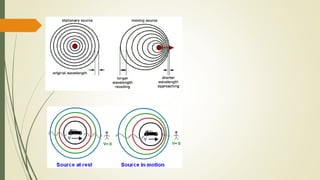
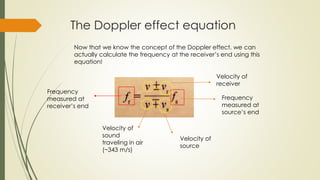
The Doppler effect describes how the frequency of a wave (such as sound) is perceived by an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. When an ambulance approaches with its siren on, the observer hears a higher pitch tone due to compression of the sound waves. As the ambulance passes and moves away, the observer hears a lower pitch tone due to expansion of the sound waves. The Doppler effect can be calculated using an equation that takes into account the velocity of sound, velocity of the source, and velocity of the receiver.