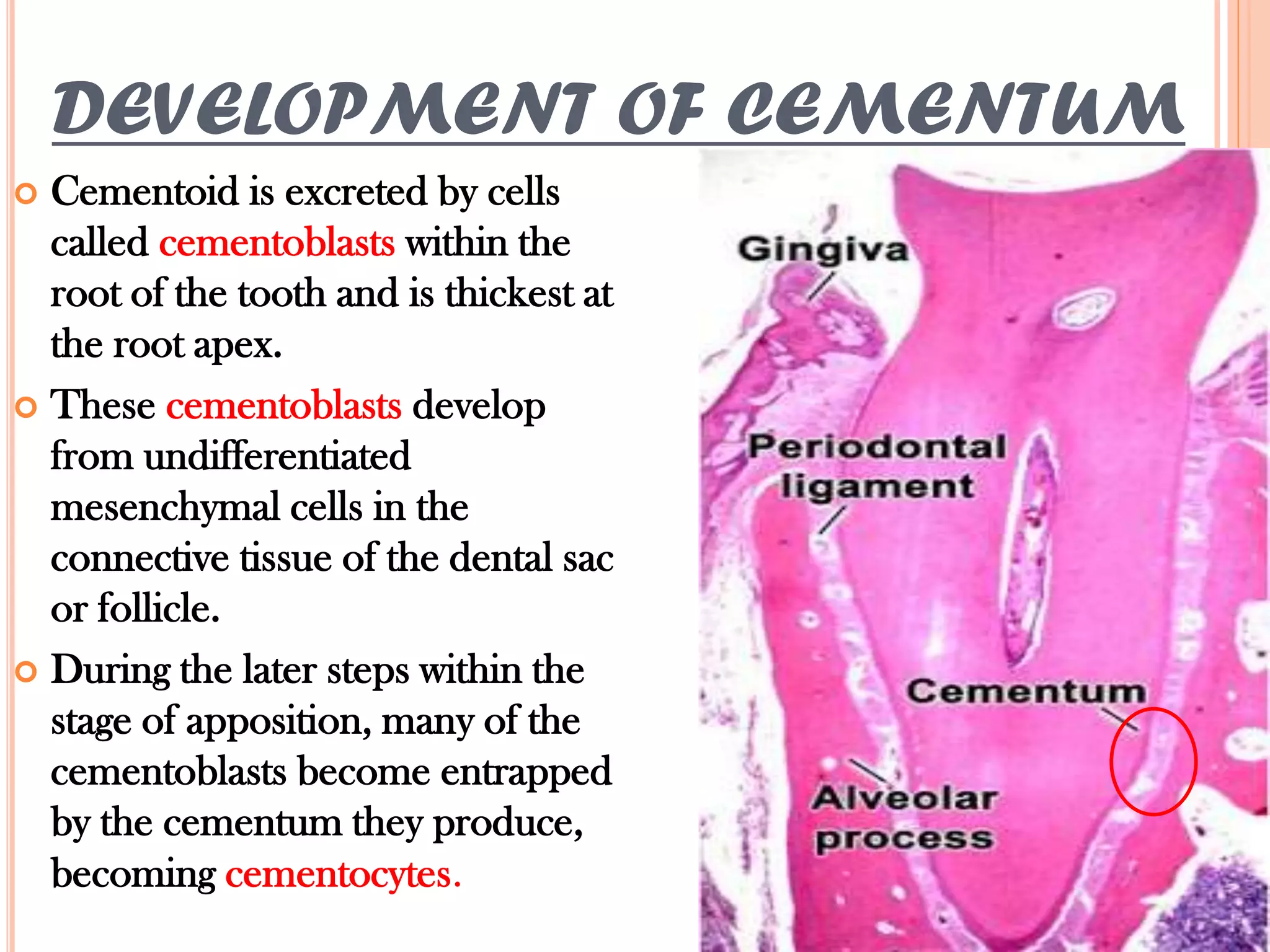
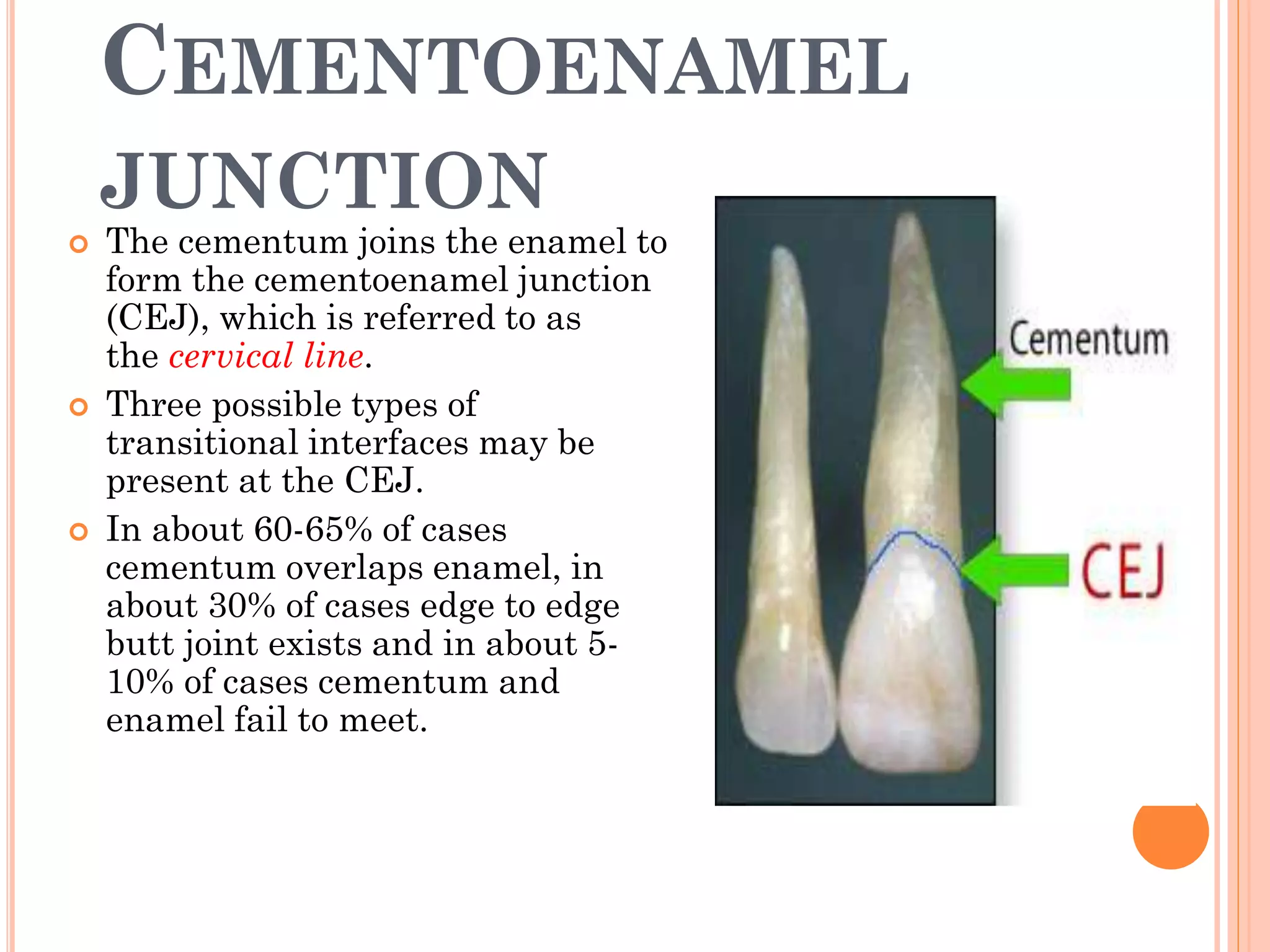
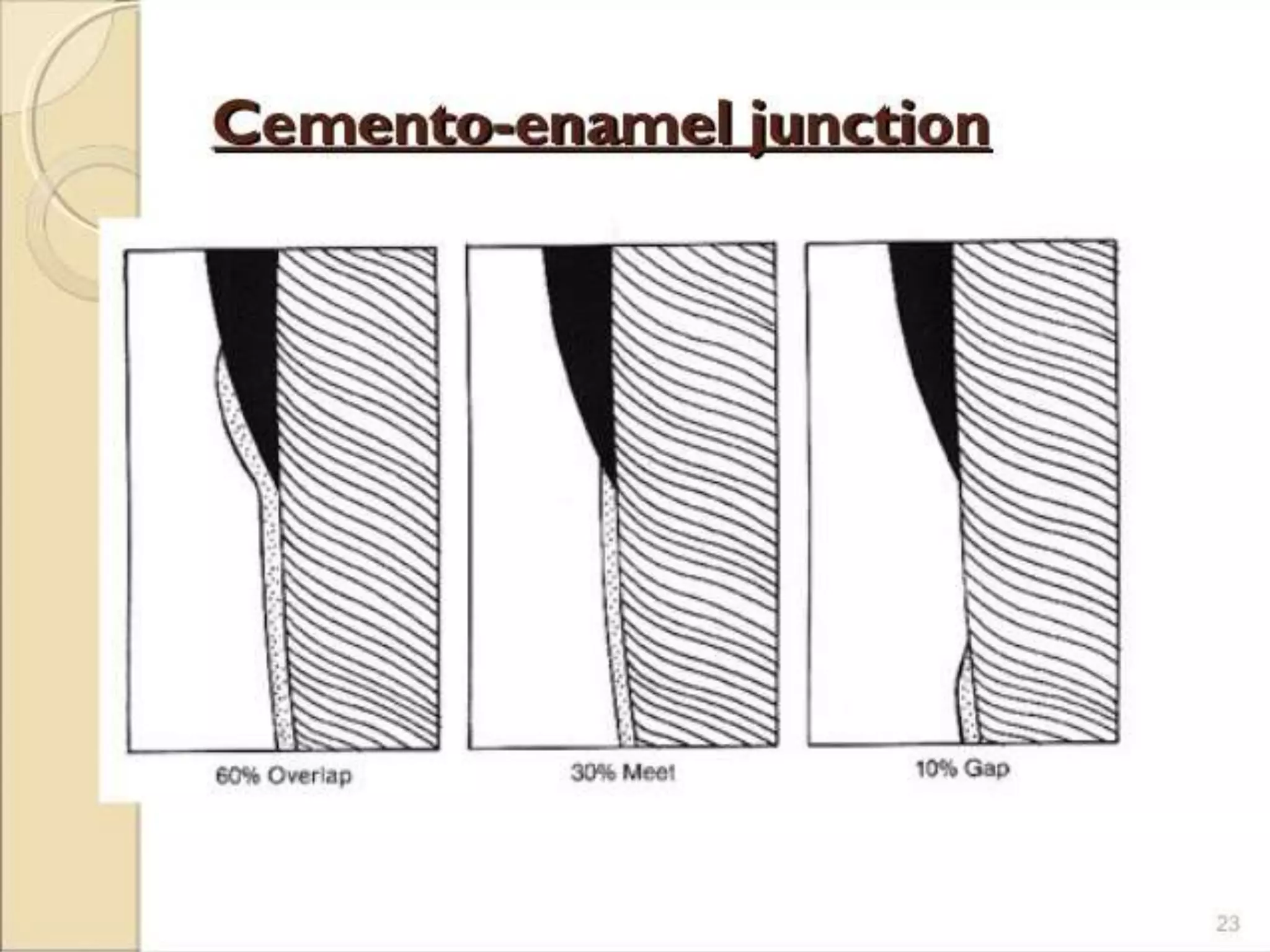
Cementum is the calcified tissue that covers the roots of teeth and anchors the periodontal ligament. It develops from mesenchymal cells and is laid down by cementoblasts. There are two types of cementum: acellular cementum makes up the cervical third of roots and contains no cells, while cellular cementum contains cementocytes and covers the middle and apical thirds of roots. Cementum attaches to enamel at the cementoenamel junction and to dentin at the dentinocemental junction. Pathologies include hypercementosis, ankylosis and cementum resorption due to trauma, disease or orthodontic movement.