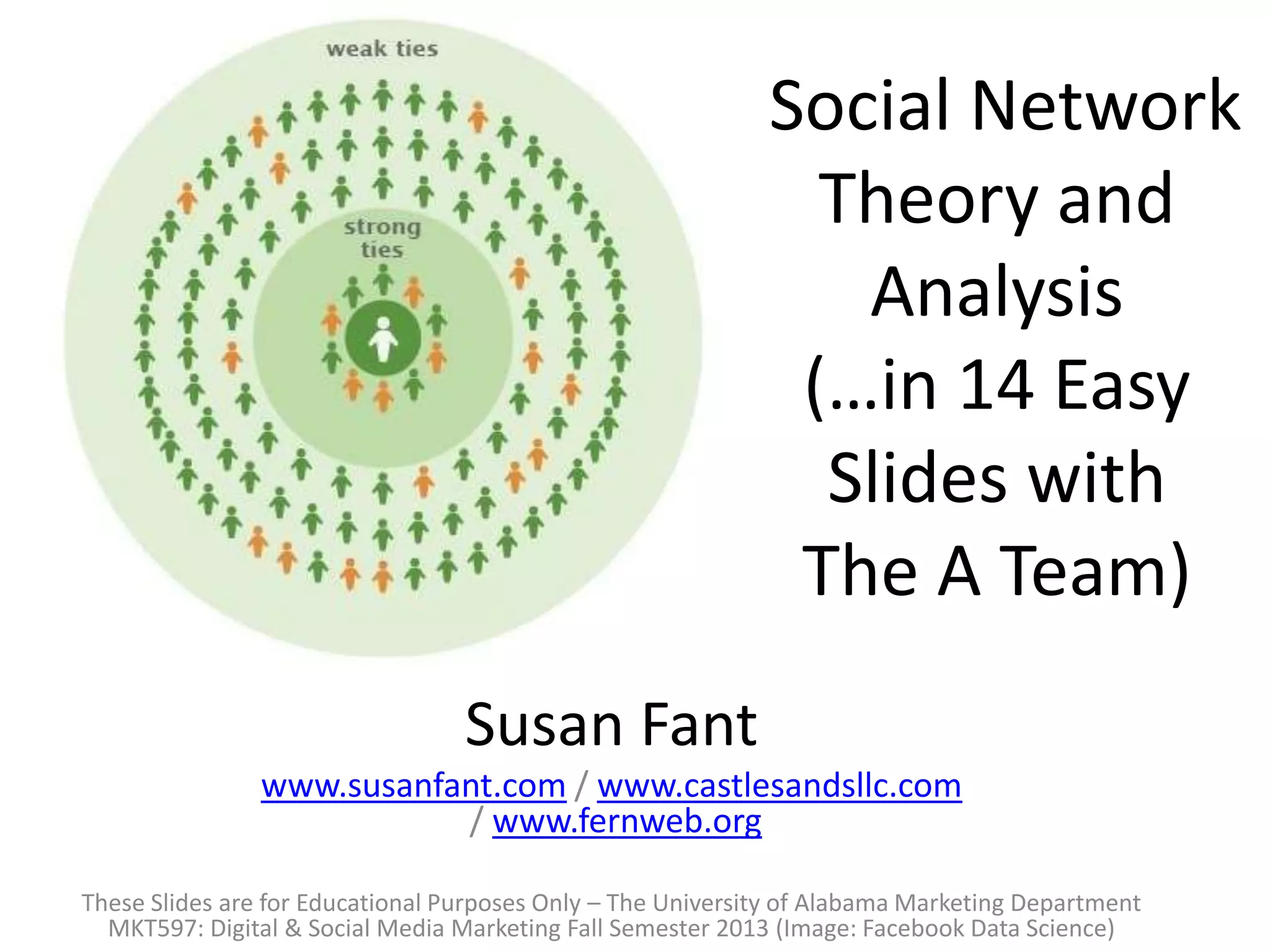
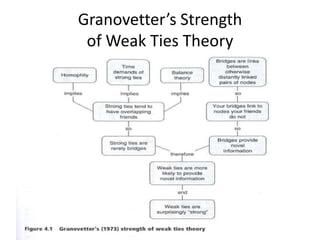
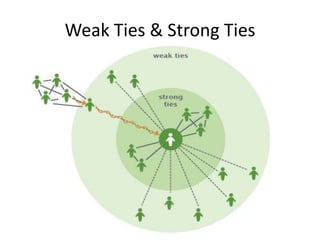
The document explores social network theory and its relevance to marketing, particularly the concepts of tie formation and social capital. It discusses how connections through educational and professional mobility create diverse knowledge sources, and highlights the importance of weak ties for accessing novel information. Ultimately, it emphasizes how businesses can leverage weak ties on platforms like Facebook to increase their reach and attract new followers.