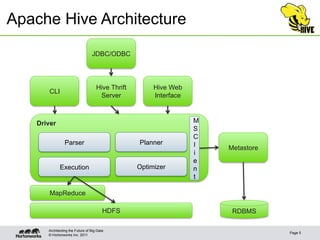
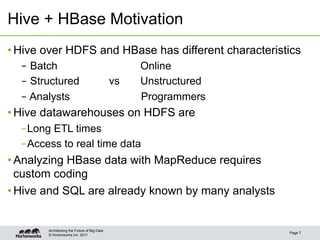
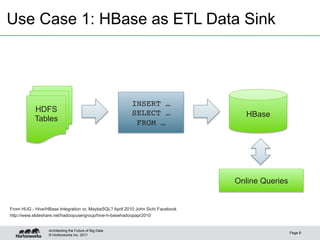
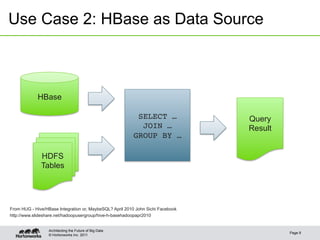
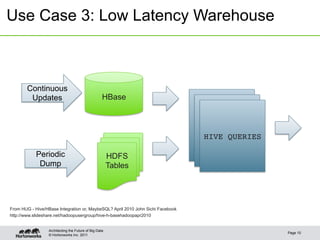
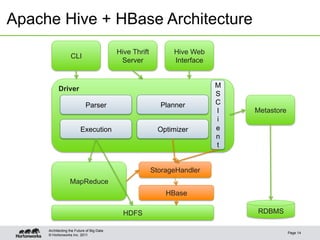
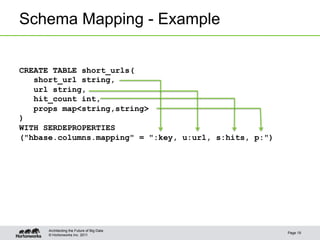
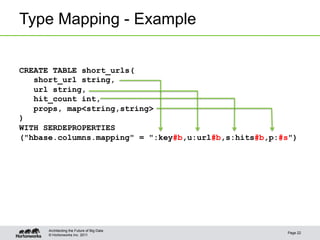
This document discusses integrating Apache Hive with HBase. It describes how Hive can be used to query HBase tables via a storage handler. Key features covered include using HBase as a data source or sink for Hive, mapping Hive schemas and types to HBase schemas, pushing filters down to HBase, and bulk loading data. The future of Hive and HBase integration could include improvements to schema mapping, filter pushdown support, and leveraging new HBase typing APIs.
![© Hortonworks Inc. 2011
Integration of Apache Hive
and HBase
Enis Soztutar
enis [at] apache [dot] org
Page 1
Ashutosh Chauhan
hashutosh [at] apache [dot] org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecosystem-session1a-130709112436-phpapp01/75/HBaseCon-2013-Integration-of-Apache-Hive-and-HBase-1-2048.jpg)