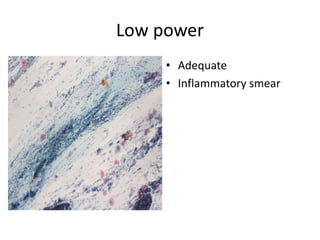
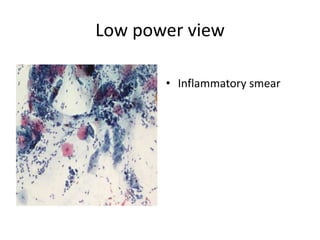
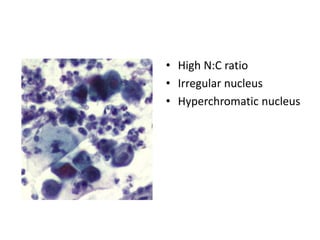
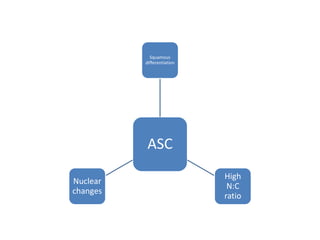
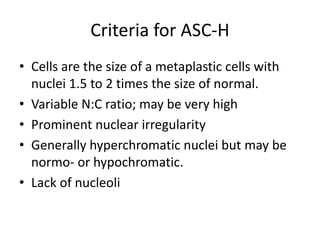
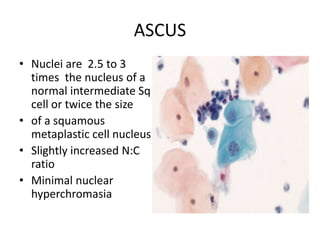
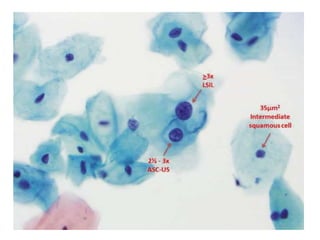
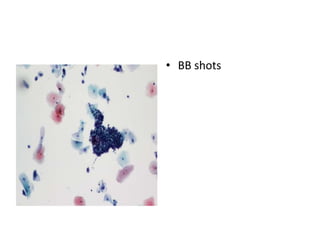
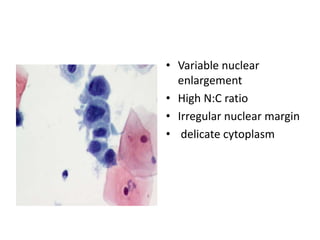
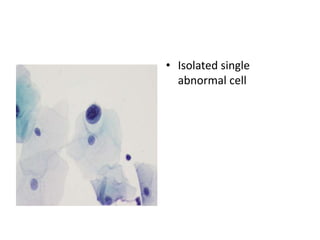
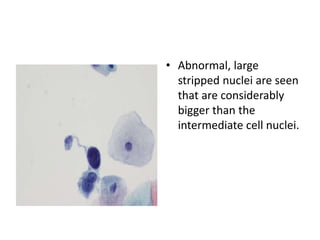
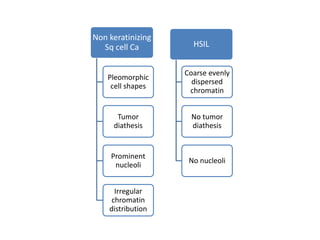
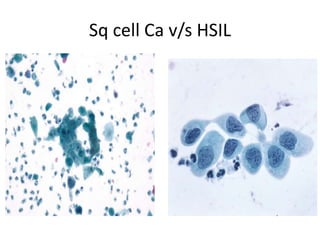
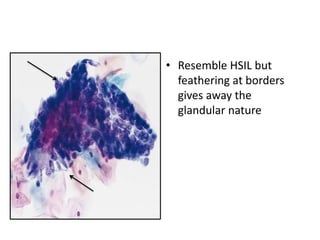
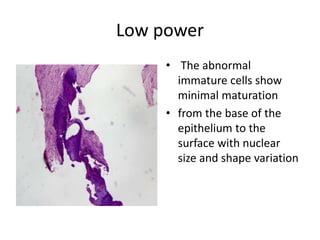
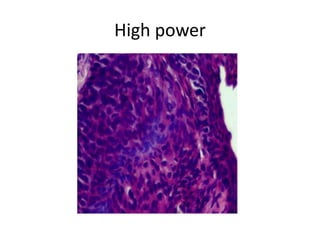
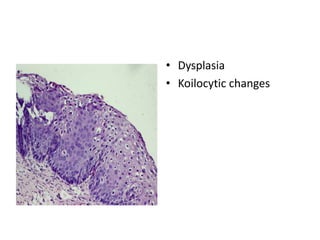
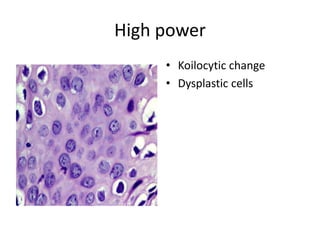
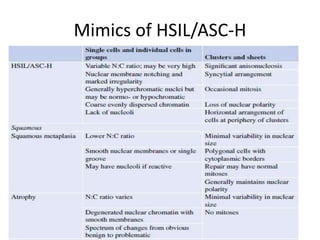
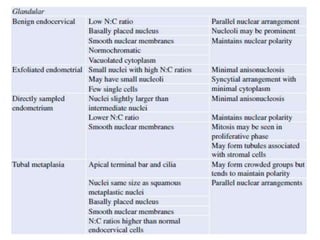
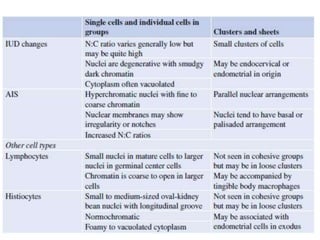
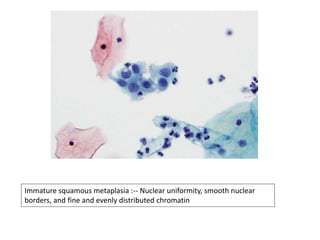
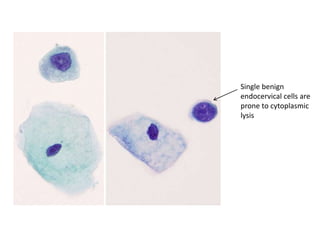
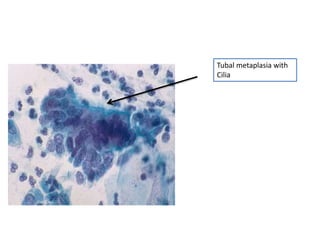
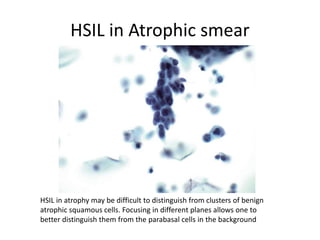
This document summarizes the Pap smear examination results of a 39-year-old HIV-positive female patient. On initial examination, the patient was found to have an inflammatory smear with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio and irregular, hyperchromatic nuclei. This was assessed as atypical squamous cells cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H). On follow up, a syncytial cluster was seen with similar abnormal cellular features, leading to a diagnosis of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL). A cervical biopsy confirmed carcinoma in situ of the cervix. The document discusses the criteria used to make these assessments and differentiate HSIL from