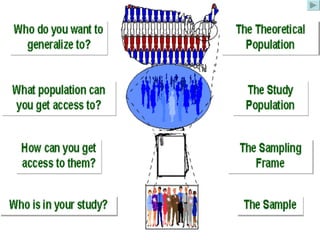
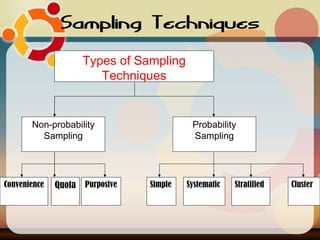
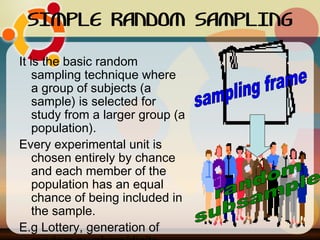
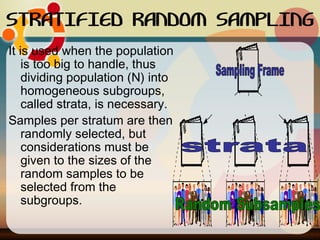
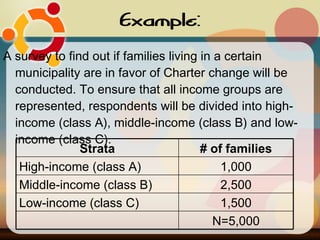
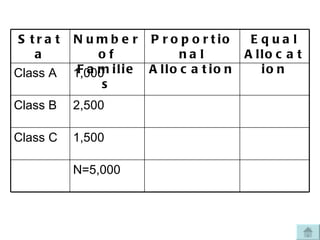
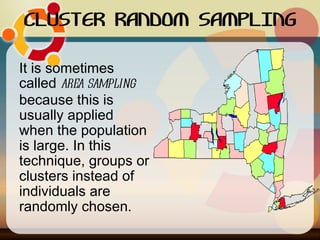
The document discusses common sampling techniques used in statistics, defining sampling as the process of selecting units from a population to generalize results. It covers various methods including probability and non-probability sampling, along with strategies like simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling, highlighting their advantages and procedures. Additionally, it explains sample size determination using Slovin's formula and provides examples to illustrate the concepts, emphasizing the importance of selecting representative samples for accurate research outcomes.