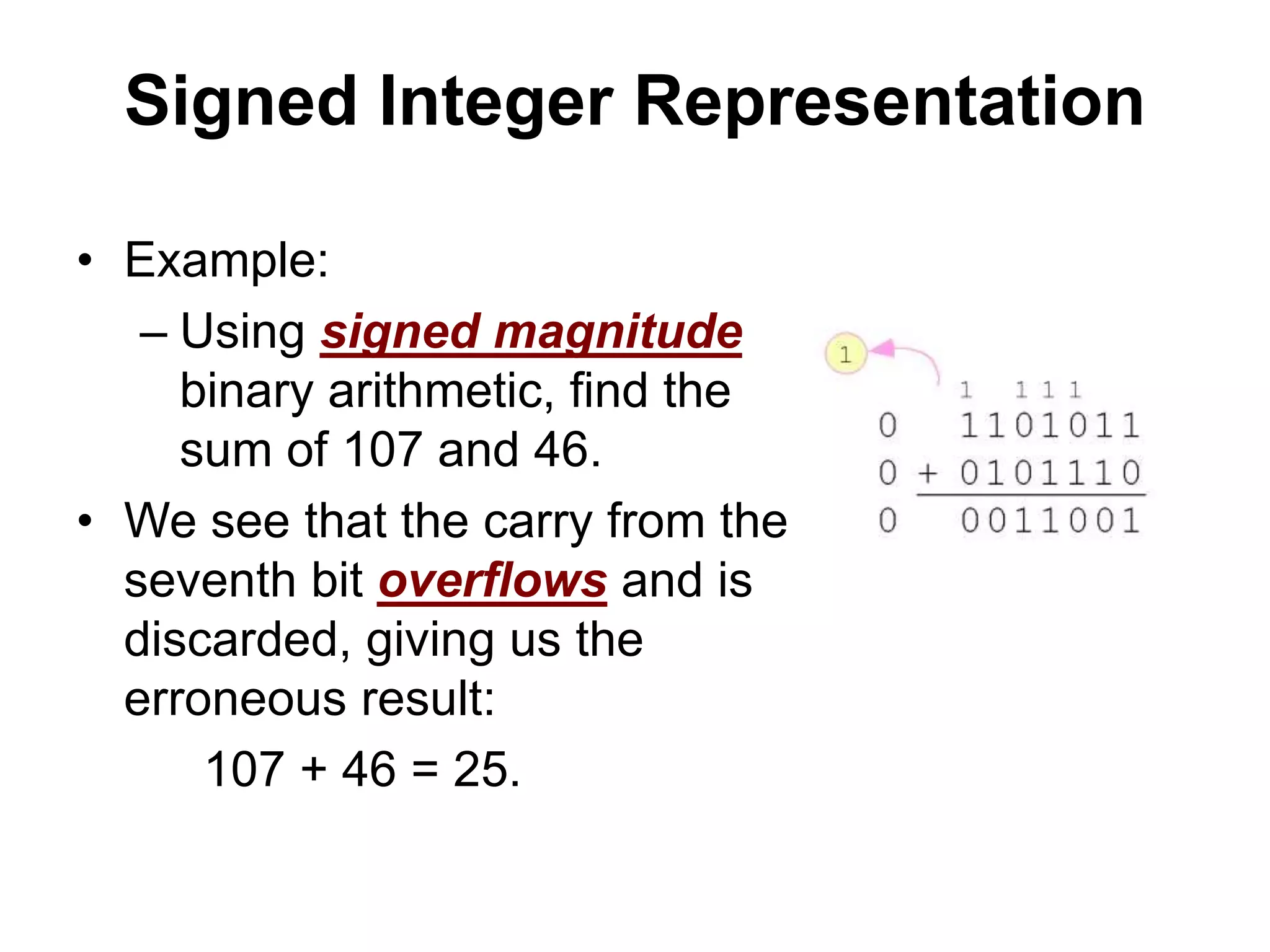
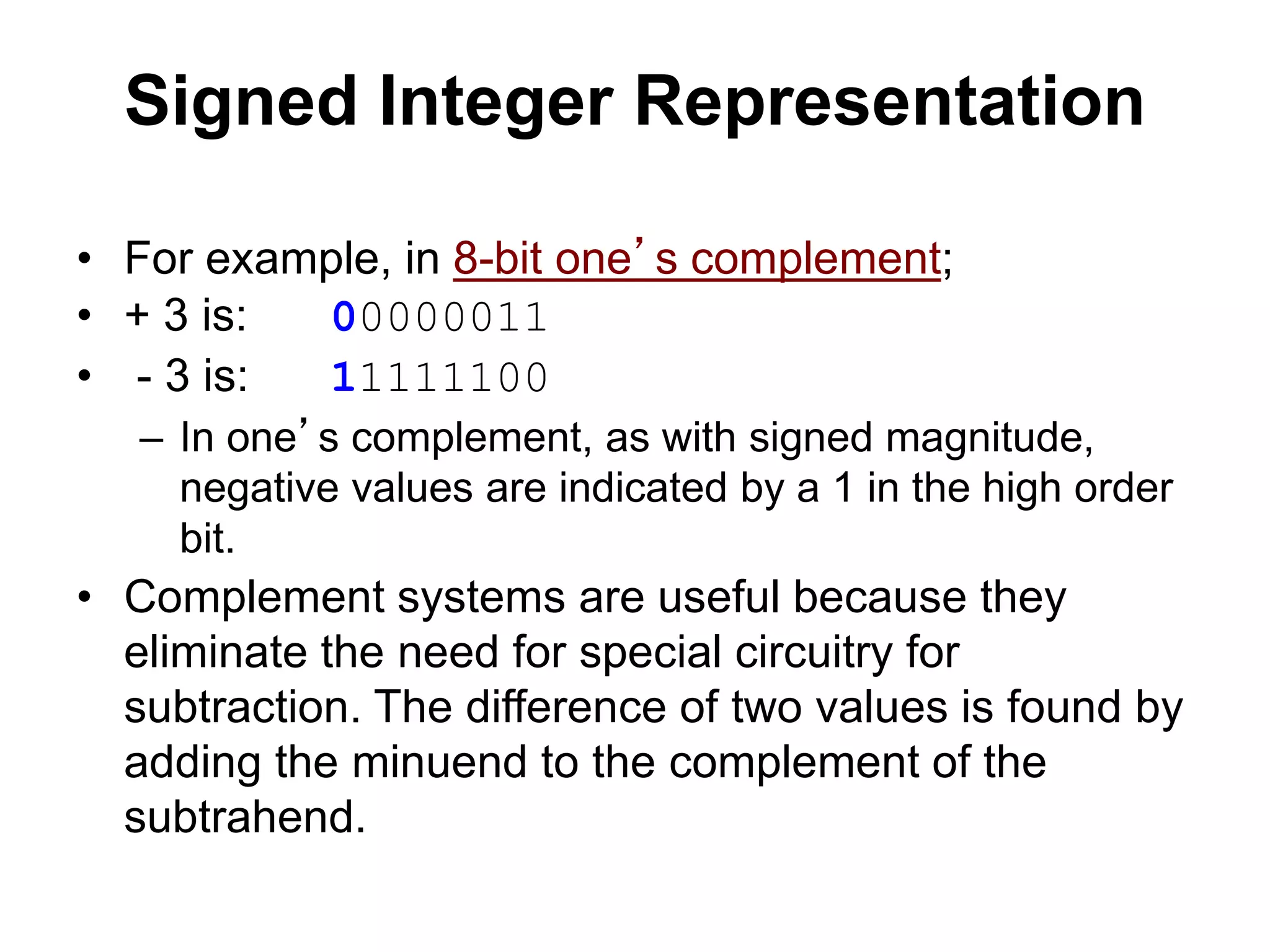
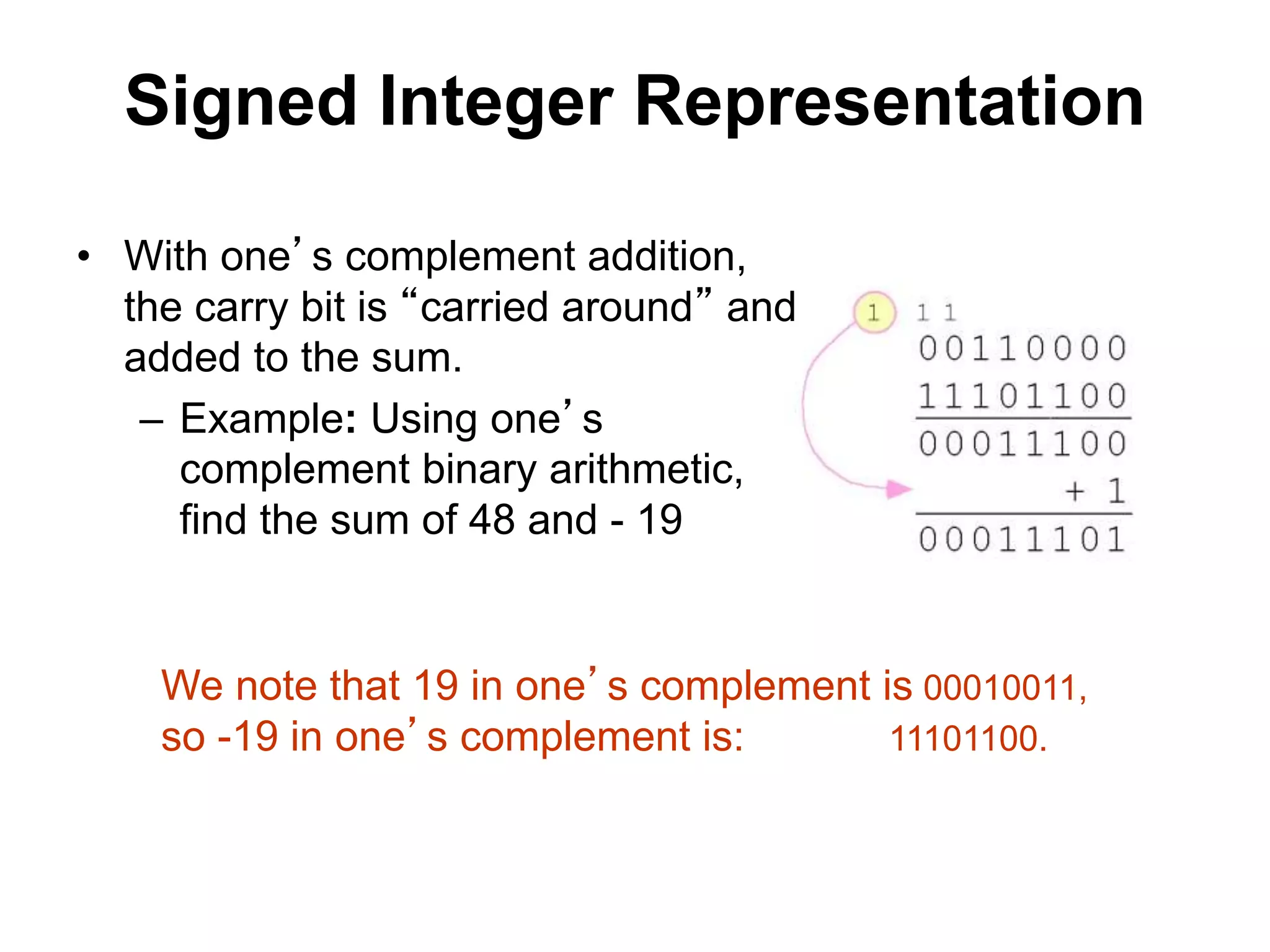
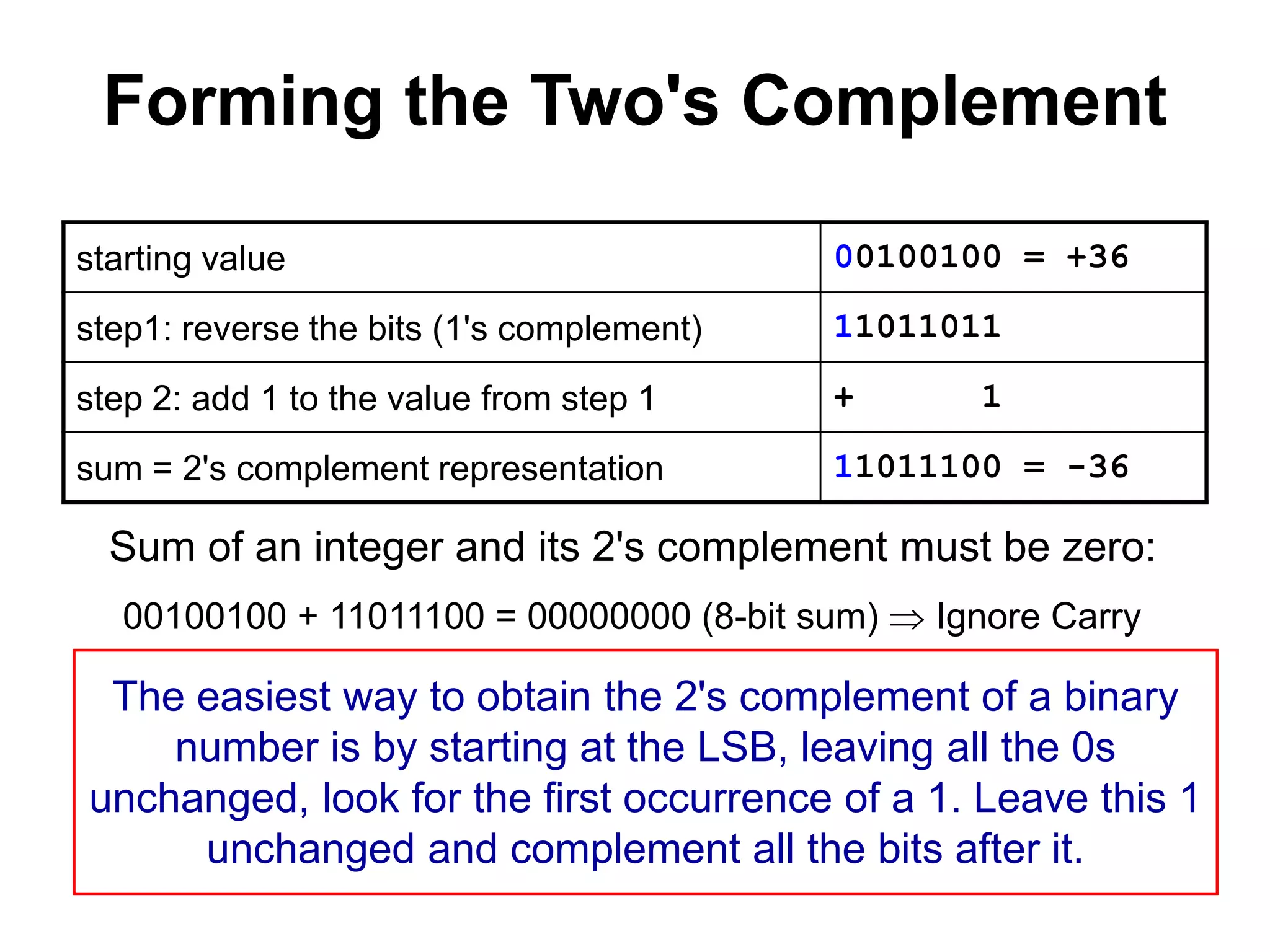
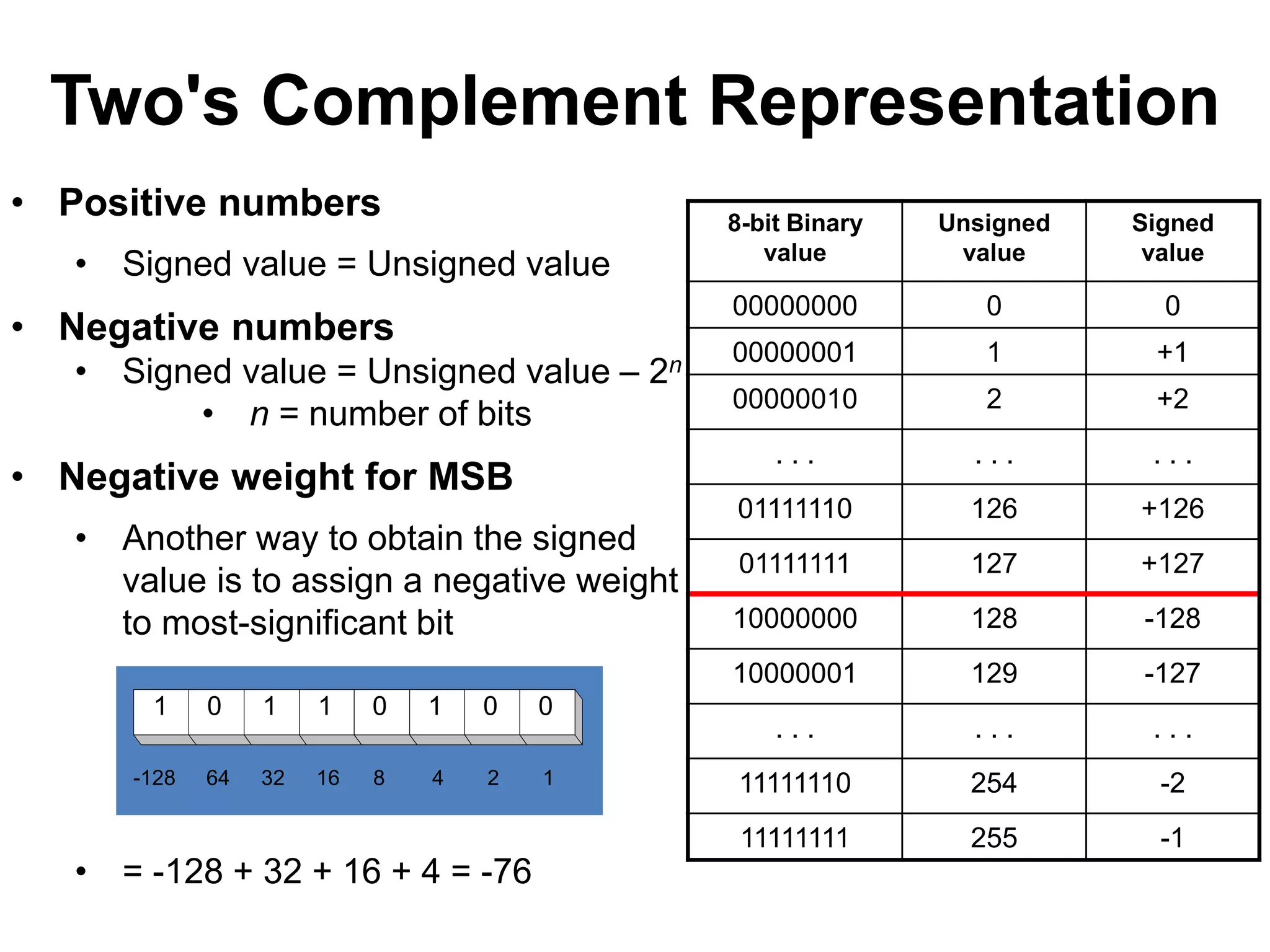
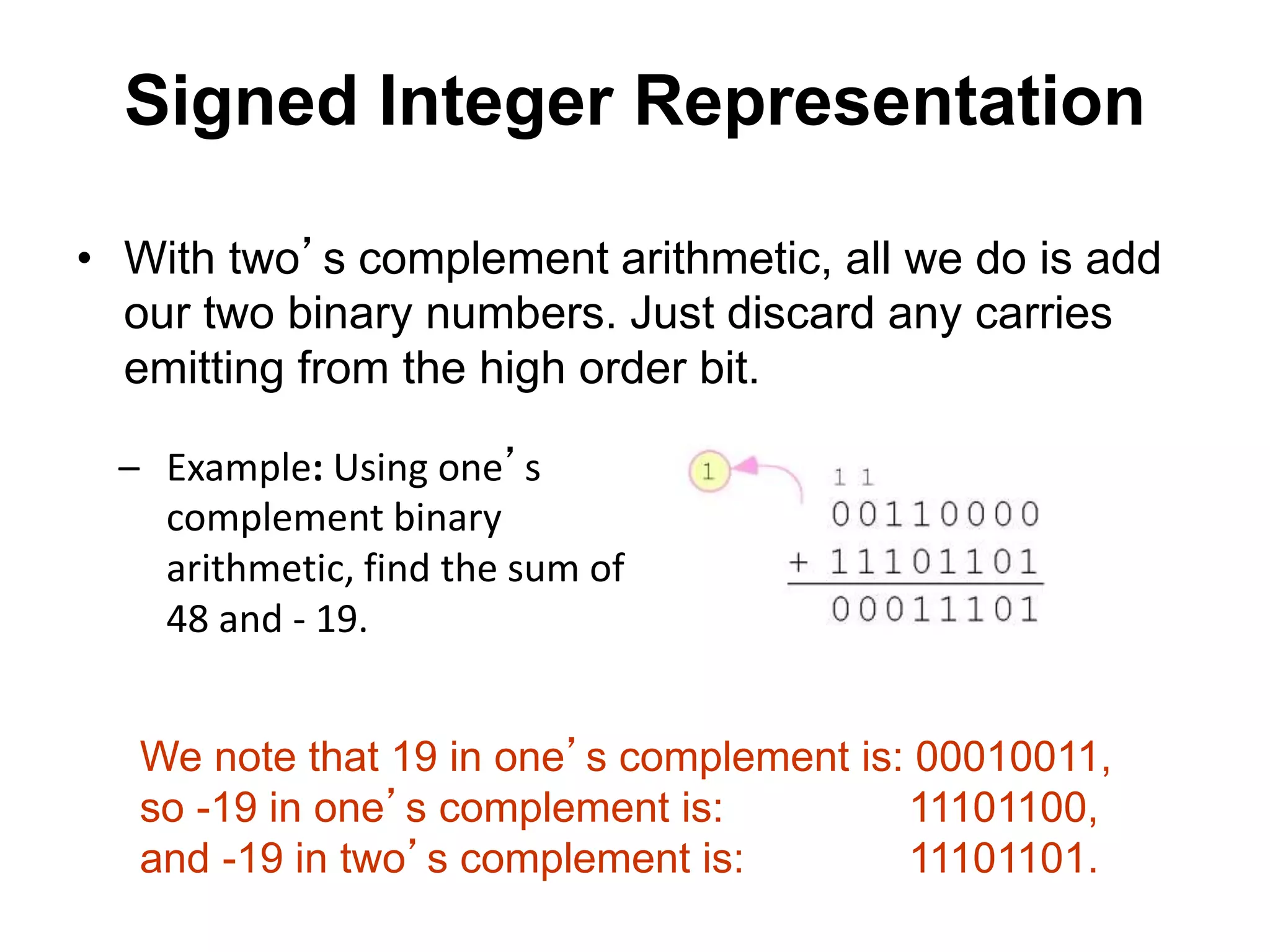
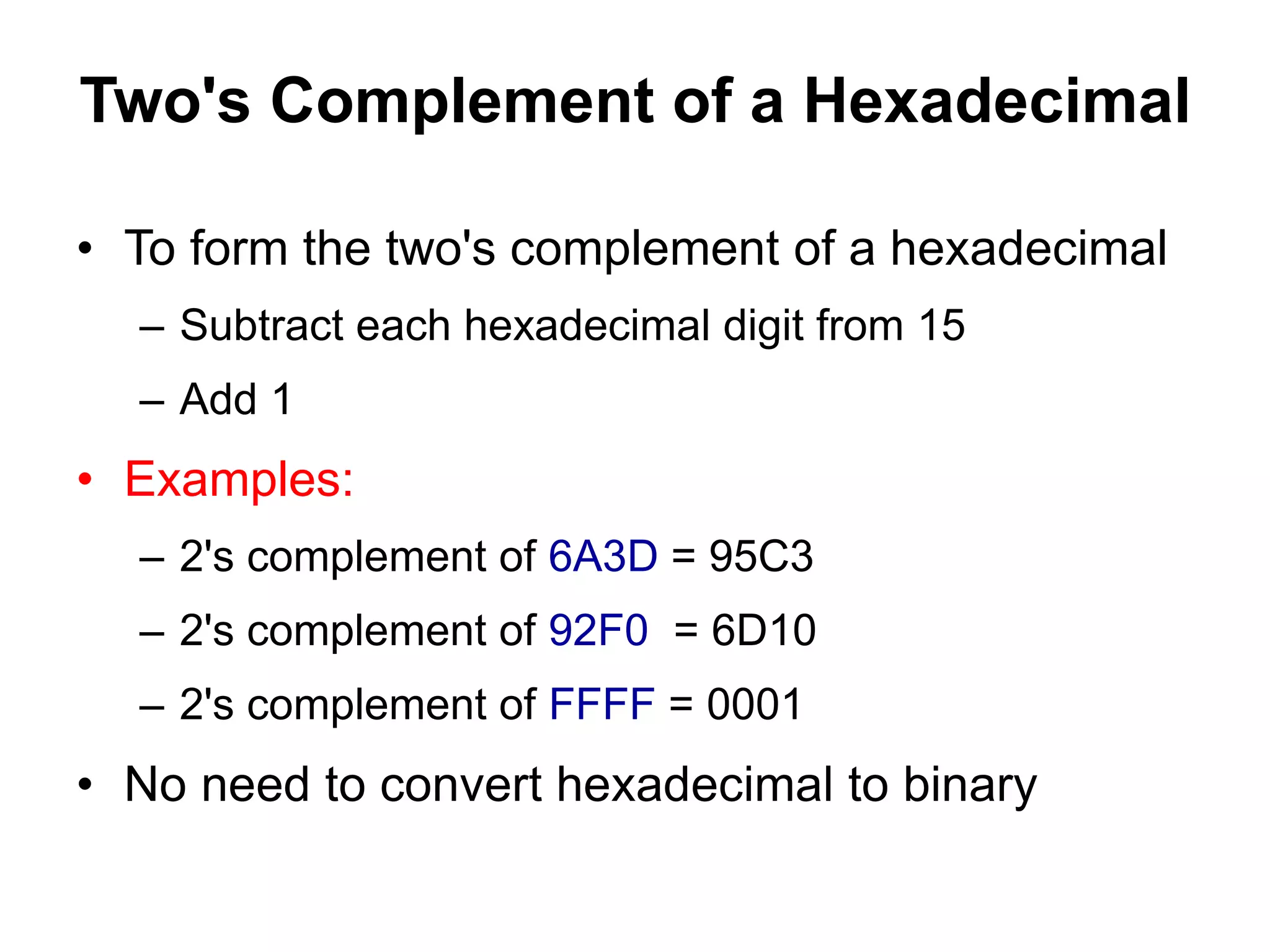
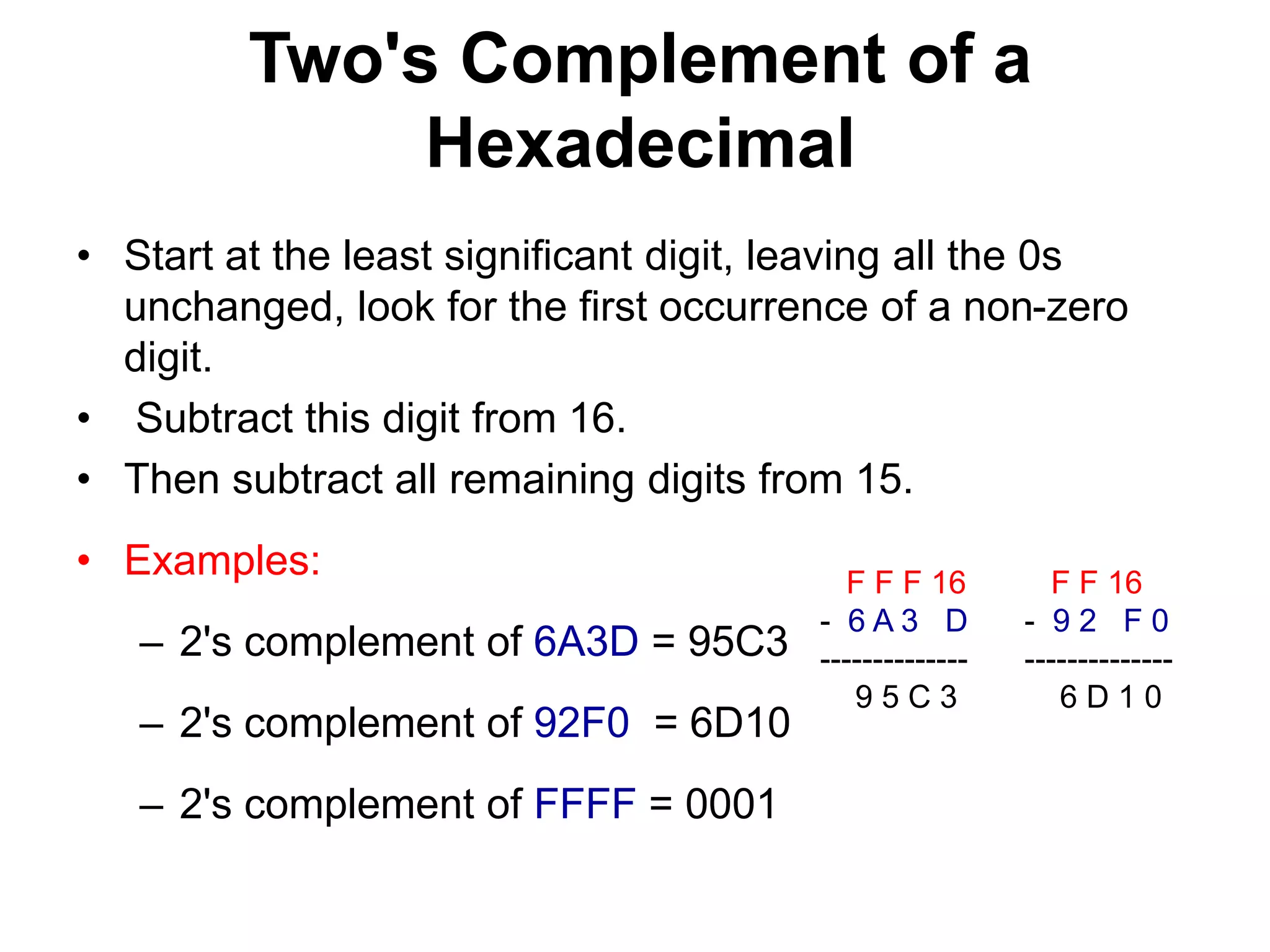
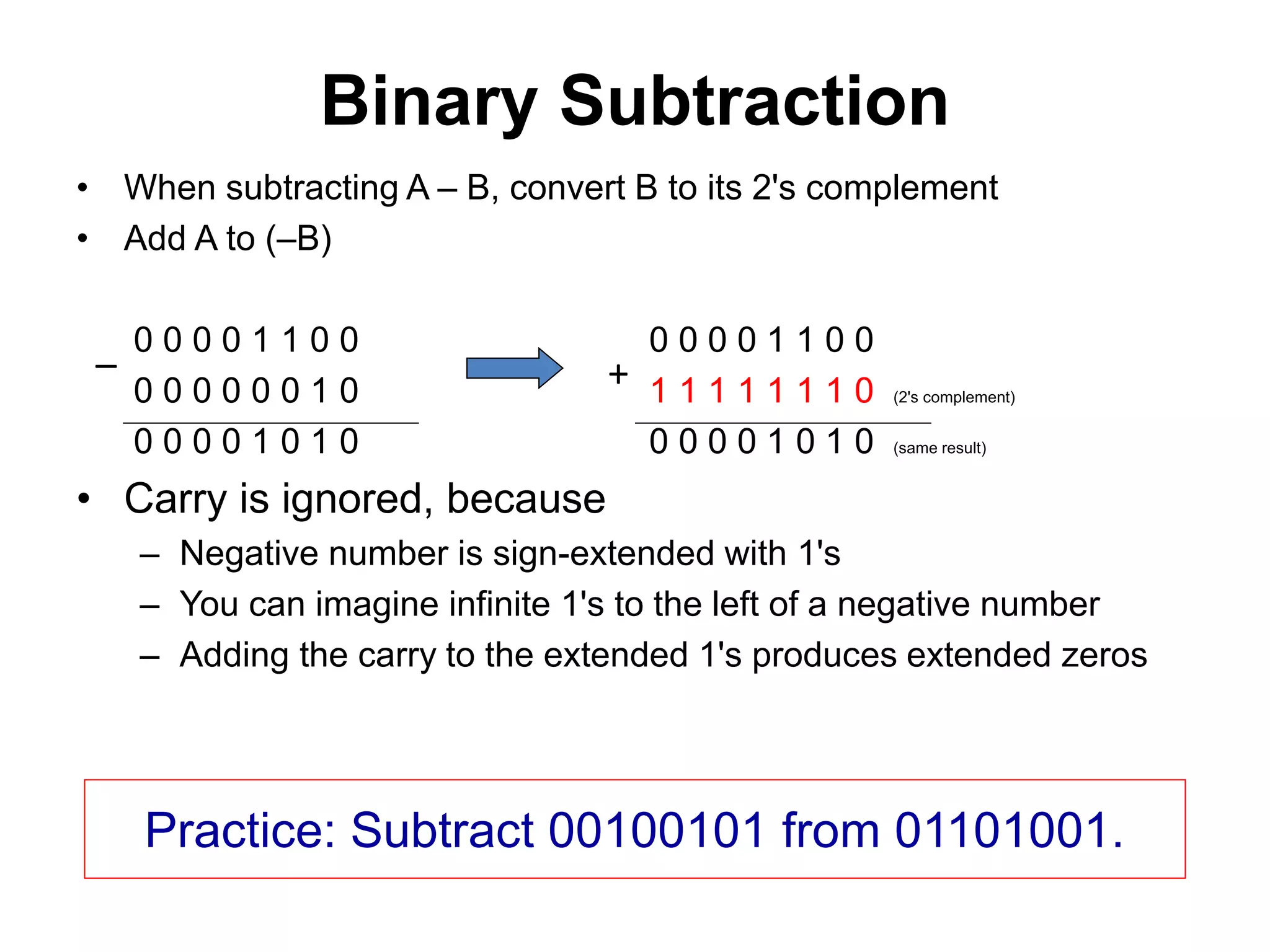
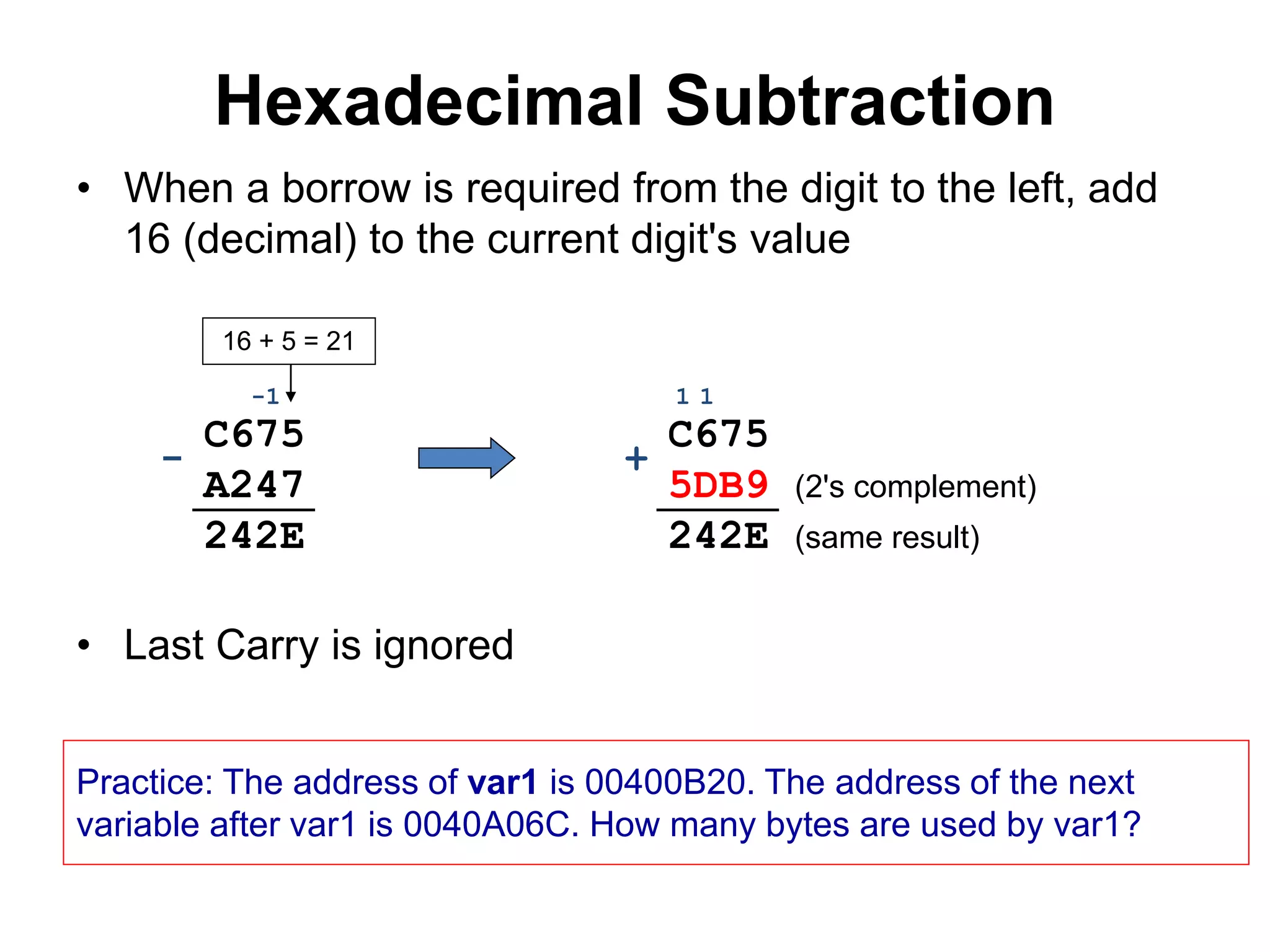
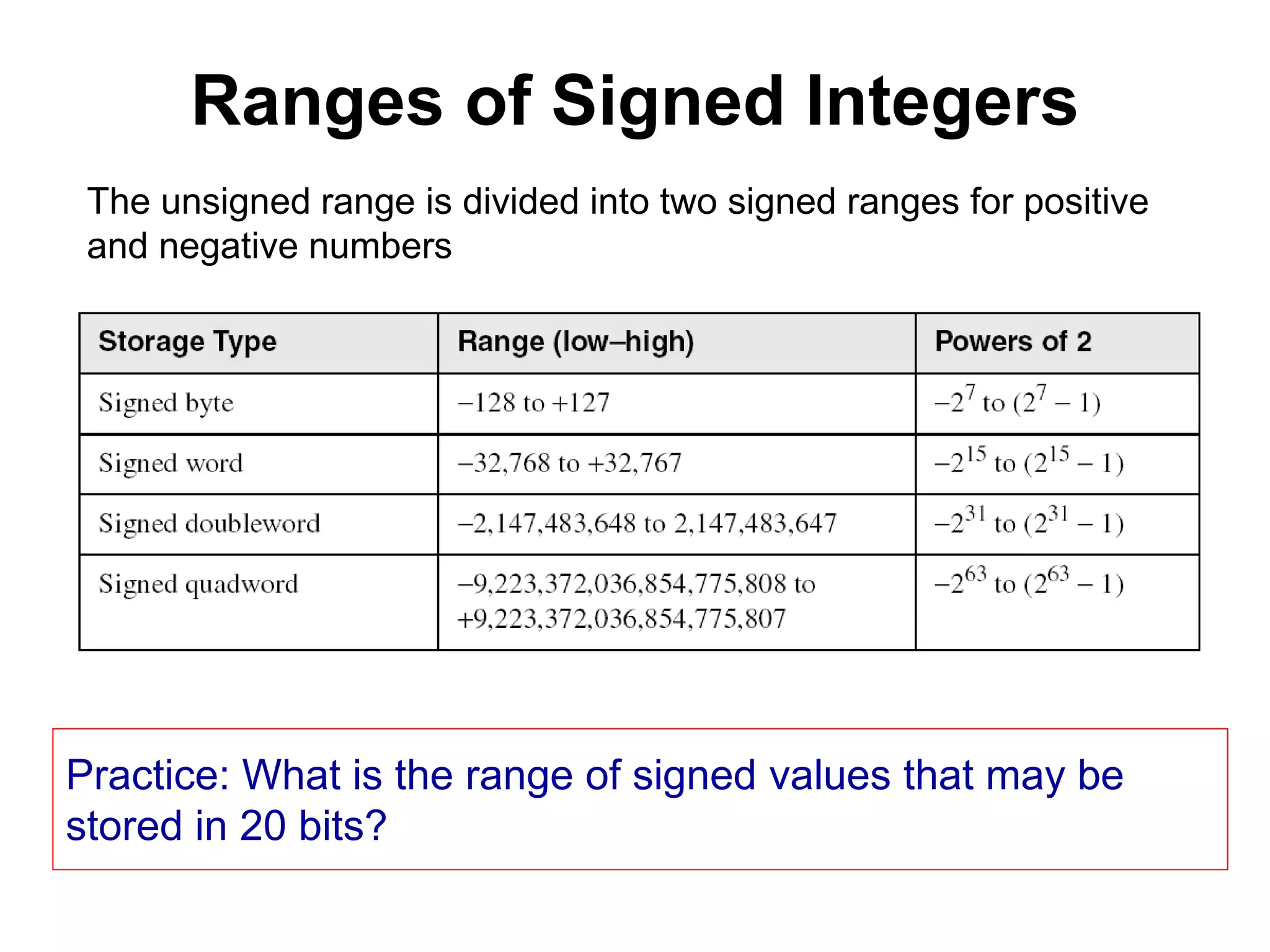
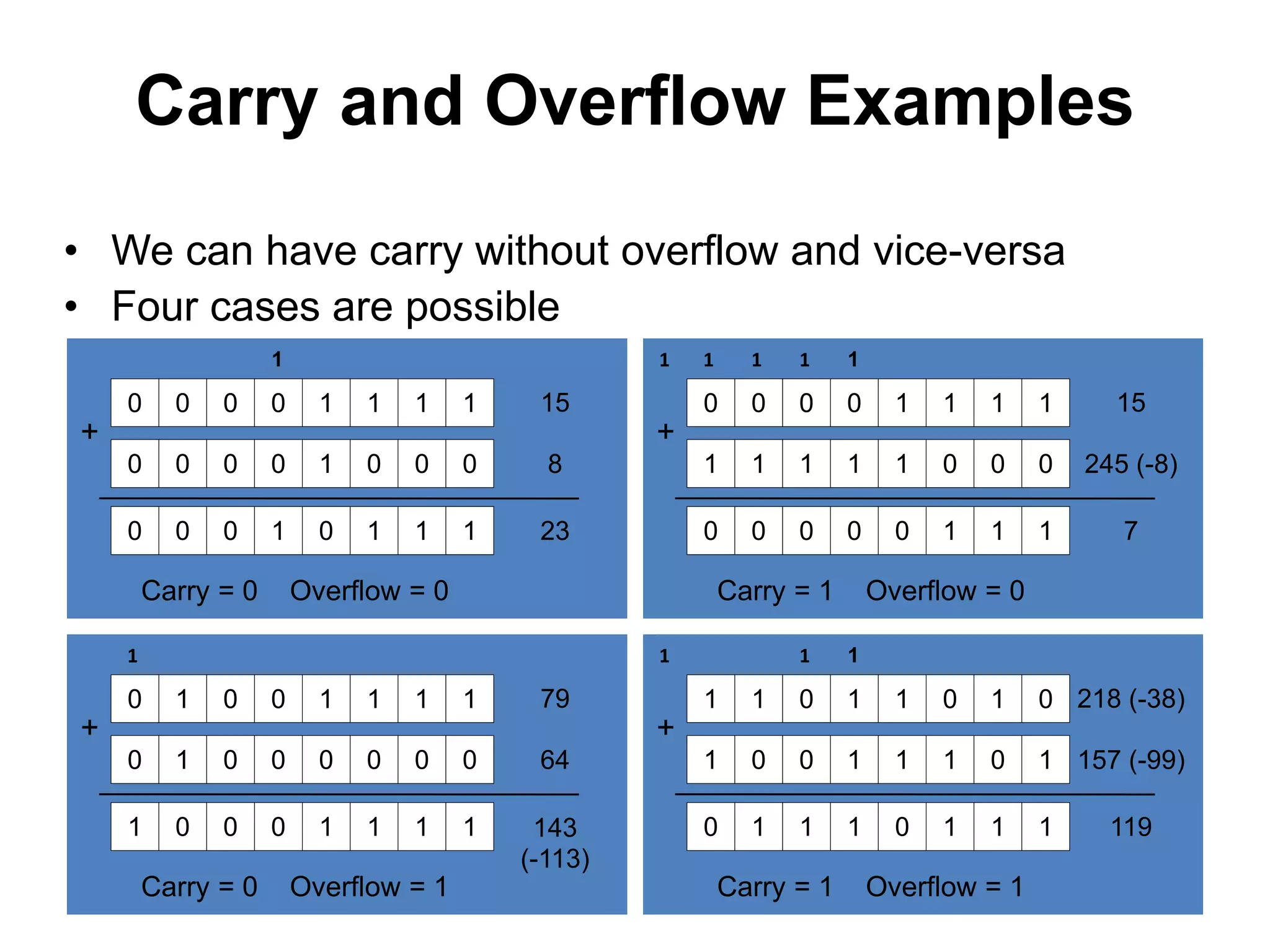
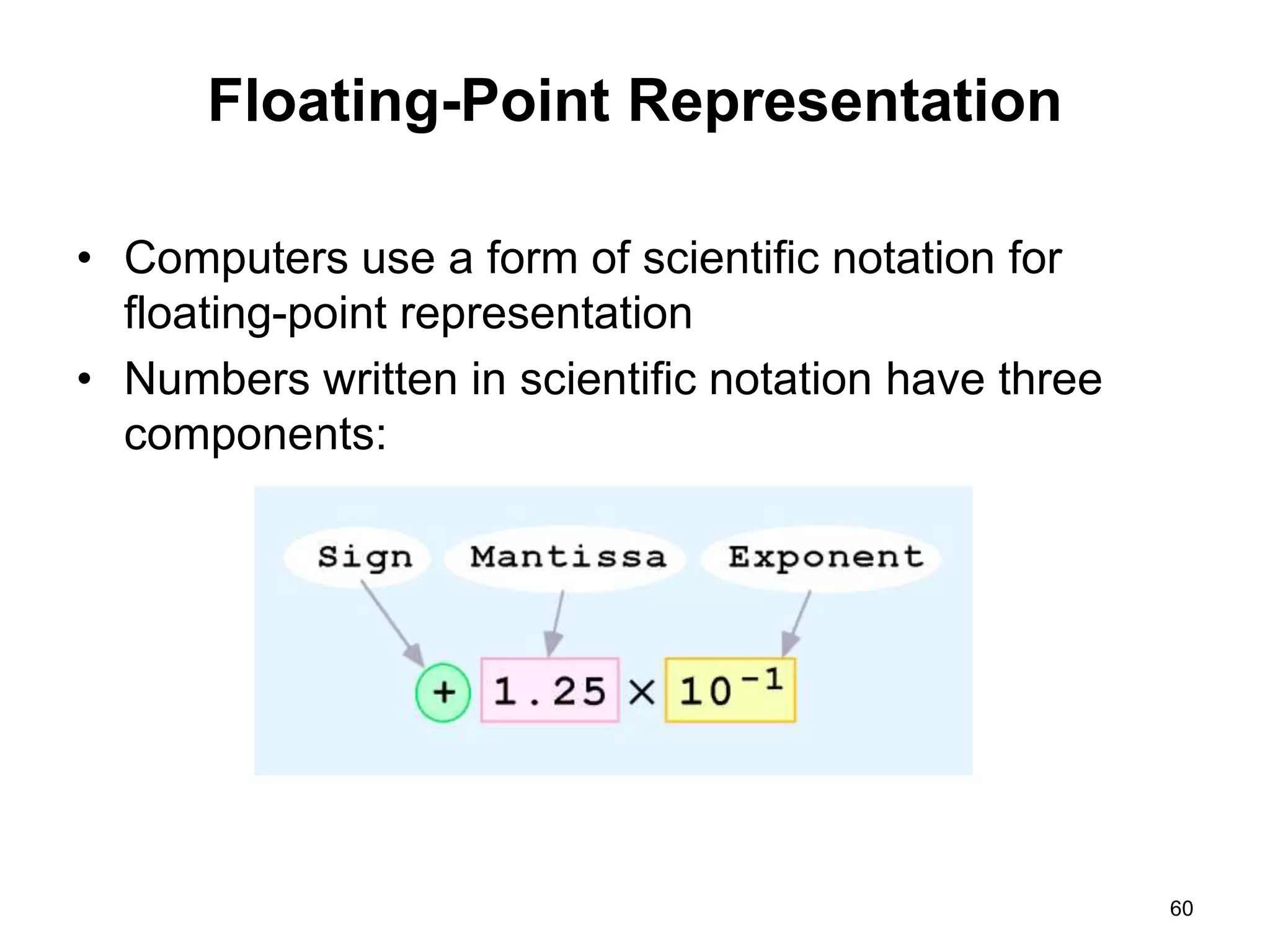
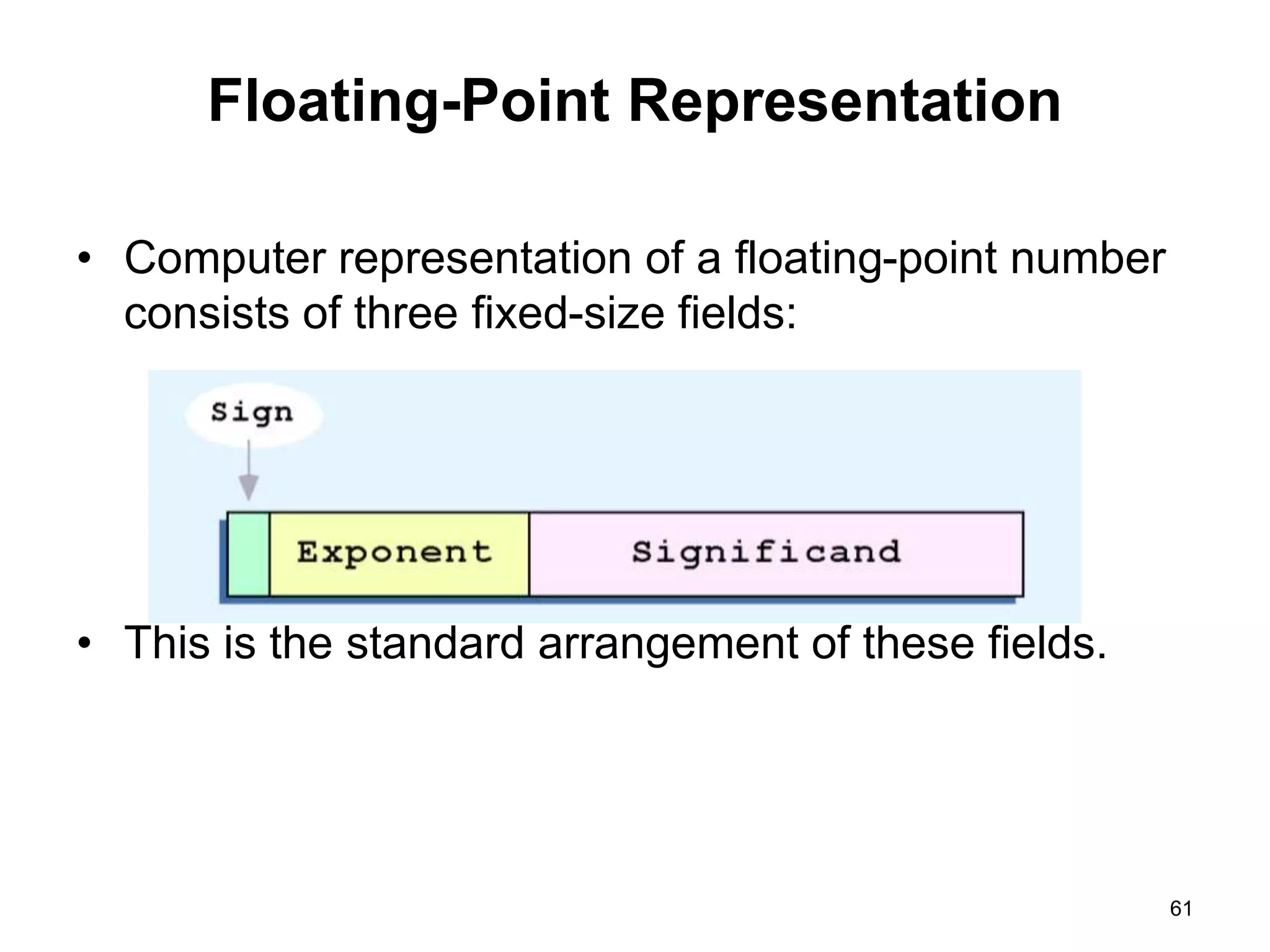
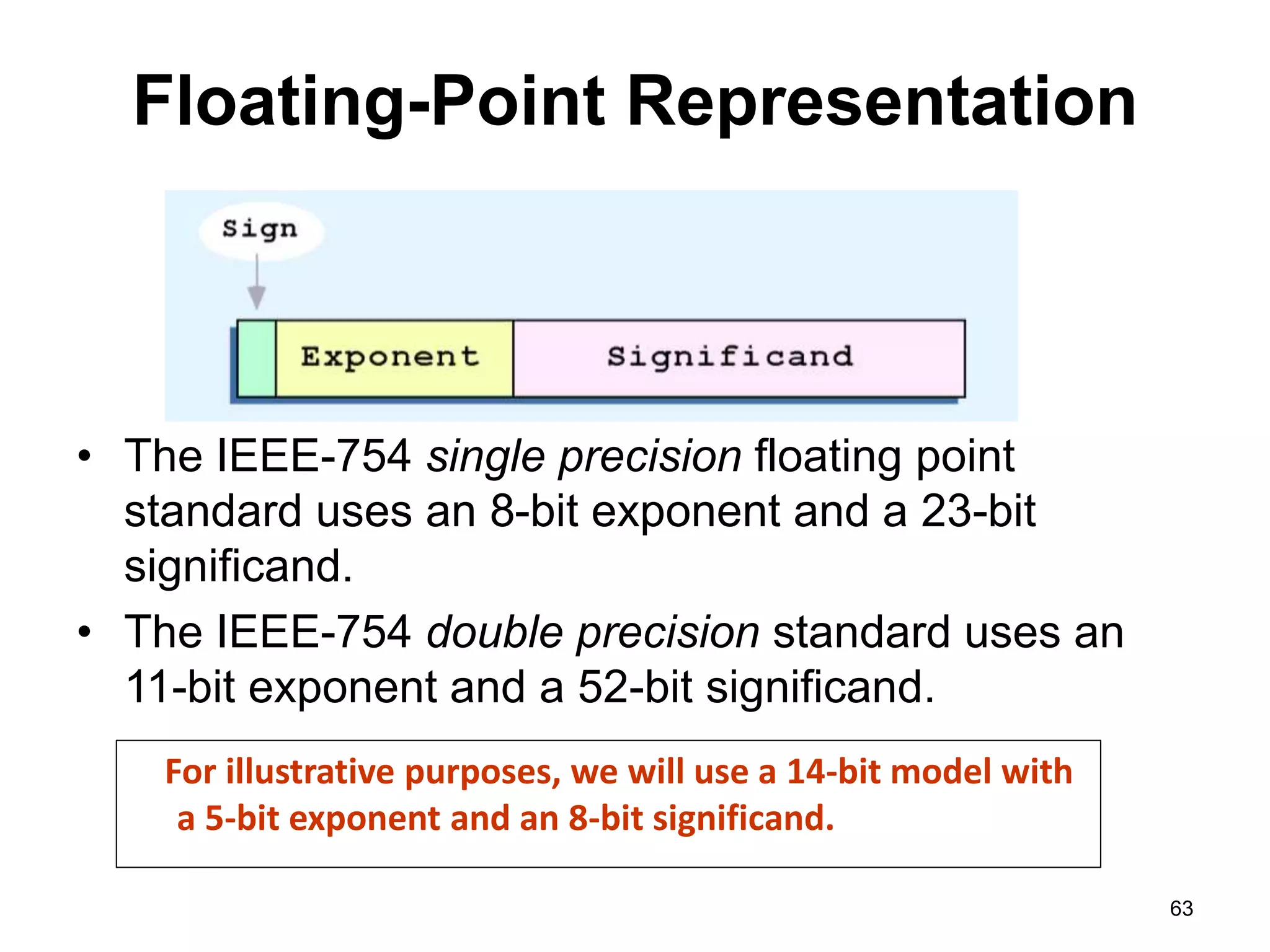
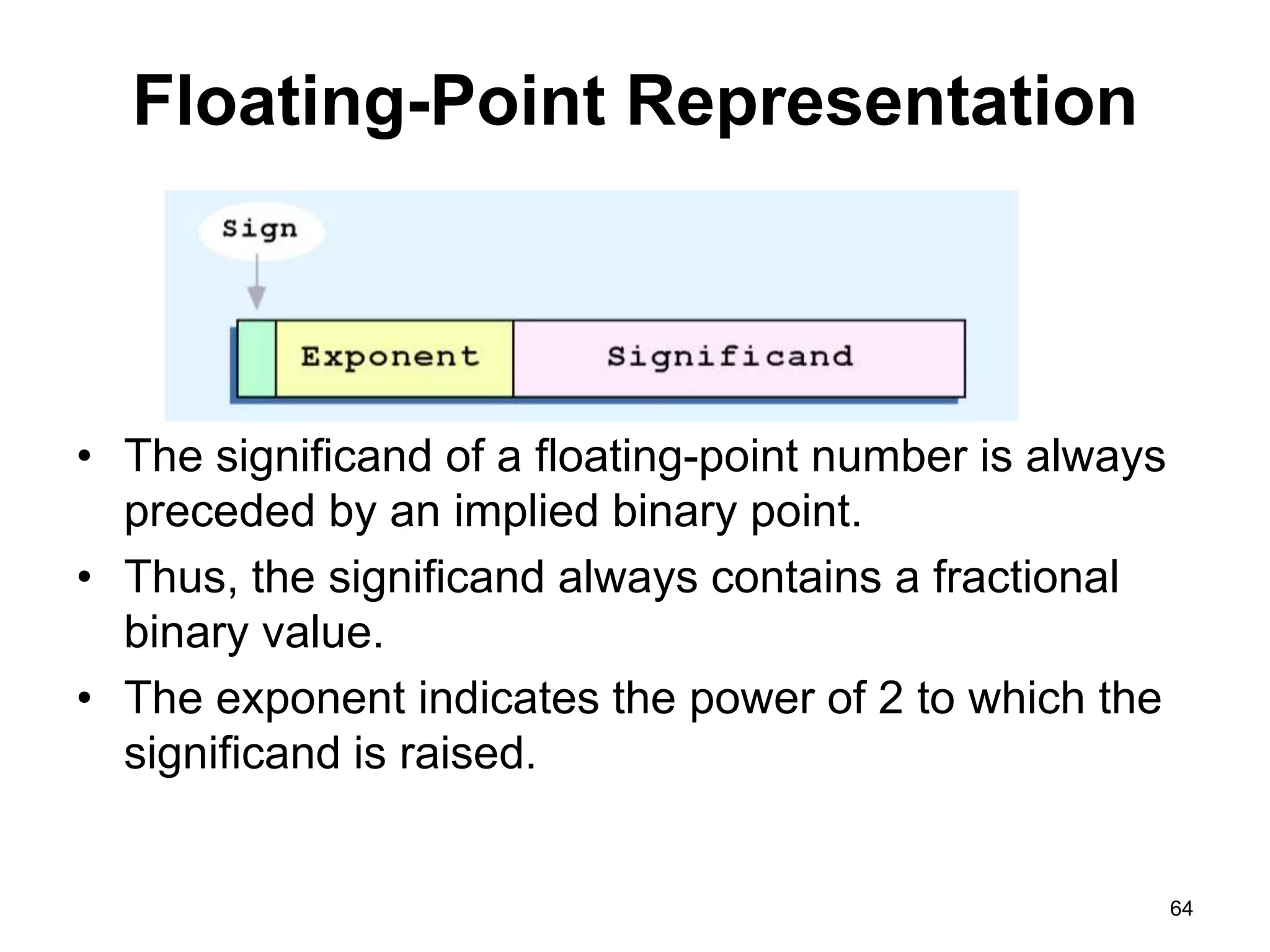
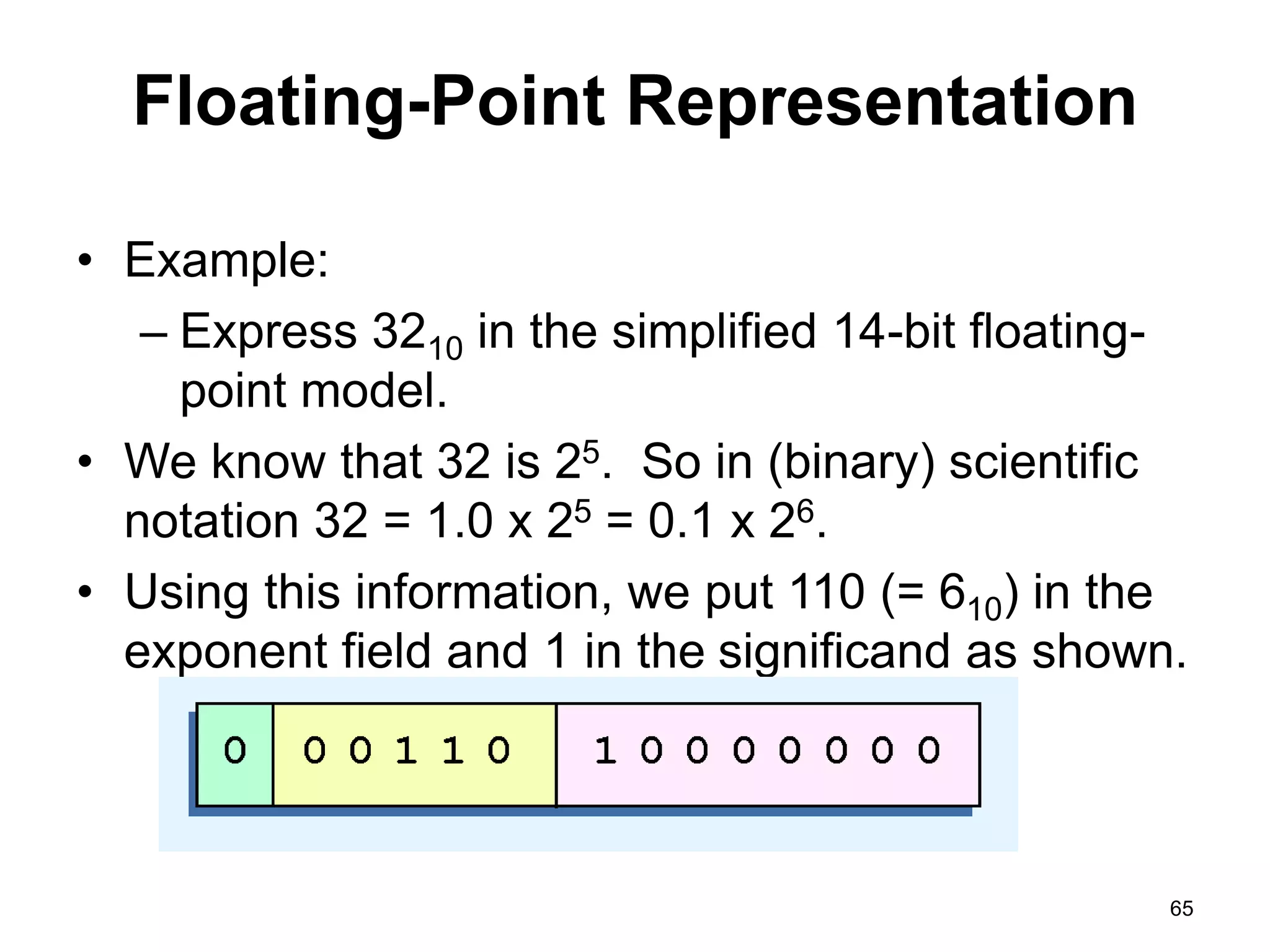
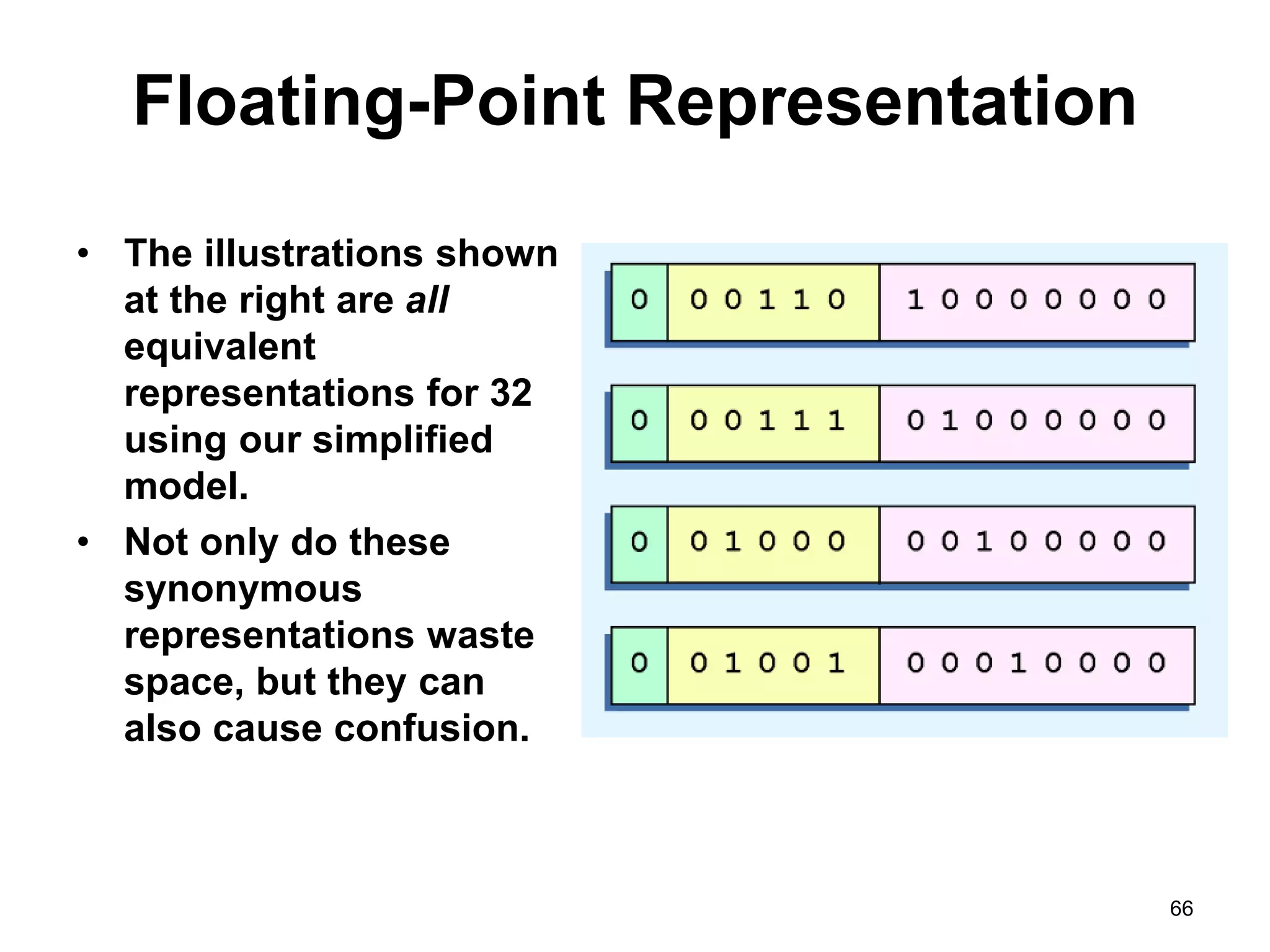
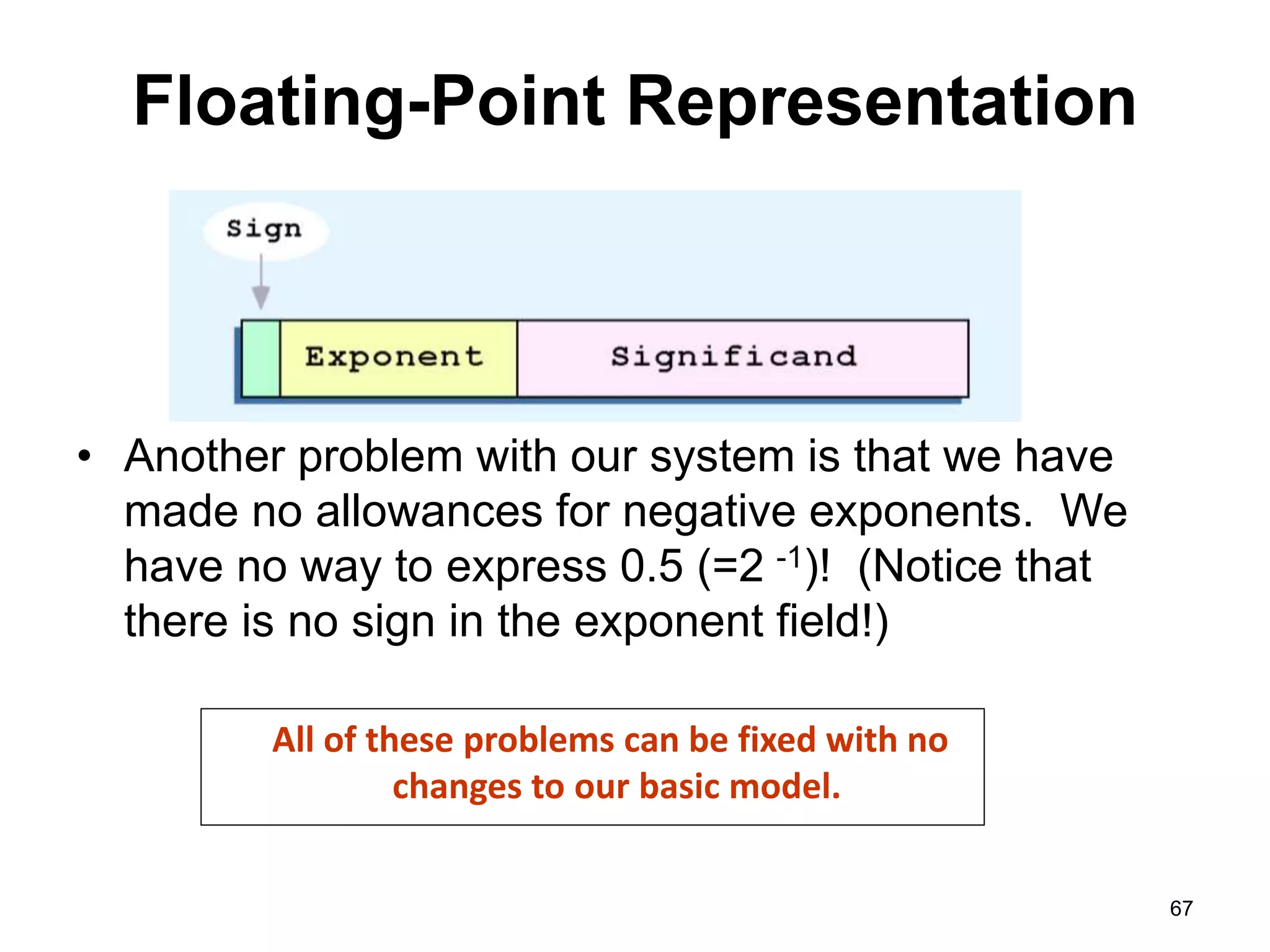
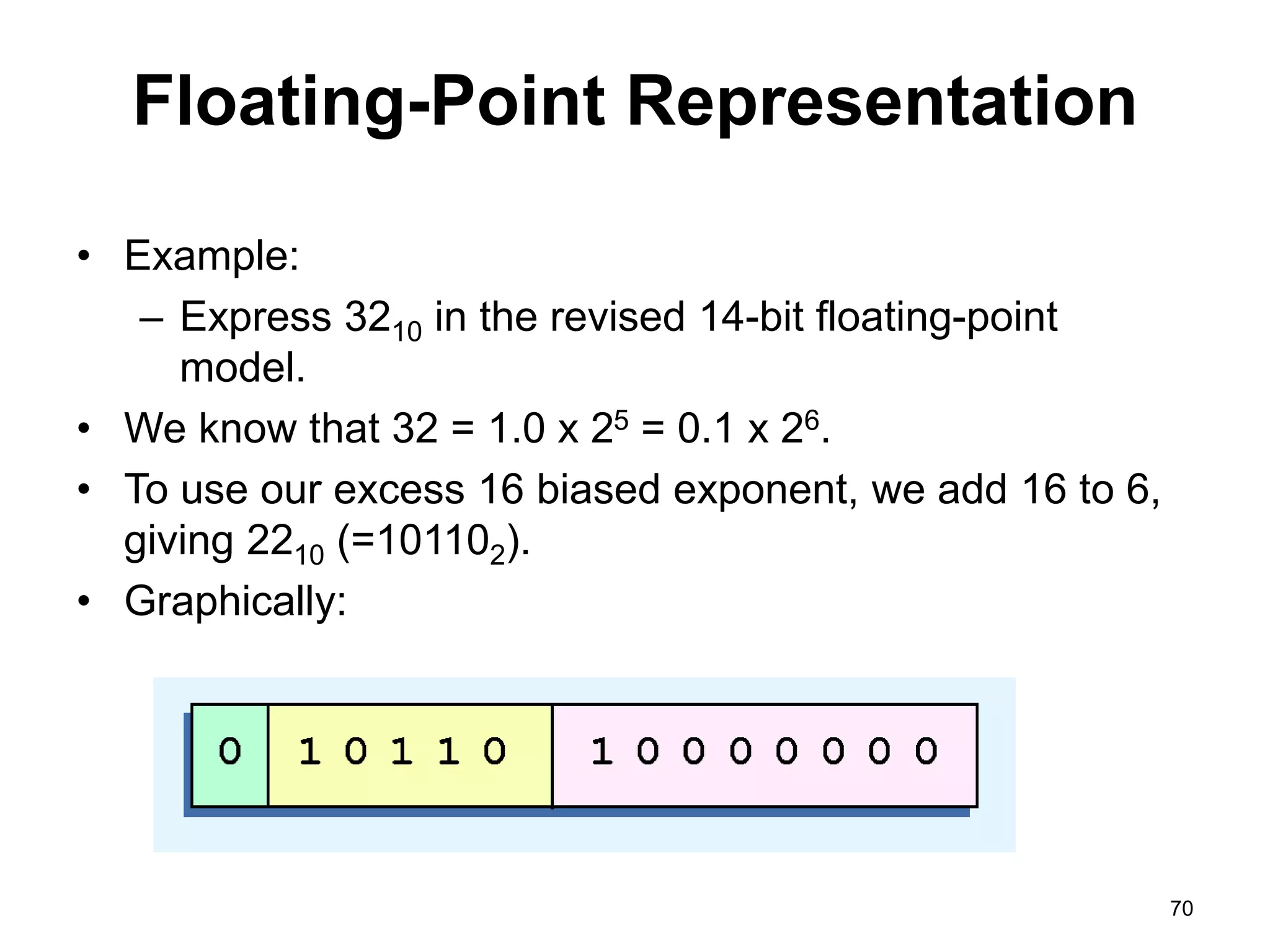
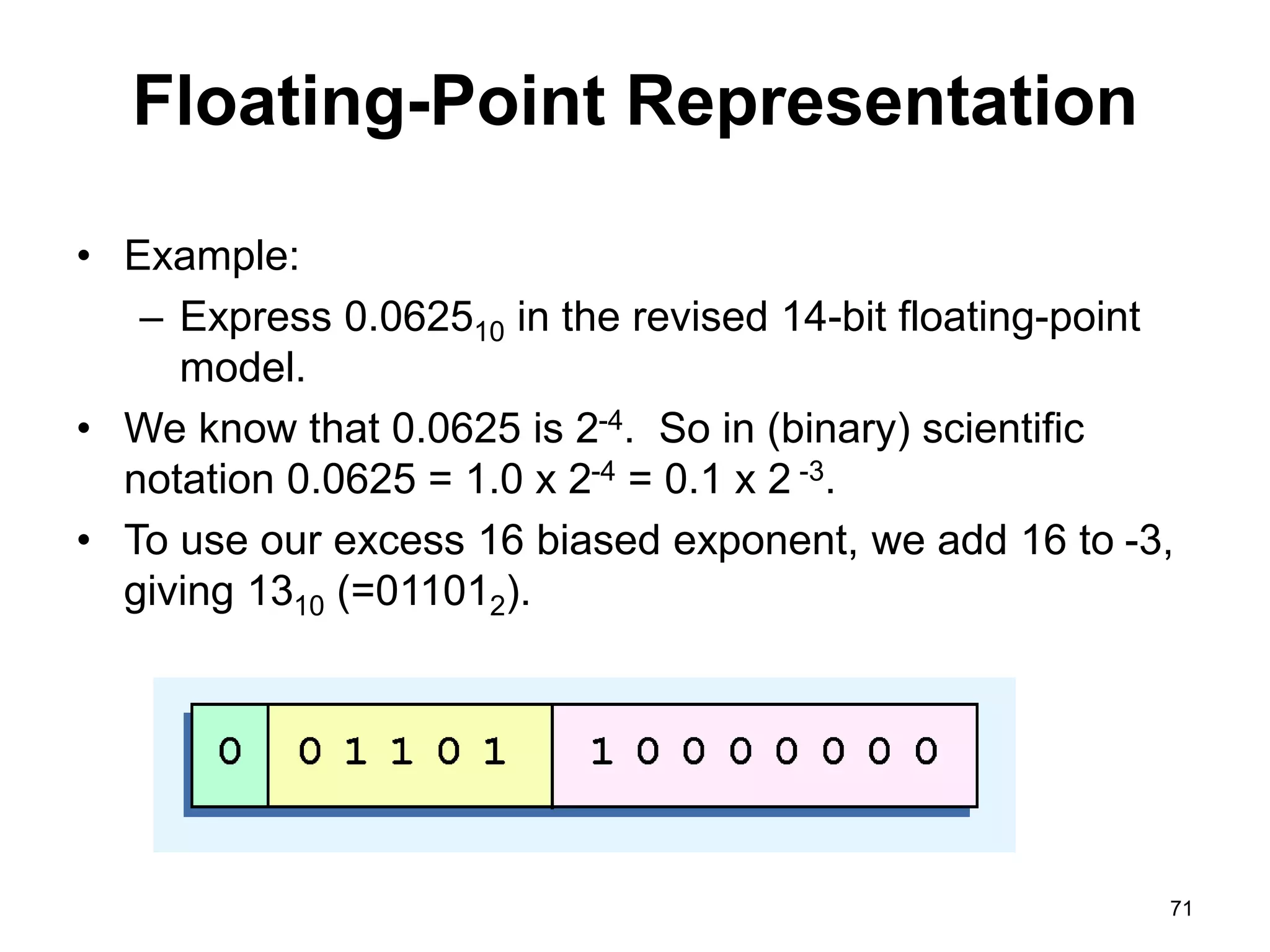
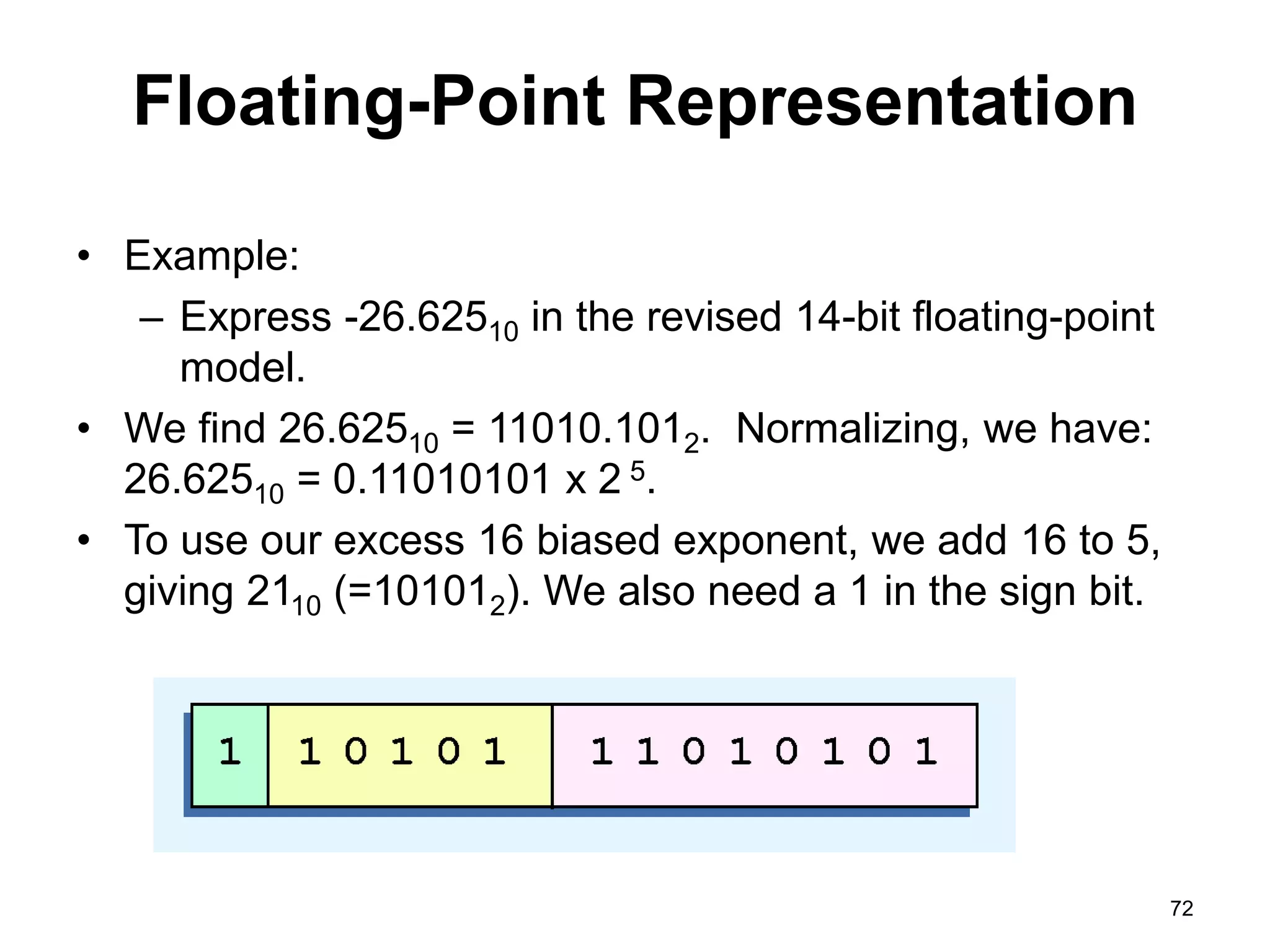
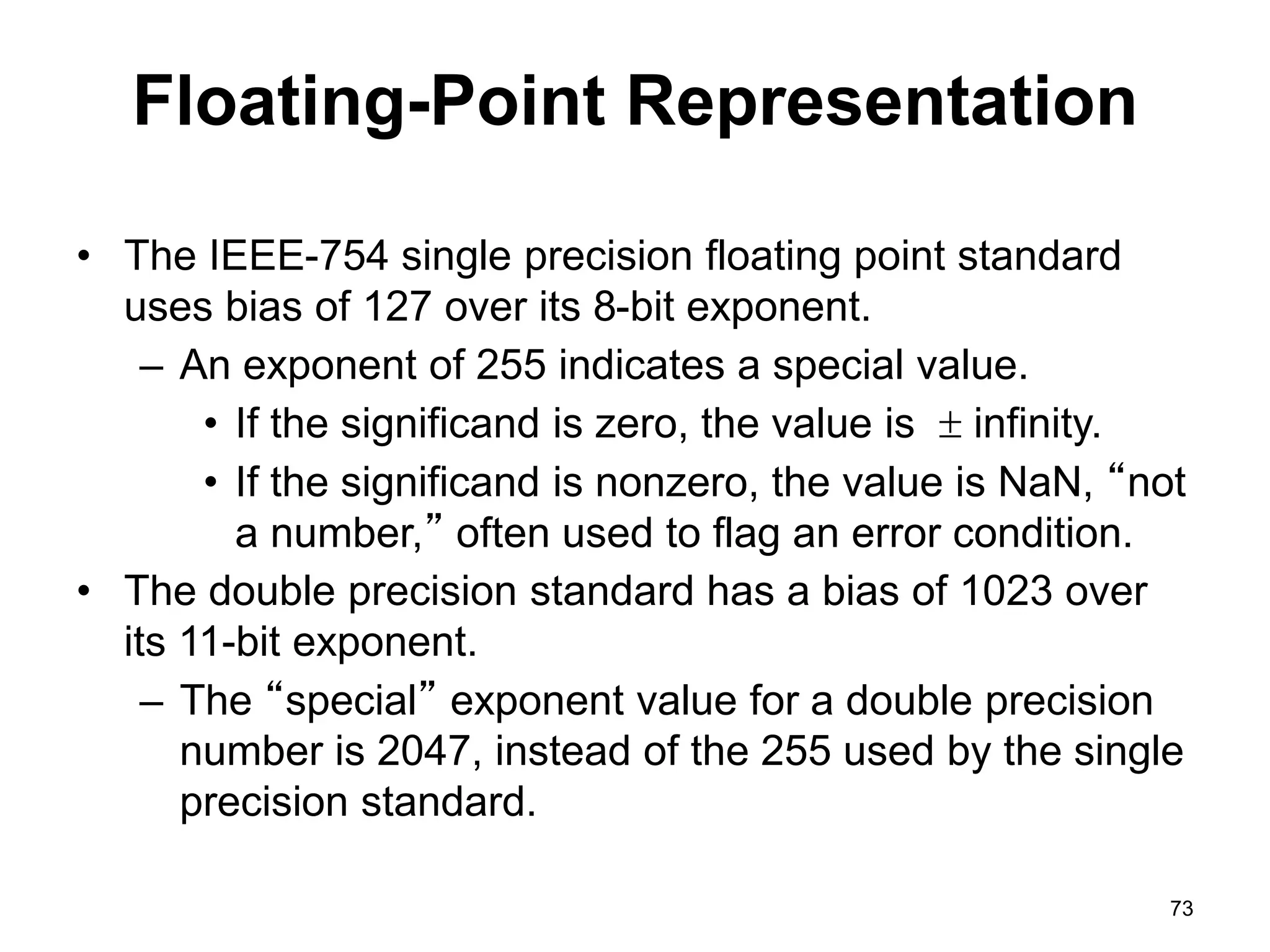
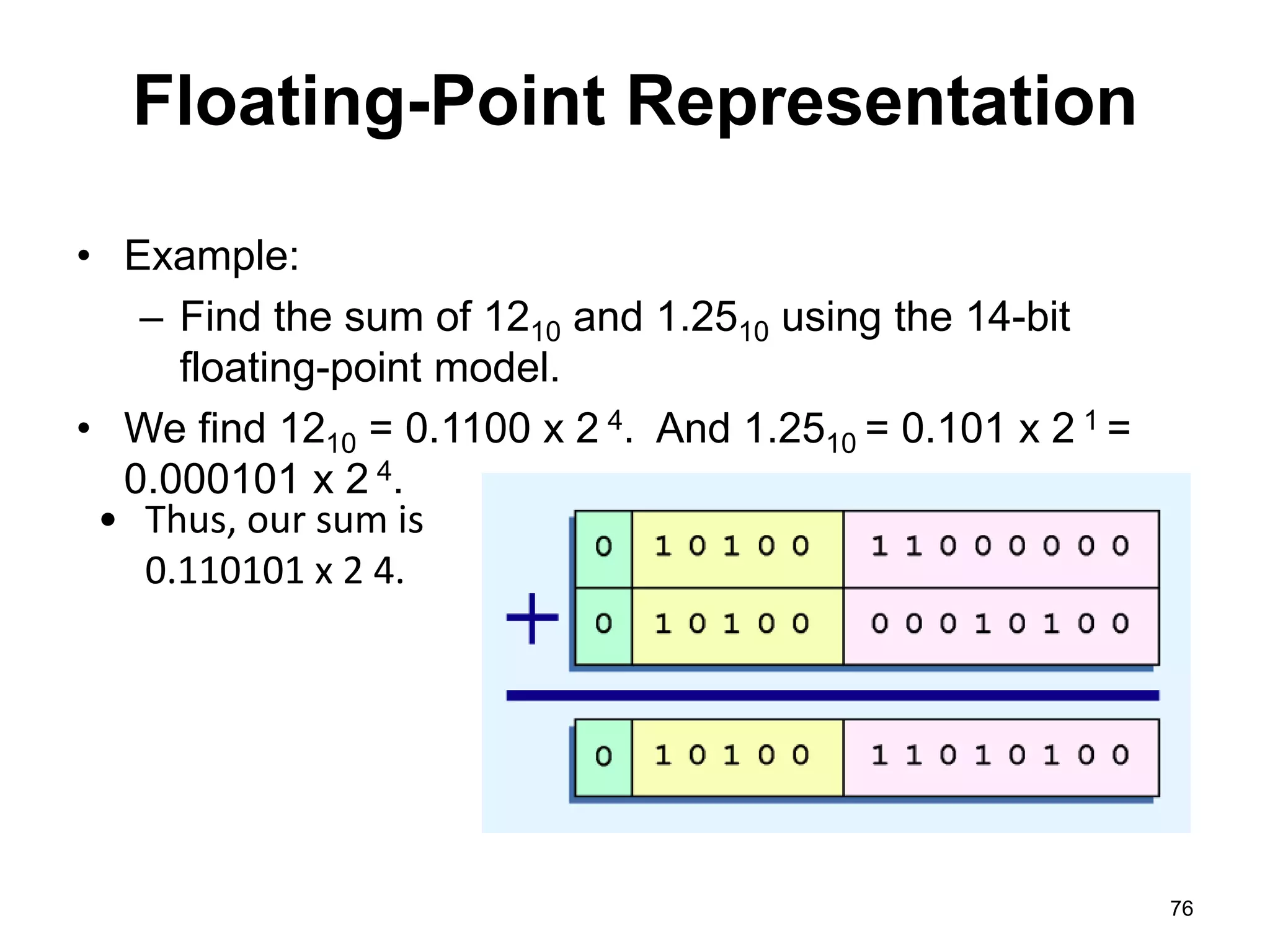
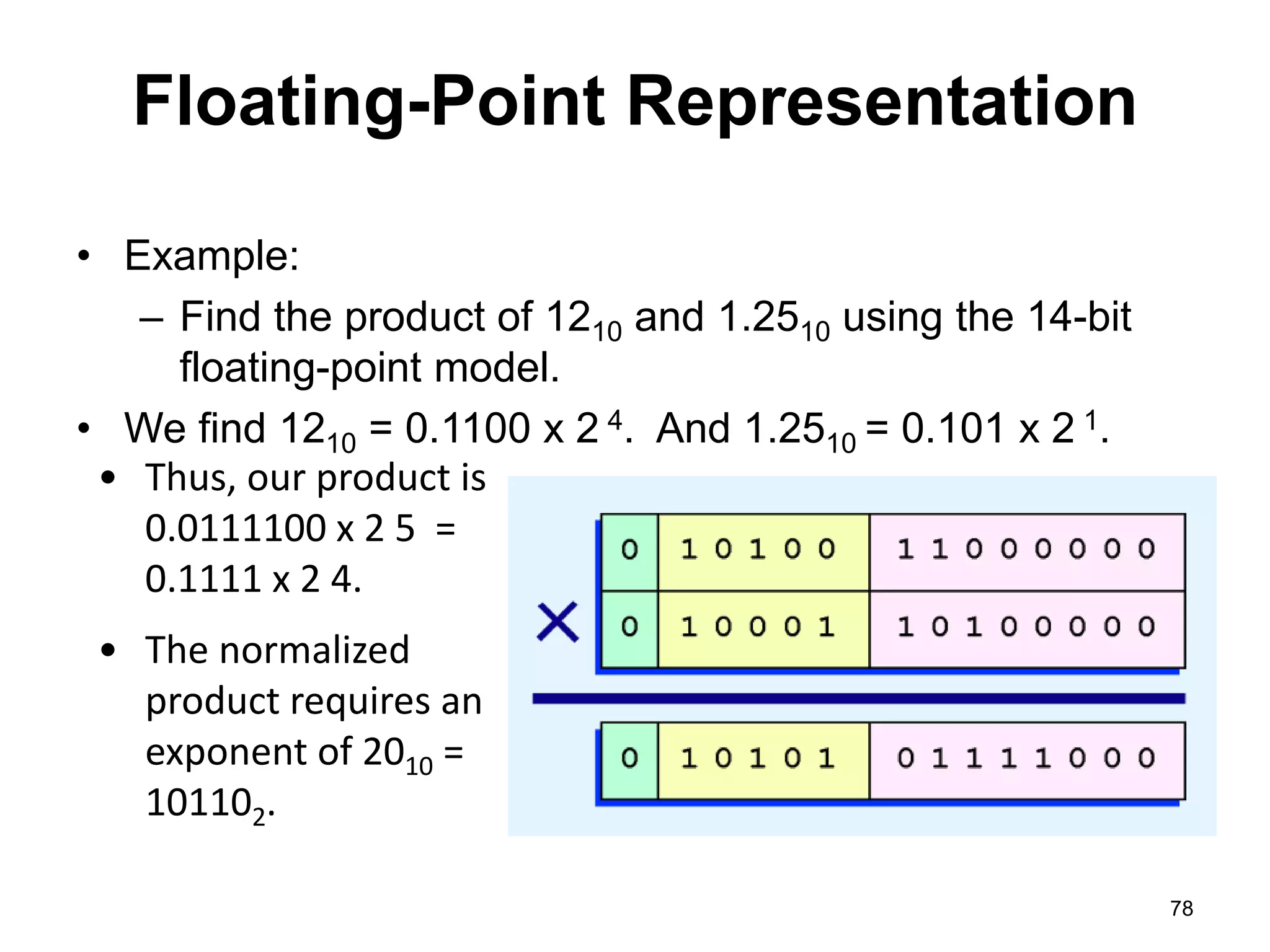
This document provides an overview of data representation in computers. It discusses binary, decimal, hexadecimal, and floating point number systems. Binary numbers use only two digits, 0 and 1, and can represent values as sums of powers of two. Decimal uses ten digits from 0-9. Hexadecimal uses sixteen values from 0-9 and A-F. Negative binary integers can be represented using ones' complement or twos' complement methods. Twos' complement avoids multiple representations of zero and is commonly used in computers. Converting between number bases involves expressing the value in one base using the digits of another.