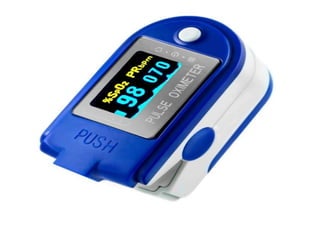
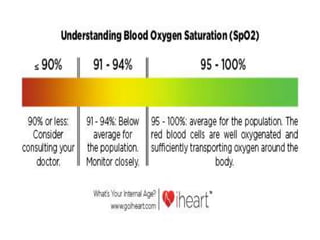
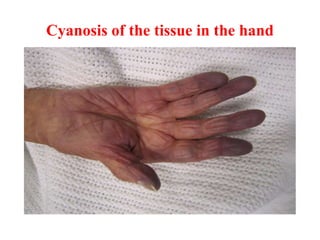
This document discusses SpO2 levels, also known as blood oxygen saturation. It defines SpO2 as a measure of the amount of oxygen-carrying hemoglobin in the blood. Very low SpO2 levels can cause hypoxemia and result in serious symptoms or turn into hypoxia. The body normally maintains healthy SpO2 levels through breathing and adapting oxygen intake during times of stress. SpO2 can be measured using a pulse oximeter, which is placed on the finger and displays a percentage between 94-100%, indicating a healthy level. Symptoms of low SpO2 include fatigue, lightheadedness, and numbness.