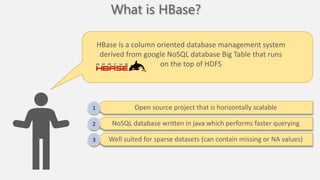
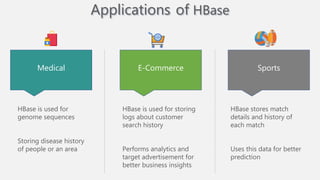
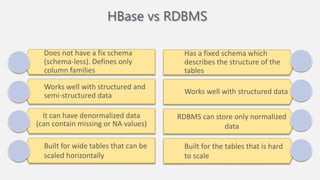
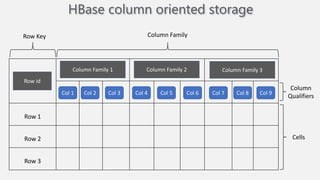
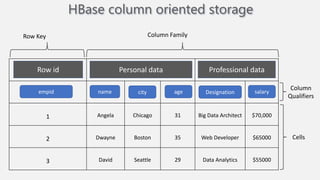
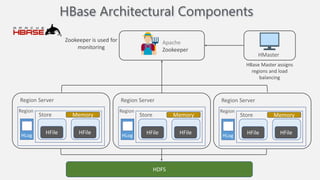
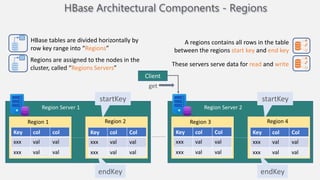
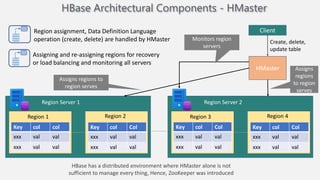
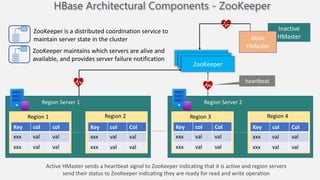
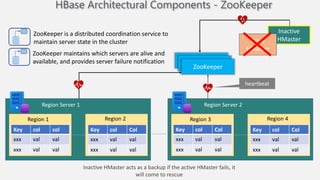
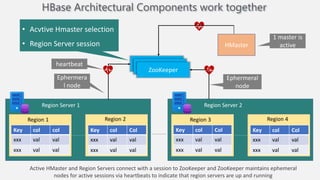
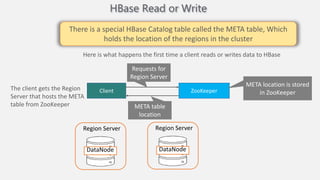
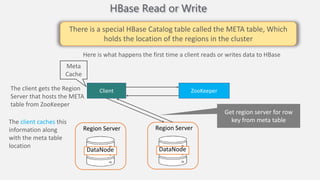
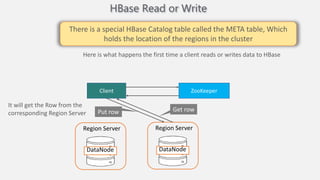
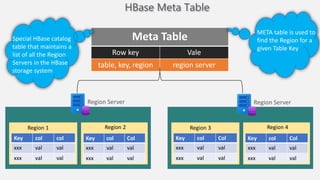
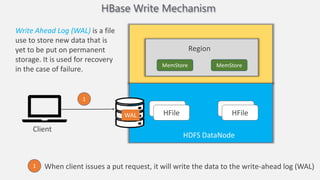
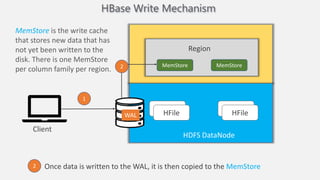
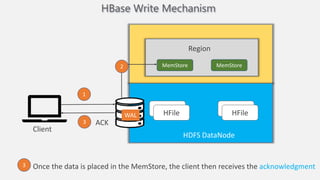
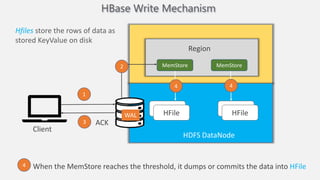
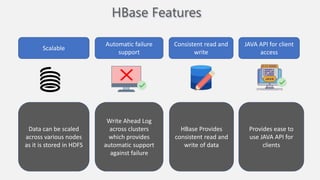
Atilim University hosted a presentation on HBase given by Dr. Ziya Karakaya and Mirwais Doost. The presentation covered what HBase is, its features and applications, how it compares to relational databases, its storage model, and architectural components. HBase is a column-oriented NoSQL database that runs on HDFS and is well-suited for sparse datasets. It provides horizontal scalability and supports features like consistent reads/writes and failure recovery through its use of write-ahead logging.