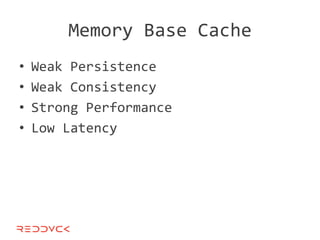
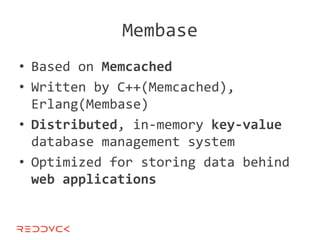
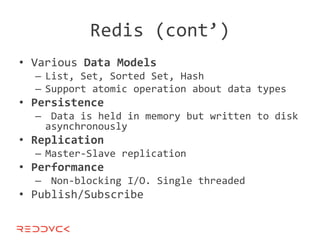
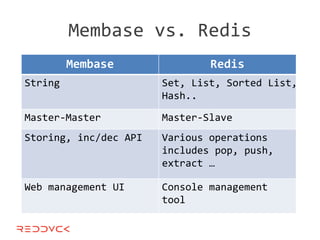
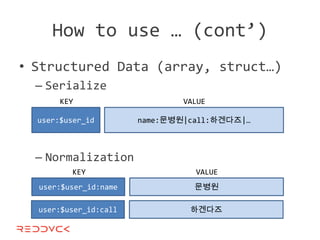
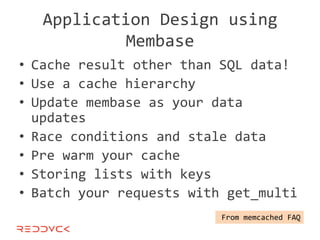
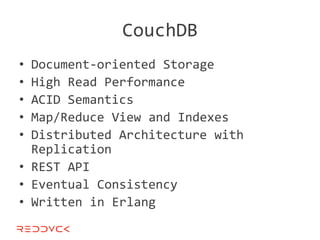
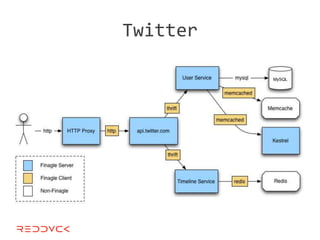
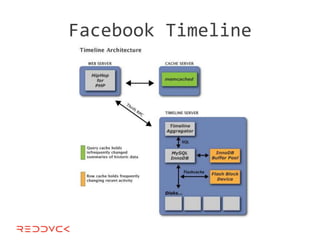
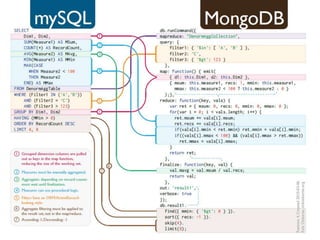
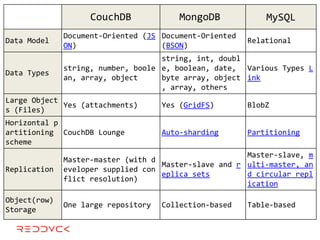
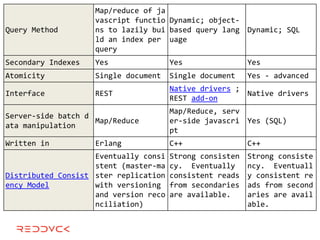
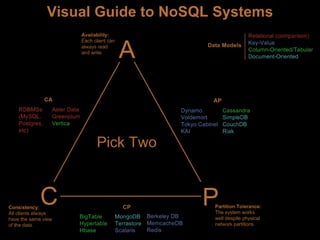
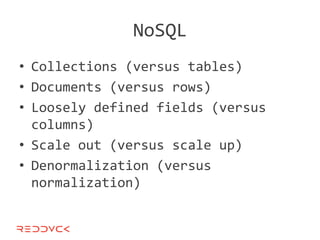
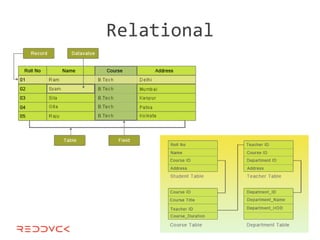
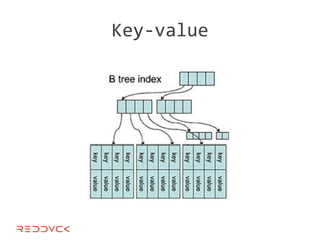
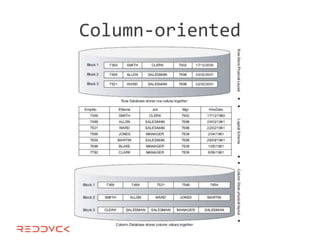
This document compares NoSQL solutions like Redis, Couchbase, MongoDB, and Membase. It discusses their data models, features, and how they differ from relational databases. Key-value, column-oriented, and document-oriented databases are covered. Specific products like Membase, Redis, MongoDB, and CouchDB are also summarized, including their data models, replication methods, and typical uses in applications.


![Document-oriented
FirstName="Jonathan",
Address="15 Wanamassa Point
Road",
K Children=[
E {Name:"Michael",Age:10},
Y {Name:"Jennifer", Age:8},
{Name:"Samantha", Age:5},
{Name:"Elena", Age:2}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlsolutions-121207231634-phpapp01/85/No-sql-solutions-10-320.jpg)