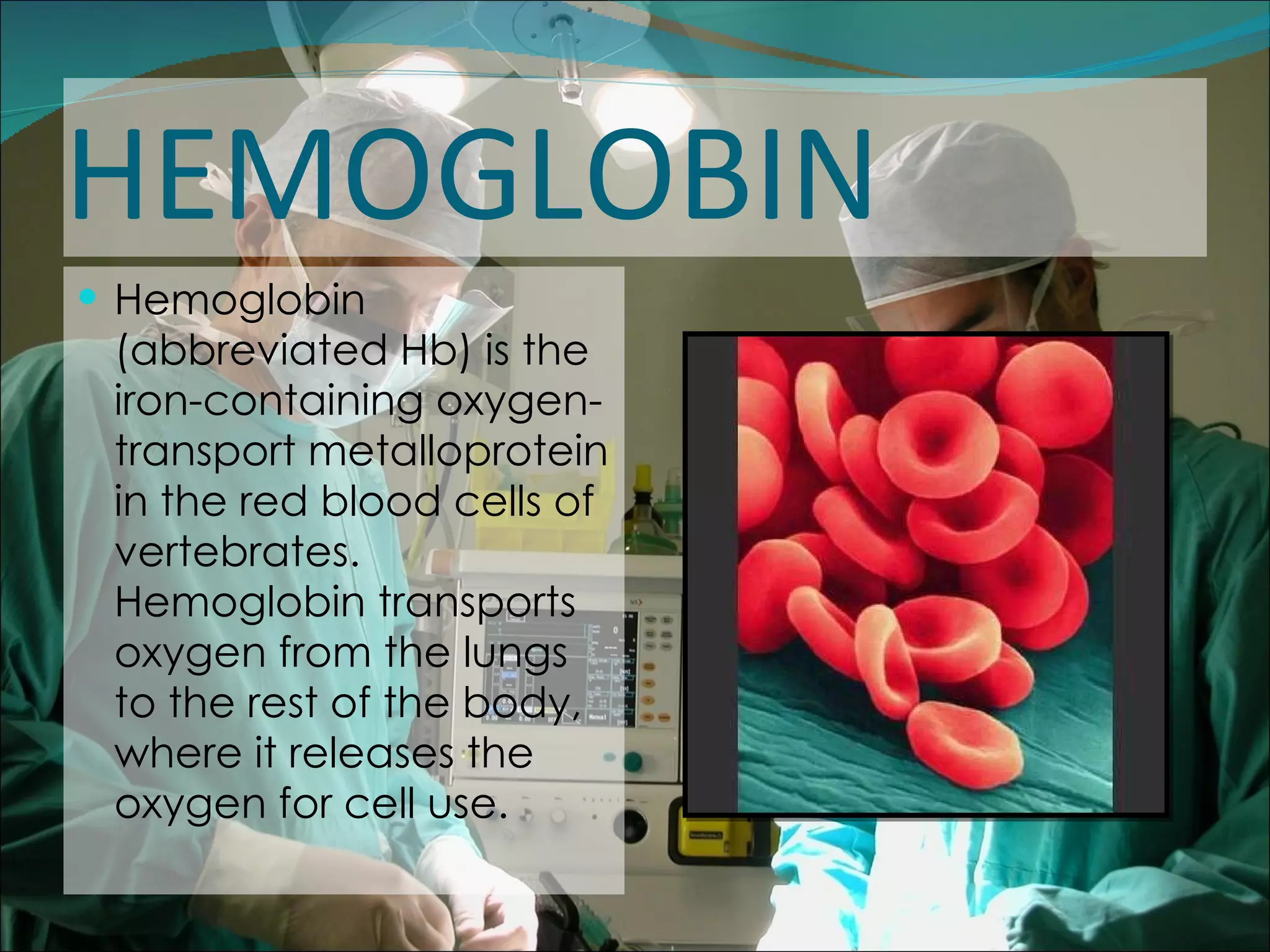
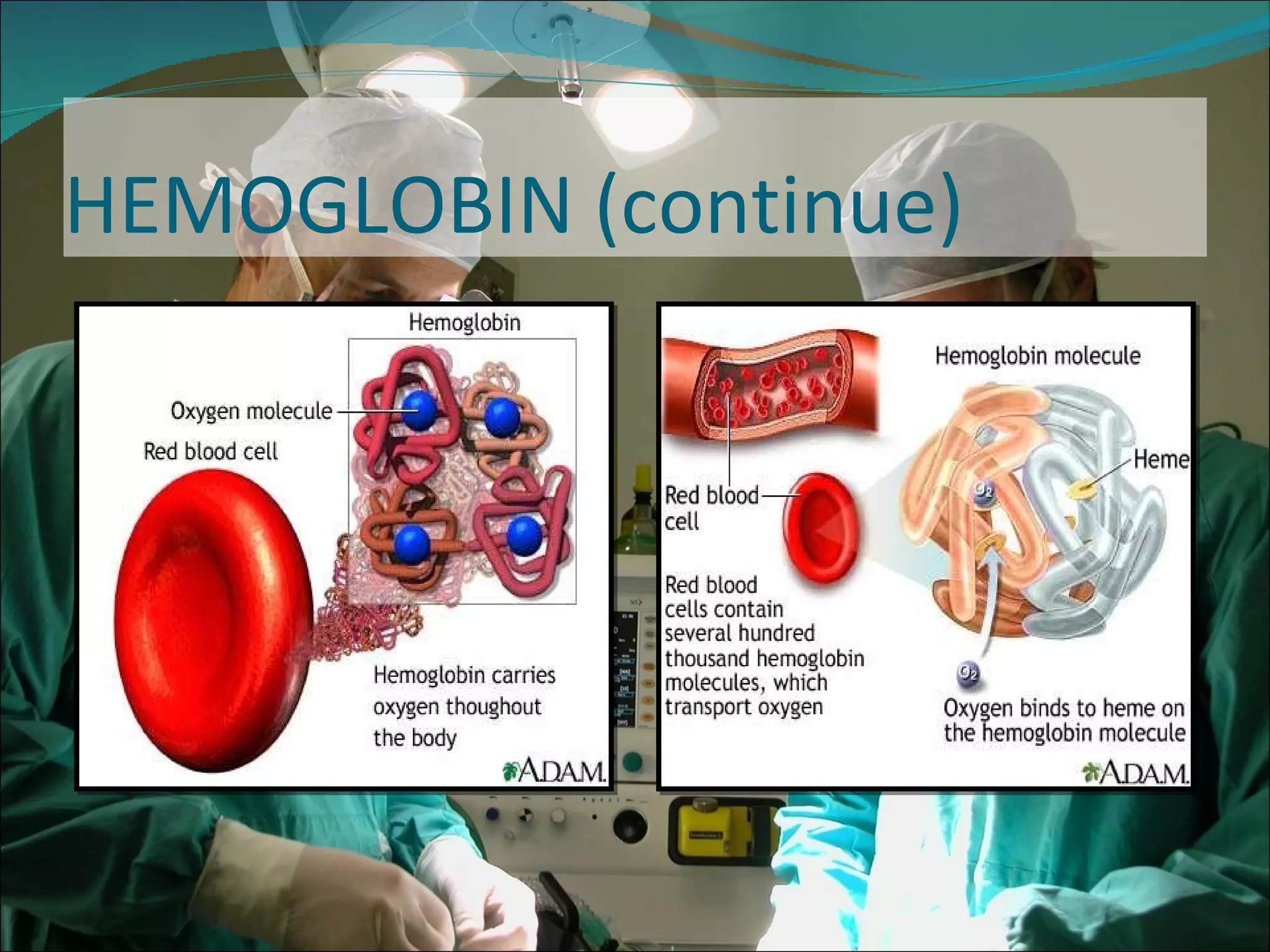
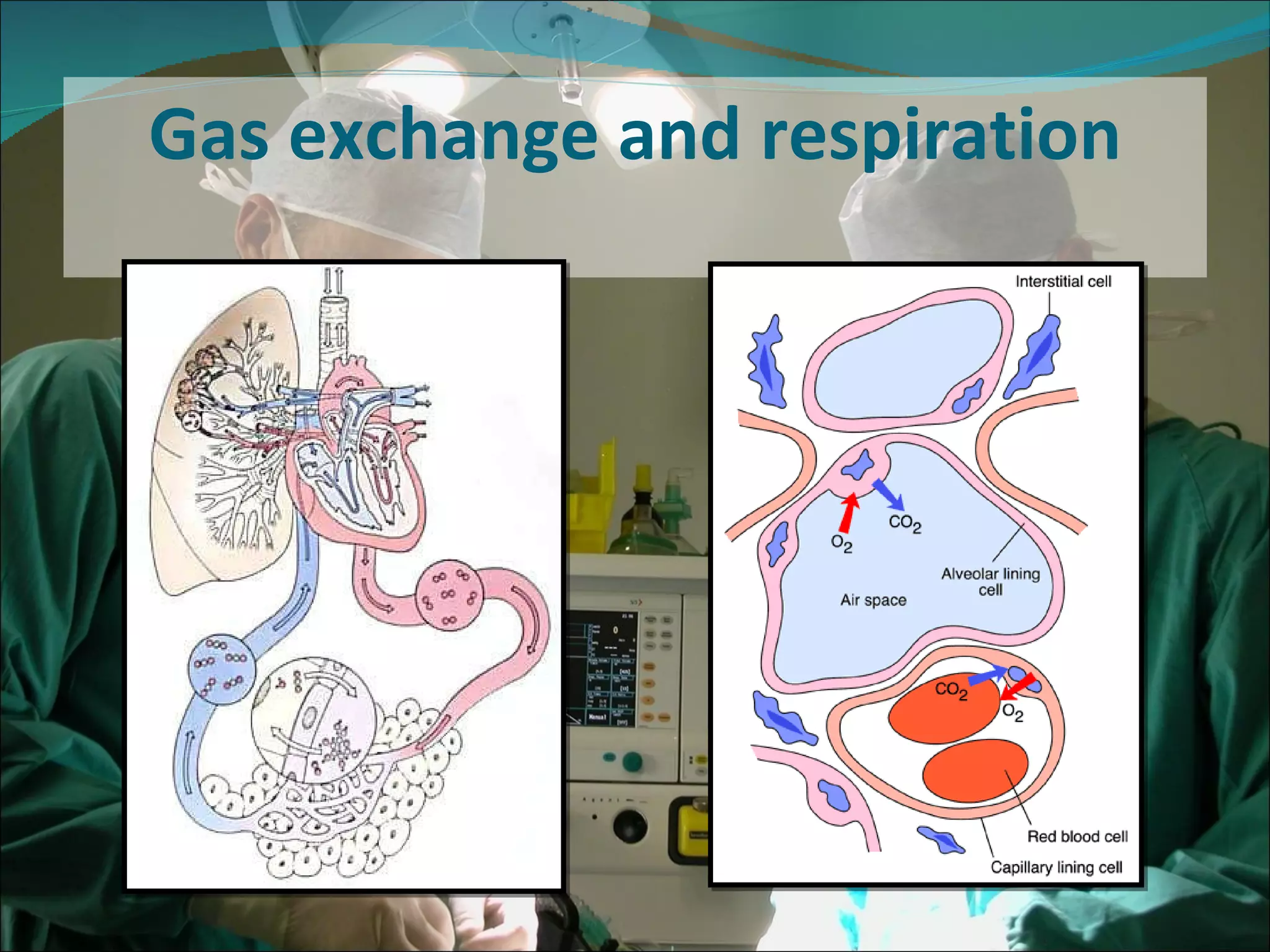
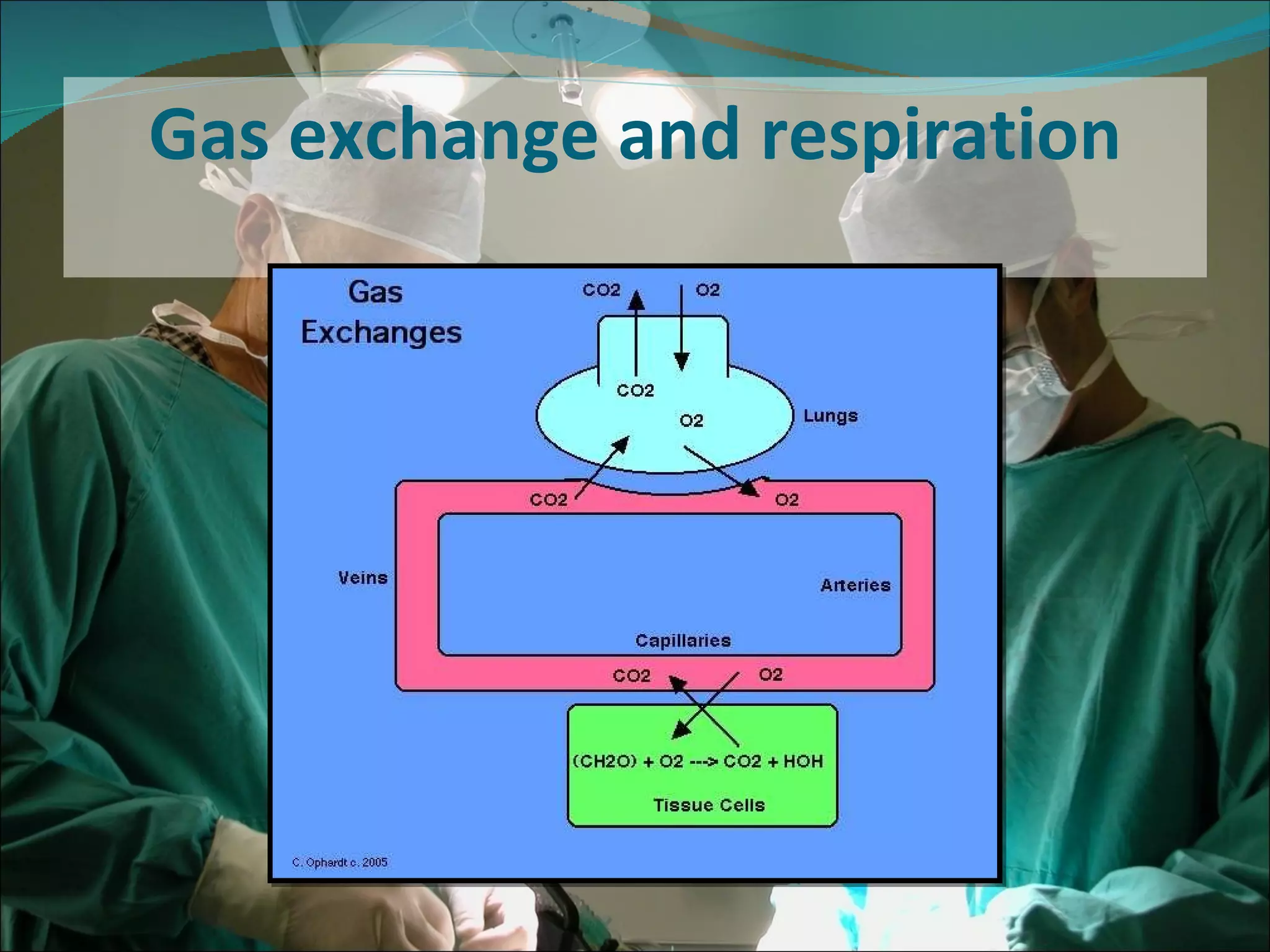
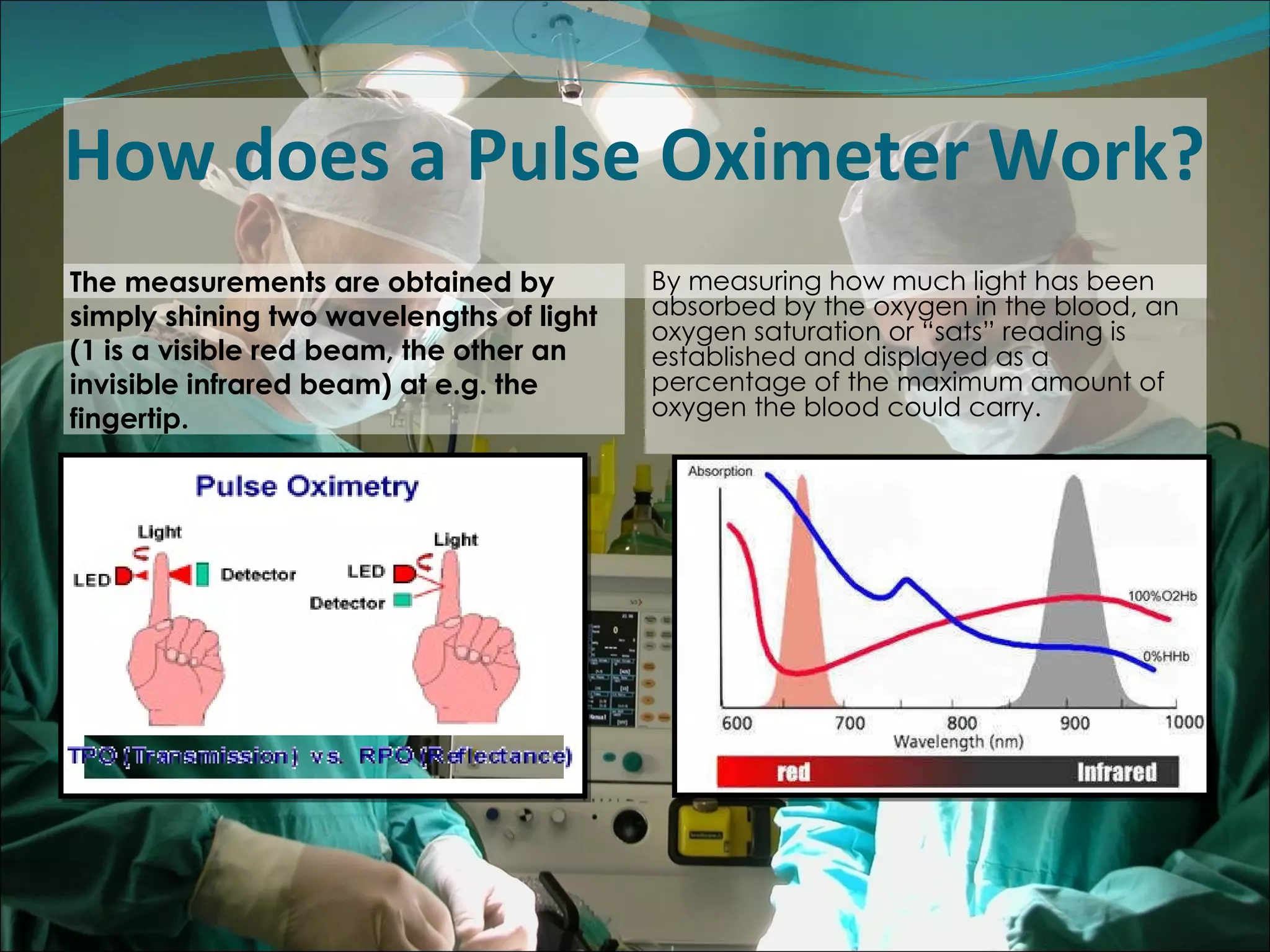
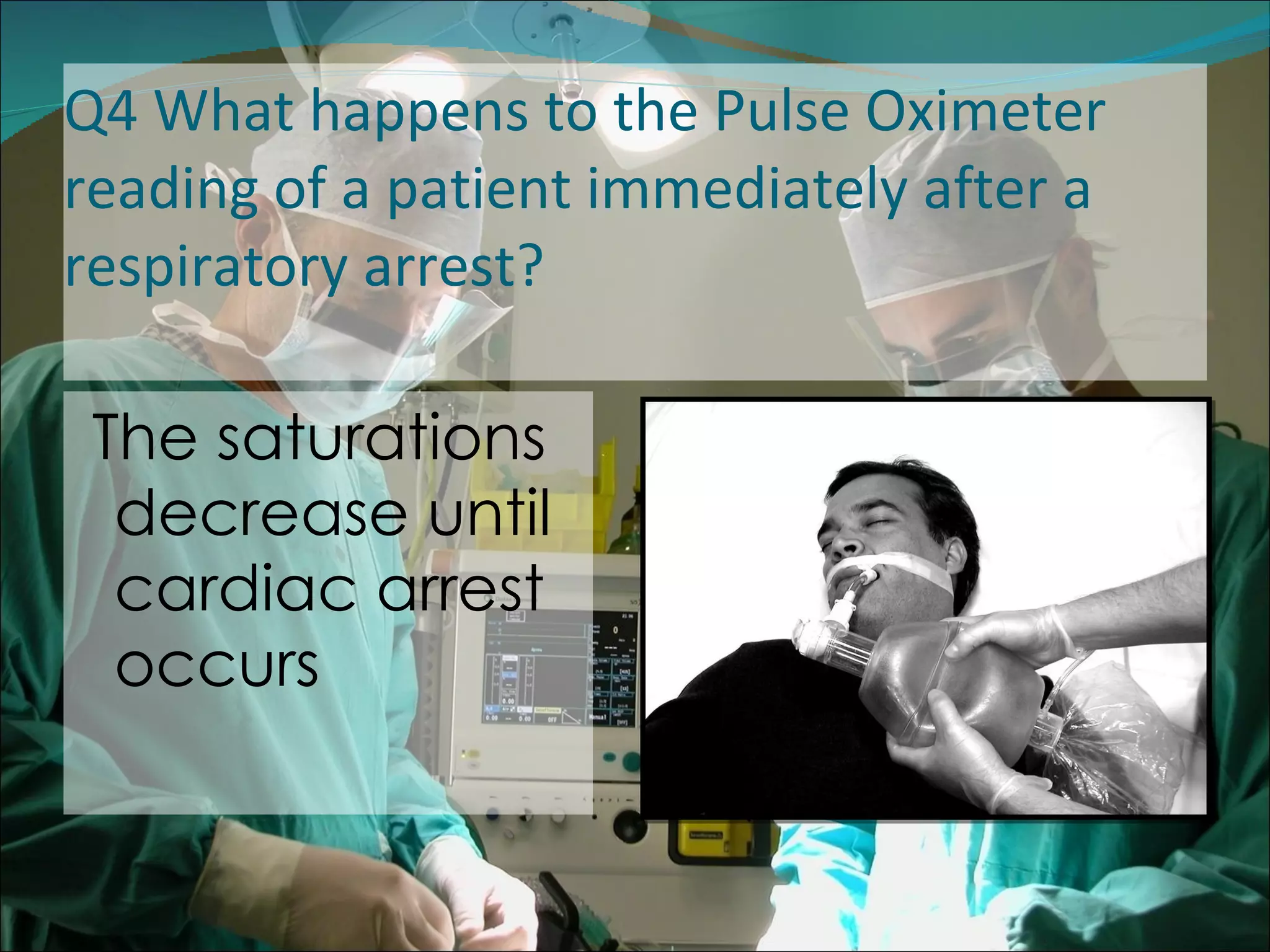
A pulse oximeter is a non-invasive device used to measure oxygen saturation and heart rate. It works by shining two wavelengths of light through tissues like a finger or earlobe to determine the ratio of oxygenated to deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. Normal oxygen saturation is between 95-99% but can be lower in conditions like COPD or circulatory issues. If saturation is low, actions like increasing oxygen delivery or checking ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation) may be needed. The device provides useful information but can be affected by factors like low blood flow, so clinical judgement is also important.