Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
Antibiotics are medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria in humans and animals by either killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply. Bacteria are germsABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...ABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
More Related Content
Similar to Volumelab
Similar to Volumelab (20)
Solutions Manual for Biology Laboratory Manual 11th Edition by Vodopich

Solutions Manual for Biology Laboratory Manual 11th Edition by Vodopich
Lab 1 Measurement Accuracy and Precision Lab Materi.docx

Lab 1 Measurement Accuracy and Precision Lab Materi.docx
Water Testing Lab Background Information Chemists can .docx

Water Testing Lab Background Information Chemists can .docx
Department of biochemistry cell ad molecular biology (1)

Department of biochemistry cell ad molecular biology (1)
Recently uploaded
Antibiotics are medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria in humans and animals by either killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply. Bacteria are germsABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...ABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
Recently uploaded (20)
ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...
Classification of Kerogen, Perspective on palynofacies in depositional envi...

Classification of Kerogen, Perspective on palynofacies in depositional envi...
Mining Activity and Investment Opportunity in Myanmar.pptx

Mining Activity and Investment Opportunity in Myanmar.pptx
Harry Coumnas Thinks That Human Teleportation is Possible in Quantum Mechanic...

Harry Coumnas Thinks That Human Teleportation is Possible in Quantum Mechanic...
Vital Signs of Animals Presentation By Aftab Ahmed Rahimoon

Vital Signs of Animals Presentation By Aftab Ahmed Rahimoon
Costs to heap leach gold ore tailings in Karamoja region of Uganda

Costs to heap leach gold ore tailings in Karamoja region of Uganda
Manganese‐RichSandstonesasanIndicatorofAncientOxic LakeWaterConditionsinGale...

Manganese‐RichSandstonesasanIndicatorofAncientOxic LakeWaterConditionsinGale...
Fun for mover student's book- English book for teaching.pdf

Fun for mover student's book- English book for teaching.pdf
Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease_102718.pptx

Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease_102718.pptx
Factor Causing low production and physiology of mamary Gland

Factor Causing low production and physiology of mamary Gland
Information science research with large language models: between science and ...

Information science research with large language models: between science and ...
Volumelab
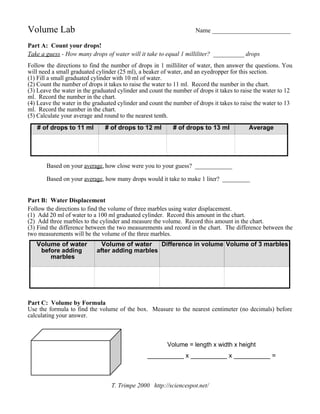
- 1. Volume Lab Name _________________________ Part A: Count your drops! Take a guess - How many drops of water will it take to equal 1 milliliter? __________ drops Follow the directions to find the number of drops in 1 milliliter of water, then answer the questions. You will need a small graduated cylinder (25 ml), a beaker of water, and an eyedropper for this section. (1) Fill a small graduated cylinder with 10 ml of water. (2) Count the number of drops it takes to raise the water to 11 ml. Record the number in the chart. (3) Leave the water in the graduated cylinder and count the number of drops it takes to raise the water to 12 ml. Record the number in the chart. (4) Leave the water in the graduated cylinder and count the number of drops it takes to raise the water to 13 ml. Record the number in the chart. (5) Calculate your average and round to the nearest tenth. Based on your average, how close were you to your guess? ____________ Based on your average, how many drops would it take to make 1 liter? _________ Part B: Water Displacement Follow the directions to find the volume of three marbles using water displacement. (1) Add 20 ml of water to a 100 ml graduated cylinder. Record this amount in the chart. (2) Add three marbles to the cylinder and measure the volume. Record this amount in the chart. (3) Find the difference between the two measurements and record in the chart. The difference between the two measurements will be the volume of the three marbles. Part C: Volume by Formula Use the formula to find the volume of the box. Measure to the nearest centimeter (no decimals) before calculating your answer. T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ Volume of water before adding marbles Volume of water after adding marbles Difference in volume Volume of 3 marbles Volume = length x width x height __________ x __________ x __________ = __________ # of drops to 11 ml # of drops to 12 ml # of drops to 13 ml Average
- 2. Part D: Color Challenge 1. Obtain the following items from your teacher: 3 beakers with colored water- 25 ml of each color (red, blue, and yellow) 1 graduated cylinder (25 ml - 50 ml) 1 eyedropper 6 test tubes labeled A, B, C, D, E, and F 2. Perform each step outlined below using accurate measurements. (1) Measure 17 ml of RED water from the beaker and pour into test tube A. (2) Measure 21 ml of YELLOW water from the beaker and pour into test tube C. (3) Measure 22 ml of BLUE water from the beaker and pour into test tube E. (4) Measure 5 ml of water from test tube A and pour it into test tube B. (5) Measure 6 ml of water from test tube C and pour it into test tube D. (6) Measure 8 ml of water from test tube E and pour it into test tube F. (7) Measure 5 ml of water from test tube C and pour it into test tube B. (8) Measure 2 ml of water from test tube A and pour it into test tube F. (9) Measure 4 ml of water from test tube E and pour it into test tube D. 3. Complete the chart. T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/ Test Tube Color Final Amount (ml) A B C D E F
- 3. Volume Lab Answer Key Part A: Answers will vary; however, my students usually end up with an average of 20 drops per milliliter. The biggest problem I encounter is that students count the number of drops to 11 ml. They should fill the cylinder to 10 ml (meniscus is on the 10 ml mark) and count the number of drops it takes to reach 11 ml. Part B: Answers will vary. My students usually end up with a volume of 5-6 ml for three marbles. Part C: Students should end up with measurements of 5 cm, 2 cm, and 1 cm if they measure to the nearest centimeter (no decimals). The answer would be 5 x 2 x 1 = 10 cm3. Part D: Students should end up with final measurements of 10 ml in each test tube if they measured carefully for each step. I allow ±0.5 ml for error. The final colors should be A - red, B - orange, C yellow, D - blue, E - green, and F - purple. TIP: When mixing the main colors, make all of them dark. It is a good idea to test the colors before the lab to make sure the final results are close to the colors listed above. The purple often ends up as a very dark purple. It does help to hold the test tubes up to a light to determine the final colors. Safety Rules: After the lab, ask students if anyone has colored hands or papers and relate to lab safety rules. If the water samples were chemicals, colored hands or papers would indicate that the person came in contact with the “chemicals.” T. Trimpe 2000 http://sciencespot.net/