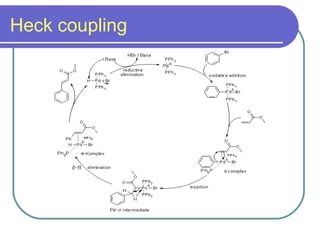
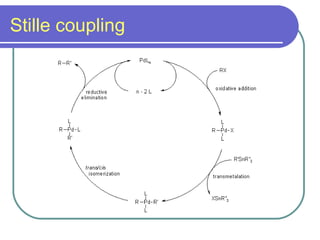
Coupling reactions involve joining two molecules together using a metal catalyst. There are two main types of coupling reactions: cross-coupling reactions where two different molecules react to form a new molecule, and homocoupling where two similar molecules couple together. Common metal catalysts include palladium, zinc, nickel, copper, boron, and tin. Important coupling reactions include Kumada, Heck, Sonogashira, Negishi, Stille, Suzuki, Hiyama, Buchwald-Hartwig, and Fukuyama reactions.