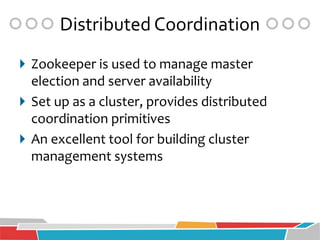
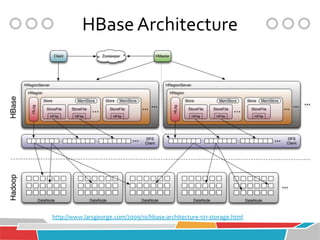
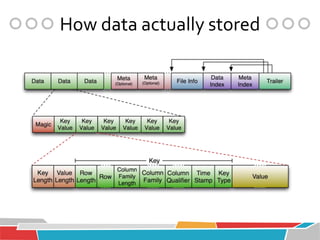
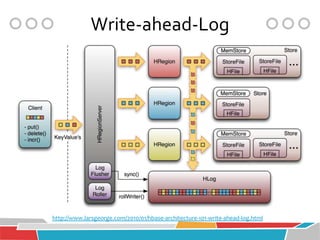
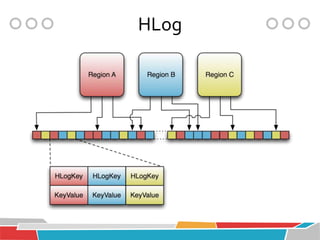
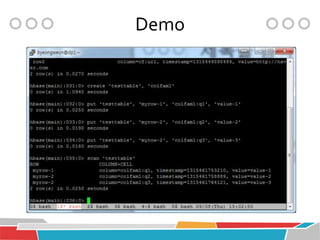
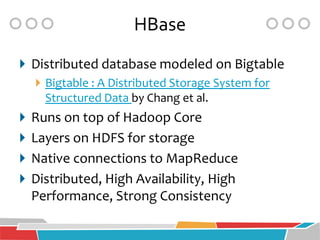
HBase is a distributed, column-oriented database that runs on top of Hadoop and HDFS, providing Bigtable-like capabilities for massive tables of structured and unstructured data. It is modeled after Google's Bigtable and provides a distributed, scalable, versioned storage system with strong consistency for random read/write access to billions of rows and millions of columns. HBase is well-suited for handling large datasets and providing real-time read/write access across clusters of commodity servers.


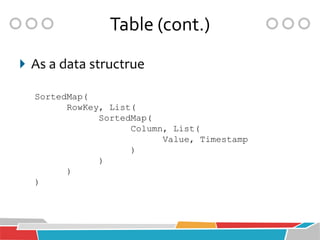
![Table (cont.)
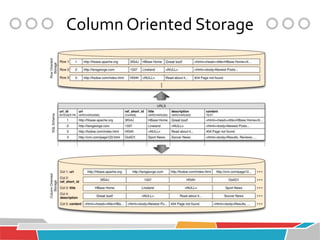
Tables are sorted by Row
Table schema defines column families
Families consist of any number of columns
Columns consist of any number of versions
Everything except table name is byte[]
(Table, Row, Family:Column, Timestamp) -> Value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontohbase-121207231302-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HBase-9-320.jpg)