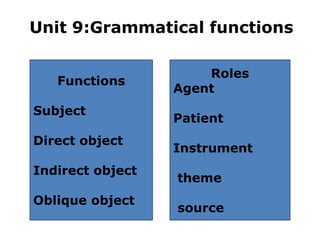
This document discusses grammatical functions and the subject and object in English syntax. It defines the subject as the grammatical function that precedes the verb, agrees with the verb in number, and is compulsory. The three types of objects are defined as the direct object, which follows the main verb, the indirect object, which benefits from the verb's action, and the oblique object, which follows a preposition. Criteria for identifying the subject include syntactic, morphosyntactic, and semantic criteria. Types of subjects are also defined as grammatical, logical, and psychological subjects.