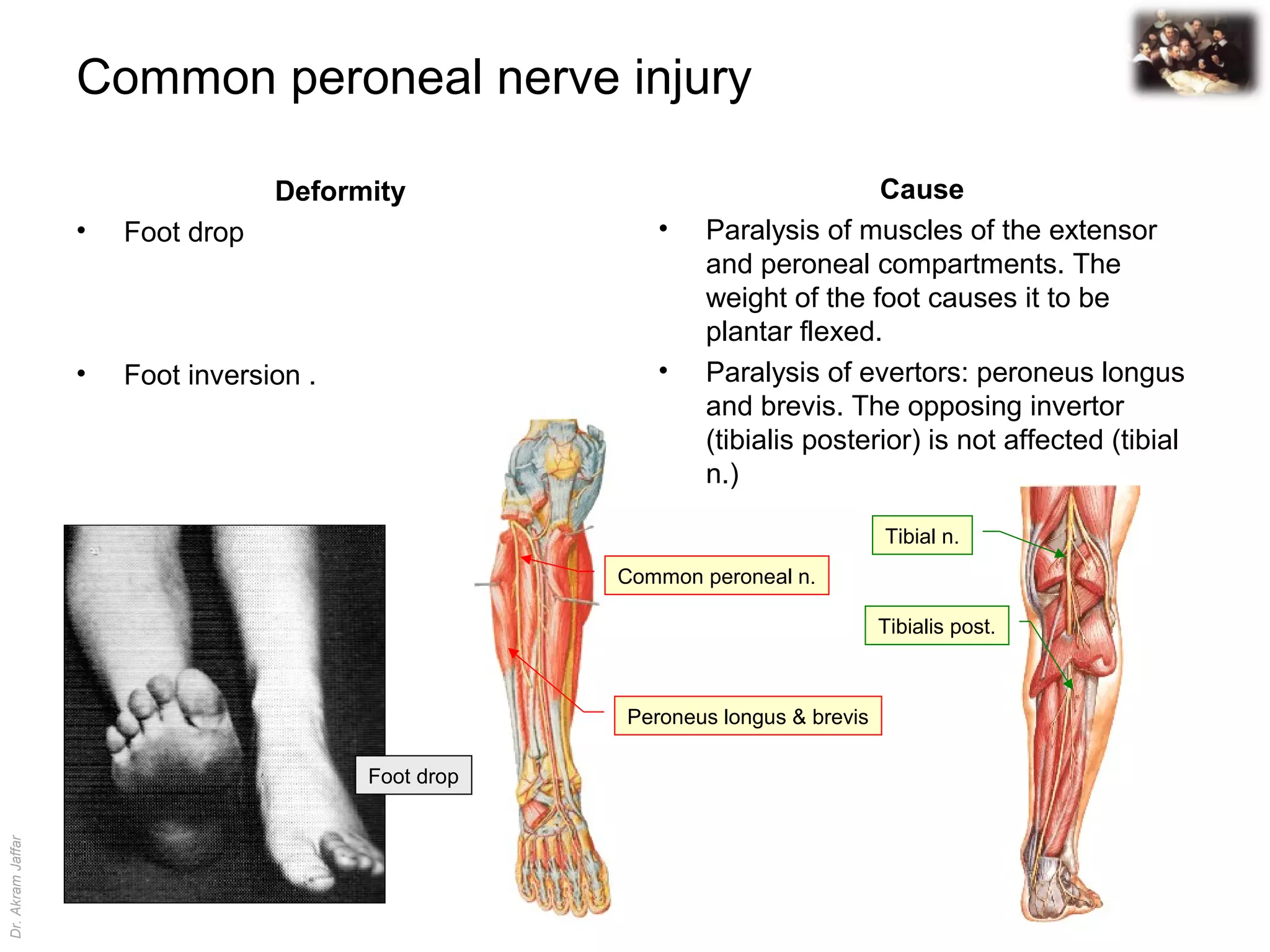
The common peroneal nerve is most commonly injured in the lower limb because it winds superficially around the neck of the fibula. Injury to this nerve can result in foot drop and foot inversion due to paralysis of the muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg. This causes the patient to have an abnormal "steppage gait" and sensory loss on the front and sides of the leg and foot. Surgical treatment may involve rerouting the tibialis posterior muscle, which is innervated by the intact tibial nerve, to the dorsal foot to help correct deformities caused by common peroneal nerve injury.