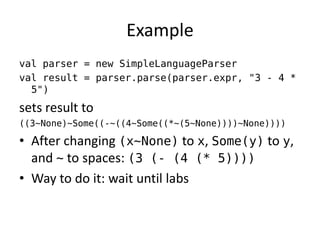
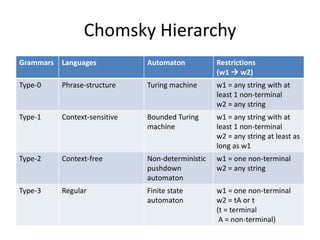
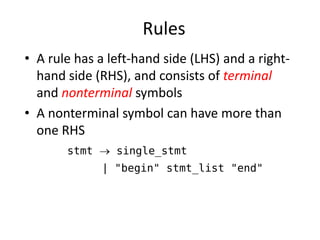
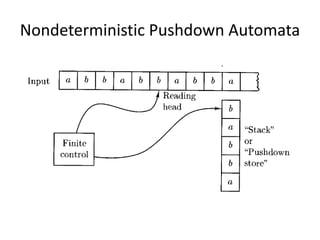
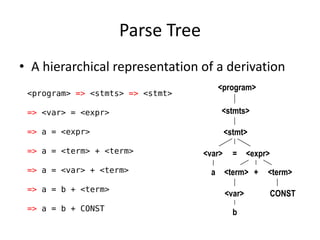
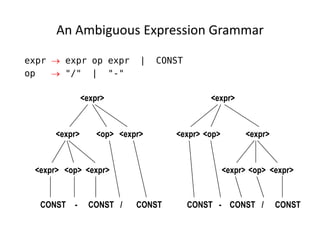
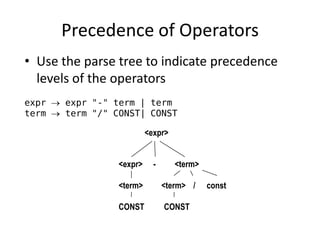
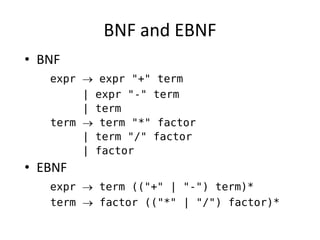
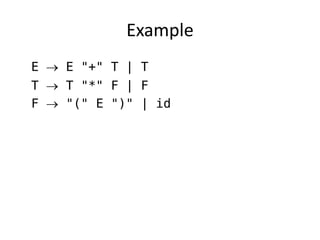
The document discusses syntax analysis and parsing. It covers context-free grammars, Backus-Naur Form (BNF), Extended BNF, and different parsing techniques like recursive descent parsing and LL parsing. It also discusses Scala's combinator parser, which uses parser combinators to parse input based on a grammar.

































![Pairwise Disjointness
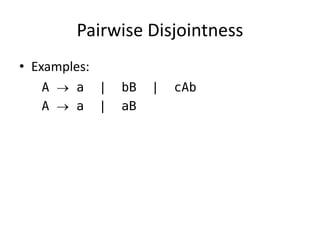
•Left factoring can resolve the problem
Replace
variable IDENTIFIER | IDENTIFIER "[" expression "]"
with
variable IDENTIFIER new
new e | "[" expression "]"
or
variable IDENTIFIER ("["expression"]")?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-141110164832-conversion-gate02/85/Control-structure-44-320.jpg)
![Building Grammar Techniques
•Repetition
–[10][10][20]
•Repetition with separators
–id(arg1, arg2, arg3,…)
•Operator precedence
•Operator associativity
•Avoiding left recursion
•Left factoring
•Disambiguation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-141110164832-conversion-gate02/85/Control-structure-46-320.jpg)
![Combinator Parser
expr term (("+" | "-") expr)?
term factor (("*" | "/") term)?
factor wholeNumber | "(" expr ")"
class SimpleLanguageParser extends JavaTokenParsers {
def expr: Parser[Any] = term ~ opt(("+" | "-") ~ expr)
def term: Parser[Any] = factor ~ opt(("*" | "/" ) ~ term)
def factor: Parser[Any] = wholeNumber | "(" ~ expr ~ ")"
}
•Will replace Parser[Any] with something more useful later](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-141110164832-conversion-gate02/85/Control-structure-48-320.jpg)