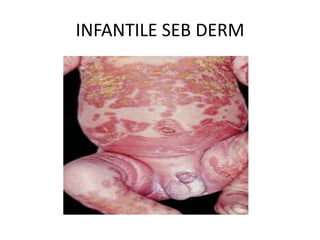
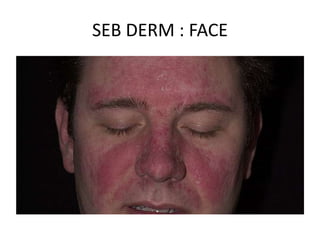
This document discusses seborrheic dermatitis, a chronic papulosquamous skin condition associated with seborrhea and seen along sebaceous gland distributions like the scalp, face, and trunk. It presents in infants as cradle cap and in adults as flaky, greasy, or powdery erythematous patches with scaling. Causative factors may include sebum retention, Malassezia yeasts, and genetic or nutritional factors. Treatment involves topical antifungals, corticosteroids, keratolytics, immunomodulators, coal tar, or systemic antifungals. Differential diagnoses include atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and tinea